// @(#)root/base:$Name: $:$Id: TMath.cxx,v 1.107 2005/09/03 07:09:59 brun Exp $
// Authors: Rene Brun, Anna Kreshuk, Eddy Offermann, Fons Rademakers 29/07/95
/*************************************************************************
* Copyright (C) 1995-2004, Rene Brun and Fons Rademakers. *
* All rights reserved. *
* *
* For the licensing terms see $ROOTSYS/LICENSE. *
* For the list of contributors see $ROOTSYS/README/CREDITS. *
*************************************************************************/
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// //
// TMath //
// //
// Encapsulate math routines. //
// //
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
#include "TMath.h"
#include "TError.h"
#include <math.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <algorithm>
#include "Riostream.h"
#include "TString.h"
//const Double_t
// TMath::Pi = 3.14159265358979323846,
// TMath::E = 2.7182818284590452354;
const Int_t kWorkMax = 100;
// Without this macro the THtml doc for TMath can not be generated
#if !defined(R__ALPHA) && !defined(R__SOLARIS) && !defined(R__ACC) && !defined(R__FBSD)
NamespaceImp(TMath)
#endif
namespace TMath {
Double_t GamCf(Double_t a,Double_t x);
Double_t GamSer(Double_t a,Double_t x);
Double_t VavilovDenEval(Double_t rlam, Double_t *AC, Double_t *HC, Int_t itype);
void VavilovSet(Double_t rkappa, Double_t beta2, Bool_t mode, Double_t *WCM, Double_t *AC, Double_t *HC, Int_t &itype, Int_t &npt);
}
#if defined(_MSC_VER) && (_MSC_VER<1300)
// Work around a problem in MSC++ 6 where it can not really handle
// static templated member functions
#define SortImp SortImpStandalone
template <class Element, class Index, class Size>
void SortImpStandalone(Size n1, const Element *a,
Index *index, Bool_t down);
#define MedianImp MedianImpStandalone
template <class Element, class Index, class Size>
Double_t MedianImpStandalone(Size n, const Element *a, const Double_t *w, Index *work);
#define KOrdStatImp KOrdStatImpStandalone
template <class Element, class Index, class Size>
Element KOrdStatImpStandalone(Size n, const Element *a, Size k, Index *work);
#endif
//______________________________________________________________________________
#if defined(R__KCC)
static Double_t hypot(Double_t x, Double_t y)
{
Double_t ax = TMath::Abs(x), ay = TMath::Abs(y);
Double_t amax, amin;
if(ax > ay){
amax = ax;
amin = ay;
} else {
amin = ax;
amax = ay;
}
if(amin == 0.0) return amax;
Double_t f = amin/amax;
return amax*sqrt(1.0 + f*f);
}
#endif
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long_t TMath::Hypot(Long_t x, Long_t y)
{
return (Long_t) (hypot((Double_t)x, (Double_t)y) + 0.5);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::Hypot(Double_t x, Double_t y)
{
return hypot(x, y);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::ASinH(Double_t x)
{
#if defined(WIN32) || defined(R__KCC)
if(x==0.0) return 0.0;
Double_t ax = Abs(x);
return log(x+ax*sqrt(1.+1./(ax*ax)));
#else
return asinh(x);
#endif
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::ACosH(Double_t x)
{
#if defined(WIN32) || defined(R__KCC)
if(x==0.0) return 0.0;
Double_t ax = Abs(x);
return log(x+ax*sqrt(1.-1./(ax*ax)));
#else
return acosh(x);
#endif
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::ATanH(Double_t x)
{
#if defined(WIN32) || defined(R__KCC)
return log((1+x)/(1-x))/2;
#else
return atanh(x);
#endif
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::Log2(Double_t x)
{
return log(x)/log(2.0);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long_t TMath::NextPrime(Long_t x)
{
// Return next prime number after x, unless x is a prime in which case
// x is returned.
if (x < 2)
return 2;
if (x == 3)
return 3;
if (x % 2 == 0)
x++;
Long_t sqr = (Long_t) sqrt((Double_t)x) + 1;
for (;;) {
Long_t n;
for (n = 3; (n <= sqr) && ((x % n) != 0); n += 2)
;
if (n > sqr)
return x;
x += 2;
}
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TMath::Nint(Float_t x)
{
// Round to nearest integer. Rounds half integers to the nearest
// even integer.
int i;
if (x >= 0) {
i = int(x + 0.5);
if (x + 0.5 == Float_t(i) && i & 1) i--;
} else {
i = int(x - 0.5);
if (x - 0.5 == Float_t(i) && i & 1) i++;
}
return i;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TMath::Nint(Double_t x)
{
// Round to nearest integer. Rounds half integers to the nearest
// even integer.
int i;
if (x >= 0) {
i = int(x + 0.5);
if (x + 0.5 == Double_t(i) && i & 1) i--;
} else {
i = int(x - 0.5);
if (x - 0.5 == Double_t(i) && i & 1) i++;
}
return i;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Float_t *TMath::Cross(const Float_t v1[3],const Float_t v2[3],Float_t out[3])
{
// Calculate the Cross Product of two vectors:
// out = [v1 x v2]
out[0] = v1[1] * v2[2] - v1[2] * v2[1];
out[1] = v1[2] * v2[0] - v1[0] * v2[2];
out[2] = v1[0] * v2[1] - v1[1] * v2[0];
return out;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t *TMath::Cross(const Double_t v1[3],const Double_t v2[3],Double_t out[3])
{
// Calculate the Cross Product of two vectors:
// out = [v1 x v2]
out[0] = v1[1] * v2[2] - v1[2] * v2[1];
out[1] = v1[2] * v2[0] - v1[0] * v2[2];
out[2] = v1[0] * v2[1] - v1[1] * v2[0];
return out;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::DiLog(Double_t x)
{
// The DiLogarithm function
// Code translated by R.Brun from CERNLIB DILOG function C332
const Double_t hf = 0.5;
const Double_t pi = TMath::Pi();
const Double_t pi2 = pi*pi;
const Double_t pi3 = pi2/3;
const Double_t pi6 = pi2/6;
const Double_t pi12 = pi2/12;
const Double_t c[20] = {0.42996693560813697, 0.40975987533077105,
-0.01858843665014592, 0.00145751084062268,-0.00014304184442340,
0.00001588415541880,-0.00000190784959387, 0.00000024195180854,
-0.00000003193341274, 0.00000000434545063,-0.00000000060578480,
0.00000000008612098,-0.00000000001244332, 0.00000000000182256,
-0.00000000000027007, 0.00000000000004042,-0.00000000000000610,
0.00000000000000093,-0.00000000000000014, 0.00000000000000002};
Double_t t,h,y,s,a,alfa,b1,b2,b0;
if (x == 1) {
h = pi6;
} else if (x == -1) {
h = -pi12;
} else {
t = -x;
if (t <= -2) {
y = -1/(1+t);
s = 1;
b1= TMath::Log(-t);
b2= TMath::Log(1+1/t);
a = -pi3+hf*(b1*b1-b2*b2);
} else if (t < -1) {
y = -1-t;
s = -1;
a = TMath::Log(-t);
a = -pi6+a*(a+TMath::Log(1+1/t));
} else if (t <= -0.5) {
y = -(1+t)/t;
s = 1;
a = TMath::Log(-t);
a = -pi6+a*(-hf*a+TMath::Log(1+t));
} else if (t < 0) {
y = -t/(1+t);
s = -1;
b1= TMath::Log(1+t);
a = hf*b1*b1;
} else if (t <= 1) {
y = t;
s = 1;
a = 0;
} else {
y = 1/t;
s = -1;
b1= TMath::Log(t);
a = pi6+hf*b1*b1;
}
h = y+y-1;
alfa = h+h;
b1 = 0;
b2 = 0;
for (Int_t i=19;i>=0;i--){
b0 = c[i] + alfa*b1-b2;
b2 = b1;
b1 = b0;
}
h = -(s*(b0-h*b2)+a);
}
return h;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::Erf(Double_t x)
{
// Computation of the error function erf(x).
// Erf(x) = (2/sqrt(pi)) Integral(exp(-t^2))dt between 0 and x
//--- NvE 14-nov-1998 UU-SAP Utrecht
return (1-Erfc(x));
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::Erfc(Double_t x)
{
// Compute the complementary error function erfc(x).
// Erfc(x) = (2/sqrt(pi)) Integral(exp(-t^2))dt between x and infinity
//
//--- Nve 14-nov-1998 UU-SAP Utrecht
// The parameters of the Chebyshev fit
const Double_t a1 = -1.26551223, a2 = 1.00002368,
a3 = 0.37409196, a4 = 0.09678418,
a5 = -0.18628806, a6 = 0.27886807,
a7 = -1.13520398, a8 = 1.48851587,
a9 = -0.82215223, a10 = 0.17087277;
Double_t v = 1; // The return value
Double_t z = Abs(x);
if (z <= 0) return v; // erfc(0)=1
Double_t t = 1/(1+0.5*z);
v = t*Exp((-z*z) +a1+t*(a2+t*(a3+t*(a4+t*(a5+t*(a6+t*(a7+t*(a8+t*(a9+t*a10)))))))));
if (x < 0) v = 2-v; // erfc(-x)=2-erfc(x)
return v;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::ErfInverse(Double_t x)
{
// returns the inverse error function
// x must be <-1<x<1
Int_t kMaxit = 50;
Double_t kEps = 1e-14;
Double_t kConst = 0.8862269254527579; // sqrt(pi)/2.0
if(TMath::Abs(x) <= kEps) return kConst*x;
// Newton iterations
Double_t erfi, derfi, y0,y1,dy0,dy1;
if(TMath::Abs(x) < 1.0) {
erfi = kConst*TMath::Abs(x);
y0 = TMath::Erf(0.9*erfi);
derfi = 0.1*erfi;
for (Int_t iter=0; iter<kMaxit; iter++) {
y1 = 1. - TMath::Erfc(erfi);
dy1 = TMath::Abs(x) - y1;
if (TMath::Abs(dy1) < kEps) {if (x < 0) return -erfi; else return erfi;}
dy0 = y1 - y0;
derfi *= dy1/dy0;
y0 = y1;
erfi += derfi;
if(TMath::Abs(derfi/erfi) < kEps) {if (x < 0) return -erfi; else return erfi;}
}
}
return 0; //did not converge
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::Factorial(Int_t n)
{
// Compute factorial(n).
if(n <= 0) return 1.;
Double_t x = 1;
Int_t b = 0;
do {
b++;
x *= b;
} while(b!=n);
return x;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::Freq(Double_t x)
{
// Computation of the normal frequency function freq(x).
// Freq(x) = (1/sqrt(2pi)) Integral(exp(-t^2/2))dt between -infinity and x.
//
// Translated from CERNLIB C300 by Rene Brun.
const Double_t c1 = 0.56418958354775629;
const Double_t w2 = 1.41421356237309505;
const Double_t p10 = 2.4266795523053175e+2, q10 = 2.1505887586986120e+2,
p11 = 2.1979261618294152e+1, q11 = 9.1164905404514901e+1,
p12 = 6.9963834886191355e+0, q12 = 1.5082797630407787e+1,
p13 =-3.5609843701815385e-2, q13 = 1;
const Double_t p20 = 3.00459261020161601e+2, q20 = 3.00459260956983293e+2,
p21 = 4.51918953711872942e+2, q21 = 7.90950925327898027e+2,
p22 = 3.39320816734343687e+2, q22 = 9.31354094850609621e+2,
p23 = 1.52989285046940404e+2, q23 = 6.38980264465631167e+2,
p24 = 4.31622272220567353e+1, q24 = 2.77585444743987643e+2,
p25 = 7.21175825088309366e+0, q25 = 7.70001529352294730e+1,
p26 = 5.64195517478973971e-1, q26 = 1.27827273196294235e+1,
p27 =-1.36864857382716707e-7, q27 = 1;
const Double_t p30 =-2.99610707703542174e-3, q30 = 1.06209230528467918e-2,
p31 =-4.94730910623250734e-2, q31 = 1.91308926107829841e-1,
p32 =-2.26956593539686930e-1, q32 = 1.05167510706793207e+0,
p33 =-2.78661308609647788e-1, q33 = 1.98733201817135256e+0,
p34 =-2.23192459734184686e-2, q34 = 1;
Double_t v = TMath::Abs(x)/w2;
Double_t vv = v*v;
Double_t ap, aq, h, hc, y;
if (v < 0.5) {
y=vv;
ap=p13;
aq=q13;
ap = p12 +y*ap;
ap = p11 +y*ap;
ap = p10 +y*ap;
aq = q12 +y*aq;
aq = q11 +y*aq;
aq = q10 +y*aq;
h = v*ap/aq;
hc = 1-h;
} else if (v < 4) {
ap = p27;
aq = q27;
ap = p26 +v*ap;
ap = p25 +v*ap;
ap = p24 +v*ap;
ap = p23 +v*ap;
ap = p22 +v*ap;
ap = p21 +v*ap;
ap = p20 +v*ap;
aq = q26 +v*aq;
aq = q25 +v*aq;
aq = q24 +v*aq;
aq = q23 +v*aq;
aq = q22 +v*aq;
aq = q21 +v*aq;
aq = q20 +v*aq;
hc = TMath::Exp(-vv)*ap/aq;
h = 1-hc;
} else {
y = 1/vv;
ap = p34;
aq = q34;
ap = p33 +y*ap;
ap = p32 +y*ap;
ap = p31 +y*ap;
ap = p30 +y*ap;
aq = q33 +y*aq;
aq = q32 +y*aq;
aq = q31 +y*aq;
aq = q30 +y*aq;
hc = TMath::Exp(-vv)*(c1+y*ap/aq)/v;
h = 1-hc;
}
if (x > 0) return 0.5 +0.5*h;
else return 0.5*hc;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::Gamma(Double_t z)
{
// Computation of gamma(z) for all z>0.
//
// C.Lanczos, SIAM Journal of Numerical Analysis B1 (1964), 86.
//
//--- Nve 14-nov-1998 UU-SAP Utrecht
if (z<=0) return 0;
Double_t v = LnGamma(z);
return Exp(v);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::Gamma(Double_t a,Double_t x)
{
// Computation of the upper incomplete gamma function P(a,x) as defined in the
// Handbook of Mathematical Functions by Abramowitz and Stegun, formula 6.5.1 on page 260 .
//
// Note that this is the version of the incomplete gamma function as used in statistics :
// its normalization is such that TMath::Gamma(a,+infinity) = 1 .
//
//--- Nve 14-nov-1998 UU-SAP Utrecht
if (a <= 0 || x <= 0) return 0;
if (x < (a+1)) return GamSer(a,x);
else return GamCf(a,x);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::GamCf(Double_t a,Double_t x)
{
// Computation of the incomplete gamma function P(a,x)
// via its continued fraction representation.
//
//--- Nve 14-nov-1998 UU-SAP Utrecht
Int_t itmax = 100; // Maximum number of iterations
Double_t eps = 3.e-14; // Relative accuracy
Double_t fpmin = 1.e-30; // Smallest Double_t value allowed here
if (a <= 0 || x <= 0) return 0;
Double_t gln = LnGamma(a);
Double_t b = x+1-a;
Double_t c = 1/fpmin;
Double_t d = 1/b;
Double_t h = d;
Double_t an,del;
for (Int_t i=1; i<=itmax; i++) {
an = Double_t(-i)*(Double_t(i)-a);
b += 2;
d = an*d+b;
if (Abs(d) < fpmin) d = fpmin;
c = b+an/c;
if (Abs(c) < fpmin) c = fpmin;
d = 1/d;
del = d*c;
h = h*del;
if (Abs(del-1) < eps) break;
//if (i==itmax) cout << "*GamCf(a,x)* a too large or itmax too small" << endl;
}
Double_t v = Exp(-x+a*Log(x)-gln)*h;
return (1-v);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::GamSer(Double_t a,Double_t x)
{
// Computation of the incomplete gamma function P(a,x)
// via its series representation.
//
//--- Nve 14-nov-1998 UU-SAP Utrecht
Int_t itmax = 100; // Maximum number of iterations
Double_t eps = 3.e-14; // Relative accuracy
if (a <= 0 || x <= 0) return 0;
Double_t gln = LnGamma(a);
Double_t ap = a;
Double_t sum = 1/a;
Double_t del = sum;
for (Int_t n=1; n<=itmax; n++) {
ap += 1;
del = del*x/ap;
sum += del;
if (TMath::Abs(del) < Abs(sum*eps)) break;
//if (n==itmax) cout << "*GamSer(a,x)* a too large or itmax too small" << endl;
}
Double_t v = sum*Exp(-x+a*Log(x)-gln);
return v;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::BreitWigner(Double_t x, Double_t mean, Double_t gamma)
{
// Calculate a Breit Wigner function with mean and gamma.
Double_t bw = gamma/((x-mean)*(x-mean) + gamma*gamma/4);
return bw/(2*Pi());
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::Gaus(Double_t x, Double_t mean, Double_t sigma, Bool_t norm)
{
// Calculate a gaussian function with mean and sigma.
// If norm=kTRUE (default is kFALSE) the result is divided
// by sqrt(2*Pi)*sigma.
if (sigma == 0) return 1.e30;
Double_t arg = (x-mean)/sigma;
Double_t res = TMath::Exp(-0.5*arg*arg);
if (!norm) return res;
return res/(2.50662827463100024*sigma); //sqrt(2*Pi)=2.50662827463100024
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::Landau(Double_t x, Double_t mpv, Double_t sigma, Bool_t norm)
{
// The LANDAU function with mpv(most probable value) and sigma.
// This function has been adapted from the CERNLIB routine G110 denlan.
// If norm=kTRUE (default is kFALSE) the result is divided by sigma
Double_t p1[5] = {0.4259894875,-0.1249762550, 0.03984243700, -0.006298287635, 0.001511162253};
Double_t q1[5] = {1.0 ,-0.3388260629, 0.09594393323, -0.01608042283, 0.003778942063};
Double_t p2[5] = {0.1788541609, 0.1173957403, 0.01488850518, -0.001394989411, 0.0001283617211};
Double_t q2[5] = {1.0 , 0.7428795082, 0.3153932961, 0.06694219548, 0.008790609714};
Double_t p3[5] = {0.1788544503, 0.09359161662,0.006325387654, 0.00006611667319,-0.000002031049101};
Double_t q3[5] = {1.0 , 0.6097809921, 0.2560616665, 0.04746722384, 0.006957301675};
Double_t p4[5] = {0.9874054407, 118.6723273, 849.2794360, -743.7792444, 427.0262186};
Double_t q4[5] = {1.0 , 106.8615961, 337.6496214, 2016.712389, 1597.063511};
Double_t p5[5] = {1.003675074, 167.5702434, 4789.711289, 21217.86767, -22324.94910};
Double_t q5[5] = {1.0 , 156.9424537, 3745.310488, 9834.698876, 66924.28357};
Double_t p6[5] = {1.000827619, 664.9143136, 62972.92665, 475554.6998, -5743609.109};
Double_t q6[5] = {1.0 , 651.4101098, 56974.73333, 165917.4725, -2815759.939};
Double_t a1[3] = {0.04166666667,-0.01996527778, 0.02709538966};
Double_t a2[2] = {-1.845568670,-4.284640743};
if (sigma <= 0) return 0;
Double_t v = (x-mpv)/sigma;
Double_t u, ue, us, den;
if (v < -5.5) {
u = TMath::Exp(v+1.0);
ue = TMath::Exp(-1/u);
us = TMath::Sqrt(u);
den = 0.3989422803*(ue/us)*(1+(a1[0]+(a1[1]+a1[2]*u)*u)*u);
} else if(v < -1) {
u = TMath::Exp(-v-1);
den = TMath::Exp(-u)*TMath::Sqrt(u)*
(p1[0]+(p1[1]+(p1[2]+(p1[3]+p1[4]*v)*v)*v)*v)/
(q1[0]+(q1[1]+(q1[2]+(q1[3]+q1[4]*v)*v)*v)*v);
} else if(v < 1) {
den = (p2[0]+(p2[1]+(p2[2]+(p2[3]+p2[4]*v)*v)*v)*v)/
(q2[0]+(q2[1]+(q2[2]+(q2[3]+q2[4]*v)*v)*v)*v);
} else if(v < 5) {
den = (p3[0]+(p3[1]+(p3[2]+(p3[3]+p3[4]*v)*v)*v)*v)/
(q3[0]+(q3[1]+(q3[2]+(q3[3]+q3[4]*v)*v)*v)*v);
} else if(v < 12) {
u = 1/v;
den = u*u*(p4[0]+(p4[1]+(p4[2]+(p4[3]+p4[4]*u)*u)*u)*u)/
(q4[0]+(q4[1]+(q4[2]+(q4[3]+q4[4]*u)*u)*u)*u);
} else if(v < 50) {
u = 1/v;
den = u*u*(p5[0]+(p5[1]+(p5[2]+(p5[3]+p5[4]*u)*u)*u)*u)/
(q5[0]+(q5[1]+(q5[2]+(q5[3]+q5[4]*u)*u)*u)*u);
} else if(v < 300) {
u = 1/v;
den = u*u*(p6[0]+(p6[1]+(p6[2]+(p6[3]+p6[4]*u)*u)*u)*u)/
(q6[0]+(q6[1]+(q6[2]+(q6[3]+q6[4]*u)*u)*u)*u);
} else {
u = 1/(v-v*TMath::Log(v)/(v+1));
den = u*u*(1+(a2[0]+a2[1]*u)*u);
}
if (!norm) return den;
return den/sigma;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::LnGamma(Double_t z)
{
// Computation of ln[gamma(z)] for all z>0.
//
// C.Lanczos, SIAM Journal of Numerical Analysis B1 (1964), 86.
//
// The accuracy of the result is better than 2e-10.
//
//--- Nve 14-nov-1998 UU-SAP Utrecht
if (z<=0) return 0;
// Coefficients for the series expansion
Double_t c[7] = { 2.5066282746310005, 76.18009172947146, -86.50532032941677
,24.01409824083091, -1.231739572450155, 0.1208650973866179e-2
,-0.5395239384953e-5};
Double_t x = z;
Double_t y = x;
Double_t tmp = x+5.5;
tmp = (x+0.5)*Log(tmp)-tmp;
Double_t ser = 1.000000000190015;
for (Int_t i=1; i<7; i++) {
y += 1;
ser += c[i]/y;
}
Double_t v = tmp+Log(c[0]*ser/x);
return v;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Float_t TMath::Normalize(Float_t v[3])
{
// Normalize a vector v in place.
// Returns the norm of the original vector.
Float_t d = Sqrt(v[0]*v[0]+v[1]*v[1]+v[2]*v[2]);
if (d != 0) {
v[0] /= d;
v[1] /= d;
v[2] /= d;
}
return d;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::Normalize(Double_t v[3])
{
// Normalize a vector v in place.
// Returns the norm of the original vector.
// This implementation (thanks Kevin Lynch <krlynch@bu.edu>) is protected
// against possible overflows.
// Find the largest element, and divide that one out.
Double_t av0 = Abs(v[0]), av1 = Abs(v[1]), av2 = Abs(v[2]);
Double_t amax, foo, bar;
// 0 >= {1, 2}
if( av0 >= av1 && av0 >= av2 ) {
amax = av0;
foo = av1;
bar = av2;
}
// 1 >= {0, 2}
else if (av1 >= av0 && av1 >= av2) {
amax = av1;
foo = av0;
bar = av2;
}
// 2 >= {0, 1}
else {
amax = av2;
foo = av0;
bar = av1;
}
if (amax == 0.0)
return 0.;
Double_t foofrac = foo/amax, barfrac = bar/amax;
Double_t d = amax * Sqrt(1.+foofrac*foofrac+barfrac*barfrac);
v[0] /= d;
v[1] /= d;
v[2] /= d;
return d;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Float_t *TMath::Normal2Plane(const Float_t p1[3],const Float_t p2[3],const Float_t p3[3], Float_t normal[3])
{
// Calculate a normal vector of a plane.
//
// Input:
// Float_t *p1,*p2,*p3 - 3 3D points belonged the plane to define it.
//
// Return:
// Pointer to 3D normal vector (normalized)
Float_t v1[3], v2[3];
v1[0] = p2[0] - p1[0];
v1[1] = p2[1] - p1[1];
v1[2] = p2[2] - p1[2];
v2[0] = p3[0] - p1[0];
v2[1] = p3[1] - p1[1];
v2[2] = p3[2] - p1[2];
NormCross(v1,v2,normal);
return normal;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t *TMath::Normal2Plane(const Double_t p1[3],const Double_t p2[3],const Double_t p3[3], Double_t normal[3])
{
// Calculate a normal vector of a plane.
//
// Input:
// Float_t *p1,*p2,*p3 - 3 3D points belonged the plane to define it.
//
// Return:
// Pointer to 3D normal vector (normalized)
Double_t v1[3], v2[3];
v1[0] = p2[0] - p1[0];
v1[1] = p2[1] - p1[1];
v1[2] = p2[2] - p1[2];
v2[0] = p3[0] - p1[0];
v2[1] = p3[1] - p1[1];
v2[2] = p3[2] - p1[2];
NormCross(v1,v2,normal);
return normal;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
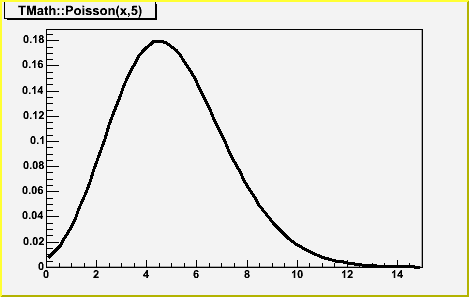
Double_t TMath::Poisson(Double_t x, Double_t par)
{
// compute the Poisson distribution function for (x,par)
// The Poisson PDF is implemented by means of Euler's Gamma-function
// (for the factorial), so for all integer arguments it is correct.
// BUT for non-integer values it IS NOT equal to the Poisson distribution.
// see TMath::PoissonI to get a non-smooth function.
// Note that for large values of par, it is better to call
// TMath::Gaus(x,par,sqrt(par),kTRUE)
//
/*
 */
//
if (x<0)
return 0;
else if (x == 0.0)
return 1./Exp(par);
else {
Double_t lnpoisson = x*log(par)-par-LnGamma(x+1.);
return Exp(lnpoisson);
}
// An alternative strategy is to transition to a Gaussian approximation for
// large values of par ...
// else {
// return Gaus(x,par,Sqrt(par),kTRUE);
// }
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
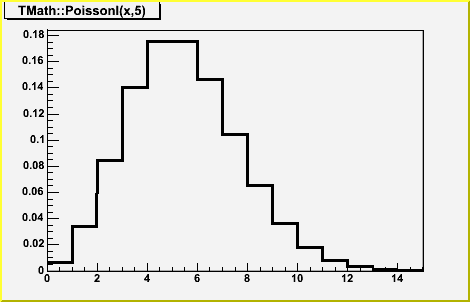
Double_t TMath::PoissonI(Double_t x, Double_t par)
{
// compute the Poisson distribution function for (x,par)
// This is a non-smooth function
//
/*
*/
//
if (x<0)
return 0;
else if (x == 0.0)
return 1./Exp(par);
else {
Double_t lnpoisson = x*log(par)-par-LnGamma(x+1.);
return Exp(lnpoisson);
}
// An alternative strategy is to transition to a Gaussian approximation for
// large values of par ...
// else {
// return Gaus(x,par,Sqrt(par),kTRUE);
// }
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::PoissonI(Double_t x, Double_t par)
{
// compute the Poisson distribution function for (x,par)
// This is a non-smooth function
//
/*
 */
//
const Double_t kMaxInt = 2e6;
if(x<0) return 0;
if(x<1) return TMath::Exp(-par);
Double_t gam;
Int_t ix = Int_t(x);
if(x < kMaxInt) gam = TMath::Power(par,ix)/TMath::Gamma(ix+1);
else gam = TMath::Power(par,x)/TMath::Gamma(x+1);
return gam/TMath::Exp(par);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::Prob(Double_t chi2,Int_t ndf)
{
// Computation of the probability for a certain Chi-squared (chi2)
// and number of degrees of freedom (ndf).
//
// Calculations are based on the incomplete gamma function P(a,x),
// where a=ndf/2 and x=chi2/2.
//
// P(a,x) represents the probability that the observed Chi-squared
// for a correct model should be less than the value chi2.
//
// The returned probability corresponds to 1-P(a,x),
// which denotes the probability that an observed Chi-squared exceeds
// the value chi2 by chance, even for a correct model.
//
//--- NvE 14-nov-1998 UU-SAP Utrecht
if (ndf <= 0) return 0; // Set CL to zero in case ndf<=0
if (chi2 <= 0) {
if (chi2 < 0) return 0;
else return 1;
}
if (ndf==1) {
Double_t v = 1.-Erf(Sqrt(chi2)/Sqrt(2.));
return v;
}
// Gaussian approximation for large ndf
Double_t q = Sqrt(2*chi2)-Sqrt(Double_t(2*ndf-1));
if (ndf > 30 && q > 5) {
Double_t v = 0.5*(1-Erf(q/Sqrt(2.)));
return v;
}
// Evaluate the incomplete gamma function
return (1-Gamma(0.5*ndf,0.5*chi2));
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::KolmogorovProb(Double_t z)
{
// Calculates the Kolmogorov distribution function,
//
/*
*/
//
const Double_t kMaxInt = 2e6;
if(x<0) return 0;
if(x<1) return TMath::Exp(-par);
Double_t gam;
Int_t ix = Int_t(x);
if(x < kMaxInt) gam = TMath::Power(par,ix)/TMath::Gamma(ix+1);
else gam = TMath::Power(par,x)/TMath::Gamma(x+1);
return gam/TMath::Exp(par);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::Prob(Double_t chi2,Int_t ndf)
{
// Computation of the probability for a certain Chi-squared (chi2)
// and number of degrees of freedom (ndf).
//
// Calculations are based on the incomplete gamma function P(a,x),
// where a=ndf/2 and x=chi2/2.
//
// P(a,x) represents the probability that the observed Chi-squared
// for a correct model should be less than the value chi2.
//
// The returned probability corresponds to 1-P(a,x),
// which denotes the probability that an observed Chi-squared exceeds
// the value chi2 by chance, even for a correct model.
//
//--- NvE 14-nov-1998 UU-SAP Utrecht
if (ndf <= 0) return 0; // Set CL to zero in case ndf<=0
if (chi2 <= 0) {
if (chi2 < 0) return 0;
else return 1;
}
if (ndf==1) {
Double_t v = 1.-Erf(Sqrt(chi2)/Sqrt(2.));
return v;
}
// Gaussian approximation for large ndf
Double_t q = Sqrt(2*chi2)-Sqrt(Double_t(2*ndf-1));
if (ndf > 30 && q > 5) {
Double_t v = 0.5*(1-Erf(q/Sqrt(2.)));
return v;
}
// Evaluate the incomplete gamma function
return (1-Gamma(0.5*ndf,0.5*chi2));
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::KolmogorovProb(Double_t z)
{
// Calculates the Kolmogorov distribution function,
//
/*
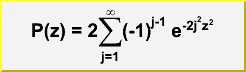 */
//
// which gives the probability that Kolmogorov's test statistic will exceed
// the value z assuming the null hypothesis. This gives a very powerful
// test for comparing two one-dimensional distributions.
// see, for example, Eadie et al, "statistocal Methods in Experimental
// Physics', pp 269-270).
//
// This function returns the confidence level for the null hypothesis, where:
// z = dn*sqrt(n), and
// dn is the maximum deviation between a hypothetical distribution
// function and an experimental distribution with
// n events
//
// NOTE: To compare two experimental distributions with m and n events,
// use z = sqrt(m*n/(m+n))*dn
//
// Accuracy: The function is far too accurate for any imaginable application.
// Probabilities less than 10^-15 are returned as zero.
// However, remember that the formula is only valid for "large" n.
// Theta function inversion formula is used for z <= 1
//
// This function was translated by Rene Brun from PROBKL in CERNLIB.
Double_t fj[4] = {-2,-8,-18,-32}, r[4];
const Double_t w = 2.50662827;
// c1 - -pi**2/8, c2 = 9*c1, c3 = 25*c1
const Double_t c1 = -1.2337005501361697;
const Double_t c2 = -11.103304951225528;
const Double_t c3 = -30.842513753404244;
Double_t u = TMath::Abs(z);
Double_t p;
if (u < 0.2) {
p = 1;
} else if (u < 0.755) {
Double_t v = 1./(u*u);
p = 1 - w*(TMath::Exp(c1*v) + TMath::Exp(c2*v) + TMath::Exp(c3*v))/u;
} else if (u < 6.8116) {
r[1] = 0;
r[2] = 0;
r[3] = 0;
Double_t v = u*u;
Int_t maxj = TMath::Max(1,TMath::Nint(3./u));
for (Int_t j=0; j<maxj;j++) {
r[j] = TMath::Exp(fj[j]*v);
}
p = 2*(r[0] - r[1] +r[2] - r[3]);
} else {
p = 0;
}
return p;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::KolmogorovTest(Int_t na, const Double_t *a, Int_t nb, const Double_t *b, Option_t *option)
{
// Statistical test whether two one-dimensional sets of points are compatible
// with coming from the same parent distribution, using the Kolmogorov test.
// That is, it is used to compare two experimental distributions of unbinned data.
//
// Input:
// a,b: One-dimensional arrays of length na, nb, respectively.
// The elements of a and b must be given in ascending order.
// option is a character string to specify options
// "D" Put out a line of "Debug" printout
// "M" Return the Maximum Kolmogorov distance instead of prob
//
// Output:
// The returned value prob is a calculated confidence level which gives a
// statistical test for compatibility of a and b.
// Values of prob close to zero are taken as indicating a small probability
// of compatibility. For two point sets drawn randomly from the same parent
// distribution, the value of prob should be uniformly distributed between
// zero and one.
// in case of error the function return -1
// If the 2 sets have a different number of points, the minimum of
// the two sets is used.
//
// Method:
// The Kolmogorov test is used. The test statistic is the maximum deviation
// between the two integrated distribution functions, multiplied by the
// normalizing factor (rdmax*sqrt(na*nb/(na+nb)).
//
// Code adapted by Rene Brun from CERNLIB routine TKOLMO (Fred James)
// (W.T. Eadie, D. Drijard, F.E. James, M. Roos and B. Sadoulet,
// Statistical Methods in Experimental Physics, (North-Holland,
// Amsterdam 1971) 269-271)
//
// NOTE1
// A good description of the Kolmogorov test can be seen at:
// http://www.itl.nist.gov/div898/handbook/eda/section3/eda35g.htm
TString opt = option;
opt.ToUpper();
Double_t prob = -1;
// Require at least two points in each graph
if (!a || !b || na <= 2 || nb <= 2) {
Error("KolmogorovTest","Sets must have more than 2 points");
return prob;
}
// Constants needed
Double_t rna = na;
Double_t rnb = nb;
Double_t sa = 1./rna;
Double_t sb = 1./rnb;
Double_t rdiff;
Int_t ia,ib;
// Starting values for main loop
if (a[0] < b[0]) {
rdiff = -sa;
ia = 2;
ib = 1;
} else {
rdiff = sb;
ib = 2;
ia = 1;
}
Double_t rdmax = TMath::Abs(rdiff);
// Main loop over point sets to find max distance
// rdiff is the running difference, and rdmax the max.
Bool_t ok = kFALSE;
for (Int_t i=0;i<na+nb;i++) {
if (a[ia-1] < b[ib-1]) {
rdiff -= sa;
ia++;
if (ia > na) {ok = kTRUE; break;}
} else if (a[ia-1] > b[ib-1]) {
rdiff += sb;
ib++;
if (ib > nb) {ok = kTRUE; break;}
} else {
ia++;
ib++;
if (ia > na) {ok = kTRUE; break;}
if (ib > nb) {ok = kTRUE; break;}
}
rdmax = TMath::Max(rdmax,TMath::Abs(rdiff));
}
// Should never terminate this loop with ok = kFALSE!
if (ok) {
rdmax = TMath::Max(rdmax,TMath::Abs(rdiff));
Double_t z = rdmax * TMath::Sqrt(rna*rnb/(rna+rnb));
prob = TMath::KolmogorovProb(z);
}
// debug printout
if (opt.Contains("D")) {
printf(" Kolmogorov Probability = %g, Max Dist = %g\n",prob,rdmax);
}
if(opt.Contains("M")) return rdmax;
else return prob;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::Voigt(Double_t xx, Double_t sigma, Double_t lg, Int_t r)
{
// Computation of Voigt function (normalised).
// Voigt is a convolution of
// gauss(xx) = 1/(sqrt(2*pi)*sigma) * exp(xx*xx/(2*sigma*sigma)
// and
// lorentz(xx) = (1/pi) * (lg/2) / (xx*xx + g*g/4)
// functions.
//
// The Voigt function is known to be the real part of Faddeeva function also
// called complex error function [2].
//
// The algoritm was developed by J. Humlicek [1].
// This code is based on fortran code presented by R. J. Wells [2].
// Translated and adapted by Miha D. Puc
//
// To calculate the Faddeeva function with relative error less than 10^(-r).
// r can be set by the the user subject to the constraints 2 <= r <= 5.
//
// [1] J. Humlicek, JQSRT, 21, 437 (1982).
// [2] R.J. Wells "Rapid Approximation to the Voigt/Faddeeva Function and its
// Derivatives" JQSRT 62 (1999), pp 29-48.
// http://www-atm.physics.ox.ac.uk/user/wells/voigt.html
if ((sigma < 0 || lg < 0) || (sigma==0 && lg==0)) {
return 0; // Not meant to be for those who want to be thinner than 0
}
if (sigma == 0) {
return lg * 0.159154943 / (xx*xx + lg*lg /4); //pure Lorentz
}
if (lg == 0) { //pure gauss
return 0.39894228 / sigma * TMath::Exp(-xx*xx / (2*sigma*sigma));
}
Double_t x, y, k;
x = xx / sigma / 1.41421356;
y = lg / 2 / sigma / 1.41421356;
Double_t r0, r1;
if (r < 2) r = 2;
if (r > 5) r = 5;
r0=1.51 * exp(1.144 * (Double_t)r);
r1=1.60 * exp(0.554 * (Double_t)r);
// Constants
const Double_t rrtpi = 0.56418958; // 1/SQRT(pi)
Double_t y0, y0py0, y0q; // for CPF12 algorithm
y0 = 1.5;
y0py0 = y0 + y0;
y0q = y0 * y0;
Double_t c[6] = { 1.0117281, -0.75197147, 0.012557727, 0.010022008, -0.00024206814, 0.00000050084806};
Double_t s[6] = { 1.393237, 0.23115241, -0.15535147, 0.0062183662, 0.000091908299, -0.00000062752596};
Double_t t[6] = { 0.31424038, 0.94778839, 1.5976826, 2.2795071, 3.0206370, 3.8897249};
// Local variables
int j; // Loop variables
int rg1, rg2, rg3; // y polynomial flags
Double_t abx, xq, yq, yrrtpi; // --x--, x^2, y^2, y/SQRT(pi)
Double_t xlim0, xlim1, xlim2, xlim3, xlim4; // --x-- on region boundaries
Double_t a0=0, d0=0, d2=0, e0=0, e2=0, e4=0, h0=0, h2=0, h4=0, h6=0;// W4 temporary variables
Double_t p0=0, p2=0, p4=0, p6=0, p8=0, z0=0, z2=0, z4=0, z6=0, z8=0;
Double_t xp[6], xm[6], yp[6], ym[6]; // CPF12 temporary values
Double_t mq[6], pq[6], mf[6], pf[6];
Double_t d, yf, ypy0, ypy0q;
//***** Start of executable code *****************************************
rg1 = 1; // Set flags
rg2 = 1;
rg3 = 1;
yq = y * y; // y^2
yrrtpi = y * rrtpi; // y/SQRT(pi)
// Region boundaries when both k and L are required or when R<>4
xlim0 = r0 - y;
xlim1 = r1 - y;
xlim3 = 3.097 * y - 0.45;
xlim2 = 6.8 - y;
xlim4 = 18.1 * y + 1.65;
if ( y <= 1e-6 ) { // When y<10^-6 avoid W4 algorithm
xlim1 = xlim0;
xlim2 = xlim0;
}
abx = fabs(x); // |x|
xq = abx * abx; // x^2
if ( abx > xlim0 ) { // Region 0 algorithm
k = yrrtpi / (xq + yq);
} else if ( abx > xlim1 ) { // Humlicek W4 Region 1
if ( rg1 != 0 ) { // First point in Region 1
rg1 = 0;
a0 = yq + 0.5; // Region 1 y-dependents
d0 = a0*a0;
d2 = yq + yq - 1.0;
}
d = rrtpi / (d0 + xq*(d2 + xq));
k = d * y * (a0 + xq);
} else if ( abx > xlim2 ) { // Humlicek W4 Region 2
if ( rg2 != 0 ) { // First point in Region 2
rg2 = 0;
h0 = 0.5625 + yq * (4.5 + yq * (10.5 + yq * (6.0 + yq)));
// Region 2 y-dependents
h2 = -4.5 + yq * (9.0 + yq * ( 6.0 + yq * 4.0));
h4 = 10.5 - yq * (6.0 - yq * 6.0);
h6 = -6.0 + yq * 4.0;
e0 = 1.875 + yq * (8.25 + yq * (5.5 + yq));
e2 = 5.25 + yq * (1.0 + yq * 3.0);
e4 = 0.75 * h6;
}
d = rrtpi / (h0 + xq * (h2 + xq * (h4 + xq * (h6 + xq))));
k = d * y * (e0 + xq * (e2 + xq * (e4 + xq)));
} else if ( abx < xlim3 ) { // Humlicek W4 Region 3
if ( rg3 != 0 ) { // First point in Region 3
rg3 = 0;
z0 = 272.1014 + y * (1280.829 + y *
(2802.870 + y *
(3764.966 + y *
(3447.629 + y *
(2256.981 + y *
(1074.409 + y *
(369.1989 + y *
(88.26741 + y *
(13.39880 + y)
)))))))); // Region 3 y-dependents
z2 = 211.678 + y * (902.3066 + y *
(1758.336 + y *
(2037.310 + y *
(1549.675 + y *
(793.4273 + y *
(266.2987 + y *
(53.59518 + y * 5.0)
))))));
z4 = 78.86585 + y * (308.1852 + y *
(497.3014 + y *
(479.2576 + y *
(269.2916 + y *
(80.39278 + y * 10.0)
))));
z6 = 22.03523 + y * (55.02933 + y *
(92.75679 + y *
(53.59518 + y * 10.0)
));
z8 = 1.496460 + y * (13.39880 + y * 5.0);
p0 = 153.5168 + y * (549.3954 + y *
(919.4955 + y *
(946.8970 + y *
(662.8097 + y *
(328.2151 + y *
(115.3772 + y *
(27.93941 + y *
(4.264678 + y * 0.3183291)
)))))));
p2 = -34.16955 + y * (-1.322256+ y *
(124.5975 + y *
(189.7730 + y *
(139.4665 + y *
(56.81652 + y *
(12.79458 + y * 1.2733163)
)))));
p4 = 2.584042 + y * (10.46332 + y *
(24.01655 + y *
(29.81482 + y *
(12.79568 + y * 1.9099744)
)));
p6 = -0.07272979 + y * (0.9377051 + y *
(4.266322 + y * 1.273316));
p8 = 0.0005480304 + y * 0.3183291;
}
d = 1.7724538 / (z0 + xq * (z2 + xq * (z4 + xq * (z6 + xq * (z8 + xq)))));
k = d * (p0 + xq * (p2 + xq * (p4 + xq * (p6 + xq * p8))));
} else { // Humlicek CPF12 algorithm
ypy0 = y + y0;
ypy0q = ypy0 * ypy0;
k = 0.0;
for (j = 0; j <= 5; j++) {
d = x - t[j];
mq[j] = d * d;
mf[j] = 1.0 / (mq[j] + ypy0q);
xm[j] = mf[j] * d;
ym[j] = mf[j] * ypy0;
d = x + t[j];
pq[j] = d * d;
pf[j] = 1.0 / (pq[j] + ypy0q);
xp[j] = pf[j] * d;
yp[j] = pf[j] * ypy0;
}
if ( abx <= xlim4 ) { // Humlicek CPF12 Region I
for (j = 0; j <= 5; j++) {
k = k + c[j]*(ym[j]+yp[j]) - s[j]*(xm[j]-xp[j]) ;
}
} else { // Humlicek CPF12 Region II
yf = y + y0py0;
for ( j = 0; j <= 5; j++) {
k = k + (c[j] *
(mq[j] * mf[j] - y0 * ym[j])
+ s[j] * yf * xm[j]) / (mq[j]+y0q)
+ (c[j] * (pq[j] * pf[j] - y0 * yp[j])
- s[j] * yf * xp[j]) / (pq[j]+y0q);
}
k = y * k + exp( -xq );
}
}
return k / 2.506628 / sigma; // Normalize by dividing by sqrt(2*pi)*sigma.
