library: libHistPainter
#include "THistPainter.h" |
THistPainter
class description - source file - inheritance tree (.pdf)
public:
THistPainter()
THistPainter(const THistPainter&)
virtual ~THistPainter()
static TClass* Class()
virtual void DefineColorLevels(Int_t ndivz)
virtual Int_t DistancetoPrimitive(Int_t px, Int_t py)
virtual void DrawPanel()
virtual void ExecuteEvent(Int_t event, Int_t px, Int_t py)
virtual void FitPanel()
static const char* GetBestFormat(Double_t v, Double_t e, const char* f) const
virtual TList* GetContourList(Double_t contour) const
virtual char* GetObjectInfo(Int_t px, Int_t py) const
virtual TList* GetStack() const
virtual TClass* IsA() const
virtual Bool_t IsInside(Int_t x, Int_t y)
virtual Bool_t IsInside(Double_t x, Double_t y)
virtual Int_t MakeChopt(Option_t* option)
virtual Int_t MakeCuts(char* cutsopt)
THistPainter& operator=(const THistPainter&)
virtual void Paint(Option_t* option = "")
virtual void Paint2DErrors(Option_t* option)
virtual void PaintArrows(Option_t* option)
virtual void PaintAxis(Bool_t drawGridOnly = kFALSE)
virtual void PaintBar(Option_t* option)
virtual void PaintBarH(Option_t* option)
virtual void PaintBoxes(Option_t* option)
virtual void PaintColorLevels(Option_t* option)
virtual void PaintContour(Option_t* option)
virtual Int_t PaintContourLine(Double_t elev1, Int_t icont1, Double_t x1, Double_t y1, Double_t elev2, Int_t icont2, Double_t x2, Double_t y2, Double_t* xarr, Double_t* yarr, Int_t* itarr, Double_t* levels)
virtual void PaintErrors(Option_t* option)
virtual void PaintFrame()
virtual void PaintFunction(Option_t* option)
virtual void PaintH3(Option_t* option = "")
virtual void PaintH3Iso()
virtual void PaintHist(Option_t* option)
virtual Int_t PaintInit()
virtual Int_t PaintInitH()
virtual void PaintLego(Option_t* option)
virtual void PaintLegoAxis(TGaxis* axis, Double_t ang)
virtual void PaintPalette()
virtual void PaintScatterPlot(Option_t* option)
virtual void PaintStat(Int_t dostat, TF1* fit)
virtual void PaintStat2(Int_t dostat, TF1* fit)
virtual void PaintSurface(Option_t* option)
virtual void PaintTable(Option_t* option)
virtual void PaintText(Option_t* option)
virtual void PaintTF3()
virtual void PaintTitle()
virtual void PaintTriangles(Option_t* option)
virtual void ProcessMessage(const char* mess, const TObject* obj)
static Int_t ProjectAitoff2xy(Double_t l, Double_t b, Double_t& Al, Double_t& Ab)
static Int_t ProjectMercator2xy(Double_t l, Double_t b, Double_t& Al, Double_t& Ab)
static Int_t ProjectParabolic2xy(Double_t l, Double_t b, Double_t& Al, Double_t& Ab)
static Int_t ProjectSinusoidal2xy(Double_t l, Double_t b, Double_t& Al, Double_t& Ab)
virtual void RecalculateRange()
virtual void RecursiveRemove(TObject*)
virtual void SetHistogram(TH1* h)
virtual void SetStack(TList* stack)
virtual void ShowMembers(TMemberInspector& insp, char* parent)
virtual void Streamer(TBuffer& b)
void StreamerNVirtual(TBuffer& b)
virtual Int_t TableInit()
protected:
TH1* fH pointer to histogram to paint
TAxis* fXaxis pointer to X axis
TAxis* fYaxis pointer to Y axis
TAxis* fZaxis pointer to Z axis
TList* fFunctions pointer to histogram list of functions
TPainter3dAlgorithms* fLego pointer to a TPainter3dAlgorithms object
TGraphPainter* fGraphPainter pointer to a fGraphPainter object
Double_t* fXbuf X buffer coordinates
Double_t* fYbuf Y buffer coordinates
Int_t fNcuts Number of graphical cuts
Int_t fCutsOpt[16] sign of each cut
TCutG* fCuts[16] Pointers to graphical cuts
TList* fStack Pointer to stack of histograms (if any)
The histogram painter class
===========================
Histograms are drawn via the THistPainter class. Each histogram has
a pointer to its own painter (to be usable in a multithreaded program).
When the canvas has to be redrawn, the Paint function of the objects
in the pad is called. In case of histograms, TH1::Paint invokes directly
THistPainter::Paint.
See THistPainter::Paint for the list of drawing options
and examples.
THistPainter()
*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*Histogram default constructor*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
=============================
~THistPainter()
*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*Histogram default destructor*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
============================
Int_t DistancetoPrimitive(Int_t px, Int_t py)
*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*Compute distance from point px,py to a line*-*-*-*-*-*
===========================================
Compute the closest distance of approach from point px,py to elements
of an histogram.
The distance is computed in pixels units.
Algorithm:
Currently, this simple model computes the distance from the mouse
to the histogram contour only.
*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
void DrawPanel()
*-*-*-*-*Display a panel with all histogram drawing options*-*-*-*-*-*
==================================================
See class TDrawPanelHist for example
void ExecuteEvent(Int_t event, Int_t px, Int_t py)
*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*Execute action corresponding to one event*-*-*-*
=========================================
This member function is called when a histogram is clicked with the locator
If Left button clicked on the bin top value, then the content of this bin
is modified according to the new position of the mouse when it is released.
*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
void FitPanel()
*-*-*-*-*Display a panel with all histogram fit options*-*-*-*-*-*
==============================================
See class TFitPanel for example
TList* GetContourList(Double_t contour) const
Get a contour (as a list of TGraphs) using the Delaunay triangulation
char* GetObjectInfo(Int_t px, Int_t py) const
Redefines TObject::GetObjectInfo.
Displays the histogram info (bin number, contents, integral up to bin
corresponding to cursor position px,py
Bool_t IsInside(Int_t ix, Int_t iy)
return kTRUE if the cell ix, iy is inside one of the graphical cuts
Bool_t IsInside(Double_t x, Double_t y)
return kTRUE if the point x,y is inside one of the graphical cuts
Int_t MakeChopt(Option_t *choptin)
*-*-*-*-*-*-*Decode string chopt and fill Hoption structure*-*-*-*-*-*-*
==============================================
Int_t MakeCuts(char *choptin)
*-*-*-*-*-*-*Decode string chopt and fill Graphical cuts structure
=====================================================
void Paint(Option_t *option)
*-*-*-*-*-*-*Control routine to paint any kind of histograms*-*-*-*-*-*-*
===============================================
When you call the Draw method of a histogram for the first time (TH1::Draw),
it creates a THistPainter object and saves a pointer to painter as a
data member of the histogram.
The THistPainter class specializes in the drawing of histograms. It is
separate from the histogram so that one can have histograms without
the graphics overhead, for example in a batch program. The choice
to give each histogram have its own painter rather than a central
singleton painter, allows two histograms to be drawn in two threads
without overwriting the painter's values.
When a displayed histogram is filled again you do not have to call the Draw
method again. The image is refreshed the next time the pad is updated.
A pad is updated after one of these three actions:::Paint
- a carriage control on the ROOT command line
- a click inside the pad
- a call to TPad::Update
By default a call to TH1::Draw clears the pad of all objects before drawing the
new image of the histogram. You can use the "SAME" option to leave the previous
display intact and superimpose the new histogram. The same histogram can be
drawn with different graphics options in different pads.
When a displayed histogram is deleted, its image is automatically removed from the pad.
To create a copy of the histogram when drawing it, you can use TH1::DrawClone. This
will clone the histogram and allow you to change and delete the original one
without affecting the clone.
Setting the Style
=================
Histograms use the current style (gStyle). When you change the current style and
would like to propagate the change to the histogram you can call TH1::UseCurrentStyle.
You will need to call UseCurrentStyle on each histogram.
When reading many histograms from a file and you wish to update them to the current
style you can use gROOT::ForceStyle and all histograms read after this call
will be updated to use the current style.
The following options are supported on all types:
=================================================
"AXIS" : Draw only axis
"HIST" : When an histogram has errors it is visualized by default with
error bars. To visualize it without errors use the option HIST
together with the required option (eg "hist same c")
"SAME" : Superimpose on previous picture in the same pad
"CYL" : Use Cylindrical coordinates
"POL" : Use Polar coordinates
"SPH" : Use Spherical coordinates
"PSR" : Use PseudoRapidity/Phi coordinates
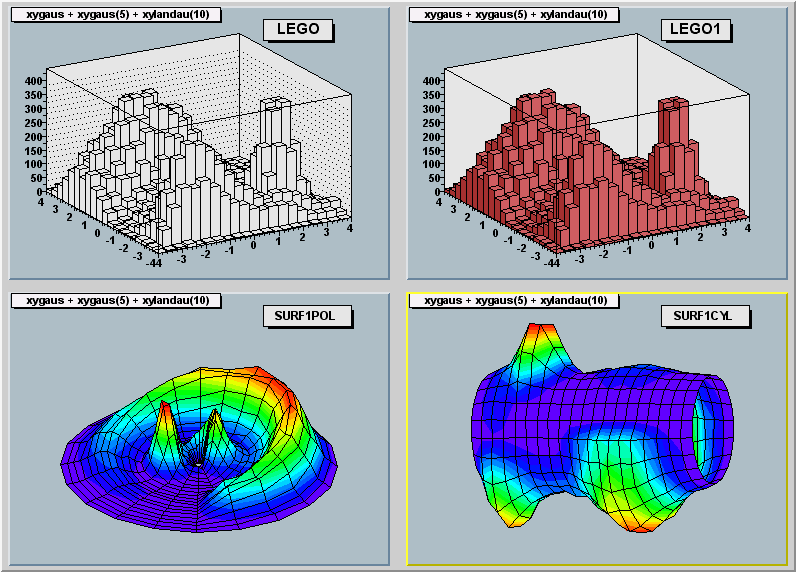
"LEGO" : Draw a lego plot with hidden line removal
"LEGO1" : Draw a lego plot with hidden surface removal
"LEGO2" : Draw a lego plot using colors to show the cell contents
"SURF" : Draw a surface plot with hidden line removal
"SURF1" : Draw a surface plot with hidden surface removal
"SURF2" : Draw a surface plot using colors to show the cell contents
"SURF3" : same as SURF with in addition a contour view drawn on the top
"SURF4" : Draw a surface using Gouraud shading
"SURF5" : Same as SURF3 but only the colored contour is drawn. Used with
option CYL, SPH or PSR it allows to draw colored contours on a
sphere, a cylinder or a in pseudo rapidy space. In cartesian
or polar coordinates, option SURF3 is used.
The following options are supported for 1-D types:
"AH" : Draw histogram, but not the axis labels and tick marks
"][" : When this option is selected the first and last vertical lines
: of the histogram are not drawn.
"B" : Bar chart option
"C" : Draw a smooth Curve througth the histogram bins
"E" : Draw error bars
"E0" : Draw error bars including bins with o contents
"E1" : Draw error bars with perpendicular lines at the edges
"E2" : Draw error bars with rectangles
"E3" : Draw a fill area througth the end points of the vertical error bars
"E4" : Draw a smoothed filled area through the end points of the error bars
"L" : Draw a line througth the bin contents
"P" : Draw current marker at each bin except empty bins
"P0" : Draw current marker at each bin including empty bins
"*H" : Draw histogram with a * at each bin
"LF2" : Draw histogram like with option "L" but with a fill area.
: Note that "L" draws also a fill area if the hist fillcolor is set
: but the fill area corresponds to the histogram contour.
"9" : Force histogram to be drawn in high resolution mode.
: By default, the histogram is drawn in low resolution
: in case the number of bins is greater than the number of pixels
: in the current pad.
The following options are supported for 2-D types:
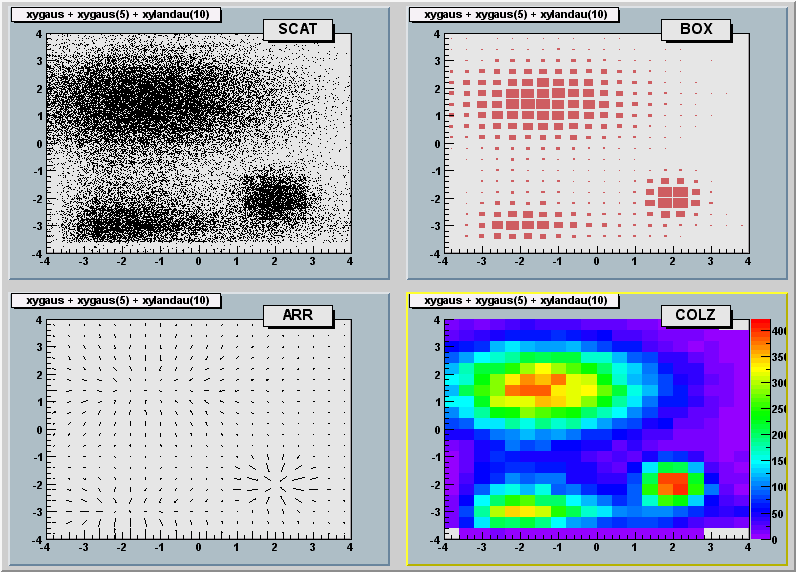
"ARR" : arrow mode. Shows gradient between adjacent cells
"BOX" : a box is drawn for each cell with surface proportional to the
content's absolute value. A negative content is marked with a X.
"BOX1" : a button is drawn for each cell with surface proportional to
content's absolute value. A sunken button is drawn for negative values
a raised one for positive.
"COL" : a box is drawn for each cell with a color scale varying with contents
"COLZ" : same as "COL". In addition the color palette is also drawn
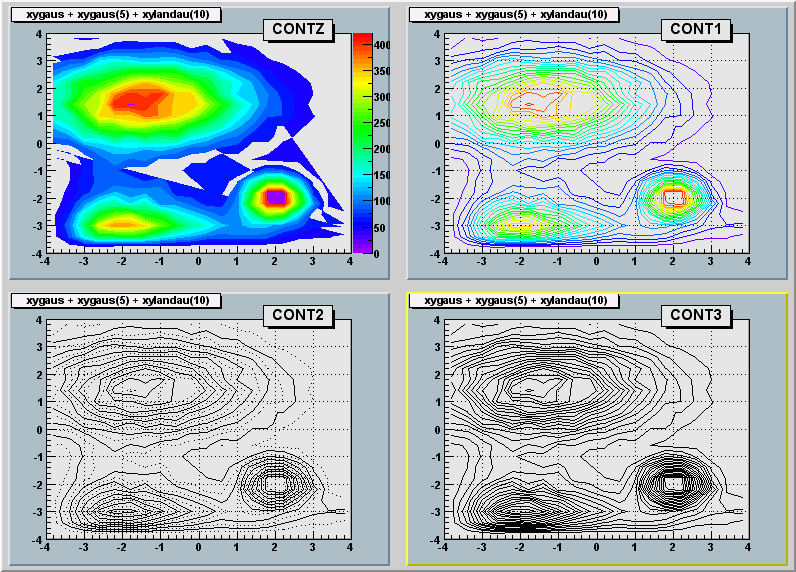
"CONT" : Draw a contour plot (same as CONT0)
"CONT0" : Draw a contour plot using surface colors to distinguish contours
"CONT1" : Draw a contour plot using line styles to distinguish contours
"CONT2" : Draw a contour plot using the same line style for all contours
"CONT3" : Draw a contour plot using fill area colors
"CONT4" : Draw a contour plot using surface colors (SURF option at theta = 0)
"CONT5" : (TGraph2D only) Draw a contour plot using Delaunay triangles
"LIST" : Generate a list of TGraph objects for each contour
"FB" : With LEGO or SURFACE, suppress the Front-Box
"BB" : With LEGO or SURFACE, suppress the Back-Box
"SCAT" : Draw a scatter-plot (default)
"TEXT" : Draw bin contents as text
"TEXTnn" : Draw bin contents as text at angle nn (0 < nn < 90)
"[cutg]" : Draw only the sub-range selected by the TCutG named "cutg"
Most options can be concatenated without spaces or commas, for example:
h->Draw("E1 SAME");
The options are not case sensitive:
h->Draw("e1 same");
The options "BOX", "COL" or "COLZ", use the color palette
defined in the current style (see TStyle::SeTPaletteAxis)
The options "CONT" or "SURF" or "LEGO" have by default 20 equidistant contour
levels, you can change the number of levels with TH1::SetContour or
TStyle::SetNumberContours.