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TMath::RootsCubic(const Double_t coef[4],Double_t &a, Double_t &b, Double_t &c)
{
// Computes the roots of a cubic polynomial
// coef: Coefficients
// a,b,c: references to the roots
// Author: Jan Conrad
Double_t pi= TMath::Pi();
Int_t threeroots = 0;
Double_t phi,q,r,s,t,p,d,r1,x,temp;
a = 0.0;
b = 0.0;
c = 0.0;
if (coef[3] == 0) return;
r = coef[2]/coef[3];
s = coef[1]/coef[3];
t = coef[0]/coef[3];
p = (3 * s - r*r)/3;
q = (2 * r*r*r)/27 - (r * s)/3 + t;
d = (p/3)*(p/3)*(p/3) + (q/2)*(q/2);
r1 = q/TMath::Abs(q) * TMath::Sqrt(TMath::Abs(p)/3);
if (p==0) {
q = 8.0;
a = TMath::Power(q,1./3.);
goto done;
}
if ( p < 0) {
if (d <= 0) {
threeroots=1;
phi = TMath::ACos(q/2/(r1*r1*r1));
a = TMath::Cos(phi/3);
b = TMath::Cos(phi/3 + (2 * pi)/3);
c = TMath::Cos(phi/3 + (4 * pi)/3);
} else {
x = q/2/(r1*r1*r1);
phi = TMath::Log(x+TMath::Sqrt(x*x-1));
b = TMath::CosH(phi/3);
}
} else {
x = q/2/(r1*r1*r1);
phi = TMath::Log(x+TMath::Sqrt(x*x+1));
b = TMath::SinH(phi/3);
}
a = (-2*r1)*a-r/3;
b = (-2*r1)*b-r/3;
c = (-2*r1)*c-r/3;
done:
if (threeroots == 1) {
if (a > b){
temp=a;
a=b;
b=temp;
}
if (b > c) {
temp=b;
b=c;
c=temp;
}
if (a > b) {
temp=a;
a=b;
b=temp;
}
}
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Short_t TMath::MinElement(Long64_t n, const Short_t *a)
{
// Return minimum of array a of length n.
return *min_element(a,a+n);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TMath::MinElement(Long64_t n, const Int_t *a)
{
// Return minimum of array a of length n.
return *min_element(a,a+n);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Float_t TMath::MinElement(Long64_t n, const Float_t *a)
{
// Return minimum of array a of length n.
return *min_element(a,a+n);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::MinElement(Long64_t n, const Double_t *a)
{
// Return minimum of array a of length n.
return *min_element(a,a+n);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long_t TMath::MinElement(Long64_t n, const Long_t *a)
{
// Return minimum of array a of length n.
return *min_element(a,a+n);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long64_t TMath::MinElement(Long64_t n, const Long64_t *a)
{
// Return minimum of array a of length n.
return *min_element(a,a+n);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Short_t TMath::MaxElement(Long64_t n, const Short_t *a)
{
// Return maximum of array a of length n.
return *max_element(a,a+n);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TMath::MaxElement(Long64_t n, const Int_t *a)
{
// Return maximum of array a of length n.
return *max_element(a,a+n);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Float_t TMath::MaxElement(Long64_t n, const Float_t *a)
{
// Return maximum of array a of length n.
return *max_element(a,a+n);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::MaxElement(Long64_t n, const Double_t *a)
{
// Return maximum of array a of length n.
return *max_element(a,a+n);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long_t TMath::MaxElement(Long64_t n, const Long_t *a)
{
// Return maximum of array a of length n.
return *max_element(a,a+n);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long64_t TMath::MaxElement(Long64_t n, const Long64_t *a)
{
// Return maximum of array a of length n.
return *max_element(a,a+n);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long64_t TMath::LocMin(Long64_t n, const Short_t *a)
{
// Return index of array with the minimum element.
// If more than one element is minimum returns first found.
if (n <= 0 || !a) return -1;
Short_t xmin = a[0];
Long64_t loc = 0;
for (Long64_t i = 1; i < n; i++) {
if (xmin > a[i]) {
xmin = a[i];
loc = i;
}
}
return loc;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long64_t TMath::LocMin(Long64_t n, const Int_t *a)
{
// Return index of array with the minimum element.
// If more than one element is minimum returns first found.
if (n <= 0 || !a) return -1;
Int_t xmin = a[0];
Long64_t loc = 0;
for (Long64_t i = 1; i < n; i++) {
if (xmin > a[i]) {
xmin = a[i];
loc = i;
}
}
return loc;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long64_t TMath::LocMin(Long64_t n, const Float_t *a)
{
// Return index of array with the minimum element.
// If more than one element is minimum returns first found.
if (n <= 0 || !a) return -1;
Float_t xmin = a[0];
Long64_t loc = 0;
for (Long64_t i = 1; i < n; i++) {
if (xmin > a[i]) {
xmin = a[i];
loc = i;
}
}
return loc;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long64_t TMath::LocMin(Long64_t n, const Double_t *a)
{
// Return index of array with the minimum element.
// If more than one element is minimum returns first found.
if (n <= 0 || !a) return -1;
Double_t xmin = a[0];
Long64_t loc = 0;
for (Long64_t i = 1; i < n; i++) {
if (xmin > a[i]) {
xmin = a[i];
loc = i;
}
}
return loc;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long64_t TMath::LocMin(Long64_t n, const Long_t *a)
{
// Return index of array with the minimum element.
// If more than one element is minimum returns first found.
if (n <= 0 || !a) return -1;
Long_t xmin = a[0];
Long64_t loc = 0;
for (Int_t i = 1; i < n; i++) {
if (xmin > a[i]) {
xmin = a[i];
loc = i;
}
}
return loc;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long64_t TMath::LocMin(Long64_t n, const Long64_t *a)
{
// Return index of array with the minimum element.
// If more than one element is minimum returns first found.
if (n <= 0 || !a) return -1;
Long64_t xmin = a[0];
Long64_t loc = 0;
for (Int_t i = 1; i < n; i++) {
if (xmin > a[i]) {
xmin = a[i];
loc = i;
}
}
return loc;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long64_t TMath::LocMax(Long64_t n, const Short_t *a)
{
// Return index of array with the maximum element.
// If more than one element is maximum returns first found.
if (n <= 0 || !a) return -1;
Short_t xmax = a[0];
Long64_t loc = 0;
for (Long64_t i = 1; i < n; i++) {
if (xmax < a[i]) {
xmax = a[i];
loc = i;
}
}
return loc;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long64_t TMath::LocMax(Long64_t n, const Int_t *a)
{
// Return index of array with the maximum element.
// If more than one element is maximum returns first found.
if (n <= 0 || !a) return -1;
Int_t xmax = a[0];
Long64_t loc = 0;
for (Long64_t i = 1; i < n; i++) {
if (xmax < a[i]) {
xmax = a[i];
loc = i;
}
}
return loc;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long64_t TMath::LocMax(Long64_t n, const Float_t *a)
{
// Return index of array with the maximum element.
// If more than one element is maximum returns first found.
if (n <= 0 || !a) return -1;
Float_t xmax = a[0];
Long64_t loc = 0;
for (Long64_t i = 1; i < n; i++) {
if (xmax < a[i]) {
xmax = a[i];
loc = i;
}
}
return loc;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long64_t TMath::LocMax(Long64_t n, const Double_t *a)
{
// Return index of array with the maximum element.
// If more than one element is maximum returns first found.
if (n <= 0 || !a) return -1;
Double_t xmax = a[0];
Long64_t loc = 0;
for (Long64_t i = 1; i < n; i++) {
if (xmax < a[i]) {
xmax = a[i];
loc = i;
}
}
return loc;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long64_t TMath::LocMax(Long64_t n, const Long64_t *a)
{
// Return index of array with the maximum element.
// If more than one element is maximum returns first found.
if (n <= 0 || !a) return -1;
Long64_t xmax = a[0];
Long64_t loc = 0;
for (Long64_t i = 1; i < n; i++) {
if (xmax < a[i]) {
xmax = a[i];
loc = i;
}
}
return loc;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long64_t TMath::LocMax(Long64_t n, const Long_t *a)
{
// Return index of array with the maximum element.
// If more than one element is maximum returns first found.
if (n <= 0 || !a) return -1;
Long_t xmax = a[0];
Long64_t loc = 0;
for (Long64_t i = 1; i < n; i++) {
if (xmax < a[i]) {
xmax = a[i];
loc = i;
}
}
return loc;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::Mean(Long64_t n, const Short_t *a, const Double_t *w)
{
// Return the weighted mean of an array a with length n.
if (n <= 0 || !a) return 0;
Double_t sum = 0;
Double_t sumw = 0;
if (w) {
for (Long64_t i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (w[i] < 0) {
::Error("TMath::Mean","w[%d] = %.4e < 0 ?!",i,w[i]);
return 0;
}
sum += w[i]*a[i];
sumw += w[i];
}
if (sumw <= 0) {
::Error("TMath::Mean","sum of weights == 0 ?!");
return 0;
}
} else {
sumw = n;
for (Long64_t i = 0; i < n; i++)
sum += a[i];
}
return sum/sumw;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::Mean(Long64_t n, const Int_t *a, const Double_t *w)
{
// Return the weighted mean of an array a with length n.
if (n <= 0 || !a) return 0;
Double_t sum = 0;
Double_t sumw = 0;
if (w) {
for (Long64_t i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (w[i] < 0) {
::Error("TMath::Mean","w[%d] = %.4e < 0 ?!",i,w[i]);
return 0;
}
sum += w[i]*a[i];
sumw += w[i];
}
if (sumw <= 0) {
::Error("TMath::Mean","sum of weights == 0 ?!");
return 0;
}
} else {
sumw = n;
for (Long64_t i = 0; i < n; i++)
sum += a[i];
}
return sum/sumw;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::Mean(Long64_t n, const Float_t *a, const Double_t *w)
{
// Return the weighted mean of an array a with length n.
if (n <= 0 || !a) return 0;
Double_t sum = 0;
Double_t sumw = 0;
if (w) {
for (Long64_t i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (w[i] < 0) {
::Error("TMath::Mean","w[%d] = %.4e < 0 ?!",i,w[i]);
return 0;
}
sum += w[i]*a[i];
sumw += w[i];
}
if (sumw <= 0) {
::Error("TMath::Mean","sum of weights == 0 ?!");
return 0;
}
} else {
sumw = n;
for (Long64_t i = 0; i < n; i++)
sum += a[i];
}
return sum/sumw;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::Mean(Long64_t n, const Double_t *a, const Double_t *w)
{
// Return the weighted mean of an array a with length n.
if (n <= 0 || !a) return 0;
Double_t sum = 0;
Double_t sumw = 0;
if (w) {
for (Long64_t i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (w[i] < 0) {
::Error("TMath::Mean","w[%d] = %.4e < 0 ?!",i,w[i]);
return 0;
}
sum += w[i]*a[i];
sumw += w[i];
}
if (sumw <= 0) {
::Error("TMath::Mean","sum of weights == 0 ?!");
return 0;
}
} else {
sumw = n;
for (Long64_t i = 0; i < n; i++)
sum += a[i];
}
return sum/sumw;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::Mean(Long64_t n, const Long_t *a, const Double_t *w)
{
// Return the weighted mean of an array a with length n.
if (n <= 0 || !a) return 0;
Double_t sum = 0;
Double_t sumw = 0;
if (w) {
for (Long64_t i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (w[i] < 0) {
::Error("TMath::Mean","w[%d] = %.4e < 0 ?!",i,w[i]);
return 0;
}
sum += w[i]*a[i];
sumw += w[i];
}
if (sumw <= 0) {
::Error("TMath::Mean","sum of weights == 0 ?!");
return 0;
}
} else {
sumw = n;
for (Long64_t i = 0; i < n; i++)
sum += a[i];
}
return sum/sumw;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::Mean(Long64_t n, const Long64_t *a, const Double_t *w)
{
// Return the weighted mean of an array a with length n.
if (n <= 0 || !a) return 0;
Double_t sum = 0;
Double_t sumw = 0;
if (w) {
for (Long64_t i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (w[i] < 0) {
::Error("TMath::Mean","w[%d] = %.4e < 0 ?!",i,w[i]);
return 0;
}
sum += w[i]*a[i];
sumw += w[i];
}
if (sumw <= 0) {
::Error("TMath::Mean","sum of weights == 0 ?!");
return 0;
}
} else {
sumw = n;
for (Long64_t i = 0; i < n; i++)
sum += a[i];
}
return sum/sumw;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::GeomMean(Long64_t n, const Short_t *a)
{
// Return the geometric mean of an array a with length n.
// geometric_mean = (Prod_i=0,n-1 |a[i]|)^1/n
if (n <= 0 || !a) return 0;
Double_t logsum = 0.;
for (Long64_t i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (a[i] == 0) return 0.;
Double_t absa = (Double_t) TMath::Abs(a[i]);
logsum += TMath::Log(absa);
}
return TMath::Exp(logsum/n);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::GeomMean(Long64_t n, const Int_t *a)
{
// Return the geometric mean of an array a with length n.
// geometric_mean = (Prod_i=0,n-1 |a[i]|)^1/n
if (n <= 0 || !a) return 0;
Double_t logsum = 0.;
for (Long64_t i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (a[i] == 0) return 0.;
Double_t absa = (Double_t) TMath::Abs(a[i]);
logsum += TMath::Log(absa);
}
return TMath::Exp(logsum/n);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::GeomMean(Long64_t n, const Float_t *a)
{
// Return the geometric mean of an array a with length n.
// geometric_mean = (Prod_i=0,n-1 |a[i]|)^1/n
if (n <= 0 || !a) return 0;
Double_t logsum = 0.;
for (Long64_t i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (a[i] == 0) return 0.;
Double_t absa = (Double_t) TMath::Abs(a[i]);
logsum += TMath::Log(absa);
}
return TMath::Exp(logsum/n);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::GeomMean(Long64_t n, const Double_t *a)
{
// Return the geometric mean of an array a with length n.
// geometric_mean = (Prod_i=0,n-1 |a[i]|)^1/n
if (n <= 0 || !a) return 0;
Double_t logsum = 0.;
for (Long64_t i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (a[i] == 0) return 0.;
Double_t absa = (Double_t) TMath::Abs(a[i]);
logsum += TMath::Log(absa);
}
return TMath::Exp(logsum/n);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::GeomMean(Long64_t n, const Long64_t *a)
{
// Return the geometric mean of an array a with length n.
// geometric_mean = (Prod_i=0,n-1 |a[i]|)^1/n
if (n <= 0 || !a) return 0;
Double_t logsum = 0.;
for (Long64_t i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (a[i] == 0) return 0.;
Double_t absa = (Double_t) TMath::Abs(a[i]);
logsum += TMath::Log(absa);
}
return TMath::Exp(logsum/n);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::GeomMean(Long64_t n, const Long_t *a)
{
// Return the geometric mean of an array a with length n.
// geometric_mean = (Prod_i=0,n-1 |a[i]|)^1/n
if (n <= 0 || !a) return 0;
Double_t logsum = 0.;
for (Long64_t i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (a[i] == 0) return 0.;
Double_t absa = (Double_t) TMath::Abs(a[i]);
logsum += TMath::Log(absa);
}
return TMath::Exp(logsum/n);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
#if defined(_MSC_VER) && (_MSC_VER<1300)
// See also the declarations at the top of this file
template <class Element, class Index, class Size>
Double_t MedianImpStandalone(Size n, const Element *a, const Double_t *w, Index *work)
#else
template <class Element, class Index, class Size>
Double_t TMath::MedianImp(Size n, const Element *a,const Double_t *w, Index *work)
#endif
{
// Return the median of the array a where each entry i has weight w[i] .
// Both arrays have a length of at least n . The median is a number obtained
// from the sorted array a through
//
// median = (a[jl]+a[jh])/2. where (using also the sorted index on the array w)
//
// sum_i=0,jl w[i] <= sumTot/2
// sum_i=0,jh w[i] >= sumTot/2
// sumTot = sum_i=0,n w[i]
//
// If w=0, the algorithm defaults to the median definition where it is
// a number that divides the sorted sequence into 2 halves.
// When n is odd or n > 1000, the median is kth element k = (n + 1) / 2.
// when n is even and n < 1000the median is a mean of the elements k = n/2 and k = n/2 + 1.
//
// If work is supplied, it is used to store the sorting index and assumed to be
// >= n . If work=0, local storage is used, either on the stack if n < kWorkMax
// or on the heap for n >= kWorkMax .
if (n <= 0 || !a) return 0;
Bool_t isAllocated = kFALSE;
Double_t median;
Index *ind;
Index workLocal[kWorkMax];
if (work) {
ind = work;
} else {
ind = workLocal;
if (n > kWorkMax) {
isAllocated = kTRUE;
ind = new Index[n];
}
}
if (w) {
Double_t sumTot2 = 0;
for (Int_t j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (w[j] < 0) {
::Error("TMath::Median","w[%d] = %.4e < 0 ?!",j,w[j]);
return 0;
}
sumTot2 += w[j];
}
sumTot2 /= 2.;
SortImp(n, a, ind, kFALSE);
Double_t sum = 0.;
Int_t jl;
for (jl = 0; jl < n; jl++) {
sum += w[ind[jl]];
if (sum >= sumTot2) break;
}
Int_t jh;
sum = 2.*sumTot2;
for (jh = n-1; jh >= 0; jh--) {
sum -= w[ind[jh]];
if (sum <= sumTot2) break;
}
median = 0.5*(a[ind[jl]]+a[ind[jh]]);
} else {
if (n%2 == 1)
median = KOrdStatImp(n, a,n/2, ind);
else {
median = 0.5*(KOrdStatImp(n, a, n/2 -1, ind)+KOrdStatImp(n, a, n/2, ind));
}
}
if (isAllocated)
delete [] ind;
return median;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::Median(Long64_t n, const Short_t *a, const Double_t *w, Long64_t *work)
{
// Return the median of the array a where each entry i has weight w[i] .
// Both arrays have a length of at least n . The median is a number obtained
// from the sorted array a through
//
// median = (a[jl]+a[jh])/2. where (using also the sorted index on the array w)
//
// sum_i=0,jl w[i] <= sumTot/2
// sum_i=0,jh w[i] >= sumTot/2
// sumTot = sum_i=0,n w[i]
//
// If w=0, the algorithm defaults to the median definition where it is
// a number that divides the sorted sequence into 2 halves.
// When n is odd or n > 1000, the median is kth element k = (n + 1) / 2.
// when n is even and n < 1000the median is a mean of the elements k = n/2 and k = n/2 + 1.
//
// If work is supplied, it is used to store the sorting index and assumed to be
// >= n . If work=0, local storage is used, either on the stack if n < kWorkMax
// or on the heap for n >= kWorkMax .
return MedianImp(n, a, w, work);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::Median(Long64_t n, const Int_t *a, const Double_t *w, Long64_t *work)
{
// Return the median of the array a where each entry i has weight w[i] .
// Both arrays have a length of at least n . The median is a number obtained
// from the sorted array a through
//
// median = (a[jl]+a[jh])/2. where (using also the sorted index on the array w)
//
// sum_i=0,jl w[i] <= sumTot/2
// sum_i=0,jh w[i] >= sumTot/2
// sumTot = sum_i=0,n w[i]
//
// If w=0, the algorithm defaults to the median definition where it is
// a number that divides the sorted sequence into 2 halves.
// When n is odd or n > 1000, the median is kth element k = (n + 1) / 2.
// when n is even and n < 1000the median is a mean of the elements k = n/2 and k = n/2 + 1.
//
// If work is supplied, it is used to store the sorting index and assumed to be
// >= n . If work=0, local storage is used, either on the stack if n < kWorkMax
// or on the heap for n >= kWorkMax .
return MedianImp(n, a, w, work);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::Median(Long64_t n, const Float_t *a, const Double_t *w, Long64_t *work)
{
// Return the median of the array a where each entry i has weight w[i] .
// Both arrays have a length of at least n . The median is a number obtained
// from the sorted array a through
//
// median = (a[jl]+a[jh])/2. where (using also the sorted index on the array w)
//
// sum_i=0,jl w[i] <= sumTot/2
// sum_i=0,jh w[i] >= sumTot/2
// sumTot = sum_i=0,n w[i]
//
// If w=0, the algorithm defaults to the median definition where it is
// a number that divides the sorted sequence into 2 halves.
// When n is odd or n > 1000, the median is kth element k = (n + 1) / 2.
// when n is even and n < 1000the median is a mean of the elements k = n/2 and k = n/2 + 1.
//
// If work is supplied, it is used to store the sorting index and assumed to be
// >= n . If work=0, local storage is used, either on the stack if n < kWorkMax
// or on the heap for n >= kWorkMax .
return MedianImp(n, a, w, work);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::Median(Long64_t n, const Double_t *a, const Double_t *w, Long64_t *work)
{
// Return the median of the array a where each entry i has weight w[i] .
// Both arrays have a length of at least n . The median is a number obtained
// from the sorted array a through
//
// median = (a[jl]+a[jh])/2. where (using also the sorted index on the array w)
//
// sum_i=0,jl w[i] <= sumTot/2
// sum_i=0,jh w[i] >= sumTot/2
// sumTot = sum_i=0,n w[i]
//
// If w=0, the algorithm defaults to the median definition where it is
// a number that divides the sorted sequence into 2 halves.
// When n is odd or n > 1000, the median is kth element k = (n + 1) / 2.
// when n is even and n < 1000the median is a mean of the elements k = n/2 and k = n/2 + 1.
//
// If work is supplied, it is used to store the sorting index and assumed to be
// >= n . If work=0, local storage is used, either on the stack if n < kWorkMax
// or on the heap for n >= kWorkMax .
return MedianImp(n, a, w, work);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::Median(Long64_t n, const Long_t *a, const Double_t *w, Long64_t *work)
{
// Return the median of the array a where each entry i has weight w[i] .
// Both arrays have a length of at least n . The median is a number obtained
// from the sorted array a through
//
// median = (a[jl]+a[jh])/2. where (using also the sorted index on the array w)
//
// sum_i=0,jl w[i] <= sumTot/2
// sum_i=0,jh w[i] >= sumTot/2
// sumTot = sum_i=0,n w[i]
//
// If w=0, the algorithm defaults to the median definition where it is
// a number that divides the sorted sequence into 2 halves.
// When n is odd or n > 1000, the median is kth element k = (n + 1) / 2.
// when n is even and n < 1000the median is a mean of the elements k = n/2 and k = n/2 + 1.
//
// If work is supplied, it is used to store the sorting index and assumed to be
// >= n . If work=0, local storage is used, either on the stack if n < kWorkMax
// or on the heap for n >= kWorkMax .
return MedianImp(n, a, w, work);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::Median(Long64_t n, const Long64_t *a, const Double_t *w, Long64_t *work)
{
// Return the median of the array a where each entry i has weight w[i] .
// Both arrays have a length of at least n . The median is a number obtained
// from the sorted array a through
//
// median = (a[jl]+a[jh])/2. where (using also the sorted index on the array w)
//
// sum_i=0,jl w[i] <= sumTot/2
// sum_i=0,jh w[i] >= sumTot/2
// sumTot = sum_i=0,n w[i]
//
// If w=0, the algorithm defaults to the median definition where it is
// a number that divides the sorted sequence into 2 halves.
// When n is odd or n > 1000, the median is kth element k = (n + 1) / 2.
// when n is even and n < 1000the median is a mean of the elements k = n/2 and k = n/2 + 1.
//
// If work is supplied, it is used to store the sorting index and assumed to be
// >= n . If work=0, local storage is used, either on the stack if n < kWorkMax
// or on the heap for n >= kWorkMax .
return MedianImp(n, a, w, work);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
#if defined(_MSC_VER) && (_MSC_VER<1300)
template <class Element, class Index, class Size>
Element KOrdStatImpStandalone(Size n, const Element *a, Size k, Index *work)
#else
template <class Element, class Index, class Size>
Element TMath::KOrdStatImp(Size n, const Element *a, Size k, Index *work)
#endif
{
// Returns k_th order statistic of the array a of size n
// (k_th smallest element out of n elements).
//
// C-convention is used for array indexing, so if you want
// the second smallest element, call KOrdStat(n, a, 1).
//
// If work is supplied, it is used to store the sorting index and
// assumed to be >= n. If work=0, local storage is used, either on
// the stack if n < kWorkMax or on the heap for n >= kWorkMax.
//
// Taken from "Numerical Recipes in C++" without the index array
// implemented by Anna Khreshuk.
//
// See also the declarations at the top of this file
Bool_t isAllocated = kFALSE;
Size i, ir, j, l, mid;
Index arr;
Index *ind;
Index workLocal[kWorkMax];
Index temp;
if (work) {
ind = work;
} else {
ind = workLocal;
if (n > kWorkMax) {
isAllocated = kTRUE;
ind = new Index[n];
}
}
for (Size ii=0; ii<n; ii++) {
ind[ii]=ii;
}
Size rk = k;
l=0;
ir = n-1;
for(;;) {
if (ir<=l+1) { //active partition contains 1 or 2 elements
if (ir == l+1 && a[ind[ir]]<a[ind[l]])
{temp = ind[l]; ind[l]=ind[ir]; ind[ir]=temp;}
Element tmp = a[ind[rk]];
if (isAllocated)
delete [] ind;
return tmp;
} else {
mid = (l+ir) >> 1; //choose median of left, center and right
{temp = ind[mid]; ind[mid]=ind[l+1]; ind[l+1]=temp;}//elements as partitioning element arr.
if (a[ind[l]]>a[ind[ir]]) //also rearrange so that a[l]<=a[l+1]
{temp = ind[l]; ind[l]=ind[ir]; ind[ir]=temp;}
if (a[ind[l+1]]>a[ind[ir]])
{temp=ind[l+1]; ind[l+1]=ind[ir]; ind[ir]=temp;}
if (a[ind[l]]>a[ind[l+1]])
{temp = ind[l]; ind[l]=ind[l+1]; ind[l+1]=temp;}
i=l+1; //initialize pointers for partitioning
j=ir;
arr = ind[l+1];
for (;;){
do i++; while (a[ind[i]]<a[arr]);
do j--; while (a[ind[j]]>a[arr]);
if (j<i) break; //pointers crossed, partitioning complete
{temp=ind[i]; ind[i]=ind[j]; ind[j]=temp;}
}
ind[l+1]=ind[j];
ind[j]=arr;
if (j>=rk) ir = j-1; //keep active the partition that
if (j<=rk) l=i; //contains the k_th element
}
}
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::KOrdStat(Long64_t n, const Double_t *a, Long64_t k, Long64_t *work)
{
// Returns k_th order statistic of the array a of size n
// (k_th smallest element out of n elements).
//
// C-convention is used for array indexing, so if you want
// the second smallest element, call KOrdStat(n, a, 1).
//
// If work is supplied, it is used to store the sorting index and
// assumed to be >= n. If work=0, local storage is used, either on
// the stack if n < kWorkMax or on the heap for n >= kWorkMax.
return KOrdStatImp(n, a, k, work);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Float_t TMath::KOrdStat(Long64_t n, const Float_t *a, Long64_t k, Long64_t *work)
{
// Returns k_th order statistic of the array a of size n
// (k_th smallest element out of n elements).
//
// C-convention is used for array indexing, so if you want
// the second smallest element, call KOrdStat(n, a, 1).
//
// If work is supplied, it is used to store the sorting index and
// assumed to be >= n. If work=0, local storage is used, either on
// the stack if n < kWorkMax or on the heap for n >= kWorkMax.
return KOrdStatImp(n, a, k, work);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TMath::KOrdStat(Long64_t n, const Int_t *a, Long64_t k, Long64_t *work)
{
// Returns k_th order statistic of the array a of size n
// (k_th smallest element out of n elements).
//
// C-convention is used for array indexing, so if you want
// the second smallest element, call KOrdStat(n, a, 1).
//
// If work is supplied, it is used to store the sorting index and
// assumed to be >= n. If work=0, local storage is used, either on
// the stack if n < kWorkMax or on the heap for n >= kWorkMax.
return KOrdStatImp(n, a, k, work);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Short_t TMath::KOrdStat(Long64_t n, const Short_t *a, Long64_t k, Long64_t *work)
{
// Returns k_th order statistic of the array a of size n
// (k_th smallest element out of n elements).
//
// C-convention is used for array indexing, so if you want
// the second smallest element, call KOrdStat(n, a, 1).
//
// If work is supplied, it is used to store the sorting index and
// assumed to be >= n . If work=0, local storage is used, either on
// the stack if n < kWorkMax or on the heap for n >= kWorkMax.
return KOrdStatImp(n, a, k, work);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long64_t TMath::KOrdStat(Long64_t n, const Long_t *a, Long64_t k, Long64_t *work)
{
// Returns k_th order statistic of the array a of size n
// (k_th smallest element out of n elements).
//
// C-convention is used for array indexing, so if you want
// the second smallest element, call KOrdStat(n, a, 1).
//
// If work is supplied, it is used to store the sorting index and
// assumed to be >= n. If work=0, local storage is used, either on
// the stack if n < kWorkMax or on the heap for n >= kWorkMax.
return KOrdStatImp(n, a, k, work);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long64_t TMath::KOrdStat(Long64_t n, const Long64_t *a, Long64_t k, Long64_t *work)
{
// Returns k_th order statistic of the array a of size n
// (k_th smallest element out of n elements).
//
// C-convention is used for array indexing, so if you want
// the second smallest element, call KOrdStat(n, a, 1).
//
// If work is supplied, it is used to store the sorting index and
// assumed to be >= n. If work=0, local storage is used, either on
// the stack if n < kWorkMax or on the heap for n >= kWorkMax.
return KOrdStatImp(n, a, k, work);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::RMS(Long64_t n, const Short_t *a)
{
// Return the RMS of an array a with length n.
if (n <= 0 || !a) return 0;
Double_t tot = 0, tot2 =0, adouble;
for (Long64_t i=0;i<n;i++) {
adouble=Double_t(a[i]);
tot += adouble; tot2 += adouble*adouble;
}
Double_t n1 = 1./n;
Double_t mean = tot*n1;
Double_t rms = TMath::Sqrt(TMath::Abs(tot2*n1 -mean*mean));
return rms;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::RMS(Long64_t n, const Int_t *a)
{
// Return the RMS of an array a with length n.
if (n <= 0 || !a) return 0;
Double_t tot = 0, tot2 =0, adouble;
for (Long64_t i=0;i<n;i++) {
adouble=Double_t(a[i]);
tot += adouble; tot2 += adouble*adouble;
}
Double_t n1 = 1./n;
Double_t mean = tot*n1;
Double_t rms = TMath::Sqrt(TMath::Abs(tot2*n1 -mean*mean));
return rms;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::RMS(Long64_t n, const Float_t *a)
{
// Return the RMS of an array a with length n.
if (n <= 0 || !a) return 0;
Double_t tot = 0, tot2 =0, adouble;
for (Long64_t i=0;i<n;i++) {
adouble=Double_t(a[i]);
tot += adouble; tot2 += adouble*adouble;
}
Double_t n1 = 1./n;
Double_t mean = tot*n1;
Double_t rms = TMath::Sqrt(TMath::Abs(tot2*n1 -mean*mean));
return rms;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::RMS(Long64_t n, const Double_t *a)
{
// Return the RMS of an array a with length n.
if (n <= 0 || !a) return 0;
Double_t tot = 0, tot2 =0;
for (Long64_t i=0;i<n;i++) {tot += a[i]; tot2 += a[i]*a[i]; }
Double_t n1 = 1./n;
Double_t mean = tot*n1;
Double_t rms = TMath::Sqrt(TMath::Abs(tot2*n1 -mean*mean));
return rms;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::RMS(Long64_t n, const Long_t *a)
{
// Return the RMS of an array a with length n.
if (n <= 0 || !a) return 0;
Double_t tot = 0, tot2 =0, adouble;
for (Long64_t i=0;i<n;i++) {
adouble=Double_t(a[i]);
tot += adouble; tot2 += adouble*adouble;
}
Double_t n1 = 1./n;
Double_t mean = tot*n1;
Double_t rms = TMath::Sqrt(TMath::Abs(tot2*n1 -mean*mean));
return rms;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::RMS(Long64_t n, const Long64_t *a)
{
// Return the RMS of an array a with length n.
if (n <= 0 || !a) return 0;
Double_t tot = 0, tot2 =0, adouble;
for (Long64_t i=0;i<n;i++) {
adouble=Double_t(a[i]);
tot += adouble; tot2 += adouble*adouble;
}
Double_t n1 = 1./n;
Double_t mean = tot*n1;
Double_t rms = TMath::Sqrt(TMath::Abs(tot2*n1 -mean*mean));
return rms;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long64_t TMath::BinarySearch(Long64_t n, const Short_t *array, Short_t value)
{
// Binary search in an array of n values to locate value.
//
// Array is supposed to be sorted prior to this call.
// If match is found, function returns position of element.
// If no match found, function gives nearest element smaller than value.
Long64_t nabove, nbelow, middle;
nabove = n+1;
nbelow = 0;
while(nabove-nbelow > 1) {
middle = (nabove+nbelow)/2;
if (value == array[middle-1]) return middle-1;
if (value < array[middle-1]) nabove = middle;
else nbelow = middle;
}
return nbelow-1;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long64_t TMath::BinarySearch(Long64_t n, const Short_t **array, Short_t value)
{
// Binary search in an array of n values to locate value.
//
// Array is supposed to be sorted prior to this call.
// If match is found, function returns position of element.
// If no match found, function gives nearest element smaller than value.
Long64_t nabove, nbelow, middle;
nabove = n+1;
nbelow = 0;
while(nabove-nbelow > 1) {
middle = (nabove+nbelow)/2;
if (value == *array[middle-1]) return middle-1;
if (value < *array[middle-1]) nabove = middle;
else nbelow = middle;
}
return nbelow-1;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long64_t TMath::BinarySearch(Long64_t n, const Int_t *array, Int_t value)
{
// Binary search in an array of n values to locate value.
//
// Array is supposed to be sorted prior to this call.
// If match is found, function returns position of element.
// If no match found, function gives nearest element smaller than value.
Long64_t nabove, nbelow, middle;
nabove = n+1;
nbelow = 0;
while(nabove-nbelow > 1) {
middle = (nabove+nbelow)/2;
if (value == array[middle-1]) return middle-1;
if (value < array[middle-1]) nabove = middle;
else nbelow = middle;
}
return nbelow-1;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long64_t TMath::BinarySearch(Long64_t n, const Int_t **array, Int_t value)
{
// Binary search in an array of n values to locate value.
//
// Array is supposed to be sorted prior to this call.
// If match is found, function returns position of element.
// If no match found, function gives nearest element smaller than value.
Long64_t nabove, nbelow, middle;
nabove = n+1;
nbelow = 0;
while(nabove-nbelow > 1) {
middle = (nabove+nbelow)/2;
if (value == *array[middle-1]) return middle-1;
if (value < *array[middle-1]) nabove = middle;
else nbelow = middle;
}
return nbelow-1;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long64_t TMath::BinarySearch(Long64_t n, const Float_t *array, Float_t value)
{
// Binary search in an array of n values to locate value.
//
// Array is supposed to be sorted prior to this call.
// If match is found, function returns position of element.
// If no match found, function gives nearest element smaller than value.
Long64_t nabove, nbelow, middle;
nabove = n+1;
nbelow = 0;
while(nabove-nbelow > 1) {
middle = (nabove+nbelow)/2;
if (value == array[middle-1]) return middle-1;
if (value < array[middle-1]) nabove = middle;
else nbelow = middle;
}
return nbelow-1;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long64_t TMath::BinarySearch(Long64_t n, const Float_t **array, Float_t value)
{
// Binary search in an array of n values to locate value.
//
// Array is supposed to be sorted prior to this call.
// If match is found, function returns position of element.
// If no match found, function gives nearest element smaller than value.
Long64_t nabove, nbelow, middle;
nabove = n+1;
nbelow = 0;
while(nabove-nbelow > 1) {
middle = (nabove+nbelow)/2;
if (value == *array[middle-1]) return middle-1;
if (value < *array[middle-1]) nabove = middle;
else nbelow = middle;
}
return nbelow-1;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long64_t TMath::BinarySearch(Long64_t n, const Double_t *array, Double_t value)
{
// Binary search in an array of n values to locate value.
//
// Array is supposed to be sorted prior to this call.
// If match is found, function returns position of element.
// If no match found, function gives nearest element smaller than value.
Long64_t nabove, nbelow, middle;
nabove = n+1;
nbelow = 0;
while(nabove-nbelow > 1) {
middle = (nabove+nbelow)/2;
if (value == array[middle-1]) return middle-1;
if (value < array[middle-1]) nabove = middle;
else nbelow = middle;
}
return nbelow-1;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long64_t TMath::BinarySearch(Long64_t n, const Double_t **array, Double_t value)
{
// Binary search in an array of n values to locate value.
//
// Array is supposed to be sorted prior to this call.
// If match is found, function returns position of element.
// If no match found, function gives nearest element smaller than value.
Long64_t nabove, nbelow, middle;
nabove = n+1;
nbelow = 0;
while(nabove-nbelow > 1) {
middle = (nabove+nbelow)/2;
if (value == *array[middle-1]) return middle-1;
if (value < *array[middle-1]) nabove = middle;
else nbelow = middle;
}
return nbelow-1;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long64_t TMath::BinarySearch(Long64_t n, const Long_t *array, Long_t value)
{
// Binary search in an array of n values to locate value.
//
// Array is supposed to be sorted prior to this call.
// If match is found, function returns position of element.
// If no match found, function gives nearest element smaller than value.
Long64_t nabove, nbelow, middle;
nabove = n+1;
nbelow = 0;
while(nabove-nbelow > 1) {
middle = (nabove+nbelow)/2;
if (value == array[middle-1]) return middle-1;
if (value < array[middle-1]) nabove = middle;
else nbelow = middle;
}
return nbelow-1;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long64_t TMath::BinarySearch(Long64_t n, const Long_t **array, Long_t value)
{
// Binary search in an array of n values to locate value.
//
// Array is supposed to be sorted prior to this call.
// If match is found, function returns position of element.
// If no match found, function gives nearest element smaller than value.
Long64_t nabove, nbelow, middle;
nabove = n+1;
nbelow = 0;
while(nabove-nbelow > 1) {
middle = (nabove+nbelow)/2;
if (value == *array[middle-1]) return middle-1;
if (value < *array[middle-1]) nabove = middle;
else nbelow = middle;
}
return nbelow-1;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long64_t TMath::BinarySearch(Long64_t n, const Long64_t *array, Long64_t value)
{
// Binary search in an array of n values to locate value.
//
// Array is supposed to be sorted prior to this call.
// If match is found, function returns position of element.
// If no match found, function gives nearest element smaller than value.
Long64_t nabove, nbelow, middle;
nabove = n+1;
nbelow = 0;
while(nabove-nbelow > 1) {
middle = (nabove+nbelow)/2;
if (value == array[middle-1]) return middle-1;
if (value < array[middle-1]) nabove = middle;
else nbelow = middle;
}
return nbelow-1;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long64_t TMath::BinarySearch(Long64_t n, const Long64_t **array, Long64_t value)
{
// Binary search in an array of n values to locate value.
//
// Array is supposed to be sorted prior to this call.
// If match is found, function returns position of element.
// If no match found, function gives nearest element smaller than value.
Long64_t nabove, nbelow, middle;
nabove = n+1;
nbelow = 0;
while(nabove-nbelow > 1) {
middle = (nabove+nbelow)/2;
if (value == *array[middle-1]) return middle-1;
if (value < *array[middle-1]) nabove = middle;
else nbelow = middle;
}
return nbelow-1;
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
Bool_t TMath::IsInside(Double_t xp, Double_t yp, Int_t np, Double_t *x, Double_t *y)
{
// Function which returns kTRUE if point xp,yp lies inside the
// polygon defined by the np points in arrays x and y, kFALSE otherwise
// NOTE that the polygon must be a closed polygon (1st and last point
// must be identical).
Double_t xint;
Int_t i;
Int_t inter = 0;
for (i=0;i<np-1;i++) {
if (y[i] == y[i+1]) continue;
if (yp <= y[i] && yp <= y[i+1]) continue;
if (y[i] < yp && y[i+1] < yp) continue;
xint = x[i] + (yp-y[i])*(x[i+1]-x[i])/(y[i+1]-y[i]);
if (xp < xint) inter++;
}
if (inter%2) return kTRUE;
return kFALSE;
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
Bool_t TMath::IsInside(Float_t xp, Float_t yp, Int_t np, Float_t *x, Float_t *y)
{
// Function which returns kTRUE if point xp,yp lies inside the
// polygon defined by the np points in arrays x and y, kFALSE otherwise
// NOTE that the polygon must be a closed polygon (1st and last point
// must be identical).