You can also set the default drawing option with TH1::SetOption. To see the current
option use TH1::GetOption.
Setting line, fill, marker, and text attributes
=====================================
The histogram classes inherit from the attribute classes:
TAttLine, TAttFill, TAttMarker and TAttText.
See the description of these classes for the list of options.
Setting Tick marks on the histogram axis
========================================
The TPad::SetTicks method specifies the type of tick marks on the axis.
Assume tx = gPad->GetTickx() and ty = gPad->GetTicky().
tx = 1 ; tick marks on top side are drawn (inside)
tx = 2; tick marks and labels on top side are drawn
ty = 1; tick marks on right side are drawn (inside)
ty = 2; tick marks and labels on right side are drawn
By default only the left Y axis and X bottom axis are drawn (tx = ty = 0)
Use TPad::SetTicks(tx,ty) to set these options
See also The TAxis functions to set specific axis attributes.
In case multiple collor filled histograms are drawn on the same pad, the fill
area may hide the axis tick marks. One can force a redraw of the axis
over all the histograms by calling:
gPad->RedrawAxis();
Giving titles to the X, Y and Z axis
=================================
h->GetXaxis()->SetTitle("X axis title");
h->GetYaxis()->SetTitle("Y axis title");
The histogram title and the axis titles can be any TLatex string.
The titles are part of the persistent histogram.
Superimposing two histograms with different scales in the same pad
==================================================================
The following script creates two histograms, the second histogram is
the bins integral of the first one. It shows a procedure to
draw the two histograms in the same pad and it draws the scale of
the second histogram using a new vertical axis on the right side.
(see also tutorial transpad.C for a variant of this example)
void twoscales() {
TCanvas *c1 = new TCanvas("c1","hists with different scales",600,400);
//create/fill draw h1
gStyle->SetOptStat(kFALSE);
TH1F *h1 = new TH1F("h1","my histogram",100,-3,3);
Int_t i;
for (i=0;i<10000;i++) h1->Fill(gRandom->Gaus(0,1));
h1->Draw();
c1->Update();
//create hint1 filled with the bins integral of h1
TH1F *hint1 = new TH1F("hint1","h1 bins integral",100,-3,3);
Float_t sum = 0;
for (i=1;i<=100;i++) {
sum += h1->GetBinContent(i);
hint1->SetBinContent(i,sum);
}
//scale hint1 to the pad coordinates
Float_t rightmax = 1.1*hint1->GetMaximum();
Float_t scale = gPad->GetUymax()/rightmax;
hint1->SetLineColor(kRed);
hint1->Scale(scale);
hint1->Draw("same");
//draw an axis on the right side
TGaxis *axis = new TGaxis(gPad->GetUxmax(),gPad->GetUymin(),
gPad->GetUxmax(), gPad->GetUymax(),0,rightmax,510,"+L");
axis->SetLineColor(kRed);
axis->SetTextColor(kRed);
axis->Draw();
}
/*
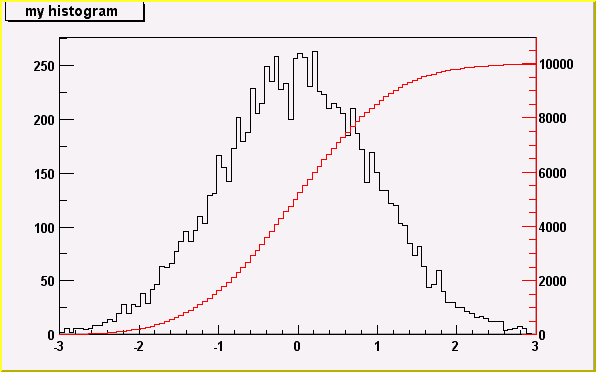 */
*/
Statistics Display
======================================
The type of information shown in the histogram statistics box
can be selected with gStyle->SetOptStat(mode).
The mode has up to seven digits that can be set to on(1) or off(0).
mode = iourmen (default = 0001111)
n = 1; name of histogram is printed
e = 1; number of entries printed
m = 1; mean value printed
r = 1; rms printed
u = 1; number of underflows printed
o = 1; number of overflows printed
i = 1; integral of bins printed
For example: gStyle->SetOptStat(11);
displays only the name of histogram and the number of entries.
For example: gStyle->SetOptStat(1101);
displays the name of histogram, mean value and RMS.
WARNING: never call SetOptStat(000111); but SetOptStat(1111), 0001111 will
be taken as an octal number !!
SetOptStat can also take any combination of letters IOURMEN as its argument.
For example gStyle->SetOptStat("NE"), gStyle->SetOptStat("NMR") and
gStyle->SetOptStat("RMEN") are equivalent to the examples above.
When the histogram is drawn, a TPaveStats object is created and added
to the list of functions of the histogram. If a TPaveStats object already
exists in the histogram list of functions, the existing object is just
updated with the current histogram parameters.
With the option "same", the statistic box is not redrawn.
With the option "sames", the statistic box is drawn. If it hiddes
the previous statistics box, you can change its position
with these lines (if h is the pointer to the histogram):
Root > TPaveStats *st = (TPaveStats*)h->FindObject("stats")
Root > st->SetX1NDC(newx1); //new x start position
Root > st->SetX2NDC(newx2); //new x end position
To change the type of information for an histogram with an existing TPaveStats
you should do: st->SetOptStat(mode) where mode has the same meaning than
when calling gStyle->SetOptStat(mode) (see above).
You can delete the stats box for a histogram TH1* h with h->SetStats(0)
and activate it again with h->SetStats(1).
Fit Statistics
==============
You can change the statistics box to display the fit parameters with
the TStyle::SetOptFit(mode) method. This mode has four digits.
mode = pcev (default = 0111)
v = 1; print name/values of parameters
e = 1; print errors (if e=1, v must be 1)
c = 1; print Chisquare/Number of degress of freedom
p = 1; print Probability
For example: gStyle->SetOptFit(1011);
prints the fit probability, parameter names/values, and errors.
The ERROR bars options
======================
'E' default. Shows only the error bars, not a marker
'E1' Small lines are drawn at the end of the error bars.
'E2' Error rectangles are drawn.
'E3' A filled area is drawn through the end points of the vertical error bars.
'4' A smoothed filled area is drawn through the end points of the
vertical error bars.
'E0' Draw also bins with null contents.
/*
 */
*/
The BAR options
===============
When the option "bar" or "hbar" is specified, a bar chart is drawn.
----Vertical BAR chart: Options "bar","bar0","bar1","bar2","bar3","bar4"
The bar is filled with the histogram fill color
The left side of the bar is drawn with a light fill color
The right side of the bar is drawn with a dark fill color
The percentage of the bar drawn with either the light or dark color
is 0 per cent for option "bar" or "bar0"
is 10 per cent for option "bar1"
is 20 per cent for option "bar2"
is 30 per cent for option "bar3"
is 40 per cent for option "bar4"
Use TH1::SetBarWidth to control the bar width (default is the bin width)
Use TH1::SetBarOffset to control the bar offset (default is 0)
See example in $ROOTSYS/tutorials/hbars.C
/*
 */
*/
----Horizontal BAR chart: Options "hbar","hbar0","hbar1","hbar2","hbar3","hbar4"
An horizontal bar is drawn for each bin.
The bar is filled with the histogram fill color
The bottom side of the bar is drawn with a light fill color
The top side of the bar is drawn with a dark fill color
The percentage of the bar drawn with either the light or dark color
is 0 per cent for option "hbar" or "hbar0"
is 10 per cent for option "hbar1"
is 20 per cent for option "hbar2"
is 30 per cent for option "hbar3"
is 40 per cent for option "hbar4"
Use TH1::SetBarWidth to control the bar width (default is the bin width)
Use TH1::SetBarOffset to control the bar offset (default is 0)
See example in $ROOTSYS/tutorials/hbars.C
/*
 */
*/
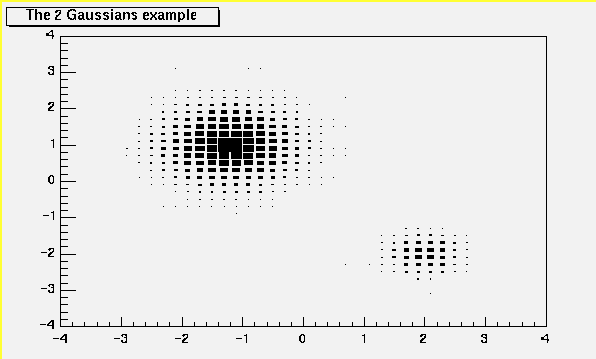
The SCATter plot option (default for 2-D histograms)
=======================
For each cell (i,j) a number of points proportional to the cell content is drawn.
A maximum of 500 points per cell are drawn. If the maximum is above 500
contents are normalized to 500.
The ARRow option. Shows gradient between adjacent cells
================
For each cell (i,j) an arrow is drawn
The orientation of the arrow follows the cell gradient
The BOX option
==============
For each cell (i,j) a box is drawn with surface proportional to contents
The COLor option
==============
For each cell (i,j) a box is drawn with a color proportional
to the cell content.
The color table used is defined in the current style (gStyle).
The color palette in TStyle can be modified via TStyle::SeTPaletteAxis.
/*
 */
*/
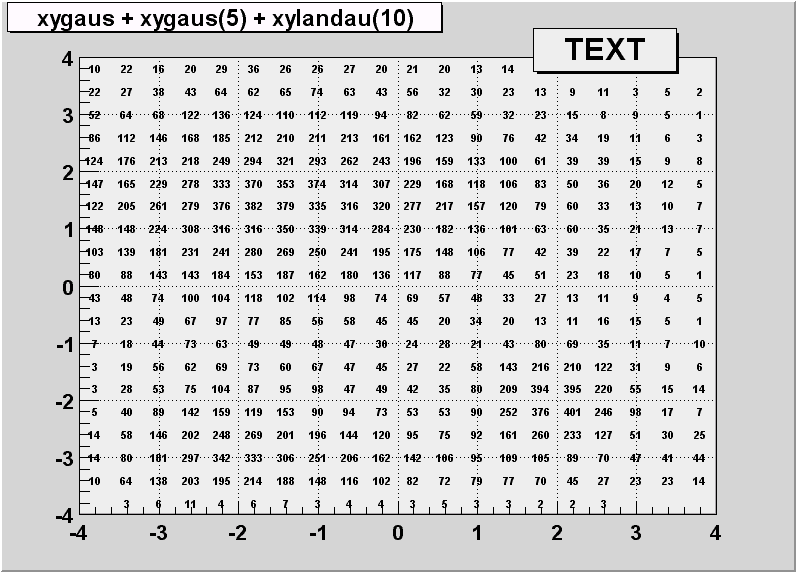
The TEXT and TEXTnn Option
==========================
For each bin the content is printed.
The text attributes are:
- text font = current TStyle font
- text size = 0.02*padheight*markersize
- text color= marker color
"nn" is the angle used to draw the text (0 < nn < 90)
/*
 */
*/
The CONTour options
===================
The following contour options are supported:
"CONT" : Draw a contour plot (same as CONT0)
"CONT0" : Draw a contour plot using surface colors to distinguish contours
"CONT1" : Draw a contour plot using line styles to distinguish contours
"CONT2" : Draw a contour plot using the same line style for all contours
"CONT3" : Draw a contour plot using fill area colors
"CONT4" : Draw a contour plot using surface colors (SURF option at theta = 0)
"CONT5" : Draw a contour plot using Delaunay triangles
The following options select the "CONT4" option and are usefull for
skymaps or exposure maps. (see example in tutorial earth.C)
"AITOFF" : Draw a contour via an AITOFF projection
"MERCATOR" : Draw a contour via an Mercator projection
"SINUSOIDAL" : Draw a contour via an Sinusoidal projection
"PARABOLIC" : Draw a contour via an Parabolic projection
The default number of contour levels is 20 equidistant levels and can
be changed with TH1::SetContour or TStyle::SetNumberContours.
When option "LIST" is specified together with option "CONT",
the points used to draw the contours are saved in the TGraph object
and are accessible in the following way:
TObjArray *contours =
gROOT->GetListOfSpecials()->FindObject("contours")
Int_t ncontours = contours->GetSize();
TList *list = (TList*)contours->At(i);
Where i is a contour number, and list contains a list of TGraph objects.
For one given contour, more than one disjoint polyline may be generated.
The number of TGraphs per countour is given by list->GetSize().
Here we show only the case to access the first graph in the list.
TGraph *gr1 = (TGraph*)list->First();
/*
 */
*/
The LEGO options
================
In a lego plot the cell contents are drawn as 3-d boxes, with
the height of the box proportional to the cell content.
A lego plot can be represented in several coordinate systems, the
default system is Cartesian coordinates.
Other possible coordinate systems are CYL,POL,SPH,PSR.
"LEGO" : Draw a lego plot with hidden line removal
"LEGO1" : Draw a lego plot with hidden surface removal
"LEGO2" : Draw a lego plot using colors to show the cell contents
See TStyle::SeTPaletteAxis to change the color palette.
We suggest you use palette 1 with the call
gStyle->SetColorPalette(1)
/*
 */
*/
The "SURFace" options
=====================
In a surface plot, cell contents are represented as a mesh.
The height of the mesh is proportional to the cell content.
A surface plot can be represented in several coordinate systems.
The default is cartesian coordinates, and the other possible systems
are CYL,POL,SPH,PSR.
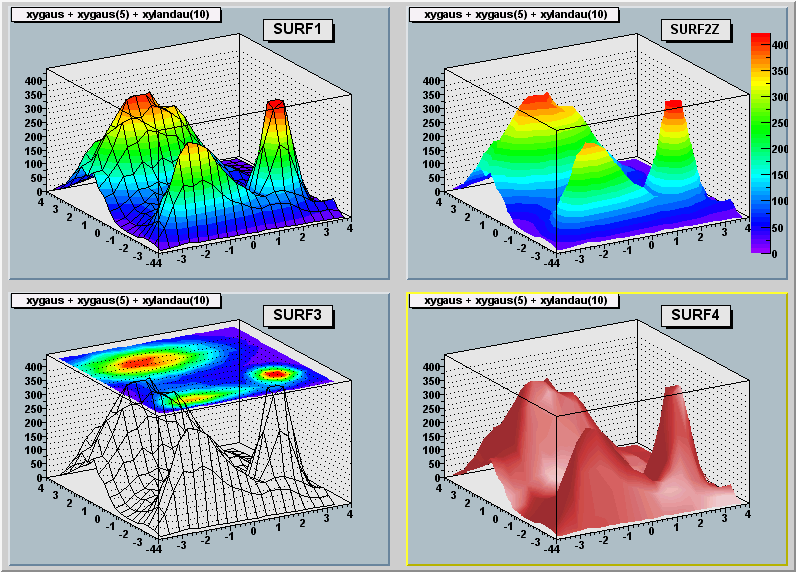
"SURF" : Draw a surface plot with hidden line removal
"SURF1" : Draw a surface plot with hidden surface removal
"SURF2" : Draw a surface plot using colors to show the cell contents
"SURF3" : same as SURF with in addition a contour view drawn on the top
"SURF4" : Draw a surface using Gouraud shading
The following picture uses SURF1.