Double_t xint;
Int_t i;
Int_t inter = 0;
for (i=0;i<np-1;i++) {
if (y[i] == y[i+1]) continue;
if (yp <= y[i] && yp <= y[i+1]) continue;
if (y[i] < yp && y[i+1] < yp) continue;
xint = x[i] + (yp-y[i])*(x[i+1]-x[i])/(y[i+1]-y[i]);
if ((Double_t)xp < xint) inter++;
}
if (inter%2) return kTRUE;
return kFALSE;
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
Bool_t TMath::IsInside(Int_t xp, Int_t yp, Int_t np, Int_t *x, Int_t *y)
{
// Function which returns kTRUE if point xp,yp lies inside the
// polygon defined by the np points in arrays x and y, kFALSE otherwise
// NOTE that the polygon must be a closed polygon (1st and last point
// must be identical).
Double_t xint;
Int_t i;
Int_t inter = 0;
for (i=0;i<np-1;i++) {
if (y[i] == y[i+1]) continue;
if (yp <= y[i] && yp <= y[i+1]) continue;
if (y[i] < yp && y[i+1] < yp) continue;
xint = x[i] + (yp-y[i])*(x[i+1]-x[i])/(y[i+1]-y[i]);
if ((Double_t)xp < xint) inter++;
}
if (inter%2) return kTRUE;
return kFALSE;
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
#if defined(_MSC_VER) && (_MSC_VER<1300)
template <class Element, class Index, class Size>
void SortImpStandalone(Size n1, const Element *a,
Index *index, Bool_t down)
#else
template <class Element, class Index, class Size>
void TMath::SortImp(Size n1, const Element *a,
Index *index, Bool_t down)
#endif
{
// Templated version of the Sort.
//
// Sort the n1 elements of the array a.of Element
// In output the array index contains the indices of the sorted array.
// If down is false sort in increasing order (default is decreasing order).
// This is a translation of the CERNLIB routine sortzv (M101)
// based on the quicksort algorithm.
// NOTE that the array index must be created with a length >= n1
// before calling this function.
//
// See also the declarations at the top of this file.
Size i,i1,n,i2,i3,i33,i222,iswap,n2;
Size i22 = 0;
Element ai;
n = n1;
if (n <= 0 || !a) return;
if (n == 1) {index[0] = 0; return;}
for (i=0;i<n;i++) index[i] = i+1;
for (i1=2;i1<=n;i1++) {
i3 = i1;
i33 = index[i3-1];
ai = a[i33-1];
while(1) {
i2 = i3/2;
if (i2 <= 0) break;
i22 = index[i2-1];
if (ai <= a[i22-1]) break;
index[i3-1] = i22;
i3 = i2;
}
index[i3-1] = i33;
}
while(1) {
i3 = index[n-1];
index[n-1] = index[0];
ai = a[i3-1];
n--;
if(n-1 < 0) {index[0] = i3; break;}
i1 = 1;
while(2) {
i2 = i1+i1;
if (i2 <= n) i22 = index[i2-1];
if (i2-n > 0) {index[i1-1] = i3; break;}
if (i2-n < 0) {
i222 = index[i2];
if (a[i22-1] - a[i222-1] < 0) {
i2++;
i22 = i222;
}
}
if (ai - a[i22-1] > 0) {index[i1-1] = i3; break;}
index[i1-1] = i22;
i1 = i2;
}
}
for (i=0;i<n1;i++) index[i]--;
if (!down) return;
n2 = n1/2;
for (i=0;i<n2;i++) {
iswap = index[i];
index[i] = index[n1-i-1];
index[n1-i-1] = iswap;
}
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
void TMath::Sort(Int_t n1, const Short_t *a, Int_t *index, Bool_t down)
{
// Sort the n1 elements of the Short_t array a.
// In output the array index contains the indices of the sorted array.
// If down is false sort in increasing order (default is decreasing order).
// This is a translation of the CERNLIB routine sortzv (M101)
// based on the quicksort algorithm.
// NOTE that the array index must be created with a length >= n1
// before calling this function.
SortImp(n1,a,index,down);
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
void TMath::Sort(Int_t n1, const Int_t *a, Int_t *index, Bool_t down)
{
// Sort the n1 elements of the Int_t array a.
// In output the array index contains the indices of the sorted array.
// If down is false sort in increasing order (default is decreasing order).
// This is a translation of the CERNLIB routine sortzv (M101)
// based on the quicksort algorithm.
// NOTE that the array index must be created with a length >= n1
// before calling this function.
SortImp(n1,a,index,down);
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
void TMath::Sort(Int_t n1, const Float_t *a, Int_t *index, Bool_t down)
{
// Sort the n1 elements of the Float_t array a.
// In output the array index contains the indices of the sorted array.
// If down is false sort in increasing order (default is decreasing order).
// This is a translation of the CERNLIB routine sortzv (M101)
// based on the quicksort algorithm.
// NOTE that the array index must be created with a length >= n1
// before calling this function.
SortImp(n1,a,index,down);
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
void TMath::Sort(Int_t n1, const Double_t *a, Int_t *index, Bool_t down)
{
// Sort the n1 elements of the Double_t array a.
// In output the array index contains the indices of the sorted array.
// If down is false sort in increasing order (default is decreasing order).
// This is a translation of the CERNLIB routine sortzv (M101)
// based on the quicksort algorithm.
// NOTE that the array index must be created with a length >= n1
// before calling this function.
SortImp(n1,a,index,down);
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
void TMath::Sort(Int_t n1, const Long_t *a, Int_t *index, Bool_t down)
{
// Sort the n1 elements of the Long64_t array a.
// In output the array index contains the indices of the sorted array.
// If down is false sort in increasing order (default is decreasing order).
// This is a translation of the CERNLIB routine sortzv (M101)
// based on the quicksort algorithm.
// NOTE that the array index must be created with a length >= n1
// before calling this function.
SortImp(n1,a,index,down);
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
void TMath::Sort(Int_t n1, const Long64_t *a, Int_t *index, Bool_t down)
{
// Sort the n1 elements of the Long64_t array a.
// In output the array index contains the indices of the sorted array.
// If down is false sort in increasing order (default is decreasing order).
// This is a translation of the CERNLIB routine sortzv (M101)
// based on the quicksort algorithm.
// NOTE that the array index must be created with a length >= n1
// before calling this function.
SortImp(n1,a,index,down);
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
void TMath::Sort(Long64_t n1, const Short_t *a, Long64_t *index, Bool_t down)
{
// Sort the n1 elements of the Short_t array a.
// In output the array index contains the indices of the sorted array.
// If down is false sort in increasing order (default is decreasing order).
// This is a translation of the CERNLIB routine sortzv (M101)
// based on the quicksort algorithm.
// NOTE that the array index must be created with a length >= n1
// before calling this function.
SortImp(n1,a,index,down);
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
void TMath::Sort(Long64_t n1, const Int_t *a, Long64_t *index, Bool_t down)
{
// Sort the n1 elements of the Int_t array a.
// In output the array index contains the indices of the sorted array.
// If down is false sort in increasing order (default is decreasing order).
// This is a translation of the CERNLIB routine sortzv (M101)
// based on the quicksort algorithm.
// NOTE that the array index must be created with a length >= n1
// before calling this function.
SortImp(n1,a,index,down);
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
void TMath::Sort(Long64_t n1, const Float_t *a, Long64_t *index, Bool_t down)
{
// Sort the n1 elements of the Float_t array a.
// In output the array index contains the indices of the sorted array.
// If down is false sort in increasing order (default is decreasing order).
// This is a translation of the CERNLIB routine sortzv (M101)
// based on the quicksort algorithm.
// NOTE that the array index must be created with a length >= n1
// before calling this function.
SortImp(n1,a,index,down);
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
void TMath::Sort(Long64_t n1, const Double_t *a, Long64_t *index, Bool_t down)
{
// Sort the n1 elements of the Double_t array a.
// In output the array index contains the indices of the sorted array.
// If down is false sort in increasing order (default is decreasing order).
// This is a translation of the CERNLIB routine sortzv (M101)
// based on the quicksort algorithm.
// NOTE that the array index must be created with a length >= n1
// before calling this function.
SortImp(n1,a,index,down);
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
void TMath::Sort(Long64_t n1, const Long_t *a, Long64_t *index, Bool_t down)
{
// Sort the n1 elements of the Long64_t array a.
// In output the array index contains the indices of the sorted array.
// If down is false sort in increasing order (default is decreasing order).
// This is a translation of the CERNLIB routine sortzv (M101)
// based on the quicksort algorithm.
// NOTE that the array index must be created with a length >= n1
// before calling this function.
SortImp(n1,a,index,down);
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
void TMath::Sort(Long64_t n1, const Long64_t *a, Long64_t *index, Bool_t down)
{
// Sort the n1 elements of the Long64_t array a.
// In output the array index contains the indices of the sorted array.
// If down is false sort in increasing order (default is decreasing order).
// This is a translation of the CERNLIB routine sortzv (M101)
// based on the quicksort algorithm.
// NOTE that the array index must be created with a length >= n1
// before calling this function.
SortImp(n1,a,index,down);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TMath::BubbleHigh(Int_t Narr, Double_t *arr1, Int_t *arr2)
{
// Bubble sort variant to obtain the order of an array's elements into
// an index in order to do more useful things than the standard built
// in functions.
// *arr1 is unchanged;
// *arr2 is the array of indicies corresponding to the decending value
// of arr1 with arr2[0] corresponding to the largest arr1 value and
// arr2[Narr] the smallest.
//
// Author: Adrian Bevan (bevan@slac.stanford.edu)
// Copyright: Liverpool University, July 2001
if (Narr <= 0) return;
double *localArr1 = new double[Narr];
int *localArr2 = new int[Narr];
int iEl;
int iEl2;
for(iEl = 0; iEl < Narr; iEl++) {
localArr1[iEl] = arr1[iEl];
localArr2[iEl] = iEl;
}
for (iEl = 0; iEl < Narr; iEl++) {
for (iEl2 = Narr-1; iEl2 > iEl; --iEl2) {
if (localArr1[iEl2-1] < localArr1[iEl2]) {
double tmp = localArr1[iEl2-1];
localArr1[iEl2-1] = localArr1[iEl2];
localArr1[iEl2] = tmp;
int tmp2 = localArr2[iEl2-1];
localArr2[iEl2-1] = localArr2[iEl2];
localArr2[iEl2] = tmp2;
}
}
}
for (iEl = 0; iEl < Narr; iEl++) {
arr2[iEl] = localArr2[iEl];
}
delete [] localArr2;
delete [] localArr1;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TMath::BubbleLow(Int_t Narr, Double_t *arr1, Int_t *arr2)
{
// Opposite ordering of the array arr2[] to that of BubbleHigh.
//
// Author: Adrian Bevan (bevan@slac.stanford.edu)
// Copyright: Liverpool University, July 2001
if (Narr <= 0) return;
double *localArr1 = new double[Narr];
int *localArr2 = new int[Narr];
int iEl;
int iEl2;
for (iEl = 0; iEl < Narr; iEl++) {
localArr1[iEl] = arr1[iEl];
localArr2[iEl] = iEl;
}
for (iEl = 0; iEl < Narr; iEl++) {
for (iEl2 = Narr-1; iEl2 > iEl; --iEl2) {
if (localArr1[iEl2-1] > localArr1[iEl2]) {
double tmp = localArr1[iEl2-1];
localArr1[iEl2-1] = localArr1[iEl2];
localArr1[iEl2] = tmp;
int tmp2 = localArr2[iEl2-1];
localArr2[iEl2-1] = localArr2[iEl2];
localArr2[iEl2] = tmp2;
}
}
}
for (iEl = 0; iEl < Narr; iEl++) {
arr2[iEl] = localArr2[iEl];
}
delete [] localArr2;
delete [] localArr1;
}
#ifdef OLD_HASH
//______________________________________________________________________________
ULong_t TMath::Hash(const void *txt, Int_t ntxt)
{
// Calculates hash index from any char string.
// Based on precalculated table of 256 specially selected random numbers.
//
// For string: i = TMath::Hash(string,nstring);
// For int: i = TMath::Hash(&intword,sizeof(int));
// For pointer: i = TMath::Hash(&pointer,sizeof(void*));
//
// Limitation: for ntxt>256 calculates hash only from first 256 bytes
//
// V.Perev
const UChar_t *uc = (const UChar_t*) txt;
ULong_t u = 0, uu = 0;
static ULong_t utab[256] =
{0xb93f6fc0,0x553dfc51,0xb22c1e8c,0x638462c0,0x13e81418,0x2836e171,0x7c4abb90,0xda1a4f39
,0x38f211d1,0x8c804829,0x95a6602d,0x4c590993,0x1810580a,0x721057d4,0x0f587215,0x9f49ce2a
,0xcd5ab255,0xab923a99,0x80890f39,0xbcfa2290,0x16587b52,0x6b6d3f0d,0xea8ff307,0x51542d5c
,0x189bf223,0x39643037,0x0e4a326a,0x214eca01,0x47645a9b,0x0f364260,0x8e9b2da4,0x5563ebd9
,0x57a31c1c,0xab365854,0xdd63ab1f,0x0b89acbd,0x23d57d33,0x1800a0fd,0x225ac60a,0xd0e51943
,0x6c65f669,0xcb966ea0,0xcbafda95,0x2e5c0c5f,0x2988e87e,0xc781cbab,0x3add3dc7,0x693a2c30
,0x42d6c23c,0xebf85f26,0x2544987e,0x2e315e3f,0xac88b5b5,0x7ebd2bbb,0xda07c87b,0x20d460f1
,0xc61c3f40,0x182046e7,0x3b6c3b66,0x2fc10d4a,0x0780dfbb,0xc437280c,0x0988dd07,0xe1498606
,0x8e61d728,0x4f1f3909,0x040a9682,0x49411b29,0x391b0e1c,0xd7905241,0xdd77d95b,0x88426c13
,0x33033e58,0xe158e30e,0x7e342647,0x1e09544b,0x4637353d,0x18ea0924,0x39212b08,0x12580ae8
,0x269a6f06,0x3e10b73b,0x123db33b,0x085412da,0x3bb5f464,0xd9b2d442,0x103d26bb,0xd0038bab
,0x45b6177f,0xfb48f1fe,0x99074c55,0xb545e82e,0x5f79fd0d,0x570f3ae4,0x57e43255,0x037a12ae
,0x4357bdb2,0x337c2c4d,0x2982499d,0x2ab72793,0x3900e7d1,0x57a6bb81,0x7503609b,0x3f39c0d0
,0x717b389d,0x5748034f,0x4698162b,0x5801b97c,0x1dfd5d7e,0xc1386d1c,0xa387a72a,0x084547e4
,0x2e54d8e9,0x2e2f384c,0xe09ccc20,0x8904b71e,0x3e24edc5,0x06a22e16,0x8a2be1df,0x9e5058b2
,0xe01a2f16,0x03325eed,0x587ecfe6,0x584d9cd3,0x32926930,0xe943d68c,0xa9442da8,0xf9650560
,0xf003871e,0x1109c663,0x7a2f2f89,0x1c2210bb,0x37335787,0xb92b382f,0xea605cb5,0x336bbe38
,0x08126bd3,0x1f8c2bd6,0xba6c46f2,0x1a4d1b83,0xc988180d,0xe2582505,0xa8a1b375,0x59a08c49
,0x3db54b48,0x44400f35,0x272d4e7f,0x5579f733,0x98eb590e,0x8ee09813,0x12cc9301,0xc85c402d
,0x135c1039,0x22318128,0x4063c705,0x87a8a3fa,0xfc14431f,0x6e27bf47,0x2d080a19,0x01dba174
,0xe343530b,0xaa1bfced,0x283bb2c8,0x5df250c8,0x4ff9140b,0x045039c1,0xa377780d,0x750f2661
,0x2b108918,0x0b152120,0x3cbc251f,0x5e87b350,0x060625bb,0xe068ba3b,0xdb73ebd7,0x66014ff3
,0xdb003000,0x161a3a0b,0xdc24e142,0x97ea5575,0x635a3cab,0xa719100a,0x256084db,0xc1f4a1e7
,0xe13388f2,0xb8199fc9,0x50c70dc9,0x08154211,0xd60e5220,0xe52c6592,0x584c5fe1,0xfe5e0875
,0x21072b30,0x3370d773,0x92608fe2,0x2d013d93,0x53414b3c,0x2c066142,0x64676644,0x0420887c
,0x35c01187,0x6822119b,0xf9bfe6df,0x273f4ee4,0x87973149,0x7b41282d,0x635d0d1f,0x5f7ecc1e
,0x14c3608a,0x462dfdab,0xc33d8808,0x1dcd995e,0x0fcb11ba,0x11755914,0x5a62044b,0x37f76755
,0x345bd058,0x8831c2b5,0x204a8468,0x3b0b1cd2,0x444e56f4,0x97a93e2c,0xd5f15067,0x266a95fa
,0xff4f8036,0x6160060d,0x930c472f,0xed922184,0x37120251,0xc0add74f,0x1c0bc89d,0x018d47f2
,0xff59ef66,0xd1901a17,0x91f6701b,0x0960082f,0x86f6a8f3,0x1154fecd,0x9867d1de,0x0945482f
,0x790ffcac,0xe5610011,0x4765637e,0xa745dbff,0x841fdcb3,0x4f7372a0,0x3c05013d,0xf1ac4ab7
,0x3bc5b5cc,0x49a73349,0x356a7f67,0x1174f031,0x11d32634,0x4413d301,0x1dd285c4,0x3fae4800
};
if (ntxt > 255) ntxt = 255;
for ( ; ntxt--; uc++) {
uu = uu<<1 ^ utab[(*uc) ^ ntxt];
u ^= uu;
}
return u;
}
#else
//______________________________________________________________________________
ULong_t TMath::Hash(const void *txt, Int_t ntxt)
{
// Calculates hash index from any char string.
// Based on precalculated table of 256 specially selected numbers.
// These numbers are selected in such a way, that for string
// length == 4 (integer number) the hash is unambigous, i.e.
// from hash value we can recalculate input (no degeneration).
//
// The quality of hash method is good enough, that
// "random" numbers made as R = Hash(1), Hash(2), ...Hash(N)
// tested by <R>, <R*R>, <Ri*Ri+1> gives the same result
// as for libc rand().
//
// For string: i = TMath::Hash(string,nstring);
// For int: i = TMath::Hash(&intword,sizeof(int));
// For pointer: i = TMath::Hash(&pointer,sizeof(void*));
//
// V.Perev
static const ULong_t utab[] = {
0xdd367647,0x9caf993f,0x3f3cc5ff,0xfde25082,0x4c764b21,0x89affca7,0x5431965c,0xce22eeec
,0xc61ab4dc,0x59cc93bd,0xed3107e3,0x0b0a287a,0x4712475a,0xce4a4c71,0x352c8403,0x94cb3cee
,0xc3ac509b,0x09f827a2,0xce02e37e,0x7b20bbba,0x76adcedc,0x18c52663,0x19f74103,0x6f30e47b
,0x132ea5a1,0xfdd279e0,0xa3d57d00,0xcff9cb40,0x9617f384,0x6411acfa,0xff908678,0x5c796b2c
,0x4471b62d,0xd38e3275,0xdb57912d,0x26bf953f,0xfc41b2a5,0xe64bcebd,0x190b7839,0x7e8e6a56
,0x9ca22311,0xef28aa60,0xe6b9208e,0xd257fb65,0x45781c2c,0x9a558ac3,0x2743e74d,0x839417a8
,0x06b54d5d,0x1a82bcb4,0x06e97a66,0x70abdd03,0xd163f30d,0x222ed322,0x777bfeda,0xab7a2e83
,0x8494e0cf,0x2dca2d4f,0x78f94278,0x33f04a09,0x402b6452,0x0cd8b709,0xdb72a39e,0x170e00a2
,0x26354faa,0x80e57453,0xcfe8d4e1,0x19e45254,0x04c291c3,0xeb503738,0x425af3bc,0x67836f2a
,0xfac22add,0xfafc2b8c,0x59b8c2a0,0x03e806f9,0xcb4938b9,0xccc942af,0xcee3ae2e,0xfbe748fa
,0xb223a075,0x85c49b5d,0xe4576ac9,0x0fbd46e2,0xb49f9cf5,0xf3e1e86a,0x7d7927fb,0x711afe12
,0xbf61c346,0x157c9956,0x86b6b046,0x2e402146,0xb2a57d8a,0x0d064bb1,0x30ce390c,0x3a3e1eb1
,0xbe7f6f8f,0xd8e30f87,0x5be2813c,0x73a3a901,0xa3aaf967,0x59ff092c,0x1705c798,0xf610dd66
,0xb17da91e,0x8e59534e,0x2211ea5b,0xa804ba03,0xd890efbb,0xb8b48110,0xff390068,0xc8c325b4
,0xf7289c07,0x787e104f,0x3d0df3d0,0x3526796d,0x10548055,0x1d59a42b,0xed1cc5a3,0xdd45372a
,0x31c50d57,0x65757cb7,0x3cfb85be,0xa329910d,0x6ad8ce39,0xa2de44de,0x0dd32432,0xd4a5b617
,0x8f3107fc,0x96485175,0x7f94d4f3,0x35097634,0xdb3ca782,0x2c0290b8,0x2045300b,0xe0f5d15a
,0x0e8cbffa,0xaa1cc38a,0x84008d6f,0xe9a9e794,0x5c602c25,0xfa3658fa,0x98d9d82b,0x3f1497e7
,0x84b6f031,0xe381eff9,0xfc7ae252,0xb239e05d,0xe3723d1f,0xcc3bda82,0xe21b1ad3,0x9104f7c8
,0x4bb2dfcd,0x4d14a8bc,0x6ba7f28c,0x8f89886c,0xad44c97e,0xb30fd975,0x633cdab1,0xf6c2d514
,0x067a49d2,0xdc461ad9,0xebaf9f3f,0x8dc6cac3,0x7a060f16,0xbab063ad,0xf42e25e6,0x60724ca6
,0xc7245c2e,0x4e48ea3c,0x9f89a609,0xa1c49890,0x4bb7f116,0xd722865c,0xa8ee3995,0x0ee070b1
,0xd9bffcc2,0xe55b64f9,0x25507a5a,0xc7a3e2b5,0x5f395f7e,0xe7957652,0x7381ba6a,0xde3d21f1
,0xdf1708dd,0xad0c9d0c,0x00cbc9e5,0x1160e833,0x6779582c,0x29d5d393,0x3f11d7d7,0x826a6b9b
,0xe73ff12f,0x8bad3d86,0xee41d3e5,0x7f0c8917,0x8089ef24,0x90c5cb28,0x2f7f8e6b,0x6966418a
,0x345453fb,0x7a2f8a68,0xf198593d,0xc079a532,0xc1971e81,0x1ab74e26,0x329ef347,0x7423d3d0
,0x942c510b,0x7f6c6382,0x14ae6acc,0x64b59da7,0x2356fa47,0xb6749d9c,0x499de1bb,0x92ffd191
,0xe8f2fb75,0x848dc913,0x3e8727d3,0x1dcffe61,0xb6e45245,0x49055738,0x827a6b55,0xb4788887
,0x7e680125,0xd19ce7ed,0x6b4b8e30,0xa8cadea2,0x216035d8,0x1c63bc3c,0xe1299056,0x1ad3dff4
,0x0aefd13c,0x0e7b921c,0xca0173c6,0x9995782d,0xcccfd494,0xd4b0ac88,0x53d552b1,0x630dae8b
,0xa8332dad,0x7139d9a2,0x5d76f2c4,0x7a4f8f1e,0x8d1aef97,0xd1cf285d,0xc8239153,0xce2608a9
,0x7b562475,0xe4b4bc83,0xf3db0c3a,0x70a65e48,0x6016b302,0xdebd5046,0x707e786a,0x6f10200c
};
static const ULong_t msk[] = { 0x11111111, 0x33333333, 0x77777777, 0xffffffff };
const UChar_t *uc = (const UChar_t *) txt;
ULong_t uu = 0;
union {
ULong_t u;
UShort_t s[2];
} u;
u.u = 0;
Int_t i, idx;
for (i = 0; i < ntxt; i++) {
idx = (uc[i] ^ i) & 255;
uu = (uu << 1) ^ (utab[idx] & msk[i & 3]);
if ((i & 3) == 3) u.u ^= uu;
}
if (i & 3) u.u ^= uu;
u.u *= 1879048201; // prime number
u.s[0] += u.s[1];
u.u *= 1979048191; // prime number
u.s[1] ^= u.s[0];
u.u *= 2079048197; // prime number
return u.u;
}
#endif
//______________________________________________________________________________
ULong_t TMath::Hash(const char *txt)
{
return Hash(txt, Int_t(strlen(txt)));
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::BesselI0(Double_t x)
{
// Compute the modified Bessel function I_0(x) for any real x.
//
//--- NvE 12-mar-2000 UU-SAP Utrecht
// Parameters of the polynomial approximation
const Double_t p1=1.0, p2=3.5156229, p3=3.0899424,
p4=1.2067492, p5=0.2659732, p6=3.60768e-2, p7=4.5813e-3;
const Double_t q1= 0.39894228, q2= 1.328592e-2, q3= 2.25319e-3,
q4=-1.57565e-3, q5= 9.16281e-3, q6=-2.057706e-2,
q7= 2.635537e-2, q8=-1.647633e-2, q9= 3.92377e-3;
const Double_t k1 = 3.75;
Double_t ax = TMath::Abs(x);
Double_t y=0, result=0;
if (ax < k1) {
Double_t xx = x/k1;
y = xx*xx;
result = p1+y*(p2+y*(p3+y*(p4+y*(p5+y*(p6+y*p7)))));
} else {
y = k1/ax;
result = (TMath::Exp(ax)/TMath::Sqrt(ax))*(q1+y*(q2+y*(q3+y*(q4+y*(q5+y*(q6+y*(q7+y*(q8+y*q9))))))));
}
return result;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::BesselK0(Double_t x)
{
// Compute the modified Bessel function K_0(x) for positive real x.
//
// M.Abramowitz and I.A.Stegun, Handbook of Mathematical Functions,
// Applied Mathematics Series vol. 55 (1964), Washington.
//
//--- NvE 12-mar-2000 UU-SAP Utrecht
// Parameters of the polynomial approximation
const Double_t p1=-0.57721566, p2=0.42278420, p3=0.23069756,
p4= 3.488590e-2, p5=2.62698e-3, p6=1.0750e-4, p7=7.4e-6;
const Double_t q1= 1.25331414, q2=-7.832358e-2, q3= 2.189568e-2,
q4=-1.062446e-2, q5= 5.87872e-3, q6=-2.51540e-3, q7=5.3208e-4;
if (x <= 0) {
Error("TMath::BesselK0", "*K0* Invalid argument x = %g\n",x);
return 0;
}
Double_t y=0, result=0;
if (x <= 2) {
y = x*x/4;
result = (-log(x/2.)*TMath::BesselI0(x))+(p1+y*(p2+y*(p3+y*(p4+y*(p5+y*(p6+y*p7))))));
} else {
y = 2/x;
result = (exp(-x)/sqrt(x))*(q1+y*(q2+y*(q3+y*(q4+y*(q5+y*(q6+y*q7))))));
}
return result;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::BesselI1(Double_t x)
{
// Compute the modified Bessel function I_1(x) for any real x.
//
// M.Abramowitz and I.A.Stegun, Handbook of Mathematical Functions,
// Applied Mathematics Series vol. 55 (1964), Washington.
//
//--- NvE 12-mar-2000 UU-SAP Utrecht
// Parameters of the polynomial approximation
const Double_t p1=0.5, p2=0.87890594, p3=0.51498869,
p4=0.15084934, p5=2.658733e-2, p6=3.01532e-3, p7=3.2411e-4;
const Double_t q1= 0.39894228, q2=-3.988024e-2, q3=-3.62018e-3,
q4= 1.63801e-3, q5=-1.031555e-2, q6= 2.282967e-2,
q7=-2.895312e-2, q8= 1.787654e-2, q9=-4.20059e-3;
const Double_t k1 = 3.75;
Double_t ax = TMath::Abs(x);
Double_t y=0, result=0;
if (ax < k1) {
Double_t xx = x/k1;
y = xx*xx;
result = x*(p1+y*(p2+y*(p3+y*(p4+y*(p5+y*(p6+y*p7))))));
} else {
y = k1/ax;
result = (exp(ax)/sqrt(ax))*(q1+y*(q2+y*(q3+y*(q4+y*(q5+y*(q6+y*(q7+y*(q8+y*q9))))))));
if (x < 0) result = -result;
}
return result;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::BesselK1(Double_t x)
{
// Compute the modified Bessel function K_1(x) for positive real x.
//
// M.Abramowitz and I.A.Stegun, Handbook of Mathematical Functions,
// Applied Mathematics Series vol. 55 (1964), Washington.
//
//--- NvE 12-mar-2000 UU-SAP Utrecht
// Parameters of the polynomial approximation
const Double_t p1= 1., p2= 0.15443144, p3=-0.67278579,
p4=-0.18156897, p5=-1.919402e-2, p6=-1.10404e-3, p7=-4.686e-5;
const Double_t q1= 1.25331414, q2= 0.23498619, q3=-3.655620e-2,
q4= 1.504268e-2, q5=-7.80353e-3, q6= 3.25614e-3, q7=-6.8245e-4;
if (x <= 0) {
Error("TMath::BesselK1", "*K1* Invalid argument x = %g\n",x);
return 0;
}
Double_t y=0,result=0;
if (x <= 2) {
y = x*x/4;
result = (log(x/2.)*TMath::BesselI1(x))+(1./x)*(p1+y*(p2+y*(p3+y*(p4+y*(p5+y*(p6+y*p7))))));
} else {
y = 2/x;
result = (exp(-x)/sqrt(x))*(q1+y*(q2+y*(q3+y*(q4+y*(q5+y*(q6+y*q7))))));
}
return result;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::BesselK(Int_t n,Double_t x)
{
// Compute the Integer Order Modified Bessel function K_n(x)
// for n=0,1,2,... and positive real x.
//
//--- NvE 12-mar-2000 UU-SAP Utrecht
if (x <= 0 || n < 0) {
Error("TMath::BesselK", "*K* Invalid argument(s) (n,x) = (%d, %g)\n",n,x);
return 0;
}
if (n==0) return TMath::BesselK0(x);
if (n==1) return TMath::BesselK1(x);
// Perform upward recurrence for all x
Double_t tox = 2/x;
Double_t bkm = TMath::BesselK0(x);
Double_t bk = TMath::BesselK1(x);
Double_t bkp = 0;
for (Int_t j=1; j<n; j++) {
bkp = bkm+Double_t(j)*tox*bk;
bkm = bk;
bk = bkp;
}
return bk;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::BesselI(Int_t n,Double_t x)
{
// Compute the Integer Order Modified Bessel function I_n(x)
// for n=0,1,2,... and any real x.
//
//--- NvE 12-mar-2000 UU-SAP Utrecht
Int_t iacc = 40; // Increase to enhance accuracy
const Double_t kBigPositive = 1.e10;
const Double_t kBigNegative = 1.e-10;
if (n < 0) {
Error("TMath::BesselI", "*I* Invalid argument (n,x) = (%d, %g)\n",n,x);
return 0;
}
if (n==0) return TMath::BesselI0(x);
if (n==1) return TMath::BesselI1(x);
if (x == 0) return 0;
if (TMath::Abs(x) > kBigPositive) return 0;
Double_t tox = 2/TMath::Abs(x);
Double_t bip = 0, bim = 0;
Double_t bi = 1;
Double_t result = 0;
Int_t m = 2*((n+Int_t(sqrt(Float_t(iacc*n)))));
for (Int_t j=m; j>=1; j--) {
bim = bip+Double_t(j)*tox*bi;
bip = bi;
bi = bim;
// Renormalise to prevent overflows
if (TMath::Abs(bi) > kBigPositive) {
result *= kBigNegative;
bi *= kBigNegative;
bip *= kBigNegative;
}
if (j==n) result=bip;
}
result *= TMath::BesselI0(x)/bi; // Normalise with BesselI0(x)
if ((x < 0) && (n%2 == 1)) result = -result;
return result;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::BesselJ0(Double_t x)
{
// Returns the Bessel function J0(x) for any real x.
Double_t ax,z;
Double_t xx,y,result,result1,result2;
const Double_t p1 = 57568490574.0, p2 = -13362590354.0, p3 = 651619640.7;
const Double_t p4 = -11214424.18, p5 = 77392.33017, p6 = -184.9052456;
const Double_t p7 = 57568490411.0, p8 = 1029532985.0, p9 = 9494680.718;
const Double_t p10 = 59272.64853, p11 = 267.8532712;
const Double_t q1 = 0.785398164;
const Double_t q2 = -0.1098628627e-2, q3 = 0.2734510407e-4;
const Double_t q4 = -0.2073370639e-5, q5 = 0.2093887211e-6;
const Double_t q6 = -0.1562499995e-1, q7 = 0.1430488765e-3;
const Double_t q8 = -0.6911147651e-5, q9 = 0.7621095161e-6;
const Double_t q10 = 0.934935152e-7, q11 = 0.636619772;
if ((ax=fabs(x)) < 8) {
y=x*x;
result1 = p1 + y*(p2 + y*(p3 + y*(p4 + y*(p5 + y*p6))));
result2 = p7 + y*(p8 + y*(p9 + y*(p10 + y*(p11 + y))));
result = result1/result2;
} else {
z = 8/ax;
y = z*z;
xx = ax-q1;
result1 = 1 + y*(q2 + y*(q3 + y*(q4 + y*q5)));
result2 = q6 + y*(q7 + y*(q8 + y*(q9 - y*q10)));
result = sqrt(q11/ax)*(cos(xx)*result1-z*sin(xx)*result2);
}
return result;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::BesselJ1(Double_t x)
{
// Returns the Bessel function J1(x) for any real x.
Double_t ax,z;
Double_t xx,y,result,result1,result2;
const Double_t p1 = 72362614232.0, p2 = -7895059235.0, p3 = 242396853.1;
const Double_t p4 = -2972611.439, p5 = 15704.48260, p6 = -30.16036606;
const Double_t p7 = 144725228442.0, p8 = 2300535178.0, p9 = 18583304.74;
const Double_t p10 = 99447.43394, p11 = 376.9991397;
const Double_t q1 = 2.356194491;
const Double_t q2 = 0.183105e-2, q3 = -0.3516396496e-4;
const Double_t q4 = 0.2457520174e-5, q5 = -0.240337019e-6;
const Double_t q6 = 0.04687499995, q7 = -0.2002690873e-3;
const Double_t q8 = 0.8449199096e-5, q9 = -0.88228987e-6;
const Double_t q10 = 0.105787412e-6, q11 = 0.636619772;
if ((ax=fabs(x)) < 8) {
y=x*x;
result1 = x*(p1 + y*(p2 + y*(p3 + y*(p4 + y*(p5 + y*p6)))));
result2 = p7 + y*(p8 + y*(p9 + y*(p10 + y*(p11 + y))));
result = result1/result2;
} else {
z = 8/ax;
y = z*z;
xx = ax-q1;
result1 = 1 + y*(q2 + y*(q3 + y*(q4 + y*q5)));
result2 = q6 + y*(q7 + y*(q8 + y*(q9 + y*q10)));
result = sqrt(q11/ax)*(cos(xx)*result1-z*sin(xx)*result2);
if (x < 0) result = -result;
}
return result;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::BesselY0(Double_t x)
{
// Returns the Bessel function Y0(x) for positive x.
Double_t z,xx,y,result,result1,result2;
const Double_t p1 = -2957821389., p2 = 7062834065.0, p3 = -512359803.6;
const Double_t p4 = 10879881.29, p5 = -86327.92757, p6 = 228.4622733;
const Double_t p7 = 40076544269., p8 = 745249964.8, p9 = 7189466.438;
const Double_t p10 = 47447.26470, p11 = 226.1030244, p12 = 0.636619772;
const Double_t q1 = 0.785398164;
const Double_t q2 = -0.1098628627e-2, q3 = 0.2734510407e-4;
const Double_t q4 = -0.2073370639e-5, q5 = 0.2093887211e-6;
const Double_t q6 = -0.1562499995e-1, q7 = 0.1430488765e-3;
const Double_t q8 = -0.6911147651e-5, q9 = 0.7621095161e-6;
const Double_t q10 = -0.934945152e-7, q11 = 0.636619772;
if (x < 8) {
y = x*x;
result1 = p1 + y*(p2 + y*(p3 + y*(p4 + y*(p5 + y*p6))));
result2 = p7 + y*(p8 + y*(p9 + y*(p10 + y*(p11 + y))));
result = (result1/result2) + p12*TMath::BesselJ0(x)*log(x);
} else {
z = 8/x;
y = z*z;
xx = x-q1;
result1 = 1 + y*(q2 + y*(q3 + y*(q4 + y*q5)));
result2 = q6 + y*(q7 + y*(q8 + y*(q9 + y*q10)));
result = sqrt(q11/x)*(sin(xx)*result1+z*cos(xx)*result2);
}
return result;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::BesselY1(Double_t x)
{
// Returns the Bessel function Y1(x) for positive x.
Double_t z,xx,y,result,result1,result2;
const Double_t p1 = -0.4900604943e13, p2 = 0.1275274390e13;
const Double_t p3 = -0.5153438139e11, p4 = 0.7349264551e9;
const Double_t p5 = -0.4237922726e7, p6 = 0.8511937935e4;
const Double_t p7 = 0.2499580570e14, p8 = 0.4244419664e12;
const Double_t p9 = 0.3733650367e10, p10 = 0.2245904002e8;
const Double_t p11 = 0.1020426050e6, p12 = 0.3549632885e3;
const Double_t p13 = 0.636619772;
const Double_t q1 = 2.356194491;
const Double_t q2 = 0.183105e-2, q3 = -0.3516396496e-4;
const Double_t q4 = 0.2457520174e-5, q5 = -0.240337019e-6;
const Double_t q6 = 0.04687499995, q7 = -0.2002690873e-3;
const Double_t q8 = 0.8449199096e-5, q9 = -0.88228987e-6;
const Double_t q10 = 0.105787412e-6, q11 = 0.636619772;
if (x < 8) {
y=x*x;
result1 = x*(p1 + y*(p2 + y*(p3 + y*(p4 + y*(p5 + y*p6)))));
result2 = p7 + y*(p8 + y*(p9 + y*(p10 + y*(p11 + y*(p12+y)))));
result = (result1/result2) + p13*(TMath::BesselJ1(x)*log(x)-1/x);
} else {
z = 8/x;
y = z*z;
xx = x-q1;
result1 = 1 + y*(q2 + y*(q3 + y*(q4 + y*q5)));
result2 = q6 + y*(q7 + y*(q8 + y*(q9 + y*q10)));
result = sqrt(q11/x)*(sin(xx)*result1+z*cos(xx)*result2);
}
return result;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::StruveH0(Double_t x)
{
// Struve Functions of Order 0
//
// Converted from CERNLIB M342 by Rene Brun.
const Int_t n1 = 15;
const Int_t n2 = 25;
const Double_t c1[16] = { 1.00215845609911981, -1.63969292681309147,
1.50236939618292819, -.72485115302121872,
.18955327371093136, -.03067052022988,
.00337561447375194, -2.6965014312602e-4,
1.637461692612e-5, -7.8244408508e-7,
3.021593188e-8, -9.6326645e-10,
2.579337e-11, -5.8854e-13,
1.158e-14, -2e-16 };
const Double_t c2[26] = { .99283727576423943, -.00696891281138625,
1.8205103787037e-4, -1.063258252844e-5,
9.8198294287e-7, -1.2250645445e-7,
1.894083312e-8, -3.44358226e-9,
7.1119102e-10, -1.6288744e-10,
4.065681e-11, -1.091505e-11,
3.12005e-12, -9.4202e-13,
2.9848e-13, -9.872e-14,
3.394e-14, -1.208e-14,
4.44e-15, -1.68e-15,
6.5e-16, -2.6e-16,
1.1e-16, -4e-17,
2e-17, -1e-17 };
const Double_t c0 = 2/TMath::Pi();
Int_t i;
Double_t alfa, h, r, y, b0, b1, b2;
Double_t v = TMath::Abs(x);
v = TMath::Abs(x);
if (v < 8) {
y = v/8;
h = 2*y*y -1;
alfa = h + h;
b0 = 0;
b1 = 0;
b2 = 0;
for (i = n1; i >= 0; --i) {
b0 = c1[i] + alfa*b1 - b2;
b2 = b1;
b1 = b0;
}
h = y*(b0 - h*b2);
} else {
r = 1/v;
h = 128*r*r -1;
alfa = h + h;
b0 = 0;
b1 = 0;
b2 = 0;
for (i = n2; i >= 0; --i) {
b0 = c2[i] + alfa*b1 - b2;
b2 = b1;
b1 = b0;
}
h = TMath::BesselY0(v) + r*c0*(b0 - h*b2);
}
if (x < 0) h = -h;
return h;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::StruveH1(Double_t x)
{
// Struve Functions of Order 1
//
// Converted from CERNLIB M342 by Rene Brun.
const Int_t n3 = 16;
const Int_t n4 = 22;
const Double_t c3[17] = { .5578891446481605, -.11188325726569816,
-.16337958125200939, .32256932072405902,
-.14581632367244242, .03292677399374035,
-.00460372142093573, 4.434706163314e-4,
-3.142099529341e-5, 1.7123719938e-6,
-7.416987005e-8, 2.61837671e-9,
-7.685839e-11, 1.9067e-12,
-4.052e-14, 7.5e-16,
-1e-17 };
const Double_t c4[23] = { 1.00757647293865641, .00750316051248257,
-7.043933264519e-5, 2.66205393382e-6,
-1.8841157753e-7, 1.949014958e-8,
-2.6126199e-9, 4.236269e-10,
-7.955156e-11, 1.679973e-11,
-3.9072e-12, 9.8543e-13,
-2.6636e-13, 7.645e-14,
-2.313e-14, 7.33e-15,
-2.42e-15, 8.3e-16,
-3e-16, 1.1e-16,
-4e-17, 2e-17,-1e-17 };
const Double_t c0 = 2/TMath::Pi();
const Double_t cc = 2/(3*TMath::Pi());
Int_t i, i1;
Double_t alfa, h, r, y, b0, b1, b2;
Double_t v = TMath::Abs(x);
if (v == 0) {
h = 0;
} else if (v <= 0.3) {
y = v*v;
r = 1;
h = 1;
i1 = (Int_t)(-8. / TMath::Log10(v));
for (i = 1; i <= i1; ++i) {
h = -h*y / ((2*i+ 1)*(2*i + 3));
r += h;
}
h = cc*y*r;
} else if (v < 8) {
h = v*v/32 -1;
alfa = h + h;
b0 = 0;
b1 = 0;
b2 = 0;
for (i = n3; i >= 0; --i) {
b0 = c3[i] + alfa*b1 - b2;
b2 = b1;
b1 = b0;
}
h = b0 - h*b2;
} else {
h = 128/(v*v) -1;
alfa = h + h;
b0 = 0;
b1 = 0;
b2 = 0;
for (i = n4; i >= 0; --i) {
b0 = c4[i] + alfa*b1 - b2;
b2 = b1;
b1 = b0;
}
h = TMath::BesselY1(v) + c0*(b0 - h*b2);
}
return h;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::StruveL0(Double_t x)
{
// Modified Struve Function of Order 0.