See TStyle::SeTPaletteAxis to change the color palette.
We suggest you use palette 1 with the call
gStyle->SetColorPalette(1)
/*
 */
*/
Option "Z" : Adding the color palette on the right side of the pad
==================================================================
When this option is specified, a color palette with an axis indicating
the value of the corresponding color is drawn on the right side of
the picture. In case, not enough space is left, you can increase the size
of the right margin by calling TPad::SetRightMargin.
The attributes used to display the palette axis values are taken from
the Z axis of the object. For example, you can set the labels size
on the palette axis via hist->GetZaxis()->SetLabelSize().
Setting the color palette
=========================
You can set the color palette with TStyle::SeTPaletteAxis, eg
gStyle->SeTPaletteAxis(ncolors,colors);
For example the option "COL" draws a 2-D histogram with cells
represented by a box filled with a color index which is a function
of the cell content.
If the cell content is N, the color index used will be the color number
in colors[N],etc. If the maximum cell content is > ncolors, all
cell contents are scaled to ncolors.
if ncolors <= 0, a default palette (see below) of 50 colors is defined.
This palette is recommended for pads, labels
if ncolors == 1 && colors == 0, a pretty palette with a violet to red
spectrum is created. We recommend you use this palette when drawing legos,
surfaces or contours.
if ncolors > 0 and colors == 0, the default palette is used
with a maximum of ncolors.
The default palette defines:
index 0 to 9 : shades of grey
index 10 to 19 : shades of brown
index 20 to 29 : shades of blue
index 30 to 39 : shades of red
index 40 to 49 : basic colors
The color numbers specified in the palette can be viewed by selecting
the item "colors" in the "VIEW" menu of the canvas toolbar.
The color'a red, green, and blue values can be changed via TColor::SetRGB.
Drawing a sub-range of a 2-D histogram; the [cutg] option
=========================================================
Using a TCutG object, it is possible to draw a sub-range of a 2-D histogram.
One must create a graphical cut (mouse or C++) and specify the name
of the cut between [] in the Draw option.
For example, with a TCutG named "cutg", one can call:
myhist->Draw("surf1 [cutg]");
To invert the cut, it is enough to put a "-" in front of its name:
myhist->Draw("surf1 [-cutg]");
It is possible to apply several cuts ("," means logical AND):
myhist->Draw("surf1 [cutg1,cutg2]");
See a complete example in the tutorial fit2a.C. This example produces
the following picture:
/*
 */
*/
Drawing options for 3-D histograms
==================================
By default a 3-d scatter plot is drawn
If option "BOX" is specified, a 3-D box with a volume proportional
to the cell content is drawn.
--------------------------------------------------------------------
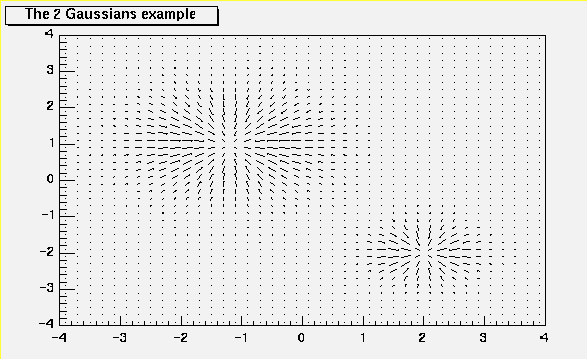
void PaintArrows(Option_t *)
*-*-*-*-*-*Control function to draw a table as an arrow plot*-*-*-*-*-*
=================================================
For each cell (i,j) an arrow is drawn
The orientation of the arrow follows the cell gradient
/*
 */
*/
*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
void PaintAxis(Bool_t drawGridOnly)
*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*Draw axis of an histogram*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
=========================
Assume tx = gPad->GetTickx() and ty = gPad->GetTicky()
by default only the left Y axis and X bottom axis are drawn (tx = ty = 0)
tx = 1 ; tick marks on top side are drawn (inside)
tx = 2; tick marks and labels on top side are drawn
ty = 1; tick marks on right side are drawn (inside)
ty = 2; tick marks and labels on right side are drawn
Use TPad::SetTicks(tx,ty) to set these options
void PaintBar(Option_t *)
Draw a bar chart in a normal pad.
(see PaintBarH to draw a bar chart in a rotated pad)
This function is called by THistPainter::Paint when the option "bar"
has been specified.
A vertical bar is drawn for each bin.
The bar is filled with the histogram fill color
The left side of the bar is drawn with a light fill color
The right side of the bar is drawn with a dark fill color
The percentage of the bar drawn with either the light or dark color
is 0 per cent for option "bar" or "bar0"
is 10 per cent for option "bar1"
is 20 per cent for option "bar2"
is 30 per cent for option "bar3"
is 40 per cent for option "bar4"
Use TH1::SetBarWidth to control the bar width (default is the bin width)
Use TH1::SetBarOffset to control the bar offset (default is 0)
See example in $ROOTSYS/tutorials/hbars.C
/*
 */
*/
void PaintBarH(Option_t *)
Draw a bar char in a rotated pad (X vertical, Y horizontal)
(see PaintBar to draw a bar chart in a normal pad)
This function is called by THistPainter::Paint when the option "hbar"
has been specified.
An horizontal bar is drawn for each bin.
The bar is filled with the histogram fill color
The bottom side of the bar is drawn with a light fill color
The top side of the bar is drawn with a dark fill color
The percentage of the bar drawn with either the light or dark color
is 0 per cent for option "hbar" or "hbar0"
is 10 per cent for option "hbar1"
is 20 per cent for option "hbar2"
is 30 per cent for option "hbar3"
is 40 per cent for option "hbar4"
Use TH1::SetBarWidth to control the bar width (default is the bin width)
Use TH1::SetBarOffset to control the bar offset (default is 0)
See example in $ROOTSYS/tutorials/hbars.C
/*
 */
*/
void PaintBoxes(Option_t *)
*Control function to draw a table as a box plot
For each cell (i,j) a box is drawn.
The size of the box is proportional to the absolute value of the cell content.
The cells with a negative content draw with a X on top of the boxes.
/*
 */
*/
With option BOX1 a button is drawn for each cell with surface proportional to
content's absolute value. A sunken button is drawn for negative values
a raised one for positive.
/*
 */
*/
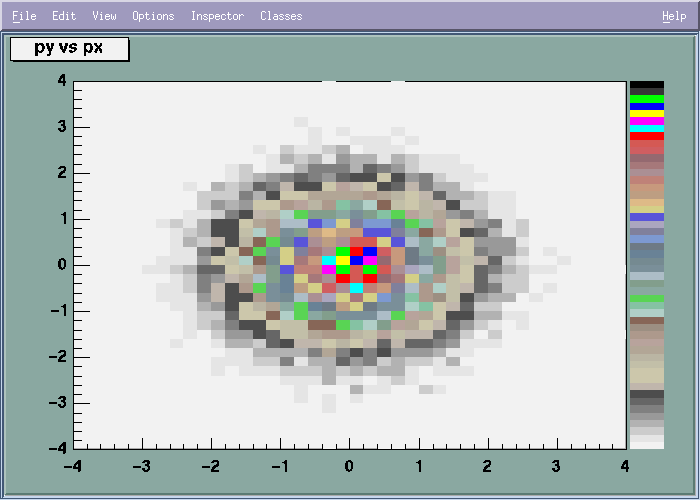
void PaintColorLevels(Option_t *)
*-*-*-*-*-*Control function to draw a table as a color plot*-*-*-*-*-*
================================================
For each cell (i,j) a box is drawn with a color proportional
to the cell content.
The color table used is defined in the current style (gStyle).
The color palette in TStyle can be modified via TStyle::SeTPaletteAxis.
/*
 */
*/
*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
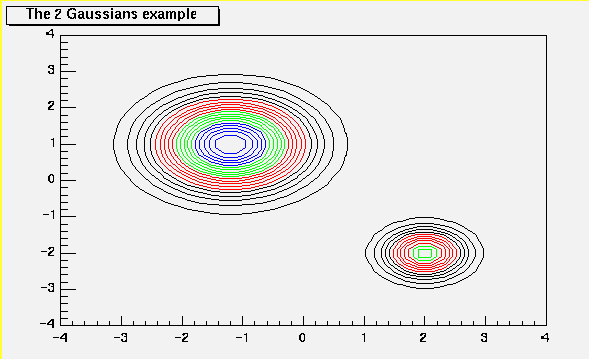
void PaintContour(Option_t *option)
*-*-*-*-*-*Control function to draw a table as a contour plot*-*-*-*-*-*
=================================================
Hoption.Contour may have the following values:
1 The contour is drawn with filled colour levels. ("cont")
11 Use colour to distinguish contours. ("cont1")
12 Use line style to distinguish contours. ("cont2")
13 Line style and colour are the same for all contours. ("cont3")
14 Same as 1 but uses the "SURF" algorithm ("cont4")
see also options "AITOFF","MERCATOR",etc below
15 Use Delaunay triangles to compute the contours
When option "List" is specified together with option "cont",
the points used to draw the contours are saved in the TGraph format
and are accessible in the following way:
TObjArray *contours =
(TObjArray*)gROOT->GetListOfSpecials()->FindObject("contours")
Int_t ncontours = contours->GetSize();
TList *list = (TList*)contours->At(i); //where i is a contour number
list contains a list of TGraph objects. For one given contour, more than
one disjoint polyline may be generated. The number of TGraphs per
countour is given by list->GetSize().
Here we show only the case to access the first graph in the list.
TGraph *gr1 = (TGraph*)list->First();
/*
 */
*/
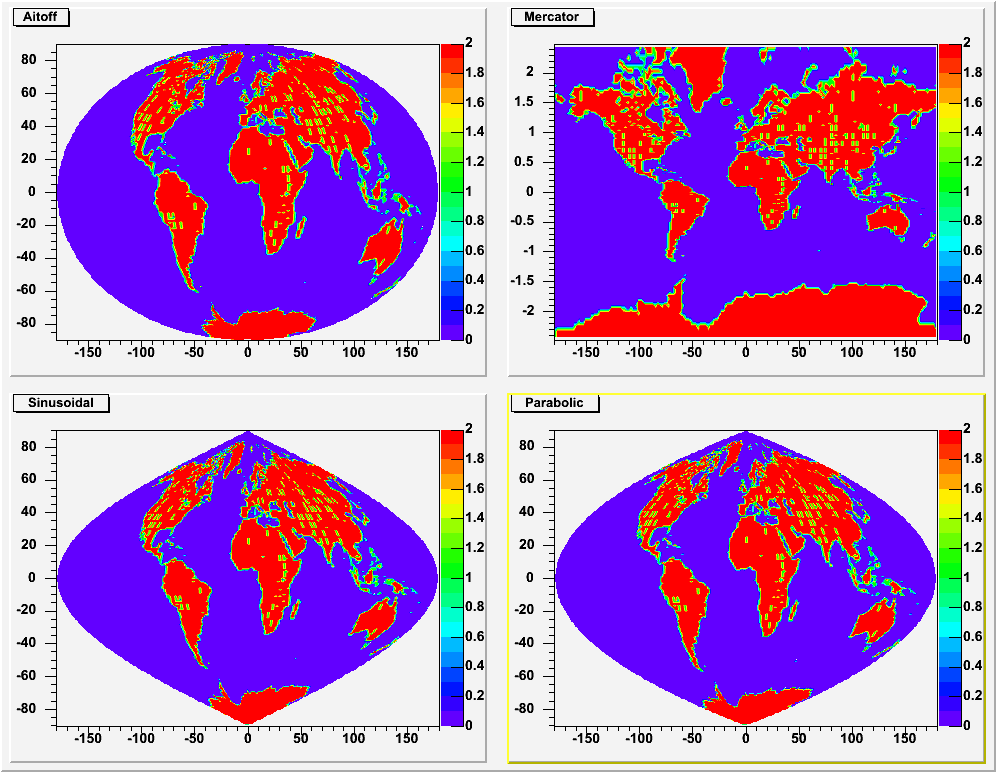
This function is also called when one of the options below is called;
skymaps or exposure maps. (see example in tutorial earth.C)
"AITOFF" : Draw a contour via an AITOFF projection
"MERCATOR" : Draw a contour via an Mercator projection
"SINUSOIDAL" : Draw a contour via an Sinusoidal projection
"PARABOLIC" : Draw a contour via an Parabolic projection
The tutorial earth.C uses these 4 options and produce the following picture:
/*
 */
*/
*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
Int_t PaintContourLine(Double_t elev1, Int_t icont1, Double_t x1, Double_t y1,
Double_t elev2, Int_t icont2, Double_t x2, Double_t y2,
Double_t *xarr, Double_t *yarr, Int_t *itarr, Double_t *levels)
*-*-*-*-*-*Fill the matrix XARR YARR for Contour Plot*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
==========================================
void PaintErrors(Option_t *)
*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*Draw histogram error bars*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
Draws error bars for the current histogram. The current polymarker
is drawn at the centre of the errors according to CHOPT:
' ' Coordinates are expressed in histogram coordinates
(of the last drawn histogram). Error bars are drawn.
'1' Small lines are drawn at the end of the error bars.
'2' Error rectangles are drawn.
'3' A filled area is drawn through the end points of the vertical
error bars.
'4' A smoothed filled area is drawn through the end points of the
vertical error bars.
'0' Turn off the symbols clipping.
Note that for all options, the line and fill attributes of the
histogram are used for the errors or errors contours.
Use gStyle->SetErrorX(dx) to control the size of the error along x.
set dx = 0 to suppress the error along x.
Use gStyle->SetEndErrorSize(np) to control the size of the lines
at the end of the error bars (when option 1 is used).
By default np=1. (np reprersents the number of pixels).
/*
 */
*/
*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
void Paint2DErrors(Option_t *)
Draw 2D histograms errors
void PaintFrame()
*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*Calculate range and clear pad (canvas)*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
======================================
void PaintFunction(Option_t *)
*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*Paint functions associated to an histogram*-*-*-*-*-*-*
==========================================
An associated function is created by THistPainter::Fit. Note that more than
on fitted function can be associated with one histogram (see THistPainter::Fit).
A TF1 object can be added to the list of associated functions directly
by a user without calling THistPainter::Fit.
To add a new function to the list of associated functions, do
h->GetListOfFunctions()->Add(f1);
or
h->GetListOfFunctions()->Add(f1,someoption);
To retrieve a function by name from this list, do:
TF1 *f1 = (TF1*)h->GetListOfFunctions()->FindObject(name);
or
TF1 *f1 = h->GetFunction(name);
void PaintHist(Option_t *)
*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*Control routine to draw an histogram*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
====================================
void PaintH3(Option_t *option)
*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*Control function to draw a 3-D histogram*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
========================================
Int_t PaintInit()
*-*-*-*-*Compute histogram parameters used by the drawing routines*-*-*-*
=========================================================
Int_t PaintInitH()
Compute histogram parameters used by the drawing routines
for a rotated pad
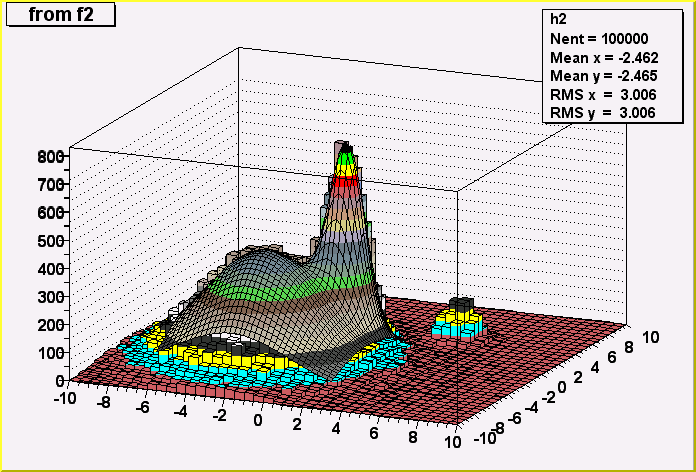
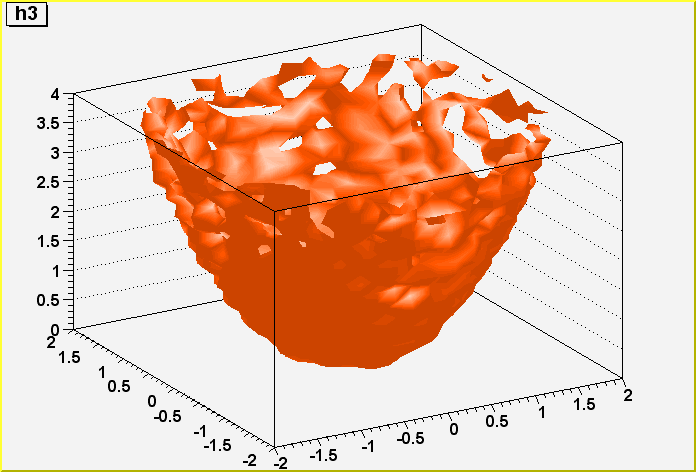
void PaintH3Iso()
Control function to draw a 3d histogram with Iso Surfaces.