// By Kirill Filimonov.
const Double_t pi=TMath::Pi();
Double_t s=1.0;
Double_t r=1.0;
Double_t a0,sl0,a1,bi0;
Int_t km,i;
if (x<=20.) {
a0=2.0*x/pi;
for (int i=1; i<=60;i++) {
r*=(x/(2*i+1))*(x/(2*i+1));
s+=r;
if(TMath::Abs(r/s)<1.e-12) break;
}
sl0=a0*s;
} else {
km=int(5*(x+1.0));
if(x>=50.0)km=25;
for (i=1; i<=km; i++) {
r*=(2*i-1)*(2*i-1)/x/x;
s+=r;
if(TMath::Abs(r/s)<1.0e-12) break;
}
a1=TMath::Exp(x)/TMath::Sqrt(2*pi*x);
r=1.0;
bi0=1.0;
for (i=1; i<=16; i++) {
r=0.125*r*(2.0*i-1.0)*(2.0*i-1.0)/(i*x);
bi0+=r;
if(TMath::Abs(r/bi0)<1.0e-12) break;
}
bi0=a1*bi0;
sl0=-2.0/(pi*x)*s+bi0;
}
return sl0;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::StruveL1(Double_t x)
{
// Modified Struve Function of Order 1.
// By Kirill Filimonov.
const Double_t pi=TMath::Pi();
Double_t a1,sl1,bi1,s;
Double_t r=1.0;
Int_t km,i;
if (x<=20.) {
s=0.0;
for (i=1; i<=60;i++) {
r*=x*x/(4.0*i*i-1.0);
s+=r;
if(TMath::Abs(r)<TMath::Abs(s)*1.e-12) break;
}
sl1=2.0/pi*s;
} else {
s=1.0;
km=int(0.5*x);
if(x>50.0)km=25;
for (i=1; i<=km; i++) {
r*=(2*i+3)*(2*i+1)/x/x;
s+=r;
if(TMath::Abs(r/s)<1.0e-12) break;
}
sl1=2.0/pi*(-1.0+1.0/(x*x)+3.0*s/(x*x*x*x));
a1=TMath::Exp(x)/TMath::Sqrt(2*pi*x);
r=1.0;
bi1=1.0;
for (i=1; i<=16; i++) {
r=-0.125*r*(4.0-(2.0*i-1.0)*(2.0*i-1.0))/(i*x);
bi1+=r;
if(TMath::Abs(r/bi1)<1.0e-12) break;
}
sl1+=a1*bi1;
}
return sl1;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::Beta(Double_t p, Double_t q)
{
// Calculates Beta-function Gamma(p)*Gamma(q)/Gamma(p+q).
return TMath::Exp(TMath::LnGamma(p)+TMath::LnGamma(q)-TMath::LnGamma(p+q));
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::BetaCf(Double_t x, Double_t a, Double_t b)
{
// Continued fraction evaluation by modified Lentz's method
// used in calculation of incomplete Beta function.
Int_t itmax = 500;
Double_t eps = 3.e-14;
Double_t fpmin = 1.e-30;
Int_t m, m2;
Double_t aa, c, d, del, qab, qam, qap;
Double_t h;
qab = a+b;
qap = a+1.0;
qam = a-1.0;
c = 1.0;
d = 1.0 - qab*x/qap;
if (TMath::Abs(d)<fpmin) d=fpmin;
d=1.0/d;
h=d;
for (m=1; m<=itmax; m++) {
m2=m*2;
aa = m*(b-m)*x/((qam+ m2)*(a+m2));
d = 1.0 +aa*d;
if(TMath::Abs(d)<fpmin) d = fpmin;
c = 1 +aa/c;
if (TMath::Abs(c)<fpmin) c = fpmin;
d=1.0/d;
h*=d*c;
aa = -(a+m)*(qab +m)*x/((a+m2)*(qap+m2));
d=1.0+aa*d;
if(TMath::Abs(d)<fpmin) d = fpmin;
c = 1.0 +aa/c;
if (TMath::Abs(c)<fpmin) c = fpmin;
d=1.0/d;
del = d*c;
h*=del;
if (TMath::Abs(del-1)<=eps) break;
}
if (m>itmax) {
Info("TMath::BetaCf", "a or b too big, or itmax too small, a=%g, b=%g, x=%g, h=%g, itmax=%d",
a,b,x,h,itmax);
}
return h;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::BetaDist(Double_t x, Double_t p, Double_t q)
{
// Computes the probability density function of the Beta distribution
// (the distribution function is computed in BetaDistI).
// The first argument is the point, where the function will be
// computed, second and third are the function parameters.
// Since the Beta distribution is bounded on both sides, it's often
// used to represent processes with natural lower and upper limits.
if ((x<0) || (x>1) || (p<=0) || (q<=0)){
Error("TMath::BetaDist", "parameter value outside allowed range");
return 0;
}
Double_t beta = TMath::Beta(p, q);
Double_t r = TMath::Power(x, p-1)*TMath::Power(1-x, q-1)/beta;
return r;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::BetaDistI(Double_t x, Double_t p, Double_t q)
{
// Computes the distribution function of the Beta distribution.
// The first argument is the point, where the function will be
// computed, second and third are the function parameters.
// Since the Beta distribution is bounded on both sides, it's often
// used to represent processes with natural lower and upper limits.
if ((x<0) || (x>1) || (p<=0) || (q<=0)){
Error("TMath::BetaDistI", "parameter value outside allowed range");
return 0;
}
Double_t betai = TMath::BetaIncomplete(x, p, q);
return betai;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::BetaIncomplete(Double_t x, Double_t a, Double_t b)
{
// Calculates the incomplete Beta-function.
// -- implementation by Anna Kreshuk
Double_t bt;
if ((x<0.0)||(x>1.0)) {
Error("TMath::BetaIncomplete", "X must between 0 and 1");
return 0.0;
}
if ((x==0.0)||(x==1.0)) {
bt=0.0;
} else {
bt = TMath::Power(x, a)*TMath::Power(1-x, b)/Beta(a, b);
}
if (x<(a+1)/(a+b+2)) {
return bt*BetaCf(x, a, b)/a;
}
else {
return (1 - bt*BetaCf(1-x, b, a)/b);
}
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::Binomial(Int_t n,Int_t k)
{
// Calculate the binomial coefficient n over k.
if (k==0 || n==k) return 1;
if (n<=0 || k<0 || n<k) return 0;
Int_t k1=TMath::Min(k,n-k);
Int_t k2=n-k1;
Double_t fact=k2+1;
for (Int_t i=k1;i>1;i--)
fact*=static_cast<Double_t>(k2+i)/i;
return fact;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::BinomialI(Double_t p, Int_t n, Int_t k)
{
// Suppose an event occurs with probability _p_ per trial
// Then the probability P of its occuring _k_ or more times
// in _n_ trials is termed a cumulative binomial probability
// the formula is P = sum_from_j=k_to_n(TMath::Binomial(n, j)*
// *TMath::Power(p, j)*TMath::Power(1-p, n-j)
// For _n_ larger than 12 BetaIncomplete is a much better way
// to evaluate the sum than would be the straightforward sum calculation
// for _n_ smaller than 12 either method is acceptable
// ("Numerical Recipes")
// --implementation by Anna Kreshuk
return BetaIncomplete(p, Double_t(k), Double_t(n-k+1));
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::CauchyDist(Double_t x, Double_t t, Double_t s)
{
// Computes the density of Cauchy distribution at point x
// by default, standard Cauchy distribution is used (t=0, s=1)
// t is the location parameter
// s is the scale parameter
// The Cauchy distribution, also called Lorentzian distribution,
// is a continuous distribution describing resonance behavior
// The mean and standard deviation of the Cauchy distribution are undefined.
// The practical meaning of this is that collecting 1,000 data points gives
// no more accurate an estimate of the mean and standard deviation than
// does a single point.
// The formula was taken from "Engineering Statistics Handbook" on site
// http://www.itl.nist.gov/div898/handbook/eda/section3/eda3663.htm
// Implementation by Anna Kreshuk.
// Example:
// TF1* fc = new TF1("fc", "TMath::CauchyDist(x, [0], [1])", -5, 5);
// fc->SetParameters(0, 1);
// fc->Draw();
Double_t temp= (x-t)*(x-t)/(s*s);
Double_t result = 1/(s*TMath::Pi()*(1+temp));
return result;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::ChisquareQuantile(Double_t p, Double_t ndf)
{
// Evaluate the quantiles of the chi-squared probability distribution function.
// Algorithm AS 91 Appl. Statist. (1975) Vol.24, P.35
// implemented by Anna Kreshuk.
// Incorporates the suggested changes in AS R85 (vol.40(1), pp.233-5, 1991)
// Parameters:
// p - the probability value, at which the quantile is computed
// ndf - number of degrees of freedom
Double_t c[]={0, 0.01, 0.222222, 0.32, 0.4, 1.24, 2.2,
4.67, 6.66, 6.73, 13.32, 60.0, 70.0,
84.0, 105.0, 120.0, 127.0, 140.0, 175.0,
210.0, 252.0, 264.0, 294.0, 346.0, 420.0,
462.0, 606.0, 672.0, 707.0, 735.0, 889.0,
932.0, 966.0, 1141.0, 1182.0, 1278.0, 1740.0,
2520.0, 5040.0};
Double_t e = 5e-7;
Double_t aa = 0.6931471806;
Int_t maxit = 20;
Double_t ch, p1, p2, q, t, a, b, x;
Double_t s1, s2, s3, s4, s5, s6;
if (ndf <= 0) return 0;
Double_t g = TMath::LnGamma(0.5*ndf);
Double_t xx = 0.5 * ndf;
Double_t cp = xx - 1;
if (ndf >= TMath::Log(p)*(-c[5])){
//starting approximation for ndf less than or equal to 0.32
if (ndf > c[3]) {
x = TMath::NormQuantile(p);
//starting approximation using Wilson and Hilferty estimate
p1=c[2]/ndf;
ch = ndf*TMath::Power((x*TMath::Sqrt(p1) + 1 - p1), 3);
if (ch > c[6]*ndf + 6)
ch = -2 * (TMath::Log(1-p) - cp * TMath::Log(0.5 * ch) + g);
} else {
ch = c[4];
a = TMath::Log(1-p);
do{
q = ch;
p1 = 1 + ch * (c[7]+ch);
p2 = ch * (c[9] + ch * (c[8] + ch));
t = -0.5 + (c[7] + 2 * ch) / p1 - (c[9] + ch * (c[10] + 3 * ch)) / p2;
ch = ch - (1 - TMath::Exp(a + g + 0.5 * ch + cp * aa) *p2 / p1) / t;
}while (TMath::Abs(q/ch - 1) > c[1]);
}
} else {
ch = TMath::Power((p * xx * TMath::Exp(g + xx * aa)),(1./xx));
if (ch < e) return ch;
}
//call to algorithm AS 239 and calculation of seven term Taylor series
for (Int_t i=0; i<maxit; i++){
q = ch;
p1 = 0.5 * ch;
p2 = p - TMath::Gamma(xx, p1);
t = p2 * TMath::Exp(xx * aa + g + p1 - cp * TMath::Log(ch));
b = t / ch;
a = 0.5 * t - b * cp;
s1 = (c[19] + a * (c[17] + a * (c[14] + a * (c[13] + a * (c[12] +c[11] * a))))) / c[24];
s2 = (c[24] + a * (c[29] + a * (c[32] + a * (c[33] + c[35] * a)))) / c[37];
s3 = (c[19] + a * (c[25] + a * (c[28] + c[31] * a))) / c[37];
s4 = (c[20] + a * (c[27] + c[34] * a) + cp * (c[22] + a * (c[30] + c[36] * a))) / c[38];
s5 = (c[13] + c[21] * a + cp * (c[18] + c[26] * a)) / c[37];
s6 = (c[15] + cp * (c[23] + c[16] * cp)) / c[38];
ch = ch + t * (1 + 0.5 * t * s1 - b * cp * (s1 - b * (s2 - b * (s3 - b * (s4 - b * (s5 - b * s6))))));
if (TMath::Abs(q / ch - 1) > e) break;
}
return ch;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::FDist(Double_t F, Double_t N, Double_t M)
{
// Computes the density function of F-distribution
// (probability function, integral of density, is computed in FDistI).
//
// Parameters N and M stand for degrees of freedom of chi-squares
// mentioned above parameter F is the actual variable x of the
// density function p(x) and the point at which the density function
// is calculated.
//
// About F distribution:
// F-distribution arises in testing whether two random samples
// have the same variance. It is the ratio of two chi-square
// distributions, with N and M degrees of freedom respectively,
// where each chi-square is first divided by it's number of degrees
// of freedom.
// Implementation by Anna Kreshuk.
if ((F<0)||(N<1)||(M<1)){
return 0;
} else {
Double_t denom = TMath::Gamma(N/2)*TMath::Gamma(M/2)*TMath::Power(M+N*F, (N+M)/2);
Double_t div = TMath::Gamma((N+M)/2)*TMath::Power(N, N/2)*TMath::Power(M, M/2)*TMath::Power(F, 0.5*N-1);
return div/denom;
}
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::FDistI(Double_t F, Double_t N, Double_t M)
{
// Calculates the cumulative distribution function of F-distribution,
// this function occurs in the statistical test of whether two observed
// samples have the same variance. For this test a certain statistic F,
// the ratio of observed dispersion of the first sample to that of the
// second sample, is calculated. N and M stand for numbers of degrees
// of freedom in the samples 1-FDistI() is the significance level at
// which the hypothesis "1 has smaller variance than 2" can be rejected.
// A small numerical value of 1 - FDistI() implies a very significant
// rejection, in turn implying high confidence in the hypothesis
// "1 has variance greater than 2".
// Implementation by Anna Kreshuk.
Double_t fi = 1 - BetaIncomplete((M/(M+N*F)), M*0.5, N*0.5);
return fi;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::GammaDist(Double_t x, Double_t gamma, Double_t mu, Double_t beta)
{
// Computes the density function of Gamma distribution at point x.
// gamma - shape parameter
// mu - location parameter
// beta - scale parameter
// The formula was taken from "Engineering Statistics Handbook" on site
// http://www.itl.nist.gov/div898/handbook/eda/section3/eda366b.htm
// Implementation by Anna Kreshuk.
//
/*
*/
//
// which gives the probability that Kolmogorov's test statistic will exceed
// the value z assuming the null hypothesis. This gives a very powerful
// test for comparing two one-dimensional distributions.
// see, for example, Eadie et al, "statistocal Methods in Experimental
// Physics', pp 269-270).
//
// This function returns the confidence level for the null hypothesis, where:
// z = dn*sqrt(n), and
// dn is the maximum deviation between a hypothetical distribution
// function and an experimental distribution with
// n events
//
// NOTE: To compare two experimental distributions with m and n events,
// use z = sqrt(m*n/(m+n))*dn
//
// Accuracy: The function is far too accurate for any imaginable application.
// Probabilities less than 10^-15 are returned as zero.
// However, remember that the formula is only valid for "large" n.
// Theta function inversion formula is used for z <= 1
//
// This function was translated by Rene Brun from PROBKL in CERNLIB.
Double_t fj[4] = {-2,-8,-18,-32}, r[4];
const Double_t w = 2.50662827;
// c1 - -pi**2/8, c2 = 9*c1, c3 = 25*c1
const Double_t c1 = -1.2337005501361697;
const Double_t c2 = -11.103304951225528;
const Double_t c3 = -30.842513753404244;
Double_t u = TMath::Abs(z);
Double_t p;
if (u < 0.2) {
p = 1;
} else if (u < 0.755) {
Double_t v = 1./(u*u);
p = 1 - w*(TMath::Exp(c1*v) + TMath::Exp(c2*v) + TMath::Exp(c3*v))/u;
} else if (u < 6.8116) {
r[1] = 0;
r[2] = 0;
r[3] = 0;
Double_t v = u*u;
Int_t maxj = TMath::Max(1,TMath::Nint(3./u));
for (Int_t j=0; j<maxj;j++) {
r[j] = TMath::Exp(fj[j]*v);
}
p = 2*(r[0] - r[1] +r[2] - r[3]);
} else {
p = 0;
}
return p;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::KolmogorovTest(Int_t na, const Double_t *a, Int_t nb, const Double_t *b, Option_t *option)
{
// Statistical test whether two one-dimensional sets of points are compatible
// with coming from the same parent distribution, using the Kolmogorov test.
// That is, it is used to compare two experimental distributions of unbinned data.
//
// Input:
// a,b: One-dimensional arrays of length na, nb, respectively.
// The elements of a and b must be given in ascending order.
// option is a character string to specify options
// "D" Put out a line of "Debug" printout
// "M" Return the Maximum Kolmogorov distance instead of prob
//
// Output:
// The returned value prob is a calculated confidence level which gives a
// statistical test for compatibility of a and b.
// Values of prob close to zero are taken as indicating a small probability
// of compatibility. For two point sets drawn randomly from the same parent
// distribution, the value of prob should be uniformly distributed between
// zero and one.
// in case of error the function return -1
// If the 2 sets have a different number of points, the minimum of
// the two sets is used.
//
// Method:
// The Kolmogorov test is used. The test statistic is the maximum deviation
// between the two integrated distribution functions, multiplied by the
// normalizing factor (rdmax*sqrt(na*nb/(na+nb)).
//
// Code adapted by Rene Brun from CERNLIB routine TKOLMO (Fred James)
// (W.T. Eadie, D. Drijard, F.E. James, M. Roos and B. Sadoulet,
// Statistical Methods in Experimental Physics, (North-Holland,
// Amsterdam 1971) 269-271)
//
// NOTE1
// A good description of the Kolmogorov test can be seen at:
// http://www.itl.nist.gov/div898/handbook/eda/section3/eda35g.htm
TString opt = option;
opt.ToUpper();
Double_t prob = -1;
// Require at least two points in each graph
if (!a || !b || na <= 2 || nb <= 2) {
Error("KolmogorovTest","Sets must have more than 2 points");
return prob;
}
// Constants needed
Double_t rna = na;
Double_t rnb = nb;
Double_t sa = 1./rna;
Double_t sb = 1./rnb;
Double_t rdiff;
Int_t ia,ib;
// Starting values for main loop
if (a[0] < b[0]) {
rdiff = -sa;
ia = 2;
ib = 1;
} else {
rdiff = sb;
ib = 2;
ia = 1;
}
Double_t rdmax = TMath::Abs(rdiff);
// Main loop over point sets to find max distance
// rdiff is the running difference, and rdmax the max.
Bool_t ok = kFALSE;
for (Int_t i=0;i<na+nb;i++) {
if (a[ia-1] < b[ib-1]) {
rdiff -= sa;
ia++;
if (ia > na) {ok = kTRUE; break;}
} else if (a[ia-1] > b[ib-1]) {
rdiff += sb;
ib++;
if (ib > nb) {ok = kTRUE; break;}
} else {
ia++;
ib++;
if (ia > na) {ok = kTRUE; break;}
if (ib > nb) {ok = kTRUE; break;}
}
rdmax = TMath::Max(rdmax,TMath::Abs(rdiff));
}
// Should never terminate this loop with ok = kFALSE!
if (ok) {
rdmax = TMath::Max(rdmax,TMath::Abs(rdiff));
Double_t z = rdmax * TMath::Sqrt(rna*rnb/(rna+rnb));
prob = TMath::KolmogorovProb(z);
}
// debug printout
if (opt.Contains("D")) {
printf(" Kolmogorov Probability = %g, Max Dist = %g\n",prob,rdmax);
}
if(opt.Contains("M")) return rdmax;
else return prob;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::Voigt(Double_t xx, Double_t sigma, Double_t lg, Int_t r)
{
// Computation of Voigt function (normalised).
// Voigt is a convolution of
// gauss(xx) = 1/(sqrt(2*pi)*sigma) * exp(xx*xx/(2*sigma*sigma)
// and
// lorentz(xx) = (1/pi) * (lg/2) / (xx*xx + g*g/4)
// functions.
//
// The Voigt function is known to be the real part of Faddeeva function also
// called complex error function [2].
//
// The algoritm was developed by J. Humlicek [1].
// This code is based on fortran code presented by R. J. Wells [2].
// Translated and adapted by Miha D. Puc
//
// To calculate the Faddeeva function with relative error less than 10^(-r).
// r can be set by the the user subject to the constraints 2 <= r <= 5.
//
// [1] J. Humlicek, JQSRT, 21, 437 (1982).
// [2] R.J. Wells "Rapid Approximation to the Voigt/Faddeeva Function and its
// Derivatives" JQSRT 62 (1999), pp 29-48.
// http://www-atm.physics.ox.ac.uk/user/wells/voigt.html
if ((sigma < 0 || lg < 0) || (sigma==0 && lg==0)) {
return 0; // Not meant to be for those who want to be thinner than 0
}
if (sigma == 0) {
return lg * 0.159154943 / (xx*xx + lg*lg /4); //pure Lorentz
}
if (lg == 0) { //pure gauss
return 0.39894228 / sigma * TMath::Exp(-xx*xx / (2*sigma*sigma));
}
Double_t x, y, k;
x = xx / sigma / 1.41421356;
y = lg / 2 / sigma / 1.41421356;
Double_t r0, r1;
if (r < 2) r = 2;
if (r > 5) r = 5;
r0=1.51 * exp(1.144 * (Double_t)r);
r1=1.60 * exp(0.554 * (Double_t)r);
// Constants
const Double_t rrtpi = 0.56418958; // 1/SQRT(pi)
Double_t y0, y0py0, y0q; // for CPF12 algorithm
y0 = 1.5;
y0py0 = y0 + y0;
y0q = y0 * y0;
Double_t c[6] = { 1.0117281, -0.75197147, 0.012557727, 0.010022008, -0.00024206814, 0.00000050084806};
Double_t s[6] = { 1.393237, 0.23115241, -0.15535147, 0.0062183662, 0.000091908299, -0.00000062752596};
Double_t t[6] = { 0.31424038, 0.94778839, 1.5976826, 2.2795071, 3.0206370, 3.8897249};
// Local variables
int j; // Loop variables
int rg1, rg2, rg3; // y polynomial flags
Double_t abx, xq, yq, yrrtpi; // --x--, x^2, y^2, y/SQRT(pi)
Double_t xlim0, xlim1, xlim2, xlim3, xlim4; // --x-- on region boundaries
Double_t a0=0, d0=0, d2=0, e0=0, e2=0, e4=0, h0=0, h2=0, h4=0, h6=0;// W4 temporary variables
Double_t p0=0, p2=0, p4=0, p6=0, p8=0, z0=0, z2=0, z4=0, z6=0, z8=0;
Double_t xp[6], xm[6], yp[6], ym[6]; // CPF12 temporary values
Double_t mq[6], pq[6], mf[6], pf[6];
Double_t d, yf, ypy0, ypy0q;
//***** Start of executable code *****************************************
rg1 = 1; // Set flags
rg2 = 1;
rg3 = 1;
yq = y * y; // y^2
yrrtpi = y * rrtpi; // y/SQRT(pi)
// Region boundaries when both k and L are required or when R<>4
xlim0 = r0 - y;
xlim1 = r1 - y;
xlim3 = 3.097 * y - 0.45;
xlim2 = 6.8 - y;
xlim4 = 18.1 * y + 1.65;
if ( y <= 1e-6 ) { // When y<10^-6 avoid W4 algorithm
xlim1 = xlim0;
xlim2 = xlim0;
}
abx = fabs(x); // |x|
xq = abx * abx; // x^2
if ( abx > xlim0 ) { // Region 0 algorithm
k = yrrtpi / (xq + yq);
} else if ( abx > xlim1 ) { // Humlicek W4 Region 1
if ( rg1 != 0 ) { // First point in Region 1
rg1 = 0;
a0 = yq + 0.5; // Region 1 y-dependents
d0 = a0*a0;
d2 = yq + yq - 1.0;
}
d = rrtpi / (d0 + xq*(d2 + xq));
k = d * y * (a0 + xq);
} else if ( abx > xlim2 ) { // Humlicek W4 Region 2
if ( rg2 != 0 ) { // First point in Region 2
rg2 = 0;
h0 = 0.5625 + yq * (4.5 + yq * (10.5 + yq * (6.0 + yq)));
// Region 2 y-dependents
h2 = -4.5 + yq * (9.0 + yq * ( 6.0 + yq * 4.0));
h4 = 10.5 - yq * (6.0 - yq * 6.0);
h6 = -6.0 + yq * 4.0;
e0 = 1.875 + yq * (8.25 + yq * (5.5 + yq));
e2 = 5.25 + yq * (1.0 + yq * 3.0);
e4 = 0.75 * h6;
}
d = rrtpi / (h0 + xq * (h2 + xq * (h4 + xq * (h6 + xq))));
k = d * y * (e0 + xq * (e2 + xq * (e4 + xq)));
} else if ( abx < xlim3 ) { // Humlicek W4 Region 3
if ( rg3 != 0 ) { // First point in Region 3
rg3 = 0;
z0 = 272.1014 + y * (1280.829 + y *
(2802.870 + y *
(3764.966 + y *
(3447.629 + y *
(2256.981 + y *
(1074.409 + y *
(369.1989 + y *
(88.26741 + y *
(13.39880 + y)
)))))))); // Region 3 y-dependents
z2 = 211.678 + y * (902.3066 + y *
(1758.336 + y *
(2037.310 + y *
(1549.675 + y *
(793.4273 + y *
(266.2987 + y *
(53.59518 + y * 5.0)
))))));
z4 = 78.86585 + y * (308.1852 + y *
(497.3014 + y *
(479.2576 + y *
(269.2916 + y *
(80.39278 + y * 10.0)
))));
z6 = 22.03523 + y * (55.02933 + y *
(92.75679 + y *
(53.59518 + y * 10.0)
));
z8 = 1.496460 + y * (13.39880 + y * 5.0);
p0 = 153.5168 + y * (549.3954 + y *
(919.4955 + y *
(946.8970 + y *
(662.8097 + y *
(328.2151 + y *
(115.3772 + y *
(27.93941 + y *
(4.264678 + y * 0.3183291)
)))))));
p2 = -34.16955 + y * (-1.322256+ y *
(124.5975 + y *
(189.7730 + y *
(139.4665 + y *
(56.81652 + y *
(12.79458 + y * 1.2733163)
)))));
p4 = 2.584042 + y * (10.46332 + y *
(24.01655 + y *
(29.81482 + y *
(12.79568 + y * 1.9099744)
)));
p6 = -0.07272979 + y * (0.9377051 + y *
(4.266322 + y * 1.273316));
p8 = 0.0005480304 + y * 0.3183291;
}
d = 1.7724538 / (z0 + xq * (z2 + xq * (z4 + xq * (z6 + xq * (z8 + xq)))));
k = d * (p0 + xq * (p2 + xq * (p4 + xq * (p6 + xq * p8))));
} else { // Humlicek CPF12 algorithm
ypy0 = y + y0;
ypy0q = ypy0 * ypy0;
k = 0.0;
for (j = 0; j <= 5; j++) {
d = x - t[j];
mq[j] = d * d;
mf[j] = 1.0 / (mq[j] + ypy0q);
xm[j] = mf[j] * d;
ym[j] = mf[j] * ypy0;
d = x + t[j];
pq[j] = d * d;
pf[j] = 1.0 / (pq[j] + ypy0q);
xp[j] = pf[j] * d;
yp[j] = pf[j] * ypy0;
}
if ( abx <= xlim4 ) { // Humlicek CPF12 Region I
for (j = 0; j <= 5; j++) {
k = k + c[j]*(ym[j]+yp[j]) - s[j]*(xm[j]-xp[j]) ;
}
} else { // Humlicek CPF12 Region II
yf = y + y0py0;
for ( j = 0; j <= 5; j++) {
k = k + (c[j] *
(mq[j] * mf[j] - y0 * ym[j])
+ s[j] * yf * xm[j]) / (mq[j]+y0q)
+ (c[j] * (pq[j] * pf[j] - y0 * yp[j])
- s[j] * yf * xp[j]) / (pq[j]+y0q);
}
k = y * k + exp( -xq );
}
}
return k / 2.506628 / sigma; // Normalize by dividing by sqrt(2*pi)*sigma.
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TMath::RootsCubic(const Double_t coef[4],Double_t &a, Double_t &b, Double_t &c)
{
// Computes the roots of a cubic polynomial
// coef: Coefficients
// a,b,c: references to the roots
// Author: Jan Conrad
Double_t pi= TMath::Pi();
Int_t threeroots = 0;
Double_t phi,q,r,s,t,p,d,r1,x,temp;
a = 0.0;
b = 0.0;
c = 0.0;
if (coef[3] == 0) return;
r = coef[2]/coef[3];
s = coef[1]/coef[3];
t = coef[0]/coef[3];
p = (3 * s - r*r)/3;
q = (2 * r*r*r)/27 - (r * s)/3 + t;
d = (p/3)*(p/3)*(p/3) + (q/2)*(q/2);
r1 = q/TMath::Abs(q) * TMath::Sqrt(TMath::Abs(p)/3);
if (p==0) {
q = 8.0;
a = TMath::Power(q,1./3.);
goto done;
}
if ( p < 0) {
if (d <= 0) {
threeroots=1;
phi = TMath::ACos(q/2/(r1*r1*r1));
a = TMath::Cos(phi/3);
b = TMath::Cos(phi/3 + (2 * pi)/3);
c = TMath::Cos(phi/3 + (4 * pi)/3);
} else {
x = q/2/(r1*r1*r1);
phi = TMath::Log(x+TMath::Sqrt(x*x-1));
b = TMath::CosH(phi/3);
}
} else {
x = q/2/(r1*r1*r1);
phi = TMath::Log(x+TMath::Sqrt(x*x+1));
b = TMath::SinH(phi/3);
}
a = (-2*r1)*a-r/3;
b = (-2*r1)*b-r/3;
c = (-2*r1)*c-r/3;
done:
if (threeroots == 1) {
if (a > b){
temp=a;
a=b;
b=temp;
}
if (b > c) {
temp=b;
b=c;
c=temp;
}
if (a > b) {
temp=a;
a=b;
b=temp;
}
}
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Short_t TMath::MinElement(Long64_t n, const Short_t *a)
{
// Return minimum of array a of length n.
return *min_element(a,a+n);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TMath::MinElement(Long64_t n, const Int_t *a)
{
// Return minimum of array a of length n.
return *min_element(a,a+n);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Float_t TMath::MinElement(Long64_t n, const Float_t *a)
{
// Return minimum of array a of length n.
return *min_element(a,a+n);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::MinElement(Long64_t n, const Double_t *a)
{
// Return minimum of array a of length n.
return *min_element(a,a+n);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long_t TMath::MinElement(Long64_t n, const Long_t *a)
{
// Return minimum of array a of length n.
return *min_element(a,a+n);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long64_t TMath::MinElement(Long64_t n, const Long64_t *a)
{
// Return minimum of array a of length n.
return *min_element(a,a+n);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Short_t TMath::MaxElement(Long64_t n, const Short_t *a)
{
// Return maximum of array a of length n.
return *max_element(a,a+n);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TMath::MaxElement(Long64_t n, const Int_t *a)
{
// Return maximum of array a of length n.
return *max_element(a,a+n);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Float_t TMath::MaxElement(Long64_t n, const Float_t *a)
{
// Return maximum of array a of length n.
return *max_element(a,a+n);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::MaxElement(Long64_t n, const Double_t *a)
{
// Return maximum of array a of length n.
return *max_element(a,a+n);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long_t TMath::MaxElement(Long64_t n, const Long_t *a)
{
// Return maximum of array a of length n.
return *max_element(a,a+n);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long64_t TMath::MaxElement(Long64_t n, const Long64_t *a)
{
// Return maximum of array a of length n.
return *max_element(a,a+n);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long64_t TMath::LocMin(Long64_t n, const Short_t *a)
{
// Return index of array with the minimum element.
// If more than one element is minimum returns first found.
if (n <= 0 || !a) return -1;
Short_t xmin = a[0];
Long64_t loc = 0;
for (Long64_t i = 1; i < n; i++) {
if (xmin > a[i]) {
xmin = a[i];
loc = i;
}
}
return loc;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long64_t TMath::LocMin(Long64_t n, const Int_t *a)
{
// Return index of array with the minimum element.
// If more than one element is minimum returns first found.
if (n <= 0 || !a) return -1;
Int_t xmin = a[0];
Long64_t loc = 0;
for (Long64_t i = 1; i < n; i++) {
if (xmin > a[i]) {
xmin = a[i];
loc = i;
}
}
return loc;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long64_t TMath::LocMin(Long64_t n, const Float_t *a)
{
// Return index of array with the minimum element.
// If more than one element is minimum returns first found.
if (n <= 0 || !a) return -1;
Float_t xmin = a[0];
Long64_t loc = 0;
for (Long64_t i = 1; i < n; i++) {
if (xmin > a[i]) {
xmin = a[i];
loc = i;
}
}
return loc;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long64_t TMath::LocMin(Long64_t n, const Double_t *a)
{
// Return index of array with the minimum element.
// If more than one element is minimum returns first found.
if (n <= 0 || !a) return -1;
Double_t xmin = a[0];
Long64_t loc = 0;
for (Long64_t i = 1; i < n; i++) {
if (xmin > a[i]) {
xmin = a[i];
loc = i;
}
}
return loc;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long64_t TMath::LocMin(Long64_t n, const Long_t *a)
{
// Return index of array with the minimum element.
// If more than one element is minimum returns first found.
if (n <= 0 || !a) return -1;
Long_t xmin = a[0];
Long64_t loc = 0;
for (Int_t i = 1; i < n; i++) {
if (xmin > a[i]) {
xmin = a[i];
loc = i;
}
}
return loc;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long64_t TMath::LocMin(Long64_t n, const Long64_t *a)
{
// Return index of array with the minimum element.
// If more than one element is minimum returns first found.
if (n <= 0 || !a) return -1;
Long64_t xmin = a[0];
Long64_t loc = 0;
for (Int_t i = 1; i < n; i++) {
if (xmin > a[i]) {
xmin = a[i];
loc = i;
}
}
return loc;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long64_t TMath::LocMax(Long64_t n, const Short_t *a)
{
// Return index of array with the maximum element.
// If more than one element is maximum returns first found.
if (n <= 0 || !a) return -1;
Short_t xmax = a[0];
Long64_t loc = 0;
for (Long64_t i = 1; i < n; i++) {
if (xmax < a[i]) {
xmax = a[i];
loc = i;
}
}
return loc;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long64_t TMath::LocMax(Long64_t n, const Int_t *a)
{
// Return index of array with the maximum element.
// If more than one element is maximum returns first found.
if (n <= 0 || !a) return -1;
Int_t xmax = a[0];
Long64_t loc = 0;
for (Long64_t i = 1; i < n; i++) {
if (xmax < a[i]) {
xmax = a[i];
loc = i;
}
}
return loc;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long64_t TMath::LocMax(Long64_t n, const Float_t *a)
{
// Return index of array with the maximum element.
// If more than one element is maximum returns first found.
if (n <= 0 || !a) return -1;
Float_t xmax = a[0];
Long64_t loc = 0;
for (Long64_t i = 1; i < n; i++) {
if (xmax < a[i]) {
xmax = a[i];
loc = i;
}
}
return loc;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long64_t TMath::LocMax(Long64_t n, const Double_t *a)
{
// Return index of array with the maximum element.
// If more than one element is maximum returns first found.
if (n <= 0 || !a) return -1;
Double_t xmax = a[0];
Long64_t loc = 0;
for (Long64_t i = 1; i < n; i++) {
if (xmax < a[i]) {
xmax = a[i];
loc = i;
}
}
return loc;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long64_t TMath::LocMax(Long64_t n, const Long64_t *a)
{
// Return index of array with the maximum element.
// If more than one element is maximum returns first found.
if (n <= 0 || !a) return -1;
Long64_t xmax = a[0];
Long64_t loc = 0;
for (Long64_t i = 1; i < n; i++) {
if (xmax < a[i]) {
xmax = a[i];
loc = i;
}
}
return loc;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long64_t TMath::LocMax(Long64_t n, const Long_t *a)
{
// Return index of array with the maximum element.
// If more than one element is maximum returns first found.
if (n <= 0 || !a) return -1;
Long_t xmax = a[0];
Long64_t loc = 0;
for (Long64_t i = 1; i < n; i++) {
if (xmax < a[i]) {
xmax = a[i];
loc = i;
}
}
return loc;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::Mean(Long64_t n, const Short_t *a, const Double_t *w)
{
// Return the weighted mean of an array a with length n.
if (n <= 0 || !a) return 0;
Double_t sum = 0;
Double_t sumw = 0;
if (w) {
for (Long64_t i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (w[i] < 0) {
::Error("TMath::Mean","w[%d] = %.4e < 0 ?!",i,w[i]);
return 0;
}
sum += w[i]*a[i];
sumw += w[i];
}
if (sumw <= 0) {
::Error("TMath::Mean","sum of weights == 0 ?!");
return 0;
}
} else {
sumw = n;
for (Long64_t i = 0; i < n; i++)
sum += a[i];
}
return sum/sumw;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::Mean(Long64_t n, const Int_t *a, const Double_t *w)
{
// Return the weighted mean of an array a with length n.
if (n <= 0 || !a) return 0;
Double_t sum = 0;
Double_t sumw = 0;
if (w) {
for (Long64_t i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (w[i] < 0) {
::Error("TMath::Mean","w[%d] = %.4e < 0 ?!",i,w[i]);
return 0;
}
sum += w[i]*a[i];
sumw += w[i];
}
if (sumw <= 0) {
::Error("TMath::Mean","sum of weights == 0 ?!");
return 0;
}
} else {
sumw = n;
for (Long64_t i = 0; i < n; i++)
sum += a[i];
}
return sum/sumw;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::Mean(Long64_t n, const Float_t *a, const Double_t *w)
{
// Return the weighted mean of an array a with length n.
if (n <= 0 || !a) return 0;
Double_t sum = 0;
Double_t sumw = 0;
if (w) {
for (Long64_t i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (w[i] < 0) {
::Error("TMath::Mean","w[%d] = %.4e < 0 ?!",i,w[i]);
return 0;
}
sum += w[i]*a[i];
sumw += w[i];
}
if (sumw <= 0) {
::Error("TMath::Mean","sum of weights == 0 ?!");
return 0;
}
} else {
sumw = n;
for (Long64_t i = 0; i < n; i++)
sum += a[i];
}
return sum/sumw;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::Mean(Long64_t n, const Double_t *a, const Double_t *w)
{
// Return the weighted mean of an array a with length n.
if (n <= 0 || !a) return 0;
Double_t sum = 0;
Double_t sumw = 0;
if (w) {
for (Long64_t i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (w[i] < 0) {
::Error("TMath::Mean","w[%d] = %.4e < 0 ?!",i,w[i]);
return 0;
}
sum += w[i]*a[i];
sumw += w[i];
}
if (sumw <= 0) {
::Error("TMath::Mean","sum of weights == 0 ?!");
return 0;
}
} else {
sumw = n;
for (Long64_t i = 0; i < n; i++)
sum += a[i];
}
return sum/sumw;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::Mean(Long64_t n, const Long_t *a, const Double_t *w)
{
// Return the weighted mean of an array a with length n.
if (n <= 0 || !a) return 0;
Double_t sum = 0;
Double_t sumw = 0;
if (w) {
for (Long64_t i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (w[i] < 0) {
::Error("TMath::Mean","w[%d] = %.4e < 0 ?!",i,w[i]);
return 0;
}
sum += w[i]*a[i];
sumw += w[i];
}
if (sumw <= 0) {
::Error("TMath::Mean","sum of weights == 0 ?!");
return 0;
}
} else {
sumw = n;
for (Long64_t i = 0; i < n; i++)
sum += a[i];
}
return sum/sumw;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::Mean(Long64_t n, const Long64_t *a, const Double_t *w)
{
// Return the weighted mean of an array a with length n.
if (n <= 0 || !a) return 0;
Double_t sum = 0;
Double_t sumw = 0;
if (w) {
for (Long64_t i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (w[i] < 0) {
::Error("TMath::Mean","w[%d] = %.4e < 0 ?!",i,w[i]);
return 0;
}
sum += w[i]*a[i];
sumw += w[i];
}
if (sumw <= 0) {
::Error("TMath::Mean","sum of weights == 0 ?!");
return 0;
}
} else {
sumw = n;
for (Long64_t i = 0; i < n; i++)
sum += a[i];
}
return sum/sumw;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::GeomMean(Long64_t n, const Short_t *a)
{
// Return the geometric mean of an array a with length n.
// geometric_mean = (Prod_i=0,n-1 |a[i]|)^1/n
if (n <= 0 || !a) return 0;
Double_t logsum = 0.;
for (Long64_t i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (a[i] == 0) return 0.;
Double_t absa = (Double_t) TMath::Abs(a[i]);
logsum += TMath::Log(absa);
}
return TMath::Exp(logsum/n);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::GeomMean(Long64_t n, const Int_t *a)
{
// Return the geometric mean of an array a with length n.
// geometric_mean = (Prod_i=0,n-1 |a[i]|)^1/n
if (n <= 0 || !a) return 0;
Double_t logsum = 0.;
for (Long64_t i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (a[i] == 0) return 0.;
Double_t absa = (Double_t) TMath::Abs(a[i]);
logsum += TMath::Log(absa);
}
return TMath::Exp(logsum/n);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::GeomMean(Long64_t n, const Float_t *a)
{
// Return the geometric mean of an array a with length n.
// geometric_mean = (Prod_i=0,n-1 |a[i]|)^1/n
if (n <= 0 || !a) return 0;
Double_t logsum = 0.;
for (Long64_t i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (a[i] == 0) return 0.;
Double_t absa = (Double_t) TMath::Abs(a[i]);
logsum += TMath::Log(absa);
}
return TMath::Exp(logsum/n);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::GeomMean(Long64_t n, const Double_t *a)
{
// Return the geometric mean of an array a with length n.
// geometric_mean = (Prod_i=0,n-1 |a[i]|)^1/n
if (n <= 0 || !a) return 0;
Double_t logsum = 0.;
for (Long64_t i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (a[i] == 0) return 0.;
Double_t absa = (Double_t) TMath::Abs(a[i]);
logsum += TMath::Log(absa);
}
return TMath::Exp(logsum/n);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::GeomMean(Long64_t n, const Long64_t *a)
{
// Return the geometric mean of an array a with length n.
// geometric_mean = (Prod_i=0,n-1 |a[i]|)^1/n
if (n <= 0 || !a) return 0;
Double_t logsum = 0.;
for (Long64_t i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (a[i] == 0) return 0.;
Double_t absa = (Double_t) TMath::Abs(a[i]);
logsum += TMath::Log(absa);
}
return TMath::Exp(logsum/n);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::GeomMean(Long64_t n, const Long_t *a)
{
// Return the geometric mean of an array a with length n.