Thanks to the function IsoSurface of the TPainter3dAlgorithms class, this
function paints a Gouraud shaded 3d iso surface though a 3d histogram.
This first implementation paint one surface at the value computed as follow:
SumOfWeights/(NbinsX*NbinsY*NbinsZ)
Example:
#include "TH3.h"
#include "TRandom.h"
void hist3d() {
TH3F *h3 = new TH3F("h3","h3",20,-2,2,20,-2,2,20,0,4);
Double_t x, y, z;
for (Int_t i=0;i<10000;i++) {
gRandom->Rannor(x, y);
z = x*x + y*y;
h3->Fill(x,y,z);
}
h3->Draw("iso");
}
/*
 */
*/
void PaintLego(Option_t *)
*-*-*-*-*-*Control function to draw a table as a lego plot*-*-*-*-*-*
===============================================
In a lego plot, cell contents are represented as 3-d boxes.
The height of the box is proportional to the cell content.
A lego plot can be represented in several coordinate systems.
Default system is Cartesian coordinates.
Possible systems are CYL,POL,SPH,PSR.
See THistPainter::Draw for the list of Lego options.
See TPainter3dAlgorithms for more examples of lego options.
See TStyle::SeTPaletteAxis to change the color palette.
It is suggested to use palette 1 via the call
gStyle->SetColorPalette(1)
/*
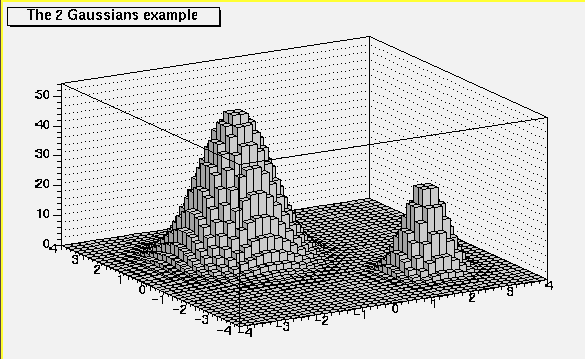 */
*/
*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
void PaintLegoAxis(TGaxis *axis, Double_t ang)
*-*-*-*-*Draw the axis for legos and surface plots*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
=========================================
void PaintPalette()
*-*-*-*-*-*Paint the color palette on the right side of the pad*-*-*-*-*
====================================================
void PaintScatterPlot(Option_t *option)
*-*-*-*-*-*Control function to draw a table as a scatter plot*-*-*-*-*
==================================================
For each cell (i,j) a number of points proportional to the cell
content is drawn.
A maximum of kNMAX points per cell is drawn. If the maximum is above kNMAX
contents are normalized to kNMAX. (kNMAX=2000)
if option is of the form "scat=ff", (eg scat=1.8, scat=1e-3), then
ff is used as a scale factor to compute the number of dots.
"scat=1" is the default.
/*
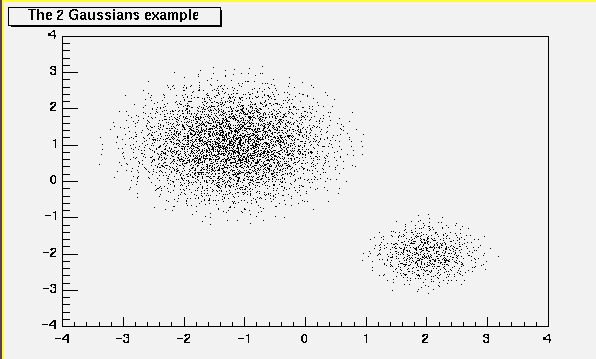 */
*/
*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
void PaintStat(Int_t dostat, TF1 *fit)
Draw the statistics box for 1D and profile histograms
The type of information printed in the histogram statistics box
can be selected via gStyle->SetOptStat(mode).
The parameter mode can be = iourmen (default = 0001111)
n = 1; name of histogram is printed
e = 1; number of entries printed
m = 1; mean value printed
m = 2; mean and mean error values printed
r = 1; rms printed
r = 2; rms and rms error printed
u = 1; number of underflows printed
o = 1; number of overflows printed
i = 1; integral of bins printed
s = 1; skewness printed
s = 2; skewness and skewness error printed
k = 1; kurtosis printed
k = 2; kurtosis and kurtosis error printed
Example: gStyle->SetOptStat(11);
print only name of histogram and number of entries.
The type of information about fit parameters printed in the histogram
statistics box can be selected via gStyle->SetOptFit(mode).
The parameter mode can be = pcev (default = 0111)
v = 1; print name/values of parameters
e = 1; print errors (if e=1, v must be 1)
c = 1; print Chisquare/Number of degrees of freedom
p = 1; print Probability
When "v"=1 is specified, only the non-fixed parameters are shown.
When "v"=2 all parameters are shown.
Example: gStyle->SetOptFit(1011);
print fit probability, parameter names/values and errors.
Note: gStyle->SetOptFit(1) means "default value", so it is equivalent to
gStyle->SetOptFit(111)
When option "same" is specified, the statistic box is not drawn.
Specify option "sames" to force painting statistics with option "same"
When option "sames" is given, one can use the following technique
to move a previous "stats" box to a new position
Root > TPaveStats *st = (TPaveStats*)gPad->GetPrimitive("stats")
Root > st->SetX1NDC(newx1); //new x start position
Root > st->SetX2NDC(newx2); //new x end position
Root > newhist->Draw("sames")
void PaintStat2(Int_t dostat, TF1 *fit)
Draw the statistics box for 2D histogram.
The type of information printed in the histogram statistics box
can be selected via gStyle->SetOptStat(mode).
The parameter mode can be = ourmen (default = 001111)
n = 1; name of histogram is printed
e = 1; number of entries printed
m = 1; mean value printed
m = 2; mean and mean error values printed
r = 1; rms printed
r = 2; rms and rms error printed
u = 1; number of underflows printed
o = 1; number of overflows printed
i = 1; integral of bins printed
s = 1; skewness printed
s = 2; skewness and skewness error printed
k = 1; kurtosis printed
k = 2; kurtosis and kurtosis error printed
Example: gStyle->SetOptStat(11);
print only name of histogram and number of entries.
void PaintSurface(Option_t *)
*-*-*-*-*-*Control function to draw a table as a surface plot*-*-*-*-*-*
==================================================
In a surface plot, cell contents are represented as a mesh.
The height of the mesh is proportional to the cell content.
A surface plot can be represented in several coordinate systems.
Default system is Cartesian coordinates.
Possible systems are CYL,POL,SPH,PSR.
See THistPainter::Draw for a list of Surface options
The following picture is generated with option SURF1.
See TStyle::SeTPaletteAxis to change the color palette.