// geometric_mean = (Prod_i=0,n-1 |a[i]|)^1/n
if (n <= 0 || !a) return 0;
Double_t logsum = 0.;
for (Long64_t i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (a[i] == 0) return 0.;
Double_t absa = (Double_t) TMath::Abs(a[i]);
logsum += TMath::Log(absa);
}
return TMath::Exp(logsum/n);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
#if defined(_MSC_VER) && (_MSC_VER<1300)
// See also the declarations at the top of this file
template <class Element, class Index, class Size>
Double_t MedianImpStandalone(Size n, const Element *a, const Double_t *w, Index *work)
#else
template <class Element, class Index, class Size>
Double_t TMath::MedianImp(Size n, const Element *a,const Double_t *w, Index *work)
#endif
{
// Return the median of the array a where each entry i has weight w[i] .
// Both arrays have a length of at least n . The median is a number obtained
// from the sorted array a through
//
// median = (a[jl]+a[jh])/2. where (using also the sorted index on the array w)
//
// sum_i=0,jl w[i] <= sumTot/2
// sum_i=0,jh w[i] >= sumTot/2
// sumTot = sum_i=0,n w[i]
//
// If w=0, the algorithm defaults to the median definition where it is
// a number that divides the sorted sequence into 2 halves.
// When n is odd or n > 1000, the median is kth element k = (n + 1) / 2.
// when n is even and n < 1000the median is a mean of the elements k = n/2 and k = n/2 + 1.
//
// If work is supplied, it is used to store the sorting index and assumed to be
// >= n . If work=0, local storage is used, either on the stack if n < kWorkMax
// or on the heap for n >= kWorkMax .
if (n <= 0 || !a) return 0;
Bool_t isAllocated = kFALSE;
Double_t median;
Index *ind;
Index workLocal[kWorkMax];
if (work) {
ind = work;
} else {
ind = workLocal;
if (n > kWorkMax) {
isAllocated = kTRUE;
ind = new Index[n];
}
}
if (w) {
Double_t sumTot2 = 0;
for (Int_t j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (w[j] < 0) {
::Error("TMath::Median","w[%d] = %.4e < 0 ?!",j,w[j]);
return 0;
}
sumTot2 += w[j];
}
sumTot2 /= 2.;
SortImp(n, a, ind, kFALSE);
Double_t sum = 0.;
Int_t jl;
for (jl = 0; jl < n; jl++) {
sum += w[ind[jl]];
if (sum >= sumTot2) break;
}
Int_t jh;
sum = 2.*sumTot2;
for (jh = n-1; jh >= 0; jh--) {
sum -= w[ind[jh]];
if (sum <= sumTot2) break;
}
median = 0.5*(a[ind[jl]]+a[ind[jh]]);
} else {
if (n%2 == 1)
median = KOrdStatImp(n, a,n/2, ind);
else {
median = 0.5*(KOrdStatImp(n, a, n/2 -1, ind)+KOrdStatImp(n, a, n/2, ind));
}
}
if (isAllocated)
delete [] ind;
return median;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::Median(Long64_t n, const Short_t *a, const Double_t *w, Long64_t *work)
{
// Return the median of the array a where each entry i has weight w[i] .
// Both arrays have a length of at least n . The median is a number obtained
// from the sorted array a through
//
// median = (a[jl]+a[jh])/2. where (using also the sorted index on the array w)
//
// sum_i=0,jl w[i] <= sumTot/2
// sum_i=0,jh w[i] >= sumTot/2
// sumTot = sum_i=0,n w[i]
//
// If w=0, the algorithm defaults to the median definition where it is
// a number that divides the sorted sequence into 2 halves.
// When n is odd or n > 1000, the median is kth element k = (n + 1) / 2.
// when n is even and n < 1000the median is a mean of the elements k = n/2 and k = n/2 + 1.
//
// If work is supplied, it is used to store the sorting index and assumed to be
// >= n . If work=0, local storage is used, either on the stack if n < kWorkMax
// or on the heap for n >= kWorkMax .
return MedianImp(n, a, w, work);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::Median(Long64_t n, const Int_t *a, const Double_t *w, Long64_t *work)
{
// Return the median of the array a where each entry i has weight w[i] .
// Both arrays have a length of at least n . The median is a number obtained
// from the sorted array a through
//
// median = (a[jl]+a[jh])/2. where (using also the sorted index on the array w)
//
// sum_i=0,jl w[i] <= sumTot/2
// sum_i=0,jh w[i] >= sumTot/2
// sumTot = sum_i=0,n w[i]
//
// If w=0, the algorithm defaults to the median definition where it is
// a number that divides the sorted sequence into 2 halves.
// When n is odd or n > 1000, the median is kth element k = (n + 1) / 2.
// when n is even and n < 1000the median is a mean of the elements k = n/2 and k = n/2 + 1.
//
// If work is supplied, it is used to store the sorting index and assumed to be
// >= n . If work=0, local storage is used, either on the stack if n < kWorkMax
// or on the heap for n >= kWorkMax .
return MedianImp(n, a, w, work);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::Median(Long64_t n, const Float_t *a, const Double_t *w, Long64_t *work)
{
// Return the median of the array a where each entry i has weight w[i] .
// Both arrays have a length of at least n . The median is a number obtained
// from the sorted array a through
//
// median = (a[jl]+a[jh])/2. where (using also the sorted index on the array w)
//
// sum_i=0,jl w[i] <= sumTot/2
// sum_i=0,jh w[i] >= sumTot/2
// sumTot = sum_i=0,n w[i]
//
// If w=0, the algorithm defaults to the median definition where it is
// a number that divides the sorted sequence into 2 halves.
// When n is odd or n > 1000, the median is kth element k = (n + 1) / 2.
// when n is even and n < 1000the median is a mean of the elements k = n/2 and k = n/2 + 1.
//
// If work is supplied, it is used to store the sorting index and assumed to be
// >= n . If work=0, local storage is used, either on the stack if n < kWorkMax
// or on the heap for n >= kWorkMax .
return MedianImp(n, a, w, work);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::Median(Long64_t n, const Double_t *a, const Double_t *w, Long64_t *work)
{
// Return the median of the array a where each entry i has weight w[i] .
// Both arrays have a length of at least n . The median is a number obtained
// from the sorted array a through
//
// median = (a[jl]+a[jh])/2. where (using also the sorted index on the array w)
//
// sum_i=0,jl w[i] <= sumTot/2
// sum_i=0,jh w[i] >= sumTot/2
// sumTot = sum_i=0,n w[i]
//
// If w=0, the algorithm defaults to the median definition where it is
// a number that divides the sorted sequence into 2 halves.
// When n is odd or n > 1000, the median is kth element k = (n + 1) / 2.
// when n is even and n < 1000the median is a mean of the elements k = n/2 and k = n/2 + 1.
//
// If work is supplied, it is used to store the sorting index and assumed to be
// >= n . If work=0, local storage is used, either on the stack if n < kWorkMax
// or on the heap for n >= kWorkMax .
return MedianImp(n, a, w, work);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::Median(Long64_t n, const Long_t *a, const Double_t *w, Long64_t *work)
{
// Return the median of the array a where each entry i has weight w[i] .
// Both arrays have a length of at least n . The median is a number obtained
// from the sorted array a through
//
// median = (a[jl]+a[jh])/2. where (using also the sorted index on the array w)
//
// sum_i=0,jl w[i] <= sumTot/2
// sum_i=0,jh w[i] >= sumTot/2
// sumTot = sum_i=0,n w[i]
//
// If w=0, the algorithm defaults to the median definition where it is
// a number that divides the sorted sequence into 2 halves.
// When n is odd or n > 1000, the median is kth element k = (n + 1) / 2.
// when n is even and n < 1000the median is a mean of the elements k = n/2 and k = n/2 + 1.
//
// If work is supplied, it is used to store the sorting index and assumed to be
// >= n . If work=0, local storage is used, either on the stack if n < kWorkMax
// or on the heap for n >= kWorkMax .
return MedianImp(n, a, w, work);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::Median(Long64_t n, const Long64_t *a, const Double_t *w, Long64_t *work)
{
// Return the median of the array a where each entry i has weight w[i] .
// Both arrays have a length of at least n . The median is a number obtained
// from the sorted array a through
//
// median = (a[jl]+a[jh])/2. where (using also the sorted index on the array w)
//
// sum_i=0,jl w[i] <= sumTot/2
// sum_i=0,jh w[i] >= sumTot/2
// sumTot = sum_i=0,n w[i]
//
// If w=0, the algorithm defaults to the median definition where it is
// a number that divides the sorted sequence into 2 halves.
// When n is odd or n > 1000, the median is kth element k = (n + 1) / 2.
// when n is even and n < 1000the median is a mean of the elements k = n/2 and k = n/2 + 1.
//
// If work is supplied, it is used to store the sorting index and assumed to be
// >= n . If work=0, local storage is used, either on the stack if n < kWorkMax
// or on the heap for n >= kWorkMax .
return MedianImp(n, a, w, work);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
#if defined(_MSC_VER) && (_MSC_VER<1300)
template <class Element, class Index, class Size>
Element KOrdStatImpStandalone(Size n, const Element *a, Size k, Index *work)
#else
template <class Element, class Index, class Size>
Element TMath::KOrdStatImp(Size n, const Element *a, Size k, Index *work)
#endif
{
// Returns k_th order statistic of the array a of size n
// (k_th smallest element out of n elements).
//
// C-convention is used for array indexing, so if you want
// the second smallest element, call KOrdStat(n, a, 1).
//
// If work is supplied, it is used to store the sorting index and
// assumed to be >= n. If work=0, local storage is used, either on
// the stack if n < kWorkMax or on the heap for n >= kWorkMax.
//
// Taken from "Numerical Recipes in C++" without the index array
// implemented by Anna Khreshuk.
//
// See also the declarations at the top of this file
Bool_t isAllocated = kFALSE;
Size i, ir, j, l, mid;
Index arr;
Index *ind;
Index workLocal[kWorkMax];
Index temp;
if (work) {
ind = work;
} else {
ind = workLocal;
if (n > kWorkMax) {
isAllocated = kTRUE;
ind = new Index[n];
}
}
for (Size ii=0; ii<n; ii++) {
ind[ii]=ii;
}
Size rk = k;
l=0;
ir = n-1;
for(;;) {
if (ir<=l+1) { //active partition contains 1 or 2 elements
if (ir == l+1 && a[ind[ir]]<a[ind[l]])
{temp = ind[l]; ind[l]=ind[ir]; ind[ir]=temp;}
Element tmp = a[ind[rk]];
if (isAllocated)
delete [] ind;
return tmp;
} else {
mid = (l+ir) >> 1; //choose median of left, center and right
{temp = ind[mid]; ind[mid]=ind[l+1]; ind[l+1]=temp;}//elements as partitioning element arr.
if (a[ind[l]]>a[ind[ir]]) //also rearrange so that a[l]<=a[l+1]
{temp = ind[l]; ind[l]=ind[ir]; ind[ir]=temp;}
if (a[ind[l+1]]>a[ind[ir]])
{temp=ind[l+1]; ind[l+1]=ind[ir]; ind[ir]=temp;}
if (a[ind[l]]>a[ind[l+1]])
{temp = ind[l]; ind[l]=ind[l+1]; ind[l+1]=temp;}
i=l+1; //initialize pointers for partitioning
j=ir;
arr = ind[l+1];
for (;;){
do i++; while (a[ind[i]]<a[arr]);
do j--; while (a[ind[j]]>a[arr]);
if (j<i) break; //pointers crossed, partitioning complete
{temp=ind[i]; ind[i]=ind[j]; ind[j]=temp;}
}
ind[l+1]=ind[j];
ind[j]=arr;
if (j>=rk) ir = j-1; //keep active the partition that
if (j<=rk) l=i; //contains the k_th element
}
}
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::KOrdStat(Long64_t n, const Double_t *a, Long64_t k, Long64_t *work)
{
// Returns k_th order statistic of the array a of size n
// (k_th smallest element out of n elements).
//
// C-convention is used for array indexing, so if you want
// the second smallest element, call KOrdStat(n, a, 1).
//
// If work is supplied, it is used to store the sorting index and
// assumed to be >= n. If work=0, local storage is used, either on
// the stack if n < kWorkMax or on the heap for n >= kWorkMax.
return KOrdStatImp(n, a, k, work);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Float_t TMath::KOrdStat(Long64_t n, const Float_t *a, Long64_t k, Long64_t *work)
{
// Returns k_th order statistic of the array a of size n
// (k_th smallest element out of n elements).
//
// C-convention is used for array indexing, so if you want
// the second smallest element, call KOrdStat(n, a, 1).
//
// If work is supplied, it is used to store the sorting index and
// assumed to be >= n. If work=0, local storage is used, either on
// the stack if n < kWorkMax or on the heap for n >= kWorkMax.
return KOrdStatImp(n, a, k, work);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TMath::KOrdStat(Long64_t n, const Int_t *a, Long64_t k, Long64_t *work)
{
// Returns k_th order statistic of the array a of size n
// (k_th smallest element out of n elements).
//
// C-convention is used for array indexing, so if you want
// the second smallest element, call KOrdStat(n, a, 1).
//
// If work is supplied, it is used to store the sorting index and
// assumed to be >= n. If work=0, local storage is used, either on
// the stack if n < kWorkMax or on the heap for n >= kWorkMax.
return KOrdStatImp(n, a, k, work);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Short_t TMath::KOrdStat(Long64_t n, const Short_t *a, Long64_t k, Long64_t *work)
{
// Returns k_th order statistic of the array a of size n
// (k_th smallest element out of n elements).
//
// C-convention is used for array indexing, so if you want
// the second smallest element, call KOrdStat(n, a, 1).
//
// If work is supplied, it is used to store the sorting index and
// assumed to be >= n . If work=0, local storage is used, either on
// the stack if n < kWorkMax or on the heap for n >= kWorkMax.
return KOrdStatImp(n, a, k, work);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long64_t TMath::KOrdStat(Long64_t n, const Long_t *a, Long64_t k, Long64_t *work)
{
// Returns k_th order statistic of the array a of size n
// (k_th smallest element out of n elements).
//
// C-convention is used for array indexing, so if you want
// the second smallest element, call KOrdStat(n, a, 1).
//
// If work is supplied, it is used to store the sorting index and
// assumed to be >= n. If work=0, local storage is used, either on
// the stack if n < kWorkMax or on the heap for n >= kWorkMax.
return KOrdStatImp(n, a, k, work);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long64_t TMath::KOrdStat(Long64_t n, const Long64_t *a, Long64_t k, Long64_t *work)
{
// Returns k_th order statistic of the array a of size n
// (k_th smallest element out of n elements).
//
// C-convention is used for array indexing, so if you want
// the second smallest element, call KOrdStat(n, a, 1).
//
// If work is supplied, it is used to store the sorting index and
// assumed to be >= n. If work=0, local storage is used, either on
// the stack if n < kWorkMax or on the heap for n >= kWorkMax.
return KOrdStatImp(n, a, k, work);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::RMS(Long64_t n, const Short_t *a)
{
// Return the RMS of an array a with length n.
if (n <= 0 || !a) return 0;
Double_t tot = 0, tot2 =0, adouble;
for (Long64_t i=0;i<n;i++) {
adouble=Double_t(a[i]);
tot += adouble; tot2 += adouble*adouble;
}
Double_t n1 = 1./n;
Double_t mean = tot*n1;
Double_t rms = TMath::Sqrt(TMath::Abs(tot2*n1 -mean*mean));
return rms;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::RMS(Long64_t n, const Int_t *a)
{
// Return the RMS of an array a with length n.
if (n <= 0 || !a) return 0;
Double_t tot = 0, tot2 =0, adouble;
for (Long64_t i=0;i<n;i++) {
adouble=Double_t(a[i]);
tot += adouble; tot2 += adouble*adouble;
}
Double_t n1 = 1./n;
Double_t mean = tot*n1;
Double_t rms = TMath::Sqrt(TMath::Abs(tot2*n1 -mean*mean));
return rms;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::RMS(Long64_t n, const Float_t *a)
{
// Return the RMS of an array a with length n.
if (n <= 0 || !a) return 0;
Double_t tot = 0, tot2 =0, adouble;
for (Long64_t i=0;i<n;i++) {
adouble=Double_t(a[i]);
tot += adouble; tot2 += adouble*adouble;
}
Double_t n1 = 1./n;
Double_t mean = tot*n1;
Double_t rms = TMath::Sqrt(TMath::Abs(tot2*n1 -mean*mean));
return rms;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::RMS(Long64_t n, const Double_t *a)
{
// Return the RMS of an array a with length n.
if (n <= 0 || !a) return 0;
Double_t tot = 0, tot2 =0;
for (Long64_t i=0;i<n;i++) {tot += a[i]; tot2 += a[i]*a[i]; }
Double_t n1 = 1./n;
Double_t mean = tot*n1;
Double_t rms = TMath::Sqrt(TMath::Abs(tot2*n1 -mean*mean));
return rms;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::RMS(Long64_t n, const Long_t *a)
{
// Return the RMS of an array a with length n.
if (n <= 0 || !a) return 0;
Double_t tot = 0, tot2 =0, adouble;
for (Long64_t i=0;i<n;i++) {
adouble=Double_t(a[i]);
tot += adouble; tot2 += adouble*adouble;
}
Double_t n1 = 1./n;
Double_t mean = tot*n1;
Double_t rms = TMath::Sqrt(TMath::Abs(tot2*n1 -mean*mean));
return rms;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::RMS(Long64_t n, const Long64_t *a)
{
// Return the RMS of an array a with length n.
if (n <= 0 || !a) return 0;
Double_t tot = 0, tot2 =0, adouble;
for (Long64_t i=0;i<n;i++) {
adouble=Double_t(a[i]);
tot += adouble; tot2 += adouble*adouble;
}
Double_t n1 = 1./n;
Double_t mean = tot*n1;
Double_t rms = TMath::Sqrt(TMath::Abs(tot2*n1 -mean*mean));
return rms;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long64_t TMath::BinarySearch(Long64_t n, const Short_t *array, Short_t value)
{
// Binary search in an array of n values to locate value.
//
// Array is supposed to be sorted prior to this call.
// If match is found, function returns position of element.
// If no match found, function gives nearest element smaller than value.
Long64_t nabove, nbelow, middle;
nabove = n+1;
nbelow = 0;
while(nabove-nbelow > 1) {
middle = (nabove+nbelow)/2;
if (value == array[middle-1]) return middle-1;
if (value < array[middle-1]) nabove = middle;
else nbelow = middle;
}
return nbelow-1;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long64_t TMath::BinarySearch(Long64_t n, const Short_t **array, Short_t value)
{
// Binary search in an array of n values to locate value.
//
// Array is supposed to be sorted prior to this call.
// If match is found, function returns position of element.
// If no match found, function gives nearest element smaller than value.
Long64_t nabove, nbelow, middle;
nabove = n+1;
nbelow = 0;
while(nabove-nbelow > 1) {
middle = (nabove+nbelow)/2;
if (value == *array[middle-1]) return middle-1;
if (value < *array[middle-1]) nabove = middle;
else nbelow = middle;
}
return nbelow-1;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long64_t TMath::BinarySearch(Long64_t n, const Int_t *array, Int_t value)
{
// Binary search in an array of n values to locate value.
//
// Array is supposed to be sorted prior to this call.
// If match is found, function returns position of element.
// If no match found, function gives nearest element smaller than value.
Long64_t nabove, nbelow, middle;
nabove = n+1;
nbelow = 0;
while(nabove-nbelow > 1) {
middle = (nabove+nbelow)/2;
if (value == array[middle-1]) return middle-1;
if (value < array[middle-1]) nabove = middle;
else nbelow = middle;
}
return nbelow-1;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long64_t TMath::BinarySearch(Long64_t n, const Int_t **array, Int_t value)
{
// Binary search in an array of n values to locate value.
//
// Array is supposed to be sorted prior to this call.
// If match is found, function returns position of element.
// If no match found, function gives nearest element smaller than value.
Long64_t nabove, nbelow, middle;
nabove = n+1;
nbelow = 0;
while(nabove-nbelow > 1) {
middle = (nabove+nbelow)/2;
if (value == *array[middle-1]) return middle-1;
if (value < *array[middle-1]) nabove = middle;
else nbelow = middle;
}
return nbelow-1;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long64_t TMath::BinarySearch(Long64_t n, const Float_t *array, Float_t value)
{
// Binary search in an array of n values to locate value.
//
// Array is supposed to be sorted prior to this call.
// If match is found, function returns position of element.
// If no match found, function gives nearest element smaller than value.
Long64_t nabove, nbelow, middle;
nabove = n+1;
nbelow = 0;
while(nabove-nbelow > 1) {
middle = (nabove+nbelow)/2;
if (value == array[middle-1]) return middle-1;
if (value < array[middle-1]) nabove = middle;
else nbelow = middle;
}
return nbelow-1;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long64_t TMath::BinarySearch(Long64_t n, const Float_t **array, Float_t value)
{
// Binary search in an array of n values to locate value.
//
// Array is supposed to be sorted prior to this call.
// If match is found, function returns position of element.
// If no match found, function gives nearest element smaller than value.
Long64_t nabove, nbelow, middle;
nabove = n+1;
nbelow = 0;
while(nabove-nbelow > 1) {
middle = (nabove+nbelow)/2;
if (value == *array[middle-1]) return middle-1;
if (value < *array[middle-1]) nabove = middle;
else nbelow = middle;
}
return nbelow-1;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long64_t TMath::BinarySearch(Long64_t n, const Double_t *array, Double_t value)
{
// Binary search in an array of n values to locate value.
//
// Array is supposed to be sorted prior to this call.
// If match is found, function returns position of element.
// If no match found, function gives nearest element smaller than value.
Long64_t nabove, nbelow, middle;
nabove = n+1;
nbelow = 0;
while(nabove-nbelow > 1) {
middle = (nabove+nbelow)/2;
if (value == array[middle-1]) return middle-1;
if (value < array[middle-1]) nabove = middle;
else nbelow = middle;
}
return nbelow-1;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long64_t TMath::BinarySearch(Long64_t n, const Double_t **array, Double_t value)
{
// Binary search in an array of n values to locate value.
//
// Array is supposed to be sorted prior to this call.
// If match is found, function returns position of element.
// If no match found, function gives nearest element smaller than value.
Long64_t nabove, nbelow, middle;
nabove = n+1;
nbelow = 0;
while(nabove-nbelow > 1) {
middle = (nabove+nbelow)/2;
if (value == *array[middle-1]) return middle-1;
if (value < *array[middle-1]) nabove = middle;
else nbelow = middle;
}
return nbelow-1;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long64_t TMath::BinarySearch(Long64_t n, const Long_t *array, Long_t value)
{
// Binary search in an array of n values to locate value.
//
// Array is supposed to be sorted prior to this call.
// If match is found, function returns position of element.
// If no match found, function gives nearest element smaller than value.
Long64_t nabove, nbelow, middle;
nabove = n+1;
nbelow = 0;
while(nabove-nbelow > 1) {
middle = (nabove+nbelow)/2;
if (value == array[middle-1]) return middle-1;
if (value < array[middle-1]) nabove = middle;
else nbelow = middle;
}
return nbelow-1;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long64_t TMath::BinarySearch(Long64_t n, const Long_t **array, Long_t value)
{
// Binary search in an array of n values to locate value.
//
// Array is supposed to be sorted prior to this call.
// If match is found, function returns position of element.
// If no match found, function gives nearest element smaller than value.
Long64_t nabove, nbelow, middle;
nabove = n+1;
nbelow = 0;
while(nabove-nbelow > 1) {
middle = (nabove+nbelow)/2;
if (value == *array[middle-1]) return middle-1;
if (value < *array[middle-1]) nabove = middle;
else nbelow = middle;
}
return nbelow-1;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long64_t TMath::BinarySearch(Long64_t n, const Long64_t *array, Long64_t value)
{
// Binary search in an array of n values to locate value.
//
// Array is supposed to be sorted prior to this call.
// If match is found, function returns position of element.
// If no match found, function gives nearest element smaller than value.
Long64_t nabove, nbelow, middle;
nabove = n+1;
nbelow = 0;
while(nabove-nbelow > 1) {
middle = (nabove+nbelow)/2;
if (value == array[middle-1]) return middle-1;
if (value < array[middle-1]) nabove = middle;
else nbelow = middle;
}
return nbelow-1;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long64_t TMath::BinarySearch(Long64_t n, const Long64_t **array, Long64_t value)
{
// Binary search in an array of n values to locate value.
//
// Array is supposed to be sorted prior to this call.
// If match is found, function returns position of element.
// If no match found, function gives nearest element smaller than value.
Long64_t nabove, nbelow, middle;
nabove = n+1;
nbelow = 0;
while(nabove-nbelow > 1) {
middle = (nabove+nbelow)/2;
if (value == *array[middle-1]) return middle-1;
if (value < *array[middle-1]) nabove = middle;
else nbelow = middle;
}
return nbelow-1;
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
Bool_t TMath::IsInside(Double_t xp, Double_t yp, Int_t np, Double_t *x, Double_t *y)
{
// Function which returns kTRUE if point xp,yp lies inside the
// polygon defined by the np points in arrays x and y, kFALSE otherwise
// NOTE that the polygon must be a closed polygon (1st and last point
// must be identical).
Double_t xint;
Int_t i;
Int_t inter = 0;
for (i=0;i<np-1;i++) {
if (y[i] == y[i+1]) continue;
if (yp <= y[i] && yp <= y[i+1]) continue;
if (y[i] < yp && y[i+1] < yp) continue;
xint = x[i] + (yp-y[i])*(x[i+1]-x[i])/(y[i+1]-y[i]);
if (xp < xint) inter++;
}
if (inter%2) return kTRUE;
return kFALSE;
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
Bool_t TMath::IsInside(Float_t xp, Float_t yp, Int_t np, Float_t *x, Float_t *y)
{
// Function which returns kTRUE if point xp,yp lies inside the
// polygon defined by the np points in arrays x and y, kFALSE otherwise
// NOTE that the polygon must be a closed polygon (1st and last point
// must be identical).
Double_t xint;
Int_t i;
Int_t inter = 0;
for (i=0;i<np-1;i++) {
if (y[i] == y[i+1]) continue;
if (yp <= y[i] && yp <= y[i+1]) continue;
if (y[i] < yp && y[i+1] < yp) continue;
xint = x[i] + (yp-y[i])*(x[i+1]-x[i])/(y[i+1]-y[i]);
if ((Double_t)xp < xint) inter++;
}
if (inter%2) return kTRUE;
return kFALSE;
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
Bool_t TMath::IsInside(Int_t xp, Int_t yp, Int_t np, Int_t *x, Int_t *y)
{
// Function which returns kTRUE if point xp,yp lies inside the
// polygon defined by the np points in arrays x and y, kFALSE otherwise
// NOTE that the polygon must be a closed polygon (1st and last point
// must be identical).
Double_t xint;
Int_t i;
Int_t inter = 0;
for (i=0;i<np-1;i++) {
if (y[i] == y[i+1]) continue;
if (yp <= y[i] && yp <= y[i+1]) continue;
if (y[i] < yp && y[i+1] < yp) continue;
xint = x[i] + (yp-y[i])*(x[i+1]-x[i])/(y[i+1]-y[i]);
if ((Double_t)xp < xint) inter++;
}
if (inter%2) return kTRUE;
return kFALSE;
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
#if defined(_MSC_VER) && (_MSC_VER<1300)
template <class Element, class Index, class Size>
void SortImpStandalone(Size n1, const Element *a,
Index *index, Bool_t down)
#else
template <class Element, class Index, class Size>
void TMath::SortImp(Size n1, const Element *a,
Index *index, Bool_t down)
#endif
{
// Templated version of the Sort.
//
// Sort the n1 elements of the array a.of Element
// In output the array index contains the indices of the sorted array.
// If down is false sort in increasing order (default is decreasing order).
// This is a translation of the CERNLIB routine sortzv (M101)
// based on the quicksort algorithm.
// NOTE that the array index must be created with a length >= n1
// before calling this function.
//
// See also the declarations at the top of this file.
Size i,i1,n,i2,i3,i33,i222,iswap,n2;
Size i22 = 0;
Element ai;
n = n1;
if (n <= 0 || !a) return;
if (n == 1) {index[0] = 0; return;}
for (i=0;i<n;i++) index[i] = i+1;
for (i1=2;i1<=n;i1++) {
i3 = i1;
i33 = index[i3-1];
ai = a[i33-1];
while(1) {
i2 = i3/2;
if (i2 <= 0) break;
i22 = index[i2-1];
if (ai <= a[i22-1]) break;
index[i3-1] = i22;
i3 = i2;
}
index[i3-1] = i33;
}
while(1) {
i3 = index[n-1];
index[n-1] = index[0];
ai = a[i3-1];
n--;
if(n-1 < 0) {index[0] = i3; break;}
i1 = 1;
while(2) {
i2 = i1+i1;
if (i2 <= n) i22 = index[i2-1];
if (i2-n > 0) {index[i1-1] = i3; break;}
if (i2-n < 0) {
i222 = index[i2];
if (a[i22-1] - a[i222-1] < 0) {
i2++;
i22 = i222;
}
}
if (ai - a[i22-1] > 0) {index[i1-1] = i3; break;}
index[i1-1] = i22;
i1 = i2;
}
}
for (i=0;i<n1;i++) index[i]--;
if (!down) return;
n2 = n1/2;
for (i=0;i<n2;i++) {
iswap = index[i];
index[i] = index[n1-i-1];
index[n1-i-1] = iswap;
}
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
void TMath::Sort(Int_t n1, const Short_t *a, Int_t *index, Bool_t down)
{
// Sort the n1 elements of the Short_t array a.
// In output the array index contains the indices of the sorted array.
// If down is false sort in increasing order (default is decreasing order).
// This is a translation of the CERNLIB routine sortzv (M101)
// based on the quicksort algorithm.
// NOTE that the array index must be created with a length >= n1
// before calling this function.
SortImp(n1,a,index,down);
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
void TMath::Sort(Int_t n1, const Int_t *a, Int_t *index, Bool_t down)
{
// Sort the n1 elements of the Int_t array a.
// In output the array index contains the indices of the sorted array.
// If down is false sort in increasing order (default is decreasing order).
// This is a translation of the CERNLIB routine sortzv (M101)
// based on the quicksort algorithm.
// NOTE that the array index must be created with a length >= n1
// before calling this function.
SortImp(n1,a,index,down);
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
void TMath::Sort(Int_t n1, const Float_t *a, Int_t *index, Bool_t down)
{
// Sort the n1 elements of the Float_t array a.
// In output the array index contains the indices of the sorted array.
// If down is false sort in increasing order (default is decreasing order).
// This is a translation of the CERNLIB routine sortzv (M101)
// based on the quicksort algorithm.
// NOTE that the array index must be created with a length >= n1
// before calling this function.
SortImp(n1,a,index,down);
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
void TMath::Sort(Int_t n1, const Double_t *a, Int_t *index, Bool_t down)
{
// Sort the n1 elements of the Double_t array a.
// In output the array index contains the indices of the sorted array.
// If down is false sort in increasing order (default is decreasing order).
// This is a translation of the CERNLIB routine sortzv (M101)
// based on the quicksort algorithm.
// NOTE that the array index must be created with a length >= n1
// before calling this function.
SortImp(n1,a,index,down);
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
void TMath::Sort(Int_t n1, const Long_t *a, Int_t *index, Bool_t down)
{
// Sort the n1 elements of the Long64_t array a.
// In output the array index contains the indices of the sorted array.
// If down is false sort in increasing order (default is decreasing order).
// This is a translation of the CERNLIB routine sortzv (M101)
// based on the quicksort algorithm.
// NOTE that the array index must be created with a length >= n1
// before calling this function.
SortImp(n1,a,index,down);
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
void TMath::Sort(Int_t n1, const Long64_t *a, Int_t *index, Bool_t down)
{
// Sort the n1 elements of the Long64_t array a.
// In output the array index contains the indices of the sorted array.
// If down is false sort in increasing order (default is decreasing order).
// This is a translation of the CERNLIB routine sortzv (M101)
// based on the quicksort algorithm.
// NOTE that the array index must be created with a length >= n1
// before calling this function.
SortImp(n1,a,index,down);
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
void TMath::Sort(Long64_t n1, const Short_t *a, Long64_t *index, Bool_t down)
{
// Sort the n1 elements of the Short_t array a.
// In output the array index contains the indices of the sorted array.
// If down is false sort in increasing order (default is decreasing order).
// This is a translation of the CERNLIB routine sortzv (M101)
// based on the quicksort algorithm.
// NOTE that the array index must be created with a length >= n1
// before calling this function.
SortImp(n1,a,index,down);
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
void TMath::Sort(Long64_t n1, const Int_t *a, Long64_t *index, Bool_t down)
{
// Sort the n1 elements of the Int_t array a.
// In output the array index contains the indices of the sorted array.
// If down is false sort in increasing order (default is decreasing order).
// This is a translation of the CERNLIB routine sortzv (M101)
// based on the quicksort algorithm.
// NOTE that the array index must be created with a length >= n1
// before calling this function.
SortImp(n1,a,index,down);
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
void TMath::Sort(Long64_t n1, const Float_t *a, Long64_t *index, Bool_t down)
{
// Sort the n1 elements of the Float_t array a.
// In output the array index contains the indices of the sorted array.
// If down is false sort in increasing order (default is decreasing order).
// This is a translation of the CERNLIB routine sortzv (M101)
// based on the quicksort algorithm.
// NOTE that the array index must be created with a length >= n1
// before calling this function.
SortImp(n1,a,index,down);
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
void TMath::Sort(Long64_t n1, const Double_t *a, Long64_t *index, Bool_t down)
{
// Sort the n1 elements of the Double_t array a.
// In output the array index contains the indices of the sorted array.
// If down is false sort in increasing order (default is decreasing order).
// This is a translation of the CERNLIB routine sortzv (M101)
// based on the quicksort algorithm.
// NOTE that the array index must be created with a length >= n1
// before calling this function.
SortImp(n1,a,index,down);
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
void TMath::Sort(Long64_t n1, const Long_t *a, Long64_t *index, Bool_t down)
{
// Sort the n1 elements of the Long64_t array a.
// In output the array index contains the indices of the sorted array.
// If down is false sort in increasing order (default is decreasing order).
// This is a translation of the CERNLIB routine sortzv (M101)
// based on the quicksort algorithm.
// NOTE that the array index must be created with a length >= n1
// before calling this function.
SortImp(n1,a,index,down);
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
void TMath::Sort(Long64_t n1, const Long64_t *a, Long64_t *index, Bool_t down)
{
// Sort the n1 elements of the Long64_t array a.
// In output the array index contains the indices of the sorted array.
// If down is false sort in increasing order (default is decreasing order).
// This is a translation of the CERNLIB routine sortzv (M101)
// based on the quicksort algorithm.
// NOTE that the array index must be created with a length >= n1
// before calling this function.
SortImp(n1,a,index,down);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TMath::BubbleHigh(Int_t Narr, Double_t *arr1, Int_t *arr2)
{
// Bubble sort variant to obtain the order of an array's elements into
// an index in order to do more useful things than the standard built
// in functions.
// *arr1 is unchanged;
// *arr2 is the array of indicies corresponding to the decending value
// of arr1 with arr2[0] corresponding to the largest arr1 value and
// arr2[Narr] the smallest.
//
// Author: Adrian Bevan (bevan@slac.stanford.edu)
// Copyright: Liverpool University, July 2001
if (Narr <= 0) return;
double *localArr1 = new double[Narr];
int *localArr2 = new int[Narr];
int iEl;
int iEl2;
for(iEl = 0; iEl < Narr; iEl++) {
localArr1[iEl] = arr1[iEl];
localArr2[iEl] = iEl;
}
for (iEl = 0; iEl < Narr; iEl++) {
for (iEl2 = Narr-1; iEl2 > iEl; --iEl2) {
if (localArr1[iEl2-1] < localArr1[iEl2]) {
double tmp = localArr1[iEl2-1];
localArr1[iEl2-1] = localArr1[iEl2];
localArr1[iEl2] = tmp;
int tmp2 = localArr2[iEl2-1];
localArr2[iEl2-1] = localArr2[iEl2];
localArr2[iEl2] = tmp2;
}
}
}
for (iEl = 0; iEl < Narr; iEl++) {
arr2[iEl] = localArr2[iEl];
}
delete [] localArr2;
delete [] localArr1;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TMath::BubbleLow(Int_t Narr, Double_t *arr1, Int_t *arr2)
{
// Opposite ordering of the array arr2[] to that of BubbleHigh.
//
// Author: Adrian Bevan (bevan@slac.stanford.edu)
// Copyright: Liverpool University, July 2001
if (Narr <= 0) return;
double *localArr1 = new double[Narr];
int *localArr2 = new int[Narr];
int iEl;
int iEl2;
for (iEl = 0; iEl < Narr; iEl++) {
localArr1[iEl] = arr1[iEl];
localArr2[iEl] = iEl;
}
for (iEl = 0; iEl < Narr; iEl++) {
for (iEl2 = Narr-1; iEl2 > iEl; --iEl2) {
if (localArr1[iEl2-1] > localArr1[iEl2]) {
double tmp = localArr1[iEl2-1];
localArr1[iEl2-1] = localArr1[iEl2];
localArr1[iEl2] = tmp;
int tmp2 = localArr2[iEl2-1];
localArr2[iEl2-1] = localArr2[iEl2];
localArr2[iEl2] = tmp2;
}
}
}
for (iEl = 0; iEl < Narr; iEl++) {
arr2[iEl] = localArr2[iEl];
}
delete [] localArr2;
delete [] localArr1;
}
#ifdef OLD_HASH
//______________________________________________________________________________
ULong_t TMath::Hash(const void *txt, Int_t ntxt)
{
// Calculates hash index from any char string.
// Based on precalculated table of 256 specially selected random numbers.
//
// For string: i = TMath::Hash(string,nstring);
// For int: i = TMath::Hash(&intword,sizeof(int));
// For pointer: i = TMath::Hash(&pointer,sizeof(void*));
//
// Limitation: for ntxt>256 calculates hash only from first 256 bytes
//
// V.Perev
const UChar_t *uc = (const UChar_t*) txt;
ULong_t u = 0, uu = 0;
static ULong_t utab[256] =
{0xb93f6fc0,0x553dfc51,0xb22c1e8c,0x638462c0,0x13e81418,0x2836e171,0x7c4abb90,0xda1a4f39
,0x38f211d1,0x8c804829,0x95a6602d,0x4c590993,0x1810580a,0x721057d4,0x0f587215,0x9f49ce2a
,0xcd5ab255,0xab923a99,0x80890f39,0xbcfa2290,0x16587b52,0x6b6d3f0d,0xea8ff307,0x51542d5c
,0x189bf223,0x39643037,0x0e4a326a,0x214eca01,0x47645a9b,0x0f364260,0x8e9b2da4,0x5563ebd9
,0x57a31c1c,0xab365854,0xdd63ab1f,0x0b89acbd,0x23d57d33,0x1800a0fd,0x225ac60a,0xd0e51943
,0x6c65f669,0xcb966ea0,0xcbafda95,0x2e5c0c5f,0x2988e87e,0xc781cbab,0x3add3dc7,0x693a2c30
,0x42d6c23c,0xebf85f26,0x2544987e,0x2e315e3f,0xac88b5b5,0x7ebd2bbb,0xda07c87b,0x20d460f1
,0xc61c3f40,0x182046e7,0x3b6c3b66,0x2fc10d4a,0x0780dfbb,0xc437280c,0x0988dd07,0xe1498606
,0x8e61d728,0x4f1f3909,0x040a9682,0x49411b29,0x391b0e1c,0xd7905241,0xdd77d95b,0x88426c13
,0x33033e58,0xe158e30e,0x7e342647,0x1e09544b,0x4637353d,0x18ea0924,0x39212b08,0x12580ae8
,0x269a6f06,0x3e10b73b,0x123db33b,0x085412da,0x3bb5f464,0xd9b2d442,0x103d26bb,0xd0038bab
,0x45b6177f,0xfb48f1fe,0x99074c55,0xb545e82e,0x5f79fd0d,0x570f3ae4,0x57e43255,0x037a12ae
,0x4357bdb2,0x337c2c4d,0x2982499d,0x2ab72793,0x3900e7d1,0x57a6bb81,0x7503609b,0x3f39c0d0
,0x717b389d,0x5748034f,0x4698162b,0x5801b97c,0x1dfd5d7e,0xc1386d1c,0xa387a72a,0x084547e4
,0x2e54d8e9,0x2e2f384c,0xe09ccc20,0x8904b71e,0x3e24edc5,0x06a22e16,0x8a2be1df,0x9e5058b2
,0xe01a2f16,0x03325eed,0x587ecfe6,0x584d9cd3,0x32926930,0xe943d68c,0xa9442da8,0xf9650560
,0xf003871e,0x1109c663,0x7a2f2f89,0x1c2210bb,0x37335787,0xb92b382f,0xea605cb5,0x336bbe38
,0x08126bd3,0x1f8c2bd6,0xba6c46f2,0x1a4d1b83,0xc988180d,0xe2582505,0xa8a1b375,0x59a08c49
,0x3db54b48,0x44400f35,0x272d4e7f,0x5579f733,0x98eb590e,0x8ee09813,0x12cc9301,0xc85c402d
,0x135c1039,0x22318128,0x4063c705,0x87a8a3fa,0xfc14431f,0x6e27bf47,0x2d080a19,0x01dba174
,0xe343530b,0xaa1bfced,0x283bb2c8,0x5df250c8,0x4ff9140b,0x045039c1,0xa377780d,0x750f2661
,0x2b108918,0x0b152120,0x3cbc251f,0x5e87b350,0x060625bb,0xe068ba3b,0xdb73ebd7,0x66014ff3
,0xdb003000,0x161a3a0b,0xdc24e142,0x97ea5575,0x635a3cab,0xa719100a,0x256084db,0xc1f4a1e7
,0xe13388f2,0xb8199fc9,0x50c70dc9,0x08154211,0xd60e5220,0xe52c6592,0x584c5fe1,0xfe5e0875
,0x21072b30,0x3370d773,0x92608fe2,0x2d013d93,0x53414b3c,0x2c066142,0x64676644,0x0420887c
,0x35c01187,0x6822119b,0xf9bfe6df,0x273f4ee4,0x87973149,0x7b41282d,0x635d0d1f,0x5f7ecc1e
,0x14c3608a,0x462dfdab,0xc33d8808,0x1dcd995e,0x0fcb11ba,0x11755914,0x5a62044b,0x37f76755
,0x345bd058,0x8831c2b5,0x204a8468,0x3b0b1cd2,0x444e56f4,0x97a93e2c,0xd5f15067,0x266a95fa
,0xff4f8036,0x6160060d,0x930c472f,0xed922184,0x37120251,0xc0add74f,0x1c0bc89d,0x018d47f2
,0xff59ef66,0xd1901a17,0x91f6701b,0x0960082f,0x86f6a8f3,0x1154fecd,0x9867d1de,0x0945482f
,0x790ffcac,0xe5610011,0x4765637e,0xa745dbff,0x841fdcb3,0x4f7372a0,0x3c05013d,0xf1ac4ab7
,0x3bc5b5cc,0x49a73349,0x356a7f67,0x1174f031,0x11d32634,0x4413d301,0x1dd285c4,0x3fae4800
};
if (ntxt > 255) ntxt = 255;
for ( ; ntxt--; uc++) {
uu = uu<<1 ^ utab[(*uc) ^ ntxt];
u ^= uu;
}
return u;
}
#else
//______________________________________________________________________________
ULong_t TMath::Hash(const void *txt, Int_t ntxt)
{
// Calculates hash index from any char string.
// Based on precalculated table of 256 specially selected numbers.
// These numbers are selected in such a way, that for string
// length == 4 (integer number) the hash is unambigous, i.e.
// from hash value we can recalculate input (no degeneration).
//
// The quality of hash method is good enough, that
// "random" numbers made as R = Hash(1), Hash(2), ...Hash(N)
// tested by <R>, <R*R>, <Ri*Ri+1> gives the same result
// as for libc rand().
//
// For string: i = TMath::Hash(string,nstring);
// For int: i = TMath::Hash(&intword,sizeof(int));
// For pointer: i = TMath::Hash(&pointer,sizeof(void*));
//
// V.Perev
static const ULong_t utab[] = {
0xdd367647,0x9caf993f,0x3f3cc5ff,0xfde25082,0x4c764b21,0x89affca7,0x5431965c,0xce22eeec
,0xc61ab4dc,0x59cc93bd,0xed3107e3,0x0b0a287a,0x4712475a,0xce4a4c71,0x352c8403,0x94cb3cee
,0xc3ac509b,0x09f827a2,0xce02e37e,0x7b20bbba,0x76adcedc,0x18c52663,0x19f74103,0x6f30e47b
,0x132ea5a1,0xfdd279e0,0xa3d57d00,0xcff9cb40,0x9617f384,0x6411acfa,0xff908678,0x5c796b2c
,0x4471b62d,0xd38e3275,0xdb57912d,0x26bf953f,0xfc41b2a5,0xe64bcebd,0x190b7839,0x7e8e6a56
,0x9ca22311,0xef28aa60,0xe6b9208e,0xd257fb65,0x45781c2c,0x9a558ac3,0x2743e74d,0x839417a8
,0x06b54d5d,0x1a82bcb4,0x06e97a66,0x70abdd03,0xd163f30d,0x222ed322,0x777bfeda,0xab7a2e83
,0x8494e0cf,0x2dca2d4f,0x78f94278,0x33f04a09,0x402b6452,0x0cd8b709,0xdb72a39e,0x170e00a2
,0x26354faa,0x80e57453,0xcfe8d4e1,0x19e45254,0x04c291c3,0xeb503738,0x425af3bc,0x67836f2a
,0xfac22add,0xfafc2b8c,0x59b8c2a0,0x03e806f9,0xcb4938b9,0xccc942af,0xcee3ae2e,0xfbe748fa
,0xb223a075,0x85c49b5d,0xe4576ac9,0x0fbd46e2,0xb49f9cf5,0xf3e1e86a,0x7d7927fb,0x711afe12
,0xbf61c346,0x157c9956,0x86b6b046,0x2e402146,0xb2a57d8a,0x0d064bb1,0x30ce390c,0x3a3e1eb1
,0xbe7f6f8f,0xd8e30f87,0x5be2813c,0x73a3a901,0xa3aaf967,0x59ff092c,0x1705c798,0xf610dd66
,0xb17da91e,0x8e59534e,0x2211ea5b,0xa804ba03,0xd890efbb,0xb8b48110,0xff390068,0xc8c325b4
,0xf7289c07,0x787e104f,0x3d0df3d0,0x3526796d,0x10548055,0x1d59a42b,0xed1cc5a3,0xdd45372a
,0x31c50d57,0x65757cb7,0x3cfb85be,0xa329910d,0x6ad8ce39,0xa2de44de,0x0dd32432,0xd4a5b617
,0x8f3107fc,0x96485175,0x7f94d4f3,0x35097634,0xdb3ca782,0x2c0290b8,0x2045300b,0xe0f5d15a
,0x0e8cbffa,0xaa1cc38a,0x84008d6f,0xe9a9e794,0x5c602c25,0xfa3658fa,0x98d9d82b,0x3f1497e7
,0x84b6f031,0xe381eff9,0xfc7ae252,0xb239e05d,0xe3723d1f,0xcc3bda82,0xe21b1ad3,0x9104f7c8
,0x4bb2dfcd,0x4d14a8bc,0x6ba7f28c,0x8f89886c,0xad44c97e,0xb30fd975,0x633cdab1,0xf6c2d514
,0x067a49d2,0xdc461ad9,0xebaf9f3f,0x8dc6cac3,0x7a060f16,0xbab063ad,0xf42e25e6,0x60724ca6
,0xc7245c2e,0x4e48ea3c,0x9f89a609,0xa1c49890,0x4bb7f116,0xd722865c,0xa8ee3995,0x0ee070b1
,0xd9bffcc2,0xe55b64f9,0x25507a5a,0xc7a3e2b5,0x5f395f7e,0xe7957652,0x7381ba6a,0xde3d21f1
,0xdf1708dd,0xad0c9d0c,0x00cbc9e5,0x1160e833,0x6779582c,0x29d5d393,0x3f11d7d7,0x826a6b9b
,0xe73ff12f,0x8bad3d86,0xee41d3e5,0x7f0c8917,0x8089ef24,0x90c5cb28,0x2f7f8e6b,0x6966418a
,0x345453fb,0x7a2f8a68,0xf198593d,0xc079a532,0xc1971e81,0x1ab74e26,0x329ef347,0x7423d3d0
,0x942c510b,0x7f6c6382,0x14ae6acc,0x64b59da7,0x2356fa47,0xb6749d9c,0x499de1bb,0x92ffd191
,0xe8f2fb75,0x848dc913,0x3e8727d3,0x1dcffe61,0xb6e45245,0x49055738,0x827a6b55,0xb4788887
,0x7e680125,0xd19ce7ed,0x6b4b8e30,0xa8cadea2,0x216035d8,0x1c63bc3c,0xe1299056,0x1ad3dff4
,0x0aefd13c,0x0e7b921c,0xca0173c6,0x9995782d,0xcccfd494,0xd4b0ac88,0x53d552b1,0x630dae8b
,0xa8332dad,0x7139d9a2,0x5d76f2c4,0x7a4f8f1e,0x8d1aef97,0xd1cf285d,0xc8239153,0xce2608a9
,0x7b562475,0xe4b4bc83,0xf3db0c3a,0x70a65e48,0x6016b302,0xdebd5046,0x707e786a,0x6f10200c
};
static const ULong_t msk[] = { 0x11111111, 0x33333333, 0x77777777, 0xffffffff };
const UChar_t *uc = (const UChar_t *) txt;
ULong_t uu = 0;
union {
ULong_t u;
UShort_t s[2];
} u;
u.u = 0;
Int_t i, idx;
for (i = 0; i < ntxt; i++) {
idx = (uc[i] ^ i) & 255;
uu = (uu << 1) ^ (utab[idx] & msk[i & 3]);
if ((i & 3) == 3) u.u ^= uu;
}
if (i & 3) u.u ^= uu;
u.u *= 1879048201; // prime number
u.s[0] += u.s[1];
u.u *= 1979048191; // prime number
u.s[1] ^= u.s[0];
u.u *= 2079048197; // prime number
return u.u;
}
#endif
//______________________________________________________________________________
ULong_t TMath::Hash(const char *txt)
{
return Hash(txt, Int_t(strlen(txt)));
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::BesselI0(Double_t x)
{
// Compute the modified Bessel function I_0(x) for any real x.
//
//--- NvE 12-mar-2000 UU-SAP Utrecht
// Parameters of the polynomial approximation
const Double_t p1=1.0, p2=3.5156229, p3=3.0899424,
p4=1.2067492, p5=0.2659732, p6=3.60768e-2, p7=4.5813e-3;
const Double_t q1= 0.39894228, q2= 1.328592e-2, q3= 2.25319e-3,
q4=-1.57565e-3, q5= 9.16281e-3, q6=-2.057706e-2,
q7= 2.635537e-2, q8=-1.647633e-2, q9= 3.92377e-3;
const Double_t k1 = 3.75;
Double_t ax = TMath::Abs(x);
Double_t y=0, result=0;
if (ax < k1) {
Double_t xx = x/k1;
y = xx*xx;
result = p1+y*(p2+y*(p3+y*(p4+y*(p5+y*(p6+y*p7)))));
} else {
y = k1/ax;
result = (TMath::Exp(ax)/TMath::Sqrt(ax))*(q1+y*(q2+y*(q3+y*(q4+y*(q5+y*(q6+y*(q7+y*(q8+y*q9))))))));
}
return result;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::BesselK0(Double_t x)
{
// Compute the modified Bessel function K_0(x) for positive real x.
//
// M.Abramowitz and I.A.Stegun, Handbook of Mathematical Functions,
// Applied Mathematics Series vol. 55 (1964), Washington.
//
//--- NvE 12-mar-2000 UU-SAP Utrecht
// Parameters of the polynomial approximation
const Double_t p1=-0.57721566, p2=0.42278420, p3=0.23069756,
p4= 3.488590e-2, p5=2.62698e-3, p6=1.0750e-4, p7=7.4e-6;
const Double_t q1= 1.25331414, q2=-7.832358e-2, q3= 2.189568e-2,
q4=-1.062446e-2, q5= 5.87872e-3, q6=-2.51540e-3, q7=5.3208e-4;
if (x <= 0) {
Error("TMath::BesselK0", "*K0* Invalid argument x = %g\n",x);
return 0;
}
Double_t y=0, result=0;
if (x <= 2) {
y = x*x/4;
result = (-log(x/2.)*TMath::BesselI0(x))+(p1+y*(p2+y*(p3+y*(p4+y*(p5+y*(p6+y*p7))))));
} else {
y = 2/x;
result = (exp(-x)/sqrt(x))*(q1+y*(q2+y*(q3+y*(q4+y*(q5+y*(q6+y*q7))))));
}
return result;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::BesselI1(Double_t x)
{
// Compute the modified Bessel function I_1(x) for any real x.
//
// M.Abramowitz and I.A.Stegun, Handbook of Mathematical Functions,
// Applied Mathematics Series vol. 55 (1964), Washington.
//
//--- NvE 12-mar-2000 UU-SAP Utrecht
// Parameters of the polynomial approximation
const Double_t p1=0.5, p2=0.87890594, p3=0.51498869,
p4=0.15084934, p5=2.658733e-2, p6=3.01532e-3, p7=3.2411e-4;
const Double_t q1= 0.39894228, q2=-3.988024e-2, q3=-3.62018e-3,
q4= 1.63801e-3, q5=-1.031555e-2, q6= 2.282967e-2,
q7=-2.895312e-2, q8= 1.787654e-2, q9=-4.20059e-3;
const Double_t k1 = 3.75;
Double_t ax = TMath::Abs(x);
Double_t y=0, result=0;
if (ax < k1) {
Double_t xx = x/k1;
y = xx*xx;
result = x*(p1+y*(p2+y*(p3+y*(p4+y*(p5+y*(p6+y*p7))))));
} else {
y = k1/ax;
result = (exp(ax)/sqrt(ax))*(q1+y*(q2+y*(q3+y*(q4+y*(q5+y*(q6+y*(q7+y*(q8+y*q9))))))));
if (x < 0) result = -result;
}
return result;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::BesselK1(Double_t x)
{
// Compute the modified Bessel function K_1(x) for positive real x.
//
// M.Abramowitz and I.A.Stegun, Handbook of Mathematical Functions,
// Applied Mathematics Series vol. 55 (1964), Washington.
//
//--- NvE 12-mar-2000 UU-SAP Utrecht
// Parameters of the polynomial approximation
const Double_t p1= 1., p2= 0.15443144, p3=-0.67278579,
p4=-0.18156897, p5=-1.919402e-2, p6=-1.10404e-3, p7=-4.686e-5;
const Double_t q1= 1.25331414, q2= 0.23498619, q3=-3.655620e-2,
q4= 1.504268e-2, q5=-7.80353e-3, q6= 3.25614e-3, q7=-6.8245e-4;
if (x <= 0) {
Error("TMath::BesselK1", "*K1* Invalid argument x = %g\n",x);
return 0;
}
Double_t y=0,result=0;
if (x <= 2) {
y = x*x/4;
result = (log(x/2.)*TMath::BesselI1(x))+(1./x)*(p1+y*(p2+y*(p3+y*(p4+y*(p5+y*(p6+y*p7))))));
} else {
y = 2/x;
result = (exp(-x)/sqrt(x))*(q1+y*(q2+y*(q3+y*(q4+y*(q5+y*(q6+y*q7))))));
}
return result;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::BesselK(Int_t n,Double_t x)
{
// Compute the Integer Order Modified Bessel function K_n(x)
// for n=0,1,2,... and positive real x.
//
//--- NvE 12-mar-2000 UU-SAP Utrecht
if (x <= 0 || n < 0) {
Error("TMath::BesselK", "*K* Invalid argument(s) (n,x) = (%d, %g)\n",n,x);
return 0;
}
if (n==0) return TMath::BesselK0(x);
if (n==1) return TMath::BesselK1(x);
// Perform upward recurrence for all x
Double_t tox = 2/x;
Double_t bkm = TMath::BesselK0(x);
Double_t bk = TMath::BesselK1(x);
Double_t bkp = 0;
for (Int_t j=1; j<n; j++) {
bkp = bkm+Double_t(j)*tox*bk;
bkm = bk;
bk = bkp;
}
return bk;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::BesselI(Int_t n,Double_t x)
{
// Compute the Integer Order Modified Bessel function I_n(x)
// for n=0,1,2,... and any real x.
//
//--- NvE 12-mar-2000 UU-SAP Utrecht
Int_t iacc = 40; // Increase to enhance accuracy
const Double_t kBigPositive = 1.e10;
const Double_t kBigNegative = 1.e-10;
if (n < 0) {
Error("TMath::BesselI", "*I* Invalid argument (n,x) = (%d, %g)\n",n,x);
return 0;
}
if (n==0) return TMath::BesselI0(x);
if (n==1) return TMath::BesselI1(x);
if (x == 0) return 0;
if (TMath::Abs(x) > kBigPositive) return 0;
Double_t tox = 2/TMath::Abs(x);
Double_t bip = 0, bim = 0;
Double_t bi = 1;
Double_t result = 0;
Int_t m = 2*((n+Int_t(sqrt(Float_t(iacc*n)))));
for (Int_t j=m; j>=1; j--) {
bim = bip+Double_t(j)*tox*bi;
bip = bi;
bi = bim;
// Renormalise to prevent overflows
if (TMath::Abs(bi) > kBigPositive) {
result *= kBigNegative;
bi *= kBigNegative;
bip *= kBigNegative;
}
if (j==n) result=bip;
}
result *= TMath::BesselI0(x)/bi; // Normalise with BesselI0(x)
if ((x < 0) && (n%2 == 1)) result = -result;
return result;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::BesselJ0(Double_t x)
{
// Returns the Bessel function J0(x) for any real x.
Double_t ax,z;
Double_t xx,y,result,result1,result2;
const Double_t p1 = 57568490574.0, p2 = -13362590354.0, p3 = 651619640.7;
const Double_t p4 = -11214424.18, p5 = 77392.33017, p6 = -184.9052456;
const Double_t p7 = 57568490411.0, p8 = 1029532985.0, p9 = 9494680.718;
const Double_t p10 = 59272.64853, p11 = 267.8532712;
const Double_t q1 = 0.785398164;
const Double_t q2 = -0.1098628627e-2, q3 = 0.2734510407e-4;
const Double_t q4 = -0.2073370639e-5, q5 = 0.2093887211e-6;
const Double_t q6 = -0.1562499995e-1, q7 = 0.1430488765e-3;
const Double_t q8 = -0.6911147651e-5, q9 = 0.7621095161e-6;
const Double_t q10 = 0.934935152e-7, q11 = 0.636619772;
if ((ax=fabs(x)) < 8) {
y=x*x;
result1 = p1 + y*(p2 + y*(p3 + y*(p4 + y*(p5 + y*p6))));
result2 = p7 + y*(p8 + y*(p9 + y*(p10 + y*(p11 + y))));
result = result1/result2;
} else {
z = 8/ax;
y = z*z;
xx = ax-q1;
result1 = 1 + y*(q2 + y*(q3 + y*(q4 + y*q5)));
result2 = q6 + y*(q7 + y*(q8 + y*(q9 - y*q10)));
result = sqrt(q11/ax)*(cos(xx)*result1-z*sin(xx)*result2);
}
return result;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::BesselJ1(Double_t x)
{
// Returns the Bessel function J1(x) for any real x.
Double_t ax,z;
Double_t xx,y,result,result1,result2;
const Double_t p1 = 72362614232.0, p2 = -7895059235.0, p3 = 242396853.1;
const Double_t p4 = -2972611.439, p5 = 15704.48260, p6 = -30.16036606;
const Double_t p7 = 144725228442.0, p8 = 2300535178.0, p9 = 18583304.74;
const Double_t p10 = 99447.43394, p11 = 376.9991397;
const Double_t q1 = 2.356194491;
const Double_t q2 = 0.183105e-2, q3 = -0.3516396496e-4;
const Double_t q4 = 0.2457520174e-5, q5 = -0.240337019e-6;
const Double_t q6 = 0.04687499995, q7 = -0.2002690873e-3;
const Double_t q8 = 0.8449199096e-5, q9 = -0.88228987e-6;
const Double_t q10 = 0.105787412e-6, q11 = 0.636619772;
if ((ax=fabs(x)) < 8) {
y=x*x;
result1 = x*(p1 + y*(p2 + y*(p3 + y*(p4 + y*(p5 + y*p6)))));
result2 = p7 + y*(p8 + y*(p9 + y*(p10 + y*(p11 + y))));
result = result1/result2;
} else {
z = 8/ax;
y = z*z;
xx = ax-q1;
result1 = 1 + y*(q2 + y*(q3 + y*(q4 + y*q5)));
result2 = q6 + y*(q7 + y*(q8 + y*(q9 + y*q10)));
result = sqrt(q11/ax)*(cos(xx)*result1-z*sin(xx)*result2);
if (x < 0) result = -result;
}
return result;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::BesselY0(Double_t x)
{
// Returns the Bessel function Y0(x) for positive x.
Double_t z,xx,y,result,result1,result2;
const Double_t p1 = -2957821389., p2 = 7062834065.0, p3 = -512359803.6;
const Double_t p4 = 10879881.29, p5 = -86327.92757, p6 = 228.4622733;
const Double_t p7 = 40076544269., p8 = 745249964.8, p9 = 7189466.438;
const Double_t p10 = 47447.26470, p11 = 226.1030244, p12 = 0.636619772;
const Double_t q1 = 0.785398164;
const Double_t q2 = -0.1098628627e-2, q3 = 0.2734510407e-4;
const Double_t q4 = -0.2073370639e-5, q5 = 0.2093887211e-6;
const Double_t q6 = -0.1562499995e-1, q7 = 0.1430488765e-3;
const Double_t q8 = -0.6911147651e-5, q9 = 0.7621095161e-6;
const Double_t q10 = -0.934945152e-7, q11 = 0.636619772;
if (x < 8) {
y = x*x;
result1 = p1 + y*(p2 + y*(p3 + y*(p4 + y*(p5 + y*p6))));
result2 = p7 + y*(p8 + y*(p9 + y*(p10 + y*(p11 + y))));
result = (result1/result2) + p12*TMath::BesselJ0(x)*log(x);
} else {
z = 8/x;
y = z*z;
xx = x-q1;
result1 = 1 + y*(q2 + y*(q3 + y*(q4 + y*q5)));
result2 = q6 + y*(q7 + y*(q8 + y*(q9 + y*q10)));
result = sqrt(q11/x)*(sin(xx)*result1+z*cos(xx)*result2);
}
return result;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::BesselY1(Double_t x)
{
// Returns the Bessel function Y1(x) for positive x.
Double_t z,xx,y,result,result1,result2;
const Double_t p1 = -0.4900604943e13, p2 = 0.1275274390e13;
const Double_t p3 = -0.5153438139e11, p4 = 0.7349264551e9;
const Double_t p5 = -0.4237922726e7, p6 = 0.8511937935e4;
const Double_t p7 = 0.2499580570e14, p8 = 0.4244419664e12;
const Double_t p9 = 0.3733650367e10, p10 = 0.2245904002e8;
const Double_t p11 = 0.1020426050e6, p12 = 0.3549632885e3;
const Double_t p13 = 0.636619772;
const Double_t q1 = 2.356194491;
const Double_t q2 = 0.183105e-2, q3 = -0.3516396496e-4;
const Double_t q4 = 0.2457520174e-5, q5 = -0.240337019e-6;
const Double_t q6 = 0.04687499995, q7 = -0.2002690873e-3;
const Double_t q8 = 0.8449199096e-5, q9 = -0.88228987e-6;
const Double_t q10 = 0.105787412e-6, q11 = 0.636619772;
if (x < 8) {
y=x*x;
result1 = x*(p1 + y*(p2 + y*(p3 + y*(p4 + y*(p5 + y*p6)))));
result2 = p7 + y*(p8 + y*(p9 + y*(p10 + y*(p11 + y*(p12+y)))));
result = (result1/result2) + p13*(TMath::BesselJ1(x)*log(x)-1/x);
} else {
z = 8/x;
y = z*z;
xx = x-q1;
result1 = 1 + y*(q2 + y*(q3 + y*(q4 + y*q5)));
result2 = q6 + y*(q7 + y*(q8 + y*(q9 + y*q10)));
result = sqrt(q11/x)*(sin(xx)*result1+z*cos(xx)*result2);
}
return result;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::StruveH0(Double_t x)
{
// Struve Functions of Order 0
//
// Converted from CERNLIB M342 by Rene Brun.
const Int_t n1 = 15;
const Int_t n2 = 25;
const Double_t c1[16] = { 1.00215845609911981, -1.63969292681309147,
1.50236939618292819, -.72485115302121872,
.18955327371093136, -.03067052022988,
.00337561447375194, -2.6965014312602e-4,
1.637461692612e-5, -7.8244408508e-7,
3.021593188e-8, -9.6326645e-10,
2.579337e-11, -5.8854e-13,
1.158e-14, -2e-16 };
const Double_t c2[26] = { .99283727576423943, -.00696891281138625,
1.8205103787037e-4, -1.063258252844e-5,
9.8198294287e-7, -1.2250645445e-7,
1.894083312e-8, -3.44358226e-9,
7.1119102e-10, -1.6288744e-10,
4.065681e-11, -1.091505e-11,
3.12005e-12, -9.4202e-13,
2.9848e-13, -9.872e-14,
3.394e-14, -1.208e-14,
4.44e-15, -1.68e-15,
6.5e-16, -2.6e-16,
1.1e-16, -4e-17,
2e-17, -1e-17 };
const Double_t c0 = 2/TMath::Pi();
Int_t i;
Double_t alfa, h, r, y, b0, b1, b2;
Double_t v = TMath::Abs(x);
v = TMath::Abs(x);
if (v < 8) {
y = v/8;
h = 2*y*y -1;
alfa = h + h;
b0 = 0;
b1 = 0;
b2 = 0;
for (i = n1; i >= 0; --i) {
b0 = c1[i] + alfa*b1 - b2;
b2 = b1;
b1 = b0;
}
h = y*(b0 - h*b2);
} else {
r = 1/v;
h = 128*r*r -1;
alfa = h + h;
b0 = 0;
b1 = 0;
b2 = 0;
for (i = n2; i >= 0; --i) {
b0 = c2[i] + alfa*b1 - b2;
b2 = b1;
b1 = b0;
}
h = TMath::BesselY0(v) + r*c0*(b0 - h*b2);
}
if (x < 0) h = -h;
return h;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::StruveH1(Double_t x)
{
// Struve Functions of Order 1
//
// Converted from CERNLIB M342 by Rene Brun.
const Int_t n3 = 16;
const Int_t n4 = 22;
const Double_t c3[17] = { .5578891446481605, -.11188325726569816,
-.16337958125200939, .32256932072405902,
-.14581632367244242, .03292677399374035,
-.00460372142093573, 4.434706163314e-4,
-3.142099529341e-5, 1.7123719938e-6,
-7.416987005e-8, 2.61837671e-9,
-7.685839e-11, 1.9067e-12,
-4.052e-14, 7.5e-16,
-1e-17 };
const Double_t c4[23] = { 1.00757647293865641, .00750316051248257,
-7.043933264519e-5, 2.66205393382e-6,
-1.8841157753e-7, 1.949014958e-8,
-2.6126199e-9, 4.236269e-10,
-7.955156e-11, 1.679973e-11,
-3.9072e-12, 9.8543e-13,
-2.6636e-13, 7.645e-14,
-2.313e-14, 7.33e-15,
-2.42e-15, 8.3e-16,
-3e-16, 1.1e-16,
-4e-17, 2e-17,-1e-17 };
const Double_t c0 = 2/TMath::Pi();
const Double_t cc = 2/(3*TMath::Pi());
Int_t i, i1;
Double_t alfa, h, r, y, b0, b1, b2;
Double_t v = TMath::Abs(x);
if (v == 0) {
h = 0;
} else if (v <= 0.3) {
y = v*v;
r = 1;
h = 1;
i1 = (Int_t)(-8. / TMath::Log10(v));
for (i = 1; i <= i1; ++i) {
h = -h*y / ((2*i+ 1)*(2*i + 3));
r += h;
}
h = cc*y*r;
} else if (v < 8) {
h = v*v/32 -1;
alfa = h + h;
b0 = 0;
b1 = 0;
b2 = 0;
for (i = n3; i >= 0; --i) {
b0 = c3[i] + alfa*b1 - b2;
b2 = b1;
b1 = b0;
}
h = b0 - h*b2;
} else {
h = 128/(v*v) -1;
alfa = h + h;
b0 = 0;
b1 = 0;
b2 = 0;
for (i = n4; i >= 0; --i) {
b0 = c4[i] + alfa*b1 - b2;
b2 = b1;
b1 = b0;
}
h = TMath::BesselY1(v) + c0*(b0 - h*b2);
}
return h;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::StruveL0(Double_t x)
{
// Modified Struve Function of Order 0.
// By Kirill Filimonov.
const Double_t pi=TMath::Pi();
Double_t s=1.0;
Double_t r=1.0;
Double_t a0,sl0,a1,bi0;
Int_t km,i;
if (x<=20.) {
a0=2.0*x/pi;
for (int i=1; i<=60;i++) {
r*=(x/(2*i+1))*(x/(2*i+1));
s+=r;
if(TMath::Abs(r/s)<1.e-12) break;
}
sl0=a0*s;
} else {
km=int(5*(x+1.0));
if(x>=50.0)km=25;
for (i=1; i<=km; i++) {
r*=(2*i-1)*(2*i-1)/x/x;
s+=r;
if(TMath::Abs(r/s)<1.0e-12) break;
}
a1=TMath::Exp(x)/TMath::Sqrt(2*pi*x);
r=1.0;
bi0=1.0;
for (i=1; i<=16; i++) {
r=0.125*r*(2.0*i-1.0)*(2.0*i-1.0)/(i*x);
bi0+=r;
if(TMath::Abs(r/bi0)<1.0e-12) break;
}
bi0=a1*bi0;
sl0=-2.0/(pi*x)*s+bi0;
}
return sl0;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::StruveL1(Double_t x)
{
// Modified Struve Function of Order 1.
// By Kirill Filimonov.
const Double_t pi=TMath::Pi();
Double_t a1,sl1,bi1,s;
Double_t r=1.0;
Int_t km,i;
if (x<=20.) {
s=0.0;
for (i=1; i<=60;i++) {
r*=x*x/(4.0*i*i-1.0);
s+=r;
if(TMath::Abs(r)<TMath::Abs(s)*1.e-12) break;
}
sl1=2.0/pi*s;
} else {
s=1.0;
km=int(0.5*x);
if(x>50.0)km=25;
for (i=1; i<=km; i++) {
r*=(2*i+3)*(2*i+1)/x/x;
s+=r;
if(TMath::Abs(r/s)<1.0e-12) break;
}
sl1=2.0/pi*(-1.0+1.0/(x*x)+3.0*s/(x*x*x*x));
a1=TMath::Exp(x)/TMath::Sqrt(2*pi*x);
r=1.0;
bi1=1.0;
for (i=1; i<=16; i++) {
r=-0.125*r*(4.0-(2.0*i-1.0)*(2.0*i-1.0))/(i*x);
bi1+=r;
if(TMath::Abs(r/bi1)<1.0e-12) break;
}
sl1+=a1*bi1;
}
return sl1;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::Beta(Double_t p, Double_t q)
{
// Calculates Beta-function Gamma(p)*Gamma(q)/Gamma(p+q).
return TMath::Exp(TMath::LnGamma(p)+TMath::LnGamma(q)-TMath::LnGamma(p+q));
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::BetaCf(Double_t x, Double_t a, Double_t b)
{
// Continued fraction evaluation by modified Lentz's method
// used in calculation of incomplete Beta function.
Int_t itmax = 500;
Double_t eps = 3.e-14;
Double_t fpmin = 1.e-30;
Int_t m, m2;
Double_t aa, c, d, del, qab, qam, qap;
Double_t h;
qab = a+b;
qap = a+1.0;
qam = a-1.0;
c = 1.0;
d = 1.0 - qab*x/qap;
if (TMath::Abs(d)<fpmin) d=fpmin;
d=1.0/d;
h=d;
for (m=1; m<=itmax; m++) {
m2=m*2;
aa = m*(b-m)*x/((qam+ m2)*(a+m2));
d = 1.0 +aa*d;
if(TMath::Abs(d)<fpmin) d = fpmin;
c = 1 +aa/c;
if (TMath::Abs(c)<fpmin) c = fpmin;
d=1.0/d;
h*=d*c;
aa = -(a+m)*(qab +m)*x/((a+m2)*(qap+m2));
d=1.0+aa*d;
if(TMath::Abs(d)<fpmin) d = fpmin;
c = 1.0 +aa/c;
if (TMath::Abs(c)<fpmin) c = fpmin;
d=1.0/d;
del = d*c;
h*=del;
if (TMath::Abs(del-1)<=eps) break;
}
if (m>itmax) {
Info("TMath::BetaCf", "a or b too big, or itmax too small, a=%g, b=%g, x=%g, h=%g, itmax=%d",
a,b,x,h,itmax);
}
return h;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::BetaDist(Double_t x, Double_t p, Double_t q)
{
// Computes the probability density function of the Beta distribution
// (the distribution function is computed in BetaDistI).
// The first argument is the point, where the function will be
// computed, second and third are the function parameters.
// Since the Beta distribution is bounded on both sides, it's often
// used to represent processes with natural lower and upper limits.
if ((x<0) || (x>1) || (p<=0) || (q<=0)){
Error("TMath::BetaDist", "parameter value outside allowed range");
return 0;
}
Double_t beta = TMath::Beta(p, q);
Double_t r = TMath::Power(x, p-1)*TMath::Power(1-x, q-1)/beta;
return r;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::BetaDistI(Double_t x, Double_t p, Double_t q)
{
// Computes the distribution function of the Beta distribution.
// The first argument is the point, where the function will be
// computed, second and third are the function parameters.
// Since the Beta distribution is bounded on both sides, it's often
// used to represent processes with natural lower and upper limits.
if ((x<0) || (x>1) || (p<=0) || (q<=0)){
Error("TMath::BetaDistI", "parameter value outside allowed range");
return 0;
}
Double_t betai = TMath::BetaIncomplete(x, p, q);
return betai;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::BetaIncomplete(Double_t x, Double_t a, Double_t b)
{
// Calculates the incomplete Beta-function.
// -- implementation by Anna Kreshuk
Double_t bt;
if ((x<0.0)||(x>1.0)) {
Error("TMath::BetaIncomplete", "X must between 0 and 1");
return 0.0;
}
if ((x==0.0)||(x==1.0)) {
bt=0.0;
} else {
bt = TMath::Power(x, a)*TMath::Power(1-x, b)/Beta(a, b);
}
if (x<(a+1)/(a+b+2)) {
return bt*BetaCf(x, a, b)/a;
}
else {
return (1 - bt*BetaCf(1-x, b, a)/b);
}
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::Binomial(Int_t n,Int_t k)
{
// Calculate the binomial coefficient n over k.
if (k==0 || n==k) return 1;
if (n<=0 || k<0 || n<k) return 0;
Int_t k1=TMath::Min(k,n-k);
Int_t k2=n-k1;
Double_t fact=k2+1;
for (Int_t i=k1;i>1;i--)
fact*=static_cast<Double_t>(k2+i)/i;
return fact;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::BinomialI(Double_t p, Int_t n, Int_t k)
{
// Suppose an event occurs with probability _p_ per trial
// Then the probability P of its occuring _k_ or more times
// in _n_ trials is termed a cumulative binomial probability
// the formula is P = sum_from_j=k_to_n(TMath::Binomial(n, j)*
// *TMath::Power(p, j)*TMath::Power(1-p, n-j)
// For _n_ larger than 12 BetaIncomplete is a much better way
// to evaluate the sum than would be the straightforward sum calculation
// for _n_ smaller than 12 either method is acceptable
// ("Numerical Recipes")
// --implementation by Anna Kreshuk
return BetaIncomplete(p, Double_t(k), Double_t(n-k+1));
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::CauchyDist(Double_t x, Double_t t, Double_t s)
{
// Computes the density of Cauchy distribution at point x
// by default, standard Cauchy distribution is used (t=0, s=1)
// t is the location parameter
// s is the scale parameter
// The Cauchy distribution, also called Lorentzian distribution,
// is a continuous distribution describing resonance behavior
// The mean and standard deviation of the Cauchy distribution are undefined.
// The practical meaning of this is that collecting 1,000 data points gives
// no more accurate an estimate of the mean and standard deviation than
// does a single point.
// The formula was taken from "Engineering Statistics Handbook" on site
// http://www.itl.nist.gov/div898/handbook/eda/section3/eda3663.htm
// Implementation by Anna Kreshuk.
// Example:
// TF1* fc = new TF1("fc", "TMath::CauchyDist(x, [0], [1])", -5, 5);
// fc->SetParameters(0, 1);
// fc->Draw();
Double_t temp= (x-t)*(x-t)/(s*s);
Double_t result = 1/(s*TMath::Pi()*(1+temp));
return result;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::ChisquareQuantile(Double_t p, Double_t ndf)
{
// Evaluate the quantiles of the chi-squared probability distribution function.
// Algorithm AS 91 Appl. Statist. (1975) Vol.24, P.35
// implemented by Anna Kreshuk.
// Incorporates the suggested changes in AS R85 (vol.40(1), pp.233-5, 1991)
// Parameters:
// p - the probability value, at which the quantile is computed
// ndf - number of degrees of freedom
Double_t c[]={0, 0.01, 0.222222, 0.32, 0.4, 1.24, 2.2,
4.67, 6.66, 6.73, 13.32, 60.0, 70.0,
84.0, 105.0, 120.0, 127.0, 140.0, 175.0,
210.0, 252.0, 264.0, 294.0, 346.0, 420.0,
462.0, 606.0, 672.0, 707.0, 735.0, 889.0,
932.0, 966.0, 1141.0, 1182.0, 1278.0, 1740.0,
2520.0, 5040.0};
Double_t e = 5e-7;
Double_t aa = 0.6931471806;
Int_t maxit = 20;
Double_t ch, p1, p2, q, t, a, b, x;
Double_t s1, s2, s3, s4, s5, s6;
if (ndf <= 0) return 0;
Double_t g = TMath::LnGamma(0.5*ndf);
Double_t xx = 0.5 * ndf;
Double_t cp = xx - 1;
if (ndf >= TMath::Log(p)*(-c[5])){
//starting approximation for ndf less than or equal to 0.32
if (ndf > c[3]) {
x = TMath::NormQuantile(p);
//starting approximation using Wilson and Hilferty estimate
p1=c[2]/ndf;
ch = ndf*TMath::Power((x*TMath::Sqrt(p1) + 1 - p1), 3);
if (ch > c[6]*ndf + 6)
ch = -2 * (TMath::Log(1-p) - cp * TMath::Log(0.5 * ch) + g);
} else {
ch = c[4];
a = TMath::Log(1-p);
do{
q = ch;
p1 = 1 + ch * (c[7]+ch);
p2 = ch * (c[9] + ch * (c[8] + ch));
t = -0.5 + (c[7] + 2 * ch) / p1 - (c[9] + ch * (c[10] + 3 * ch)) / p2;
ch = ch - (1 - TMath::Exp(a + g + 0.5 * ch + cp * aa) *p2 / p1) / t;
}while (TMath::Abs(q/ch - 1) > c[1]);
}
} else {
ch = TMath::Power((p * xx * TMath::Exp(g + xx * aa)),(1./xx));
if (ch < e) return ch;
}
//call to algorithm AS 239 and calculation of seven term Taylor series
for (Int_t i=0; i<maxit; i++){
q = ch;
p1 = 0.5 * ch;
p2 = p - TMath::Gamma(xx, p1);
t = p2 * TMath::Exp(xx * aa + g + p1 - cp * TMath::Log(ch));
b = t / ch;
a = 0.5 * t - b * cp;
s1 = (c[19] + a * (c[17] + a * (c[14] + a * (c[13] + a * (c[12] +c[11] * a))))) / c[24];
s2 = (c[24] + a * (c[29] + a * (c[32] + a * (c[33] + c[35] * a)))) / c[37];
s3 = (c[19] + a * (c[25] + a * (c[28] + c[31] * a))) / c[37];
s4 = (c[20] + a * (c[27] + c[34] * a) + cp * (c[22] + a * (c[30] + c[36] * a))) / c[38];
s5 = (c[13] + c[21] * a + cp * (c[18] + c[26] * a)) / c[37];
s6 = (c[15] + cp * (c[23] + c[16] * cp)) / c[38];
ch = ch + t * (1 + 0.5 * t * s1 - b * cp * (s1 - b * (s2 - b * (s3 - b * (s4 - b * (s5 - b * s6))))));
if (TMath::Abs(q / ch - 1) > e) break;
}
return ch;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::FDist(Double_t F, Double_t N, Double_t M)
{
// Computes the density function of F-distribution
// (probability function, integral of density, is computed in FDistI).
//
// Parameters N and M stand for degrees of freedom of chi-squares
// mentioned above parameter F is the actual variable x of the
// density function p(x) and the point at which the density function
// is calculated.
//
// About F distribution:
// F-distribution arises in testing whether two random samples
// have the same variance. It is the ratio of two chi-square
// distributions, with N and M degrees of freedom respectively,
// where each chi-square is first divided by it's number of degrees
// of freedom.
// Implementation by Anna Kreshuk.
if ((F<0)||(N<1)||(M<1)){
return 0;
} else {
Double_t denom = TMath::Gamma(N/2)*TMath::Gamma(M/2)*TMath::Power(M+N*F, (N+M)/2);
Double_t div = TMath::Gamma((N+M)/2)*TMath::Power(N, N/2)*TMath::Power(M, M/2)*TMath::Power(F, 0.5*N-1);
return div/denom;
}
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::FDistI(Double_t F, Double_t N, Double_t M)
{
// Calculates the cumulative distribution function of F-distribution,
// this function occurs in the statistical test of whether two observed
// samples have the same variance. For this test a certain statistic F,
// the ratio of observed dispersion of the first sample to that of the
// second sample, is calculated. N and M stand for numbers of degrees
// of freedom in the samples 1-FDistI() is the significance level at
// which the hypothesis "1 has smaller variance than 2" can be rejected.
// A small numerical value of 1 - FDistI() implies a very significant
// rejection, in turn implying high confidence in the hypothesis
// "1 has variance greater than 2".
// Implementation by Anna Kreshuk.
Double_t fi = 1 - BetaIncomplete((M/(M+N*F)), M*0.5, N*0.5);
return fi;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::GammaDist(Double_t x, Double_t gamma, Double_t mu, Double_t beta)
{
// Computes the density function of Gamma distribution at point x.
// gamma - shape parameter
// mu - location parameter
// beta - scale parameter
// The formula was taken from "Engineering Statistics Handbook" on site
// http://www.itl.nist.gov/div898/handbook/eda/section3/eda366b.htm
// Implementation by Anna Kreshuk.
//
/*
 */
//
if ((x<mu) || (gamma<=0) || (beta <=0)) {
Error("TMath::GammaDist", "illegal parameter values");
return 0;
}
Double_t temp = (x-mu)/beta;
Double_t temp2 = beta * TMath::Gamma(gamma);
Double_t result = (TMath::Power(temp, gamma-1) * TMath::Exp(-temp))/temp2;
return result;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::LaplaceDist(Double_t x, Double_t alpha, Double_t beta)
{
// Computes the probability density funciton of Laplace distribution
// at point x, with location parameter alpha and shape parameter beta.
// By default, alpha=0, beta=1
// This distribution is known under different names, most common is
// double exponential distribution, but it also appears as
// the two-tailed exponential or the bilateral exponential distribution
Double_t temp;
temp = TMath::Exp(-TMath::Abs((x-alpha)/beta));
temp /= (2.*beta);
return temp;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::LaplaceDistI(Double_t x, Double_t alpha, Double_t beta)
{
// Computes the distribution funciton of Laplace distribution
// at point x, with location parameter alpha and shape parameter beta.
// By default, alpha=0, beta=1
// This distribution is known under different names, most common is
// double exponential distribution, but it also appears as
// the two-tailed exponential or the bilateral exponential distribution
Double_t temp;
if (x<=alpha){
temp = 0.5*TMath::Exp(-TMath::Abs((x-alpha)/beta));
} else {
temp = 1-0.5*TMath::Exp(-TMath::Abs((x-alpha)/beta));
}
return temp;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::LogNormal(Double_t x, Double_t sigma, Double_t theta, Double_t m)
{
// Computes the density of LogNormal distribution at point x.
// Variable X has lognormal distribution if Y=Ln(X) has normal distribution
// sigma is the shape parameter
// theta is the location parameter
// m is the scale parameter
// The formula was taken from "Engineering Statistics Handbook" on site
// http://www.itl.nist.gov/div898/handbook/eda/section3/eda3669.htm
// Implementation by Anna Kreshuk.
//
/*
*/
//
if ((x<mu) || (gamma<=0) || (beta <=0)) {
Error("TMath::GammaDist", "illegal parameter values");
return 0;
}
Double_t temp = (x-mu)/beta;
Double_t temp2 = beta * TMath::Gamma(gamma);
Double_t result = (TMath::Power(temp, gamma-1) * TMath::Exp(-temp))/temp2;
return result;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::LaplaceDist(Double_t x, Double_t alpha, Double_t beta)
{
// Computes the probability density funciton of Laplace distribution
// at point x, with location parameter alpha and shape parameter beta.