It is suggested to use palette 1 via the call
gStyle->SetColorPalette(1)
/*
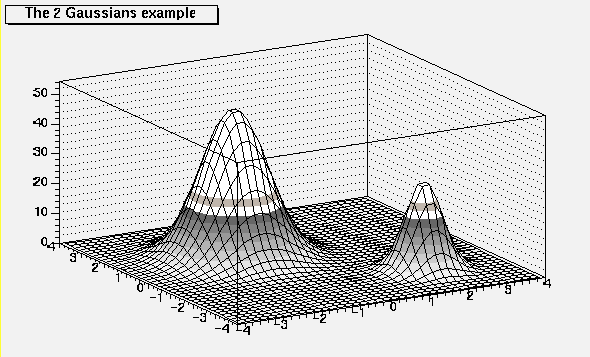 */
*/
The following picture is generated with option SURF3.
/*
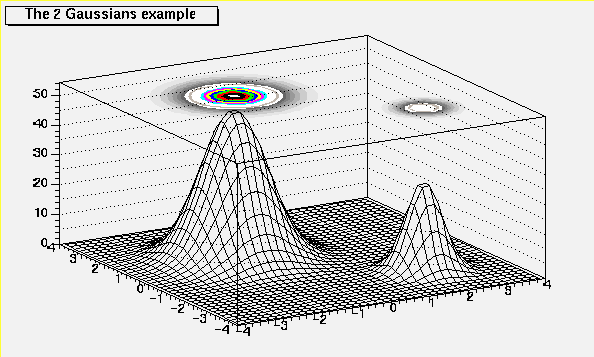 */
*/
*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
void PaintTriangles(Option_t *option)
Control function to draw a table using Delaunay triangles
void DefineColorLevels(Int_t ndivz)
void PaintTable(Option_t *option)
*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*Control function to draw 2-D/3-D tables*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
=======================================
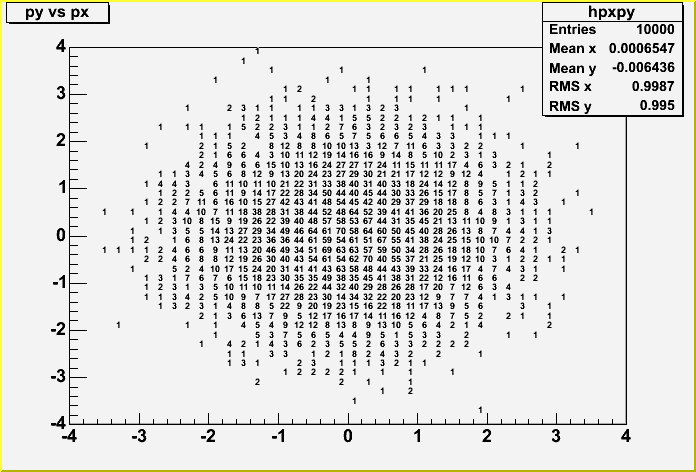
void PaintText(Option_t *)
Control function to draw a histogram with the bin values
For each bin the content is printed.
The text attributes are:
- text font = current TStyle font
- text size = 0.02*padheight*markersize
- text color = marker color
By default the format "g" is used. This format can be redefined
by calling gStyle->SetPaintTextFormat
/*
 */
*/
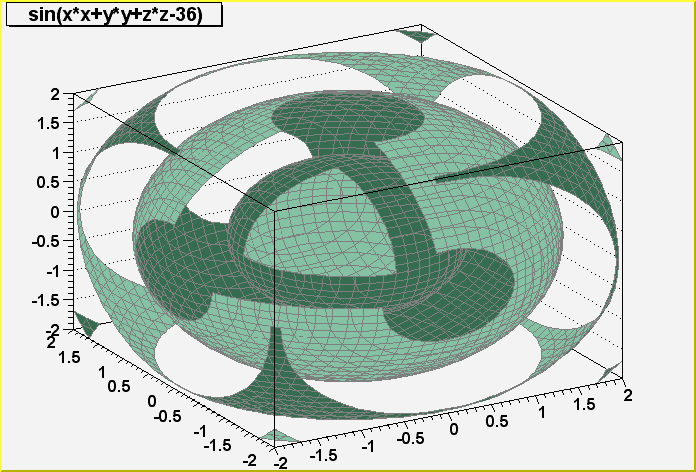
void PaintTF3()
Control function to draw a 3d implicit functions.
Thanks to the function ImplicitFunction of the TPainter3dAlgorithms class,
this function paints 3d representation of an implicit function.
Example:
TF3 *fun3 = new TF3("fun3","sin(x*x+y*y+z*z-36)",-2,2,-2,2,-2,2);
fun3->Draw();
/*
 */
*/
void PaintTitle()
Draw the histogram title
The title is drawn according to the title alignment returned by
GetTitleAlign. It is a 2 digits integer): hv
where "h" is the horizontal alignment and "v" is the vertical alignment.
"h" can get the values 1 2 3 for left, center, and right
"v" can get the values 1 2 3 for bottom, middle and top
for instance the default alignment is: 13 (left top)
void ProcessMessage(const char *mess, const TObject *obj)
Process message mess
Int_t ProjectAitoff2xy(Double_t l, Double_t b, Double_t &Al, Double_t &Ab)
static function
Convert Right Ascension, Declination to X,Y using an AITOFF projection.
This procedure can be used to create an all-sky map in Galactic
coordinates with an equal-area Aitoff projection. Output map
coordinates are zero longitude centered.
Also called Hammer-Aitoff projection (first presented by Ernst von Hammer in 1892)
source: GMT
code from Ernst-Jan Buis
Int_t ProjectMercator2xy(Double_t l, Double_t b, Double_t &Al, Double_t &Ab)
static function
Probably the most famous of the various map projections, the Mercator projection
takes its name from Mercator who presented it in 1569. It is a cylindrical, conformal projection
with no distortion along the equator.
The Mercator projection has been used extensively for world maps in which the distortion towards
the polar regions grows rather large, thus incorrectly giving the impression that, for example,
Greenland is larger than South America. In reality, the latter is about eight times the size of
Greenland. Also, the Former Soviet Union looks much bigger than Africa or South America. One may wonder
whether this illusion has had any influence on U.S. foreign policy.' (Source: GMT)
code from Ernst-Jan Buis
Int_t ProjectSinusoidal2xy(Double_t l, Double_t b, Double_t &Al, Double_t &Ab)
static function
code from Ernst-Jan Buis
Int_t ProjectParabolic2xy(Double_t l, Double_t b, Double_t &Al, Double_t &Ab)
static function
code from Ernst-Jan Buis
void RecalculateRange()
*-*-*-*Recompute the histogram range following graphics operations*-*-*
===========================================================
void SetHistogram(TH1 *h)
set current histogram to h
Int_t TableInit()
*-*-*-*-*-*-*Initialize various options to draw tables*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
=========================================
const char* GetBestFormat(Double_t v, Double_t e, const char *f)
This function returns the best format to print the error value (e)
knowing the parameter value (v) and the format (f) used to print it.
Inline Functions
TList* GetStack() const
void RecursiveRemove(TObject*)
void SetStack(TList* stack)
TClass* Class()
TClass* IsA() const
void ShowMembers(TMemberInspector& insp, char* parent)
void Streamer(TBuffer& b)
void StreamerNVirtual(TBuffer& b)
THistPainter THistPainter(const THistPainter&)
THistPainter& operator=(const THistPainter&)
Author: Rene Brun 26/08/99
Last update: root/histpainter:$Name: $:$Id: THistPainter.cxx,v 1.222 2005/09/04 10:33:36 brun Exp $
Copyright (C) 1995-2000, Rene Brun and Fons Rademakers. *
ROOT page - Class index - Class Hierarchy - Top of the page
This page has been automatically generated. If you have any comments or suggestions about the page layout send a mail to ROOT support, or contact the developers with any questions or problems regarding ROOT.
 */
*/
 */
*/
 */
*/
 */
*/
 */
*/
 */
*/
 */
*/
 */
*/
 */
*/
 */
*/
 */
*/
 */
*/
 */
*/
 */
*/
 */
*/
 */
*/
 */
*/
 */
*/
 */
*/
 */
*/
 */
*/
 */
*/
 */
*/
 */
*/
 */
*/
 */
*/