// By default, alpha=0, beta=1
// This distribution is known under different names, most common is
// double exponential distribution, but it also appears as
// the two-tailed exponential or the bilateral exponential distribution
Double_t temp;
temp = TMath::Exp(-TMath::Abs((x-alpha)/beta));
temp /= (2.*beta);
return temp;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::LaplaceDistI(Double_t x, Double_t alpha, Double_t beta)
{
// Computes the distribution funciton of Laplace distribution
// at point x, with location parameter alpha and shape parameter beta.
// By default, alpha=0, beta=1
// This distribution is known under different names, most common is
// double exponential distribution, but it also appears as
// the two-tailed exponential or the bilateral exponential distribution
Double_t temp;
if (x<=alpha){
temp = 0.5*TMath::Exp(-TMath::Abs((x-alpha)/beta));
} else {
temp = 1-0.5*TMath::Exp(-TMath::Abs((x-alpha)/beta));
}
return temp;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::LogNormal(Double_t x, Double_t sigma, Double_t theta, Double_t m)
{
// Computes the density of LogNormal distribution at point x.
// Variable X has lognormal distribution if Y=Ln(X) has normal distribution
// sigma is the shape parameter
// theta is the location parameter
// m is the scale parameter
// The formula was taken from "Engineering Statistics Handbook" on site
// http://www.itl.nist.gov/div898/handbook/eda/section3/eda3669.htm
// Implementation by Anna Kreshuk.
//
/*
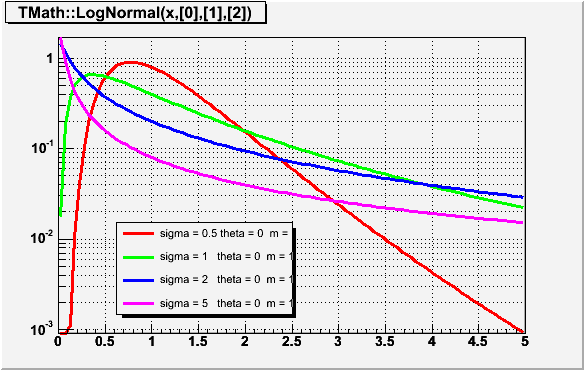 */
//
if ((x<theta) || (sigma<=0) || (m<=0)) {
Error("TMath::Lognormal", "illegal parameter values");
return 0;
}
Double_t templog2 = TMath::Log((x-theta)/m)*TMath::Log((x-theta)/m);
Double_t temp1 = TMath::Exp(-templog2/(2*sigma*sigma));
Double_t temp2 = (x-theta)*sigma*TMath::Sqrt(2*TMath::Pi());
return temp1/temp2;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::NormQuantile(Double_t p)
{
// Computes quantiles for standard normal distribution N(0, 1)
// at probability p
// ALGORITHM AS241 APPL. STATIST. (1988) VOL. 37, NO. 3, 477-484.
if ((p<=0)||(p>=1)) {
Error("TMath::NormQuantile", "probability outside (0, 1)");
return 0;
}
Double_t a0 = 3.3871328727963666080e0;
Double_t a1 = 1.3314166789178437745e+2;
Double_t a2 = 1.9715909503065514427e+3;
Double_t a3 = 1.3731693765509461125e+4;
Double_t a4 = 4.5921953931549871457e+4;
Double_t a5 = 6.7265770927008700853e+4;
Double_t a6 = 3.3430575583588128105e+4;
Double_t a7 = 2.5090809287301226727e+3;
Double_t b1 = 4.2313330701600911252e+1;
Double_t b2 = 6.8718700749205790830e+2;
Double_t b3 = 5.3941960214247511077e+3;
Double_t b4 = 2.1213794301586595867e+4;
Double_t b5 = 3.9307895800092710610e+4;
Double_t b6 = 2.8729085735721942674e+4;
Double_t b7 = 5.2264952788528545610e+3;
Double_t c0 = 1.42343711074968357734e0;
Double_t c1 = 4.63033784615654529590e0;
Double_t c2 = 5.76949722146069140550e0;
Double_t c3 = 3.64784832476320460504e0;
Double_t c4 = 1.27045825245236838258e0;
Double_t c5 = 2.41780725177450611770e-1;
Double_t c6 = 2.27238449892691845833e-2;
Double_t c7 = 7.74545014278341407640e-4;
Double_t d1 = 2.05319162663775882187e0;
Double_t d2 = 1.67638483018380384940e0;
Double_t d3 = 6.89767334985100004550e-1;
Double_t d4 = 1.48103976427480074590e-1;
Double_t d5 = 1.51986665636164571966e-2;
Double_t d6 = 5.47593808499534494600e-4;
Double_t d7 = 1.05075007164441684324e-9;
Double_t e0 = 6.65790464350110377720e0;
Double_t e1 = 5.46378491116411436990e0;
Double_t e2 = 1.78482653991729133580e0;
Double_t e3 = 2.96560571828504891230e-1;
Double_t e4 = 2.65321895265761230930e-2;
Double_t e5 = 1.24266094738807843860e-3;
Double_t e6 = 2.71155556874348757815e-5;
Double_t e7 = 2.01033439929228813265e-7;
Double_t f1 = 5.99832206555887937690e-1;
Double_t f2 = 1.36929880922735805310e-1;
Double_t f3 = 1.48753612908506148525e-2;
Double_t f4 = 7.86869131145613259100e-4;
Double_t f5 = 1.84631831751005468180e-5;
Double_t f6 = 1.42151175831644588870e-7;
Double_t f7 = 2.04426310338993978564e-15;
Double_t split1 = 0.425;
Double_t split2=5.;
Double_t konst1=0.180625;
Double_t konst2=1.6;
Double_t q, r, quantile;
q=p-0.5;
if (TMath::Abs(q)<split1) {
r=konst1-q*q;
quantile = q* (((((((a7 * r + a6) * r + a5) * r + a4) * r + a3)
* r + a2) * r + a1) * r + a0) /
(((((((b7 * r + b6) * r + b5) * r + b4) * r + b3)
* r + b2) * r + b1) * r + 1.);
} else {
if(q<0) r=p;
else r=1-p;
//error case
if (r<=0)
quantile=0;
else {
r=TMath::Sqrt(-TMath::Log(r));
if (r<=split2) {
r=r-konst2;
quantile=(((((((c7 * r + c6) * r + c5) * r + c4) * r + c3)
* r + c2) * r + c1) * r + c0) /
(((((((d7 * r + d6) * r + d5) * r + d4) * r + d3)
* r + d2) * r + d1) * r + 1);
} else{
r=r-split2;
quantile=(((((((e7 * r + e6) * r + e5) * r + e4) * r + e3)
* r + e2) * r + e1) * r + e0) /
(((((((f7 * r + f6) * r + f5) * r + f4) * r + f3)
* r + f2) * r + f1) * r + 1);
}
if (q<0) quantile=-quantile;
}
}
return quantile;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Bool_t TMath::Permute(Int_t n, Int_t *a)
{
// Simple recursive algorithm to find the permutations of
// n natural numbers, not necessarily all distinct
// adapted from CERNLIB routine PERMU.
// The input array has to be initialised with a non descending
// sequence. The method returns kFALSE when
// all combinations are exhausted.
Int_t i,itmp;
Int_t i1=-1;
// find rightmost upward transition
for(i=n-2; i>-1; i--) {
if(a[i]<a[i+1]) {
i1=i;
break;
}
}
// no more upward transitions, end of the story
if(i1==-1) return kFALSE;
else {
// find lower right element higher than the lower
// element of the upward transition
for(i=n-1;i>i1;i--) {
if(a[i] > a[i1]) {
// swap the two
itmp=a[i1];
a[i1]=a[i];
a[i]=itmp;
break;
}
}
// order the rest, in fact just invert, as there
// are only downward transitions from here on
for(i=0;i<(n-i1-1)/2;i++) {
itmp=a[i1+i+1];
a[i1+i+1]=a[n-i-1];
a[n-i-1]=itmp;
}
}
return kTRUE;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::Student(Double_t T, Double_t ndf)
{
// Computes density function for Student's t- distribution
// (the probability function (integral of density) is computed in StudentI).
//
// First parameter stands for x - the actual variable of the
// density function p(x) and the point at which the density is calculated.
// Second parameter stands for number of degrees of freedom.
//
// About Student distribution:
// Student's t-distribution is used for many significance tests, for example,
// for the Student's t-tests for the statistical significance of difference
// between two sample means and for confidence intervals for the difference
// between two population means.
//
// Example: suppose we have a random sample of size n drawn from normal
// distribution with mean Mu and st.deviation Sigma. Then the variable
//
// t = (sample_mean - Mu)/(sample_deviation / sqrt(n))
//
// has Student's t-distribution with n-1 degrees of freedom.
//
// NOTE that this function's second argument is number of degrees of freedom,
// not the sample size.
//
// As the number of degrees of freedom grows, t-distribution approaches
// Normal(0,1) distribution.
// Implementation by Anna Kreshuk.
if (ndf < 1) {
return 0;
}
Double_t r = ndf;
Double_t rh = 0.5*r;
Double_t rh1 = rh + 0.5;
Double_t denom = TMath::Sqrt(r*TMath::Pi())*TMath::Gamma(rh)*TMath::Power(1+T*T/r, rh1);
return TMath::Gamma(rh1)/denom;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::StudentI(Double_t T, Double_t ndf)
{
// Calculates the cumulative distribution function of Student's
// t-distribution second parameter stands for number of degrees of freedom,
// not for the number of samples
// if x has Student's t-distribution, the function returns the probability of
// x being less than T.
// Implementation by Anna Kreshuk.
Double_t r = ndf;
Double_t si = (T>0) ?
(1 - 0.5*BetaIncomplete((r/(r + T*T)), r*0.5, 0.5)) :
0.5*BetaIncomplete((r/(r + T*T)), r*0.5, 0.5);
return si;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::StudentQuantile(Double_t p, Double_t ndf, Bool_t lower_tail)
{
// Computes quantiles of the Student's t-distribution
// 1st argument is the probability, at which the quantile is computed
// 2nd argument - the number of degrees of freedom of the
// Student distribution
// When the 3rd argument lower_tail is kTRUE (default)-
// the algorithm returns such x0, that
// P(x < x0)=p
// upper tail (lower_tail is kFALSE)- the algorithm returns such x0, that
// P(x > x0)=p
// the algorithm was taken from
// G.W.Hill, "Algorithm 396, Student's t-quantiles"
// "Communications of the ACM", 13(10), October 1970
Double_t quantile;
Double_t temp;
Bool_t neg;
Double_t q;
if (ndf<1 || p>=1 || p<=0) {
Error("TMath::StudentQuantile", "illegal parameter values");
return 0;
}
if ((lower_tail && p>0.5)||(!lower_tail && p<0.5)){
neg=kFALSE;
q=2*(lower_tail ? (1-p) : p);
} else {
neg=kTRUE;
q=2*(lower_tail? p : (1-p));
}
if ((ndf-2)<1e-8) {
quantile = TMath::Sqrt(2./(q*(2-q))-2);
} else {
if ((ndf-1)<1e-8) {
temp=TMath::PiOver2()*q;
quantile = TMath::Cos(temp)/TMath::Sin(temp);
} else {
Double_t a=1./(ndf-0.5);
Double_t b=48./(a*a);
Double_t c=((20700*a/b -98)*a-16)*a+96.36;
Double_t d=((94.5/(b+c)-3.)/b+1)*TMath::Sqrt(a*TMath::PiOver2())*ndf;
Double_t x=q*d;
Double_t y=TMath::Power(x, (2./ndf));
if (y>0.05+a){
//asymptotic inverse expansion about normal
x=NormQuantile(q*0.5);
y=x*x;
if (ndf<5) c+=0.3*(ndf-4.5)*(x+0.6);
c+=(((0.05*d*x-5.)*x-7.)*x-2.)*x +b;
y=(((((0.4*y+6.3)*y+36.)*y+94.5)/c - y-3.)/b+1)*x;
y=a*y*y;
if(y>0.002) y = TMath::Exp(y)-1;
else y += 0.5*y*y;
} else {
y=((1./(((ndf+6.)/(ndf*y)-0.089*d-0.822)*(ndf+2.)*3)+0.5/(ndf+4.))*y-1.)*
(ndf+1.)/(ndf+2.)+1/y;
}
quantile = TMath::Sqrt(ndf*y);
}
}
if(neg) quantile=-quantile;
return quantile;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::Vavilov(Double_t x, Double_t kappa, Double_t beta2)
{
//Returns the value of the Vavilov density function
//Parameters: 1st - the point were the density function is evaluated
// 2nd - value of kappa (distribution parameter)
// 3rd - value of beta2 (distribution parameter)
//The algorithm was taken from the CernLib function vavden(G115)
//Reference: A.Rotondi and P.Montagna, Fast Calculation of Vavilov distribution
//Nucl.Instr. and Meth. B47(1990), 215-224
//Accuracy: quote from the reference above:
//"The resuls of our code have been compared with the values of the Vavilov
//density function computed numerically in an accurate way: our approximation
//shows a difference of less than 3% around the peak of the density function, slowly
//increasing going towards the extreme tails to the right and to the left"
//
/*
*/
//
if ((x<theta) || (sigma<=0) || (m<=0)) {
Error("TMath::Lognormal", "illegal parameter values");
return 0;
}
Double_t templog2 = TMath::Log((x-theta)/m)*TMath::Log((x-theta)/m);
Double_t temp1 = TMath::Exp(-templog2/(2*sigma*sigma));
Double_t temp2 = (x-theta)*sigma*TMath::Sqrt(2*TMath::Pi());
return temp1/temp2;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::NormQuantile(Double_t p)
{
// Computes quantiles for standard normal distribution N(0, 1)
// at probability p
// ALGORITHM AS241 APPL. STATIST. (1988) VOL. 37, NO. 3, 477-484.
if ((p<=0)||(p>=1)) {
Error("TMath::NormQuantile", "probability outside (0, 1)");
return 0;
}
Double_t a0 = 3.3871328727963666080e0;
Double_t a1 = 1.3314166789178437745e+2;
Double_t a2 = 1.9715909503065514427e+3;
Double_t a3 = 1.3731693765509461125e+4;
Double_t a4 = 4.5921953931549871457e+4;
Double_t a5 = 6.7265770927008700853e+4;
Double_t a6 = 3.3430575583588128105e+4;
Double_t a7 = 2.5090809287301226727e+3;
Double_t b1 = 4.2313330701600911252e+1;
Double_t b2 = 6.8718700749205790830e+2;
Double_t b3 = 5.3941960214247511077e+3;
Double_t b4 = 2.1213794301586595867e+4;
Double_t b5 = 3.9307895800092710610e+4;
Double_t b6 = 2.8729085735721942674e+4;
Double_t b7 = 5.2264952788528545610e+3;
Double_t c0 = 1.42343711074968357734e0;
Double_t c1 = 4.63033784615654529590e0;
Double_t c2 = 5.76949722146069140550e0;
Double_t c3 = 3.64784832476320460504e0;
Double_t c4 = 1.27045825245236838258e0;
Double_t c5 = 2.41780725177450611770e-1;
Double_t c6 = 2.27238449892691845833e-2;
Double_t c7 = 7.74545014278341407640e-4;
Double_t d1 = 2.05319162663775882187e0;
Double_t d2 = 1.67638483018380384940e0;
Double_t d3 = 6.89767334985100004550e-1;
Double_t d4 = 1.48103976427480074590e-1;
Double_t d5 = 1.51986665636164571966e-2;
Double_t d6 = 5.47593808499534494600e-4;
Double_t d7 = 1.05075007164441684324e-9;
Double_t e0 = 6.65790464350110377720e0;
Double_t e1 = 5.46378491116411436990e0;
Double_t e2 = 1.78482653991729133580e0;
Double_t e3 = 2.96560571828504891230e-1;
Double_t e4 = 2.65321895265761230930e-2;
Double_t e5 = 1.24266094738807843860e-3;
Double_t e6 = 2.71155556874348757815e-5;
Double_t e7 = 2.01033439929228813265e-7;
Double_t f1 = 5.99832206555887937690e-1;
Double_t f2 = 1.36929880922735805310e-1;
Double_t f3 = 1.48753612908506148525e-2;
Double_t f4 = 7.86869131145613259100e-4;
Double_t f5 = 1.84631831751005468180e-5;
Double_t f6 = 1.42151175831644588870e-7;
Double_t f7 = 2.04426310338993978564e-15;
Double_t split1 = 0.425;
Double_t split2=5.;
Double_t konst1=0.180625;
Double_t konst2=1.6;
Double_t q, r, quantile;
q=p-0.5;
if (TMath::Abs(q)<split1) {
r=konst1-q*q;
quantile = q* (((((((a7 * r + a6) * r + a5) * r + a4) * r + a3)
* r + a2) * r + a1) * r + a0) /
(((((((b7 * r + b6) * r + b5) * r + b4) * r + b3)
* r + b2) * r + b1) * r + 1.);
} else {
if(q<0) r=p;
else r=1-p;
//error case
if (r<=0)
quantile=0;
else {
r=TMath::Sqrt(-TMath::Log(r));
if (r<=split2) {
r=r-konst2;
quantile=(((((((c7 * r + c6) * r + c5) * r + c4) * r + c3)
* r + c2) * r + c1) * r + c0) /
(((((((d7 * r + d6) * r + d5) * r + d4) * r + d3)
* r + d2) * r + d1) * r + 1);
} else{
r=r-split2;
quantile=(((((((e7 * r + e6) * r + e5) * r + e4) * r + e3)
* r + e2) * r + e1) * r + e0) /
(((((((f7 * r + f6) * r + f5) * r + f4) * r + f3)
* r + f2) * r + f1) * r + 1);
}
if (q<0) quantile=-quantile;
}
}
return quantile;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Bool_t TMath::Permute(Int_t n, Int_t *a)
{
// Simple recursive algorithm to find the permutations of
// n natural numbers, not necessarily all distinct
// adapted from CERNLIB routine PERMU.
// The input array has to be initialised with a non descending
// sequence. The method returns kFALSE when
// all combinations are exhausted.
Int_t i,itmp;
Int_t i1=-1;
// find rightmost upward transition
for(i=n-2; i>-1; i--) {
if(a[i]<a[i+1]) {
i1=i;
break;
}
}
// no more upward transitions, end of the story
if(i1==-1) return kFALSE;
else {
// find lower right element higher than the lower
// element of the upward transition
for(i=n-1;i>i1;i--) {
if(a[i] > a[i1]) {
// swap the two
itmp=a[i1];
a[i1]=a[i];
a[i]=itmp;
break;
}
}
// order the rest, in fact just invert, as there
// are only downward transitions from here on
for(i=0;i<(n-i1-1)/2;i++) {
itmp=a[i1+i+1];
a[i1+i+1]=a[n-i-1];
a[n-i-1]=itmp;
}
}
return kTRUE;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::Student(Double_t T, Double_t ndf)
{
// Computes density function for Student's t- distribution
// (the probability function (integral of density) is computed in StudentI).
//
// First parameter stands for x - the actual variable of the
// density function p(x) and the point at which the density is calculated.
// Second parameter stands for number of degrees of freedom.
//
// About Student distribution:
// Student's t-distribution is used for many significance tests, for example,
// for the Student's t-tests for the statistical significance of difference
// between two sample means and for confidence intervals for the difference
// between two population means.
//
// Example: suppose we have a random sample of size n drawn from normal
// distribution with mean Mu and st.deviation Sigma. Then the variable
//
// t = (sample_mean - Mu)/(sample_deviation / sqrt(n))
//
// has Student's t-distribution with n-1 degrees of freedom.
//
// NOTE that this function's second argument is number of degrees of freedom,
// not the sample size.
//
// As the number of degrees of freedom grows, t-distribution approaches
// Normal(0,1) distribution.
// Implementation by Anna Kreshuk.
if (ndf < 1) {
return 0;
}
Double_t r = ndf;
Double_t rh = 0.5*r;
Double_t rh1 = rh + 0.5;
Double_t denom = TMath::Sqrt(r*TMath::Pi())*TMath::Gamma(rh)*TMath::Power(1+T*T/r, rh1);
return TMath::Gamma(rh1)/denom;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::StudentI(Double_t T, Double_t ndf)
{
// Calculates the cumulative distribution function of Student's
// t-distribution second parameter stands for number of degrees of freedom,
// not for the number of samples
// if x has Student's t-distribution, the function returns the probability of
// x being less than T.
// Implementation by Anna Kreshuk.
Double_t r = ndf;
Double_t si = (T>0) ?
(1 - 0.5*BetaIncomplete((r/(r + T*T)), r*0.5, 0.5)) :
0.5*BetaIncomplete((r/(r + T*T)), r*0.5, 0.5);
return si;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::StudentQuantile(Double_t p, Double_t ndf, Bool_t lower_tail)
{
// Computes quantiles of the Student's t-distribution
// 1st argument is the probability, at which the quantile is computed
// 2nd argument - the number of degrees of freedom of the
// Student distribution
// When the 3rd argument lower_tail is kTRUE (default)-
// the algorithm returns such x0, that
// P(x < x0)=p
// upper tail (lower_tail is kFALSE)- the algorithm returns such x0, that
// P(x > x0)=p
// the algorithm was taken from
// G.W.Hill, "Algorithm 396, Student's t-quantiles"
// "Communications of the ACM", 13(10), October 1970
Double_t quantile;
Double_t temp;
Bool_t neg;
Double_t q;
if (ndf<1 || p>=1 || p<=0) {
Error("TMath::StudentQuantile", "illegal parameter values");
return 0;
}
if ((lower_tail && p>0.5)||(!lower_tail && p<0.5)){
neg=kFALSE;
q=2*(lower_tail ? (1-p) : p);
} else {
neg=kTRUE;
q=2*(lower_tail? p : (1-p));
}
if ((ndf-2)<1e-8) {
quantile = TMath::Sqrt(2./(q*(2-q))-2);
} else {
if ((ndf-1)<1e-8) {
temp=TMath::PiOver2()*q;
quantile = TMath::Cos(temp)/TMath::Sin(temp);
} else {
Double_t a=1./(ndf-0.5);
Double_t b=48./(a*a);
Double_t c=((20700*a/b -98)*a-16)*a+96.36;
Double_t d=((94.5/(b+c)-3.)/b+1)*TMath::Sqrt(a*TMath::PiOver2())*ndf;
Double_t x=q*d;
Double_t y=TMath::Power(x, (2./ndf));
if (y>0.05+a){
//asymptotic inverse expansion about normal
x=NormQuantile(q*0.5);
y=x*x;
if (ndf<5) c+=0.3*(ndf-4.5)*(x+0.6);
c+=(((0.05*d*x-5.)*x-7.)*x-2.)*x +b;
y=(((((0.4*y+6.3)*y+36.)*y+94.5)/c - y-3.)/b+1)*x;
y=a*y*y;
if(y>0.002) y = TMath::Exp(y)-1;
else y += 0.5*y*y;
} else {
y=((1./(((ndf+6.)/(ndf*y)-0.089*d-0.822)*(ndf+2.)*3)+0.5/(ndf+4.))*y-1.)*
(ndf+1.)/(ndf+2.)+1/y;
}
quantile = TMath::Sqrt(ndf*y);
}
}
if(neg) quantile=-quantile;
return quantile;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::Vavilov(Double_t x, Double_t kappa, Double_t beta2)
{
//Returns the value of the Vavilov density function
//Parameters: 1st - the point were the density function is evaluated
// 2nd - value of kappa (distribution parameter)
// 3rd - value of beta2 (distribution parameter)
//The algorithm was taken from the CernLib function vavden(G115)
//Reference: A.Rotondi and P.Montagna, Fast Calculation of Vavilov distribution
//Nucl.Instr. and Meth. B47(1990), 215-224
//Accuracy: quote from the reference above:
//"The resuls of our code have been compared with the values of the Vavilov
//density function computed numerically in an accurate way: our approximation
//shows a difference of less than 3% around the peak of the density function, slowly
//increasing going towards the extreme tails to the right and to the left"
//
/*
 */
//
Double_t *ac = new Double_t[14];
Double_t *hc = new Double_t[9];
Int_t itype;
Int_t npt;
TMath::VavilovSet(kappa, beta2, 0, 0, ac, hc, itype, npt);
Double_t v = TMath::VavilovDenEval(x, ac, hc, itype);
delete [] ac;
delete [] hc;
return v;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::VavilovI(Double_t x, Double_t kappa, Double_t beta2)
{
//Returns the value of the Vavilov distribution function
//Parameters: 1st - the point were the density function is evaluated
// 2nd - value of kappa (distribution parameter)
// 3rd - value of beta2 (distribution parameter)
//The algorithm was taken from the CernLib function vavden(G115)
//Reference: A.Rotondi and P.Montagna, Fast Calculation of Vavilov distribution
//Nucl.Instr. and Meth. B47(1990), 215-224
//Accuracy: quote from the reference above:
//"The resuls of our code have been compared with the values of the Vavilov
//density function computed numerically in an accurate way: our approximation
//shows a difference of less than 3% around the peak of the density function, slowly
//increasing going towards the extreme tails to the right and to the left"
Double_t *ac = new Double_t[14];
Double_t *hc = new Double_t[9];
Double_t *wcm = new Double_t[200];
Int_t itype;
Int_t npt;
Int_t k;
Double_t xx, v;
TMath::VavilovSet(kappa, beta2, 1, wcm, ac, hc, itype, npt);
if (x < ac[0]) v = 0;
else if (x >=ac[8]) v = 1;
else {
xx = x - ac[0];
k = Int_t(xx*ac[10]);
v = TMath::Min(wcm[k] + (xx - k*ac[9])*(wcm[k+1]-wcm[k])*ac[10], 1.);
}
delete [] ac;
delete [] hc;
delete [] wcm;
return v;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::LandauI(Double_t x)
{
//Returns the value of the Landau distribution function at point x.
//The algorithm was taken from the Cernlib function dislan(G110)
//Reference: K.S.Kolbig and B.Schorr, "A program package for the Landau
//distribution", Computer Phys.Comm., 31(1984), 97-111
Double_t p1[] = {0.2514091491e+0,-0.6250580444e-1, 0.1458381230e-1, -0.2108817737e-2, 0.7411247290e-3};
Double_t q1[] = {1.0 ,-0.5571175625e-2, 0.6225310236e-1, -0.3137378427e-2, 0.1931496439e-2};
Double_t p2[] = {0.2868328584e+0, 0.3564363231e+0, 0.1523518695e+0, 0.2251304883e-1};
Double_t q2[] = {1.0 , 0.6191136137e+0, 0.1720721448e+0, 0.2278594771e-1};
Double_t p3[] = {0.2868329066e+0, 0.3003828436e+0, 0.9950951941e-1, 0.8733827185e-2};
Double_t q3[] = {1.0 , 0.4237190502e+0, 0.1095631512e+0, 0.8693851567e-2};
Double_t p4[] = {0.1000351630e+1, 0.4503592498e+1, 0.1085883880e+2, 0.7536052269e+1};
Double_t q4[] = {1.0 , 0.5539969678e+1, 0.1933581111e+2, 0.2721321508e+2};
Double_t p5[] = {0.1000006517e+1, 0.4909414111e+2, 0.8505544753e+2, 0.1532153455e+3};
Double_t q5[] = {1.0 , 0.5009928881e+2, 0.1399819104e+3, 0.4200002909e+3};
Double_t p6[] = {0.1000000983e+1, 0.1329868456e+3, 0.9162149244e+3, -0.9605054274e+3};
Double_t q6[] = {1.0 , 0.1339887843e+3, 0.1055990413e+4, 0.5532224619e+3};
Double_t a1[] = {0, -0.4583333333e+0, 0.6675347222e+0,-0.1641741416e+1};
Double_t a2[] = {0, 1.0 ,-0.4227843351e+0,-0.2043403138e+1};
Double_t u, v;
Double_t lan;
v = x;
if (v < -5.5) {
u = TMath::Exp(v+1);
lan = 0.3989422803*TMath::Exp(-1./u)*TMath::Sqrt(u)*(1+(a1[1]+(a1[2]+a1[3]*u)*u)*u);
}
else if (v < -1 ) {
u = TMath::Exp(-v-1);
lan = (TMath::Exp(-u)/TMath::Sqrt(u))*(p1[0]+(p1[1]+(p1[2]+(p1[3]+p1[4]*v)*v)*v)*v)/
(q1[0]+(q1[1]+(q1[2]+(q1[3]+q1[4]*v)*v)*v)*v);
}
else if (v < 1)
lan = (p2[0]+(p2[1]+(p2[2]+p2[3]*v)*v)*v)/(q2[0]+(q2[1]+(q2[2]+q2[3]*v)*v)*v);
else if (v < 4)
lan = (p3[0]+(p3[1]+(p3[2]+p3[3]*v)*v)*v)/(q3[0]+(q3[1]+(q3[2]+q3[3]*v)*v)*v);
else if (v < 12) {
u = 1./v;
lan = (p4[0]+(p4[1]+(p4[2]+p4[3]*u)*u)*u)/(q4[0]+(q4[1]+(q4[2]+q4[3]*u)*u)*u);
}
else if (v < 50) {
u = 1./v;
lan = (p5[0]+(p5[1]+(p5[2]+p5[3]*u)*u)*u)/(q5[0]+(q5[1]+(q5[2]+q5[3]*u)*u)*u);
}
else if (v < 300) {
u = 1./v;
lan = (p6[0]+(p6[1]+(p6[2]+p6[3]*u)*u)*u)/(q6[0]+(q6[1]+(q6[2]+q6[3]*u)*u)*u);
}
else {
u = 1./(v-v*TMath::Log(v)/(v+1));
lan = 1-(a2[1]+(a2[2]+a2[3]*u)*u)*u;
}
return lan;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TMath::VavilovSet(Double_t rkappa, Double_t beta2, Bool_t mode, Double_t *WCM, Double_t *AC, Double_t *HC, Int_t &itype, Int_t &npt)
{
//Internal function, called by Vavilov and VavilovI
Double_t BKMNX1 = 0.02, BKMNY1 = 0.05, BKMNX2 = 0.12, BKMNY2 = 0.05,
BKMNX3 = 0.22, BKMNY3 = 0.05, BKMXX1 = 0.1 , BKMXY1 = 1,
BKMXX2 = 0.2 , BKMXY2 = 1 , BKMXX3 = 0.3 , BKMXY3 = 1;
Double_t FBKX1 = 2/(BKMXX1-BKMNX1), FBKX2 = 2/(BKMXX2-BKMNX2),
FBKX3 = 2/(BKMXX3-BKMNX3), FBKY1 = 2/(BKMXY1-BKMNY1),
FBKY2 = 2/(BKMXY2-BKMNY2), FBKY3 = 2/(BKMXY3-BKMNY3);
Double_t FNINV[] = {0, 1, 0.5, 0.33333333, 0.25, 0.2};
Double_t EDGEC[]= {0, 0, 0.16666667e+0, 0.41666667e-1, 0.83333333e-2,
0.13888889e-1, 0.69444444e-2, 0.77160493e-3};
Double_t U1[] = {0, 0.25850868e+0, 0.32477982e-1, -0.59020496e-2,
0. , 0.24880692e-1, 0.47404356e-2,
-0.74445130e-3, 0.73225731e-2, 0. ,
0.11668284e-2, 0. , -0.15727318e-2,-0.11210142e-2};
Double_t U2[] = {0, 0.43142611e+0, 0.40797543e-1, -0.91490215e-2,
0. , 0.42127077e-1, 0.73167928e-2,
-0.14026047e-2, 0.16195241e-1, 0.24714789e-2,
0.20751278e-2, 0. , -0.25141668e-2,-0.14064022e-2};
Double_t U3[] = {0, 0.25225955e+0, 0.64820468e-1, -0.23615759e-1,
0. , 0.23834176e-1, 0.21624675e-2,
-0.26865597e-2, -0.54891384e-2, 0.39800522e-2,
0.48447456e-2, -0.89439554e-2, -0.62756944e-2,-0.24655436e-2};
Double_t U4[] = {0, 0.12593231e+1, -0.20374501e+0, 0.95055662e-1,
-0.20771531e-1, -0.46865180e-1, -0.77222986e-2,
0.32241039e-2, 0.89882920e-2, -0.67167236e-2,
-0.13049241e-1, 0.18786468e-1, 0.14484097e-1};
Double_t U5[] = {0, -0.24864376e-1, -0.10368495e-2, 0.14330117e-2,
0.20052730e-3, 0.18751903e-2, 0.12668869e-2,
0.48736023e-3, 0.34850854e-2, 0. ,
-0.36597173e-3, 0.19372124e-2, 0.70761825e-3, 0.46898375e-3};
Double_t U6[] = {0, 0.35855696e-1, -0.27542114e-1, 0.12631023e-1,
-0.30188807e-2, -0.84479939e-3, 0. ,
0.45675843e-3, -0.69836141e-2, 0.39876546e-2,
-0.36055679e-2, 0. , 0.15298434e-2, 0.19247256e-2};
Double_t U7[] = {0, 0.10234691e+2, -0.35619655e+1, 0.69387764e+0,
-0.14047599e+0, -0.19952390e+1, -0.45679694e+0,
0. , 0.50505298e+0};
Double_t U8[] = {0, 0.21487518e+2, -0.11825253e+2, 0.43133087e+1,
-0.14500543e+1, -0.34343169e+1, -0.11063164e+1,
-0.21000819e+0, 0.17891643e+1, -0.89601916e+0,
0.39120793e+0, 0.73410606e+0, 0. ,-0.32454506e+0};
Double_t V1[] = {0, 0.27827257e+0, -0.14227603e-2, 0.24848327e-2,
0. , 0.45091424e-1, 0.80559636e-2,
-0.38974523e-2, 0. , -0.30634124e-2,
0.75633702e-3, 0.54730726e-2, 0.19792507e-2};
Double_t V2[] = {0, 0.41421789e+0, -0.30061649e-1, 0.52249697e-2,
0. , 0.12693873e+0, 0.22999801e-1,
-0.86792801e-2, 0.31875584e-1, -0.61757928e-2,
0. , 0.19716857e-1, 0.32596742e-2};
Double_t V3[] = {0, 0.20191056e+0, -0.46831422e-1, 0.96777473e-2,
-0.17995317e-2, 0.53921588e-1, 0.35068740e-2,
-0.12621494e-1, -0.54996531e-2, -0.90029985e-2,
0.34958743e-2, 0.18513506e-1, 0.68332334e-2,-0.12940502e-2};
Double_t V4[] = {0, 0.13206081e+1, 0.10036618e+0, -0.22015201e-1,
0.61667091e-2, -0.14986093e+0, -0.12720568e-1,
0.24972042e-1, -0.97751962e-2, 0.26087455e-1,
-0.11399062e-1, -0.48282515e-1, -0.98552378e-2};
Double_t V5[] = {0, 0.16435243e-1, 0.36051400e-1, 0.23036520e-2,
-0.61666343e-3, -0.10775802e-1, 0.51476061e-2,
0.56856517e-2, -0.13438433e-1, 0. ,
0. , -0.25421507e-2, 0.20169108e-2,-0.15144931e-2};
Double_t V6[] = {0, 0.33432405e-1, 0.60583916e-2, -0.23381379e-2,
0.83846081e-3, -0.13346861e-1, -0.17402116e-2,
0.21052496e-2, 0.15528195e-2, 0.21900670e-2,
-0.13202847e-2, -0.45124157e-2, -0.15629454e-2, 0.22499176e-3};
Double_t V7[] = {0, 0.54529572e+1, -0.90906096e+0, 0.86122438e-1,
0. , -0.12218009e+1, -0.32324120e+0,
-0.27373591e-1, 0.12173464e+0, 0. ,
0. , 0.40917471e-1};
Double_t V8[] = {0, 0.93841352e+1, -0.16276904e+1, 0.16571423e+0,
0. , -0.18160479e+1, -0.50919193e+0,
-0.51384654e-1, 0.21413992e+0, 0. ,
0. , 0.66596366e-1};
Double_t W1[] = {0, 0.29712951e+0, 0.97572934e-2, 0. ,
-0.15291686e-2, 0.35707399e-1, 0.96221631e-2,
-0.18402821e-2, -0.49821585e-2, 0.18831112e-2,
0.43541673e-2, 0.20301312e-2, -0.18723311e-2,-0.73403108e-3};
Double_t W2[] = {0, 0.40882635e+0, 0.14474912e-1, 0.25023704e-2,
-0.37707379e-2, 0.18719727e+0, 0.56954987e-1,
0. , 0.23020158e-1, 0.50574313e-2,
0.94550140e-2, 0.19300232e-1};
Double_t W3[] = {0, 0.16861629e+0, 0. , 0.36317285e-2,
-0.43657818e-2, 0.30144338e-1, 0.13891826e-1,
-0.58030495e-2, -0.38717547e-2, 0.85359607e-2,
0.14507659e-1, 0.82387775e-2, -0.10116105e-1,-0.55135670e-2};
Double_t W4[] = {0, 0.13493891e+1, -0.26863185e-2, -0.35216040e-2,
0.24434909e-1, -0.83447911e-1, -0.48061360e-1,
0.76473951e-2, 0.24494430e-1, -0.16209200e-1,
-0.37768479e-1, -0.47890063e-1, 0.17778596e-1, 0.13179324e-1};
Double_t W5[] = {0, 0.10264945e+0, 0.32738857e-1, 0. ,
0.43608779e-2, -0.43097757e-1, -0.22647176e-2,
0.94531290e-2, -0.12442571e-1, -0.32283517e-2,
-0.75640352e-2, -0.88293329e-2, 0.52537299e-2, 0.13340546e-2};
Double_t W6[] = {0, 0.29568177e-1, -0.16300060e-2, -0.21119745e-3,
0.23599053e-2, -0.48515387e-2, -0.40797531e-2,
0.40403265e-3, 0.18200105e-2, -0.14346306e-2,
-0.39165276e-2, -0.37432073e-2, 0.19950380e-2, 0.12222675e-2};
Double_t W8[] = {0, 0.66184645e+1, -0.73866379e+0, 0.44693973e-1,
0. , -0.14540925e+1, -0.39529833e+0,
-0.44293243e-1, 0.88741049e-1};
itype = 0;
if (rkappa <0.01 || rkappa >12) {
Error("Vavilov distribution", "illegal value of kappa");
return;
}
Double_t DRK[6];
Double_t DSIGM[6];
Double_t ALFA[8];
Int_t j;
Double_t x, y, xx, yy, x2, x3, y2, y3, xy, p2, p3, q2, q3, pq;
if (rkappa >= 0.29) {
itype = 1;
npt = 100;
Double_t wk = 1./TMath::Sqrt(rkappa);
AC[0] = (-0.032227*beta2-0.074275)*rkappa + (0.24533*beta2+0.070152)*wk + (-0.55610*beta2-3.1579);
AC[8] = (-0.013483*beta2-0.048801)*rkappa + (-1.6921*beta2+8.3656)*wk + (-0.73275*beta2-3.5226);
DRK[1] = wk*wk;
DSIGM[1] = TMath::Sqrt(rkappa/(1-0.5*beta2));
for (j=1; j<=4; j++) {
DRK[j+1] = DRK[1]*DRK[j];
DSIGM[j+1] = DSIGM[1]*DSIGM[j];
ALFA[j+1] = (FNINV[j]-beta2*FNINV[j+1])*DRK[j];
}
HC[0]=TMath::Log(rkappa)+beta2+0.42278434;
HC[1]=DSIGM[1];
HC[2]=ALFA[3]*DSIGM[3];
HC[3]=(3*ALFA[2]*ALFA[2] + ALFA[4])*DSIGM[4]-3;
HC[4]=(10*ALFA[2]*ALFA[3]+ALFA[5])*DSIGM[5]-10*HC[2];
HC[5]=HC[2]*HC[2];
HC[6]=HC[2]*HC[3];
HC[7]=HC[2]*HC[5];
for (j=2; j<=7; j++)
HC[j]*=EDGEC[j];
HC[8]=0.39894228*HC[1];
}
else if (rkappa >=0.22) {
itype = 2;
npt = 150;
x = 1+(rkappa-BKMXX3)*FBKX3;
y = 1+(TMath::Sqrt(beta2)-BKMXY3)*FBKY3;
xx = 2*x;
yy = 2*y;
x2 = xx*x-1;
x3 = xx*x2-x;
y2 = yy*y-1;
y3 = yy*y2-y;
xy = x*y;
p2 = x2*y;
p3 = x3*y;
q2 = y2*x;
q3 = y3*x;
pq = x2*y2;
AC[1] = W1[1] + W1[2]*x + W1[4]*x3 + W1[5]*y + W1[6]*y2 + W1[7]*y3 +
W1[8]*xy + W1[9]*p2 + W1[10]*p3 + W1[11]*q2 + W1[12]*q3 + W1[13]*pq;
AC[2] = W2[1] + W2[2]*x + W2[3]*x2 + W2[4]*x3 + W2[5]*y + W2[6]*y2 +
W2[8]*xy + W2[9]*p2 + W2[10]*p3 + W2[11]*q2;
AC[3] = W3[1] + W3[3]*x2 + W3[4]*x3 + W3[5]*y + W3[6]*y2 + W3[7]*y3 +
W3[8]*xy + W3[9]*p2 + W3[10]*p3 + W3[11]*q2 + W3[12]*q3 + W3[13]*pq;
AC[4] = W4[1] + W4[2]*x + W4[3]*x2 + W4[4]*x3 + W4[5]*y + W4[6]*y2 + W4[7]*y3 +
W4[8]*xy + W4[9]*p2 + W4[10]*p3 + W4[11]*q2 + W4[12]*q3 + W4[13]*pq;
AC[5] = W5[1] + W5[2]*x + W5[4]*x3 + W5[5]*y + W5[6]*y2 + W5[7]*y3 +
W5[8]*xy + W5[9]*p2 + W5[10]*p3 + W5[11]*q2 + W5[12]*q3 + W5[13]*pq;
AC[6] = W6[1] + W6[2]*x + W6[3]*x2 + W6[4]*x3 + W6[5]*y + W6[6]*y2 + W6[7]*y3 +
W6[8]*xy + W6[9]*p2 + W6[10]*p3 + W6[11]*q2 + W6[12]*q3 + W6[13]*pq;
AC[8] = W8[1] + W8[2]*x + W8[3]*x2 + W8[5]*y + W8[6]*y2 + W8[7]*y3 + W8[8]*xy;
AC[0] = -3.05;
} else if (rkappa >= 0.12) {
itype = 3;
npt = 200;
x = 1 + (rkappa-BKMXX2)*FBKX2;
y = 1 + (TMath::Sqrt(beta2)-BKMXY2)*FBKY2;
xx = 2*x;
yy = 2*y;
x2 = xx*x-1;
x3 = xx*x2-x;
y2 = yy*y-1;
y3 = yy*y2-y;
xy = x*y;
p2 = x2*y;
p3 = x3*y;
q2 = y2*x;
q3 = y3*x;
pq = x2*y2;
AC[1] = V1[1] + V1[2]*x + V1[3]*x2 + V1[5]*y + V1[6]*y2 + V1[7]*y3 +
V1[9]*p2 + V1[10]*p3 + V1[11]*q2 + V1[12]*q3;
AC[2] = V2[1] + V2[2]*x + V2[3]*x2 + V2[5]*y + V2[6]*y2 + V2[7]*y3 +
V2[8]*xy + V2[9]*p2 + V2[11]*q2 + V2[12]*q3;
AC[3] = V3[1] + V3[2]*x + V3[3]*x2 + V3[4]*x3 + V3[5]*y + V3[6]*y2 + V3[7]*y3 +
V3[8]*xy + V3[9]*p2 + V3[10]*p3 + V3[11]*q2 + V3[12]*q3 + V3[13]*pq;
AC[4] = V4[1] + V4[2]*x + V4[3]*x2 + V4[4]*x3 + V4[5]*y + V4[6]*y2 + V4[7]*y3 +
V4[8]*xy + V4[9]*p2 + V4[10]*p3 + V4[11]*q2 + V4[12]*q3;
AC[5] = V5[1] + V5[2]*x + V5[3]*x2 + V5[4]*x3 + V5[5]*y + V5[6]*y2 + V5[7]*y3 +
V5[8]*xy + V5[11]*q2 + V5[12]*q3 + V5[13]*pq;
AC[6] = V6[1] + V6[2]*x + V6[3]*x2 + V6[4]*x3 + V6[5]*y + V6[6]*y2 + V6[7]*y3 +
V6[8]*xy + V6[9]*p2 + V6[10]*p3 + V6[11]*q2 + V6[12]*q3 + V6[13]*pq;
AC[7] = V7[1] + V7[2]*x + V7[3]*x2 + V7[5]*y + V7[6]*y2 + V7[7]*y3 +
V7[8]*xy + V7[11]*q2;
AC[8] = V8[1] + V8[2]*x + V8[3]*x2 + V8[5]*y + V8[6]*y2 + V8[7]*y3 +
V8[8]*xy + V8[11]*q2;
AC[0] = -3.04;
} else {
itype = 4;
if (rkappa >=0.02) itype = 3;
npt = 200;
x = 1+(rkappa-BKMXX1)*FBKX1;
y = 1+(TMath::Sqrt(beta2)-BKMXY1)*FBKY1;
xx = 2*x;
yy = 2*y;
x2 = xx*x-1;
x3 = xx*x2-x;
y2 = yy*y-1;
y3 = yy*y2-y;
xy = x*y;
p2 = x2*y;
p3 = x3*y;
q2 = y2*x;
q3 = y3*x;
pq = x2*y2;
if (itype==3){
AC[1] = U1[1] + U1[2]*x + U1[3]*x2 + U1[5]*y + U1[6]*y2 + U1[7]*y3 +
U1[8]*xy + U1[10]*p3 + U1[12]*q3 + U1[13]*pq;
AC[2] = U2[1] + U2[2]*x + U2[3]*x2 + U2[5]*y + U2[6]*y2 + U2[7]*y3 +
U2[8]*xy + U2[9]*p2 + U2[10]*p3 + U2[12]*q3 + U2[13]*pq;
AC[3] = U3[1] + U3[2]*x + U3[3]*x2 + U3[5]*y + U3[6]*y2 + U3[7]*y3 +
U3[8]*xy + U3[9]*p2 + U3[10]*p3 + U3[11]*q2 + U3[12]*q3 + U3[13]*pq;
AC[4] = U4[1] + U4[2]*x + U4[3]*x2 + U4[4]*x3 + U4[5]*y + U4[6]*y2 + U4[7]*y3 +
U4[8]*xy + U4[9]*p2 + U4[10]*p3 + U4[11]*q2 + U4[12]*q3;
AC[5] = U5[1] + U5[2]*x + U5[3]*x2 + U5[4]*x3 + U5[5]*y + U5[6]*y2 + U5[7]*y3 +
U5[8]*xy + U5[10]*p3 + U5[11]*q2 + U5[12]*q3 + U5[13]*pq;
AC[6] = U6[1] + U6[2]*x + U6[3]*x2 + U6[4]*x3 + U6[5]*y + U6[7]*y3 +
U6[8]*xy + U6[9]*p2 + U6[10]*p3 + U6[12]*q3 + U6[13]*pq;
AC[7] = U7[1] + U7[2]*x + U7[3]*x2 + U7[4]*x3 + U7[5]*y + U7[6]*y2 + U7[8]*xy;
}
AC[8] = U8[1] + U8[2]*x + U8[3]*x2 + U8[4]*x3 + U8[5]*y + U8[6]*y2 + U8[7]*y3 +
U8[8]*xy + U8[9]*p2 + U8[10]*p3 + U8[11]*q2 + U8[13]*pq;
AC[0] = -3.03;
}
AC[9] = (AC[8] - AC[0])/npt;
AC[10] = 1./AC[9];
if (itype == 3) {
x = (AC[7]-AC[8])/(AC[7]*AC[8]);
y = 1./TMath::Log(AC[8]/AC[7]);
p2 = AC[7]*AC[7];
AC[11] = p2*(AC[1]*TMath::Exp(-AC[2]*(AC[7]+AC[5]*p2)-
AC[3]*TMath::Exp(-AC[4]*(AC[7]+AC[6]*p2)))-0.045*y/AC[7])/(1+x*y*AC[7]);
AC[12] = (0.045+x*AC[11])*y;
}
if (itype == 4) AC[13] = 0.995/LandauI(AC[8]);
if (mode==0) return;
//
x = AC[0];
WCM[0] = 0;
Double_t fl, fu;
Int_t k;
fl = TMath::VavilovDenEval(x, AC, HC, itype);
for (k=1; k<=npt; k++) {
x += AC[9];
fu = TMath::VavilovDenEval(x, AC, HC, itype);
WCM[k] = WCM[k-1] + fl + fu;
fl = fu;
}
x = 0.5*AC[9];
for (k=1; k<=npt; k++)
WCM[k]*=x;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::VavilovDenEval(Double_t rlam, Double_t *AC, Double_t *HC, Int_t itype)
{
//Internal function, called by Vavilov and VavilovSet
Double_t v = 0;
if (rlam < AC[0] || rlam > AC[8])
return 0;
Int_t k;
Double_t x, fn, s;
Double_t h[10];
if (itype ==1 ) {
fn = 1;
x = (rlam + HC[0])*HC[1];
h[1] = x;
h[2] = x*x -1;
for (k=2; k<=8; k++) {
fn++;
h[k+1] = x*h[k]-fn*h[k-1];
}
s = 1 + HC[7]*h[9];
for (k=2; k<=6; k++)
s+=HC[k]*h[k+1];
v = HC[8]*TMath::Exp(-0.5*x*x)*TMath::Max(s, 0.);
}
else if (itype == 2) {
x = rlam*rlam;
v = AC[1]*TMath::Exp(-AC[2]*(rlam+AC[5]*x) - AC[3]*TMath::Exp(-AC[4]*(rlam+AC[6]*x)));
}
else if (itype == 3) {
if (rlam < AC[7]) {
x = rlam*rlam;
v = AC[1]*TMath::Exp(-AC[2]*(rlam+AC[5]*x)-AC[3]*TMath::Exp(-AC[4]*(rlam+AC[6]*x)));
} else {
x = 1./rlam;
v = (AC[11]*x + AC[12])*x;
}
}
else if (itype == 4) {
v = AC[13]*TMath::Landau(rlam);
}
return v;
}
*/
//
Double_t *ac = new Double_t[14];
Double_t *hc = new Double_t[9];
Int_t itype;
Int_t npt;
TMath::VavilovSet(kappa, beta2, 0, 0, ac, hc, itype, npt);
Double_t v = TMath::VavilovDenEval(x, ac, hc, itype);
delete [] ac;
delete [] hc;
return v;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::VavilovI(Double_t x, Double_t kappa, Double_t beta2)
{
//Returns the value of the Vavilov distribution function
//Parameters: 1st - the point were the density function is evaluated
// 2nd - value of kappa (distribution parameter)
// 3rd - value of beta2 (distribution parameter)
//The algorithm was taken from the CernLib function vavden(G115)
//Reference: A.Rotondi and P.Montagna, Fast Calculation of Vavilov distribution
//Nucl.Instr. and Meth. B47(1990), 215-224
//Accuracy: quote from the reference above:
//"The resuls of our code have been compared with the values of the Vavilov
//density function computed numerically in an accurate way: our approximation
//shows a difference of less than 3% around the peak of the density function, slowly
//increasing going towards the extreme tails to the right and to the left"
Double_t *ac = new Double_t[14];
Double_t *hc = new Double_t[9];
Double_t *wcm = new Double_t[200];
Int_t itype;
Int_t npt;
Int_t k;
Double_t xx, v;
TMath::VavilovSet(kappa, beta2, 1, wcm, ac, hc, itype, npt);
if (x < ac[0]) v = 0;
else if (x >=ac[8]) v = 1;
else {
xx = x - ac[0];
k = Int_t(xx*ac[10]);
v = TMath::Min(wcm[k] + (xx - k*ac[9])*(wcm[k+1]-wcm[k])*ac[10], 1.);
}
delete [] ac;
delete [] hc;
delete [] wcm;
return v;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::LandauI(Double_t x)
{
//Returns the value of the Landau distribution function at point x.
//The algorithm was taken from the Cernlib function dislan(G110)
//Reference: K.S.Kolbig and B.Schorr, "A program package for the Landau
//distribution", Computer Phys.Comm., 31(1984), 97-111
Double_t p1[] = {0.2514091491e+0,-0.6250580444e-1, 0.1458381230e-1, -0.2108817737e-2, 0.7411247290e-3};
Double_t q1[] = {1.0 ,-0.5571175625e-2, 0.6225310236e-1, -0.3137378427e-2, 0.1931496439e-2};
Double_t p2[] = {0.2868328584e+0, 0.3564363231e+0, 0.1523518695e+0, 0.2251304883e-1};
Double_t q2[] = {1.0 , 0.6191136137e+0, 0.1720721448e+0, 0.2278594771e-1};
Double_t p3[] = {0.2868329066e+0, 0.3003828436e+0, 0.9950951941e-1, 0.8733827185e-2};
Double_t q3[] = {1.0 , 0.4237190502e+0, 0.1095631512e+0, 0.8693851567e-2};
Double_t p4[] = {0.1000351630e+1, 0.4503592498e+1, 0.1085883880e+2, 0.7536052269e+1};
Double_t q4[] = {1.0 , 0.5539969678e+1, 0.1933581111e+2, 0.2721321508e+2};
Double_t p5[] = {0.1000006517e+1, 0.4909414111e+2, 0.8505544753e+2, 0.1532153455e+3};
Double_t q5[] = {1.0 , 0.5009928881e+2, 0.1399819104e+3, 0.4200002909e+3};
Double_t p6[] = {0.1000000983e+1, 0.1329868456e+3, 0.9162149244e+3, -0.9605054274e+3};
Double_t q6[] = {1.0 , 0.1339887843e+3, 0.1055990413e+4, 0.5532224619e+3};
Double_t a1[] = {0, -0.4583333333e+0, 0.6675347222e+0,-0.1641741416e+1};
Double_t a2[] = {0, 1.0 ,-0.4227843351e+0,-0.2043403138e+1};
Double_t u, v;
Double_t lan;
v = x;
if (v < -5.5) {
u = TMath::Exp(v+1);
lan = 0.3989422803*TMath::Exp(-1./u)*TMath::Sqrt(u)*(1+(a1[1]+(a1[2]+a1[3]*u)*u)*u);
}
else if (v < -1 ) {
u = TMath::Exp(-v-1);
lan = (TMath::Exp(-u)/TMath::Sqrt(u))*(p1[0]+(p1[1]+(p1[2]+(p1[3]+p1[4]*v)*v)*v)*v)/
(q1[0]+(q1[1]+(q1[2]+(q1[3]+q1[4]*v)*v)*v)*v);
}
else if (v < 1)
lan = (p2[0]+(p2[1]+(p2[2]+p2[3]*v)*v)*v)/(q2[0]+(q2[1]+(q2[2]+q2[3]*v)*v)*v);
else if (v < 4)
lan = (p3[0]+(p3[1]+(p3[2]+p3[3]*v)*v)*v)/(q3[0]+(q3[1]+(q3[2]+q3[3]*v)*v)*v);
else if (v < 12) {
u = 1./v;
lan = (p4[0]+(p4[1]+(p4[2]+p4[3]*u)*u)*u)/(q4[0]+(q4[1]+(q4[2]+q4[3]*u)*u)*u);
}
else if (v < 50) {
u = 1./v;
lan = (p5[0]+(p5[1]+(p5[2]+p5[3]*u)*u)*u)/(q5[0]+(q5[1]+(q5[2]+q5[3]*u)*u)*u);
}
else if (v < 300) {
u = 1./v;
lan = (p6[0]+(p6[1]+(p6[2]+p6[3]*u)*u)*u)/(q6[0]+(q6[1]+(q6[2]+q6[3]*u)*u)*u);
}
else {
u = 1./(v-v*TMath::Log(v)/(v+1));
lan = 1-(a2[1]+(a2[2]+a2[3]*u)*u)*u;
}
return lan;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TMath::VavilovSet(Double_t rkappa, Double_t beta2, Bool_t mode, Double_t *WCM, Double_t *AC, Double_t *HC, Int_t &itype, Int_t &npt)
{
//Internal function, called by Vavilov and VavilovI
Double_t BKMNX1 = 0.02, BKMNY1 = 0.05, BKMNX2 = 0.12, BKMNY2 = 0.05,
BKMNX3 = 0.22, BKMNY3 = 0.05, BKMXX1 = 0.1 , BKMXY1 = 1,
BKMXX2 = 0.2 , BKMXY2 = 1 , BKMXX3 = 0.3 , BKMXY3 = 1;
Double_t FBKX1 = 2/(BKMXX1-BKMNX1), FBKX2 = 2/(BKMXX2-BKMNX2),
FBKX3 = 2/(BKMXX3-BKMNX3), FBKY1 = 2/(BKMXY1-BKMNY1),
FBKY2 = 2/(BKMXY2-BKMNY2), FBKY3 = 2/(BKMXY3-BKMNY3);
Double_t FNINV[] = {0, 1, 0.5, 0.33333333, 0.25, 0.2};
Double_t EDGEC[]= {0, 0, 0.16666667e+0, 0.41666667e-1, 0.83333333e-2,
0.13888889e-1, 0.69444444e-2, 0.77160493e-3};
Double_t U1[] = {0, 0.25850868e+0, 0.32477982e-1, -0.59020496e-2,
0. , 0.24880692e-1, 0.47404356e-2,
-0.74445130e-3, 0.73225731e-2, 0. ,
0.11668284e-2, 0. , -0.15727318e-2,-0.11210142e-2};
Double_t U2[] = {0, 0.43142611e+0, 0.40797543e-1, -0.91490215e-2,
0. , 0.42127077e-1, 0.73167928e-2,
-0.14026047e-2, 0.16195241e-1, 0.24714789e-2,
0.20751278e-2, 0. , -0.25141668e-2,-0.14064022e-2};
Double_t U3[] = {0, 0.25225955e+0, 0.64820468e-1, -0.23615759e-1,
0. , 0.23834176e-1, 0.21624675e-2,
-0.26865597e-2, -0.54891384e-2, 0.39800522e-2,
0.48447456e-2, -0.89439554e-2, -0.62756944e-2,-0.24655436e-2};
Double_t U4[] = {0, 0.12593231e+1, -0.20374501e+0, 0.95055662e-1,
-0.20771531e-1, -0.46865180e-1, -0.77222986e-2,
0.32241039e-2, 0.89882920e-2, -0.67167236e-2,
-0.13049241e-1, 0.18786468e-1, 0.14484097e-1};
Double_t U5[] = {0, -0.24864376e-1, -0.10368495e-2, 0.14330117e-2,
0.20052730e-3, 0.18751903e-2, 0.12668869e-2,
0.48736023e-3, 0.34850854e-2, 0. ,
-0.36597173e-3, 0.19372124e-2, 0.70761825e-3, 0.46898375e-3};
Double_t U6[] = {0, 0.35855696e-1, -0.27542114e-1, 0.12631023e-1,
-0.30188807e-2, -0.84479939e-3, 0. ,
0.45675843e-3, -0.69836141e-2, 0.39876546e-2,
-0.36055679e-2, 0. , 0.15298434e-2, 0.19247256e-2};
Double_t U7[] = {0, 0.10234691e+2, -0.35619655e+1, 0.69387764e+0,
-0.14047599e+0, -0.19952390e+1, -0.45679694e+0,
0. , 0.50505298e+0};
Double_t U8[] = {0, 0.21487518e+2, -0.11825253e+2, 0.43133087e+1,
-0.14500543e+1, -0.34343169e+1, -0.11063164e+1,
-0.21000819e+0, 0.17891643e+1, -0.89601916e+0,
0.39120793e+0, 0.73410606e+0, 0. ,-0.32454506e+0};
Double_t V1[] = {0, 0.27827257e+0, -0.14227603e-2, 0.24848327e-2,
0. , 0.45091424e-1, 0.80559636e-2,
-0.38974523e-2, 0. , -0.30634124e-2,
0.75633702e-3, 0.54730726e-2, 0.19792507e-2};
Double_t V2[] = {0, 0.41421789e+0, -0.30061649e-1, 0.52249697e-2,
0. , 0.12693873e+0, 0.22999801e-1,
-0.86792801e-2, 0.31875584e-1, -0.61757928e-2,
0. , 0.19716857e-1, 0.32596742e-2};
Double_t V3[] = {0, 0.20191056e+0, -0.46831422e-1, 0.96777473e-2,
-0.17995317e-2, 0.53921588e-1, 0.35068740e-2,
-0.12621494e-1, -0.54996531e-2, -0.90029985e-2,
0.34958743e-2, 0.18513506e-1, 0.68332334e-2,-0.12940502e-2};
Double_t V4[] = {0, 0.13206081e+1, 0.10036618e+0, -0.22015201e-1,
0.61667091e-2, -0.14986093e+0, -0.12720568e-1,
0.24972042e-1, -0.97751962e-2, 0.26087455e-1,
-0.11399062e-1, -0.48282515e-1, -0.98552378e-2};
Double_t V5[] = {0, 0.16435243e-1, 0.36051400e-1, 0.23036520e-2,
-0.61666343e-3, -0.10775802e-1, 0.51476061e-2,
0.56856517e-2, -0.13438433e-1, 0. ,
0. , -0.25421507e-2, 0.20169108e-2,-0.15144931e-2};
Double_t V6[] = {0, 0.33432405e-1, 0.60583916e-2, -0.23381379e-2,
0.83846081e-3, -0.13346861e-1, -0.17402116e-2,
0.21052496e-2, 0.15528195e-2, 0.21900670e-2,
-0.13202847e-2, -0.45124157e-2, -0.15629454e-2, 0.22499176e-3};
Double_t V7[] = {0, 0.54529572e+1, -0.90906096e+0, 0.86122438e-1,
0. , -0.12218009e+1, -0.32324120e+0,
-0.27373591e-1, 0.12173464e+0, 0. ,
0. , 0.40917471e-1};
Double_t V8[] = {0, 0.93841352e+1, -0.16276904e+1, 0.16571423e+0,
0. , -0.18160479e+1, -0.50919193e+0,
-0.51384654e-1, 0.21413992e+0, 0. ,
0. , 0.66596366e-1};
Double_t W1[] = {0, 0.29712951e+0, 0.97572934e-2, 0. ,
-0.15291686e-2, 0.35707399e-1, 0.96221631e-2,
-0.18402821e-2, -0.49821585e-2, 0.18831112e-2,
0.43541673e-2, 0.20301312e-2, -0.18723311e-2,-0.73403108e-3};
Double_t W2[] = {0, 0.40882635e+0, 0.14474912e-1, 0.25023704e-2,
-0.37707379e-2, 0.18719727e+0, 0.56954987e-1,
0. , 0.23020158e-1, 0.50574313e-2,
0.94550140e-2, 0.19300232e-1};
Double_t W3[] = {0, 0.16861629e+0, 0. , 0.36317285e-2,
-0.43657818e-2, 0.30144338e-1, 0.13891826e-1,
-0.58030495e-2, -0.38717547e-2, 0.85359607e-2,
0.14507659e-1, 0.82387775e-2, -0.10116105e-1,-0.55135670e-2};
Double_t W4[] = {0, 0.13493891e+1, -0.26863185e-2, -0.35216040e-2,
0.24434909e-1, -0.83447911e-1, -0.48061360e-1,
0.76473951e-2, 0.24494430e-1, -0.16209200e-1,
-0.37768479e-1, -0.47890063e-1, 0.17778596e-1, 0.13179324e-1};
Double_t W5[] = {0, 0.10264945e+0, 0.32738857e-1, 0. ,
0.43608779e-2, -0.43097757e-1, -0.22647176e-2,
0.94531290e-2, -0.12442571e-1, -0.32283517e-2,
-0.75640352e-2, -0.88293329e-2, 0.52537299e-2, 0.13340546e-2};
Double_t W6[] = {0, 0.29568177e-1, -0.16300060e-2, -0.21119745e-3,
0.23599053e-2, -0.48515387e-2, -0.40797531e-2,
0.40403265e-3, 0.18200105e-2, -0.14346306e-2,
-0.39165276e-2, -0.37432073e-2, 0.19950380e-2, 0.12222675e-2};
Double_t W8[] = {0, 0.66184645e+1, -0.73866379e+0, 0.44693973e-1,
0. , -0.14540925e+1, -0.39529833e+0,
-0.44293243e-1, 0.88741049e-1};
itype = 0;
if (rkappa <0.01 || rkappa >12) {
Error("Vavilov distribution", "illegal value of kappa");
return;
}
Double_t DRK[6];
Double_t DSIGM[6];
Double_t ALFA[8];
Int_t j;
Double_t x, y, xx, yy, x2, x3, y2, y3, xy, p2, p3, q2, q3, pq;
if (rkappa >= 0.29) {
itype = 1;
npt = 100;
Double_t wk = 1./TMath::Sqrt(rkappa);
AC[0] = (-0.032227*beta2-0.074275)*rkappa + (0.24533*beta2+0.070152)*wk + (-0.55610*beta2-3.1579);
AC[8] = (-0.013483*beta2-0.048801)*rkappa + (-1.6921*beta2+8.3656)*wk + (-0.73275*beta2-3.5226);
DRK[1] = wk*wk;
DSIGM[1] = TMath::Sqrt(rkappa/(1-0.5*beta2));
for (j=1; j<=4; j++) {
DRK[j+1] = DRK[1]*DRK[j];
DSIGM[j+1] = DSIGM[1]*DSIGM[j];
ALFA[j+1] = (FNINV[j]-beta2*FNINV[j+1])*DRK[j];
}
HC[0]=TMath::Log(rkappa)+beta2+0.42278434;
HC[1]=DSIGM[1];
HC[2]=ALFA[3]*DSIGM[3];
HC[3]=(3*ALFA[2]*ALFA[2] + ALFA[4])*DSIGM[4]-3;
HC[4]=(10*ALFA[2]*ALFA[3]+ALFA[5])*DSIGM[5]-10*HC[2];
HC[5]=HC[2]*HC[2];
HC[6]=HC[2]*HC[3];
HC[7]=HC[2]*HC[5];
for (j=2; j<=7; j++)
HC[j]*=EDGEC[j];
HC[8]=0.39894228*HC[1];
}
else if (rkappa >=0.22) {
itype = 2;
npt = 150;
x = 1+(rkappa-BKMXX3)*FBKX3;
y = 1+(TMath::Sqrt(beta2)-BKMXY3)*FBKY3;
xx = 2*x;
yy = 2*y;
x2 = xx*x-1;
x3 = xx*x2-x;
y2 = yy*y-1;
y3 = yy*y2-y;
xy = x*y;
p2 = x2*y;
p3 = x3*y;
q2 = y2*x;
q3 = y3*x;
pq = x2*y2;
AC[1] = W1[1] + W1[2]*x + W1[4]*x3 + W1[5]*y + W1[6]*y2 + W1[7]*y3 +
W1[8]*xy + W1[9]*p2 + W1[10]*p3 + W1[11]*q2 + W1[12]*q3 + W1[13]*pq;
AC[2] = W2[1] + W2[2]*x + W2[3]*x2 + W2[4]*x3 + W2[5]*y + W2[6]*y2 +
W2[8]*xy + W2[9]*p2 + W2[10]*p3 + W2[11]*q2;
AC[3] = W3[1] + W3[3]*x2 + W3[4]*x3 + W3[5]*y + W3[6]*y2 + W3[7]*y3 +
W3[8]*xy + W3[9]*p2 + W3[10]*p3 + W3[11]*q2 + W3[12]*q3 + W3[13]*pq;
AC[4] = W4[1] + W4[2]*x + W4[3]*x2 + W4[4]*x3 + W4[5]*y + W4[6]*y2 + W4[7]*y3 +
W4[8]*xy + W4[9]*p2 + W4[10]*p3 + W4[11]*q2 + W4[12]*q3 + W4[13]*pq;
AC[5] = W5[1] + W5[2]*x + W5[4]*x3 + W5[5]*y + W5[6]*y2 + W5[7]*y3 +
W5[8]*xy + W5[9]*p2 + W5[10]*p3 + W5[11]*q2 + W5[12]*q3 + W5[13]*pq;
AC[6] = W6[1] + W6[2]*x + W6[3]*x2 + W6[4]*x3 + W6[5]*y + W6[6]*y2 + W6[7]*y3 +
W6[8]*xy + W6[9]*p2 + W6[10]*p3 + W6[11]*q2 + W6[12]*q3 + W6[13]*pq;
AC[8] = W8[1] + W8[2]*x + W8[3]*x2 + W8[5]*y + W8[6]*y2 + W8[7]*y3 + W8[8]*xy;
AC[0] = -3.05;
} else if (rkappa >= 0.12) {
itype = 3;
npt = 200;
x = 1 + (rkappa-BKMXX2)*FBKX2;
y = 1 + (TMath::Sqrt(beta2)-BKMXY2)*FBKY2;
xx = 2*x;
yy = 2*y;
x2 = xx*x-1;
x3 = xx*x2-x;
y2 = yy*y-1;
y3 = yy*y2-y;
xy = x*y;
p2 = x2*y;
p3 = x3*y;
q2 = y2*x;
q3 = y3*x;
pq = x2*y2;
AC[1] = V1[1] + V1[2]*x + V1[3]*x2 + V1[5]*y + V1[6]*y2 + V1[7]*y3 +
V1[9]*p2 + V1[10]*p3 + V1[11]*q2 + V1[12]*q3;
AC[2] = V2[1] + V2[2]*x + V2[3]*x2 + V2[5]*y + V2[6]*y2 + V2[7]*y3 +
V2[8]*xy + V2[9]*p2 + V2[11]*q2 + V2[12]*q3;
AC[3] = V3[1] + V3[2]*x + V3[3]*x2 + V3[4]*x3 + V3[5]*y + V3[6]*y2 + V3[7]*y3 +
V3[8]*xy + V3[9]*p2 + V3[10]*p3 + V3[11]*q2 + V3[12]*q3 + V3[13]*pq;
AC[4] = V4[1] + V4[2]*x + V4[3]*x2 + V4[4]*x3 + V4[5]*y + V4[6]*y2 + V4[7]*y3 +
V4[8]*xy + V4[9]*p2 + V4[10]*p3 + V4[11]*q2 + V4[12]*q3;
AC[5] = V5[1] + V5[2]*x + V5[3]*x2 + V5[4]*x3 + V5[5]*y + V5[6]*y2 + V5[7]*y3 +
V5[8]*xy + V5[11]*q2 + V5[12]*q3 + V5[13]*pq;
AC[6] = V6[1] + V6[2]*x + V6[3]*x2 + V6[4]*x3 + V6[5]*y + V6[6]*y2 + V6[7]*y3 +
V6[8]*xy + V6[9]*p2 + V6[10]*p3 + V6[11]*q2 + V6[12]*q3 + V6[13]*pq;
AC[7] = V7[1] + V7[2]*x + V7[3]*x2 + V7[5]*y + V7[6]*y2 + V7[7]*y3 +
V7[8]*xy + V7[11]*q2;
AC[8] = V8[1] + V8[2]*x + V8[3]*x2 + V8[5]*y + V8[6]*y2 + V8[7]*y3 +
V8[8]*xy + V8[11]*q2;
AC[0] = -3.04;
} else {
itype = 4;
if (rkappa >=0.02) itype = 3;
npt = 200;
x = 1+(rkappa-BKMXX1)*FBKX1;
y = 1+(TMath::Sqrt(beta2)-BKMXY1)*FBKY1;
xx = 2*x;
yy = 2*y;
x2 = xx*x-1;
x3 = xx*x2-x;
y2 = yy*y-1;
y3 = yy*y2-y;
xy = x*y;
p2 = x2*y;
p3 = x3*y;
q2 = y2*x;
q3 = y3*x;
pq = x2*y2;
if (itype==3){
AC[1] = U1[1] + U1[2]*x + U1[3]*x2 + U1[5]*y + U1[6]*y2 + U1[7]*y3 +
U1[8]*xy + U1[10]*p3 + U1[12]*q3 + U1[13]*pq;
AC[2] = U2[1] + U2[2]*x + U2[3]*x2 + U2[5]*y + U2[6]*y2 + U2[7]*y3 +
U2[8]*xy + U2[9]*p2 + U2[10]*p3 + U2[12]*q3 + U2[13]*pq;
AC[3] = U3[1] + U3[2]*x + U3[3]*x2 + U3[5]*y + U3[6]*y2 + U3[7]*y3 +
U3[8]*xy + U3[9]*p2 + U3[10]*p3 + U3[11]*q2 + U3[12]*q3 + U3[13]*pq;
AC[4] = U4[1] + U4[2]*x + U4[3]*x2 + U4[4]*x3 + U4[5]*y + U4[6]*y2 + U4[7]*y3 +
U4[8]*xy + U4[9]*p2 + U4[10]*p3 + U4[11]*q2 + U4[12]*q3;
AC[5] = U5[1] + U5[2]*x + U5[3]*x2 + U5[4]*x3 + U5[5]*y + U5[6]*y2 + U5[7]*y3 +
U5[8]*xy + U5[10]*p3 + U5[11]*q2 + U5[12]*q3 + U5[13]*pq;
AC[6] = U6[1] + U6[2]*x + U6[3]*x2 + U6[4]*x3 + U6[5]*y + U6[7]*y3 +
U6[8]*xy + U6[9]*p2 + U6[10]*p3 + U6[12]*q3 + U6[13]*pq;
AC[7] = U7[1] + U7[2]*x + U7[3]*x2 + U7[4]*x3 + U7[5]*y + U7[6]*y2 + U7[8]*xy;
}
AC[8] = U8[1] + U8[2]*x + U8[3]*x2 + U8[4]*x3 + U8[5]*y + U8[6]*y2 + U8[7]*y3 +
U8[8]*xy + U8[9]*p2 + U8[10]*p3 + U8[11]*q2 + U8[13]*pq;
AC[0] = -3.03;
}
AC[9] = (AC[8] - AC[0])/npt;
AC[10] = 1./AC[9];
if (itype == 3) {
x = (AC[7]-AC[8])/(AC[7]*AC[8]);
y = 1./TMath::Log(AC[8]/AC[7]);
p2 = AC[7]*AC[7];
AC[11] = p2*(AC[1]*TMath::Exp(-AC[2]*(AC[7]+AC[5]*p2)-
AC[3]*TMath::Exp(-AC[4]*(AC[7]+AC[6]*p2)))-0.045*y/AC[7])/(1+x*y*AC[7]);
AC[12] = (0.045+x*AC[11])*y;
}
if (itype == 4) AC[13] = 0.995/LandauI(AC[8]);
if (mode==0) return;
//
x = AC[0];
WCM[0] = 0;
Double_t fl, fu;
Int_t k;
fl = TMath::VavilovDenEval(x, AC, HC, itype);
for (k=1; k<=npt; k++) {
x += AC[9];
fu = TMath::VavilovDenEval(x, AC, HC, itype);
WCM[k] = WCM[k-1] + fl + fu;
fl = fu;
}
x = 0.5*AC[9];
for (k=1; k<=npt; k++)
WCM[k]*=x;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::VavilovDenEval(Double_t rlam, Double_t *AC, Double_t *HC, Int_t itype)
{
//Internal function, called by Vavilov and VavilovSet
Double_t v = 0;
if (rlam < AC[0] || rlam > AC[8])
return 0;
Int_t k;
Double_t x, fn, s;
Double_t h[10];
if (itype ==1 ) {
fn = 1;
x = (rlam + HC[0])*HC[1];
h[1] = x;
h[2] = x*x -1;
for (k=2; k<=8; k++) {
fn++;
h[k+1] = x*h[k]-fn*h[k-1];
}
s = 1 + HC[7]*h[9];
for (k=2; k<=6; k++)
s+=HC[k]*h[k+1];
v = HC[8]*TMath::Exp(-0.5*x*x)*TMath::Max(s, 0.);
}
else if (itype == 2) {
x = rlam*rlam;
v = AC[1]*TMath::Exp(-AC[2]*(rlam+AC[5]*x) - AC[3]*TMath::Exp(-AC[4]*(rlam+AC[6]*x)));
}
else if (itype == 3) {
if (rlam < AC[7]) {
x = rlam*rlam;
v = AC[1]*TMath::Exp(-AC[2]*(rlam+AC[5]*x)-AC[3]*TMath::Exp(-AC[4]*(rlam+AC[6]*x)));
} else {
x = 1./rlam;
v = (AC[11]*x + AC[12])*x;
}
}
else if (itype == 4) {
v = AC[13]*TMath::Landau(rlam);
}
return v;
}
ROOT page - Class index - Class Hierarchy - Top of the page
This page has been automatically generated. If you have any comments or suggestions about the page layout send a mail to ROOT support, or contact the developers with any questions or problems regarding ROOT.
 */
//
if (x<0)
return 0;
else if (x == 0.0)
return 1./Exp(par);
else {
Double_t lnpoisson = x*log(par)-par-LnGamma(x+1.);
return Exp(lnpoisson);
}
// An alternative strategy is to transition to a Gaussian approximation for
// large values of par ...
// else {
// return Gaus(x,par,Sqrt(par),kTRUE);
// }
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::PoissonI(Double_t x, Double_t par)
{
// compute the Poisson distribution function for (x,par)
// This is a non-smooth function
//
/*
*/
//
if (x<0)
return 0;
else if (x == 0.0)
return 1./Exp(par);
else {
Double_t lnpoisson = x*log(par)-par-LnGamma(x+1.);
return Exp(lnpoisson);
}
// An alternative strategy is to transition to a Gaussian approximation for
// large values of par ...
// else {
// return Gaus(x,par,Sqrt(par),kTRUE);
// }
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::PoissonI(Double_t x, Double_t par)
{
// compute the Poisson distribution function for (x,par)
// This is a non-smooth function
//
/*
 */
//
const Double_t kMaxInt = 2e6;
if(x<0) return 0;
if(x<1) return TMath::Exp(-par);
Double_t gam;
Int_t ix = Int_t(x);
if(x < kMaxInt) gam = TMath::Power(par,ix)/TMath::Gamma(ix+1);
else gam = TMath::Power(par,x)/TMath::Gamma(x+1);
return gam/TMath::Exp(par);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::Prob(Double_t chi2,Int_t ndf)
{
// Computation of the probability for a certain Chi-squared (chi2)
// and number of degrees of freedom (ndf).
//
// Calculations are based on the incomplete gamma function P(a,x),
// where a=ndf/2 and x=chi2/2.
//
// P(a,x) represents the probability that the observed Chi-squared
// for a correct model should be less than the value chi2.
//
// The returned probability corresponds to 1-P(a,x),
// which denotes the probability that an observed Chi-squared exceeds
// the value chi2 by chance, even for a correct model.
//
//--- NvE 14-nov-1998 UU-SAP Utrecht
if (ndf <= 0) return 0; // Set CL to zero in case ndf<=0
if (chi2 <= 0) {
if (chi2 < 0) return 0;
else return 1;
}
if (ndf==1) {
Double_t v = 1.-Erf(Sqrt(chi2)/Sqrt(2.));
return v;
}
// Gaussian approximation for large ndf
Double_t q = Sqrt(2*chi2)-Sqrt(Double_t(2*ndf-1));
if (ndf > 30 && q > 5) {
Double_t v = 0.5*(1-Erf(q/Sqrt(2.)));
return v;
}
// Evaluate the incomplete gamma function
return (1-Gamma(0.5*ndf,0.5*chi2));
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::KolmogorovProb(Double_t z)
{
// Calculates the Kolmogorov distribution function,
//
/*
*/
//
const Double_t kMaxInt = 2e6;
if(x<0) return 0;
if(x<1) return TMath::Exp(-par);
Double_t gam;
Int_t ix = Int_t(x);
if(x < kMaxInt) gam = TMath::Power(par,ix)/TMath::Gamma(ix+1);
else gam = TMath::Power(par,x)/TMath::Gamma(x+1);
return gam/TMath::Exp(par);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::Prob(Double_t chi2,Int_t ndf)
{
// Computation of the probability for a certain Chi-squared (chi2)
// and number of degrees of freedom (ndf).
//
// Calculations are based on the incomplete gamma function P(a,x),
// where a=ndf/2 and x=chi2/2.
//
// P(a,x) represents the probability that the observed Chi-squared
// for a correct model should be less than the value chi2.
//
// The returned probability corresponds to 1-P(a,x),
// which denotes the probability that an observed Chi-squared exceeds
// the value chi2 by chance, even for a correct model.
//
//--- NvE 14-nov-1998 UU-SAP Utrecht
if (ndf <= 0) return 0; // Set CL to zero in case ndf<=0
if (chi2 <= 0) {
if (chi2 < 0) return 0;
else return 1;
}
if (ndf==1) {
Double_t v = 1.-Erf(Sqrt(chi2)/Sqrt(2.));
return v;
}
// Gaussian approximation for large ndf
Double_t q = Sqrt(2*chi2)-Sqrt(Double_t(2*ndf-1));
if (ndf > 30 && q > 5) {
Double_t v = 0.5*(1-Erf(q/Sqrt(2.)));
return v;
}
// Evaluate the incomplete gamma function
return (1-Gamma(0.5*ndf,0.5*chi2));
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::KolmogorovProb(Double_t z)
{
// Calculates the Kolmogorov distribution function,
//
/*
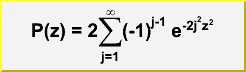 */
//
// which gives the probability that Kolmogorov's test statistic will exceed
// the value z assuming the null hypothesis. This gives a very powerful
// test for comparing two one-dimensional distributions.
// see, for example, Eadie et al, "statistocal Methods in Experimental
// Physics', pp 269-270).
//
// This function returns the confidence level for the null hypothesis, where:
// z = dn*sqrt(n), and
// dn is the maximum deviation between a hypothetical distribution
// function and an experimental distribution with
// n events
//
// NOTE: To compare two experimental distributions with m and n events,
// use z = sqrt(m*n/(m+n))*dn
//
// Accuracy: The function is far too accurate for any imaginable application.
// Probabilities less than 10^-15 are returned as zero.
// However, remember that the formula is only valid for "large" n.
// Theta function inversion formula is used for z <= 1
//
// This function was translated by Rene Brun from PROBKL in CERNLIB.
Double_t fj[4] = {-2,-8,-18,-32}, r[4];
const Double_t w = 2.50662827;
// c1 - -pi**2/8, c2 = 9*c1, c3 = 25*c1
const Double_t c1 = -1.2337005501361697;
const Double_t c2 = -11.103304951225528;
const Double_t c3 = -30.842513753404244;
Double_t u = TMath::Abs(z);
Double_t p;
if (u < 0.2) {
p = 1;
} else if (u < 0.755) {
Double_t v = 1./(u*u);
p = 1 - w*(TMath::Exp(c1*v) + TMath::Exp(c2*v) + TMath::Exp(c3*v))/u;
} else if (u < 6.8116) {
r[1] = 0;
r[2] = 0;
r[3] = 0;
Double_t v = u*u;
Int_t maxj = TMath::Max(1,TMath::Nint(3./u));
for (Int_t j=0; j<maxj;j++) {
r[j] = TMath::Exp(fj[j]*v);
}
p = 2*(r[0] - r[1] +r[2] - r[3]);
} else {
p = 0;
}
return p;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::KolmogorovTest(Int_t na, const Double_t *a, Int_t nb, const Double_t *b, Option_t *option)
{
// Statistical test whether two one-dimensional sets of points are compatible
// with coming from the same parent distribution, using the Kolmogorov test.
// That is, it is used to compare two experimental distributions of unbinned data.
//
// Input:
// a,b: One-dimensional arrays of length na, nb, respectively.
// The elements of a and b must be given in ascending order.
// option is a character string to specify options
// "D" Put out a line of "Debug" printout
// "M" Return the Maximum Kolmogorov distance instead of prob
//
// Output:
// The returned value prob is a calculated confidence level which gives a
// statistical test for compatibility of a and b.
// Values of prob close to zero are taken as indicating a small probability
// of compatibility. For two point sets drawn randomly from the same parent
// distribution, the value of prob should be uniformly distributed between
// zero and one.
// in case of error the function return -1
// If the 2 sets have a different number of points, the minimum of
// the two sets is used.
//
// Method:
// The Kolmogorov test is used. The test statistic is the maximum deviation
// between the two integrated distribution functions, multiplied by the
// normalizing factor (rdmax*sqrt(na*nb/(na+nb)).
//
// Code adapted by Rene Brun from CERNLIB routine TKOLMO (Fred James)
// (W.T. Eadie, D. Drijard, F.E. James, M. Roos and B. Sadoulet,
// Statistical Methods in Experimental Physics, (North-Holland,
// Amsterdam 1971) 269-271)
//
// NOTE1
// A good description of the Kolmogorov test can be seen at:
// http://www.itl.nist.gov/div898/handbook/eda/section3/eda35g.htm
TString opt = option;
opt.ToUpper();
Double_t prob = -1;
// Require at least two points in each graph
if (!a || !b || na <= 2 || nb <= 2) {
Error("KolmogorovTest","Sets must have more than 2 points");
return prob;
}
// Constants needed
Double_t rna = na;
Double_t rnb = nb;
Double_t sa = 1./rna;
Double_t sb = 1./rnb;
Double_t rdiff;
Int_t ia,ib;
// Starting values for main loop
if (a[0] < b[0]) {
rdiff = -sa;
ia = 2;
ib = 1;
} else {
rdiff = sb;
ib = 2;
ia = 1;
}
Double_t rdmax = TMath::Abs(rdiff);
// Main loop over point sets to find max distance
// rdiff is the running difference, and rdmax the max.
Bool_t ok = kFALSE;
for (Int_t i=0;i<na+nb;i++) {
if (a[ia-1] < b[ib-1]) {
rdiff -= sa;
ia++;
if (ia > na) {ok = kTRUE; break;}
} else if (a[ia-1] > b[ib-1]) {
rdiff += sb;
ib++;
if (ib > nb) {ok = kTRUE; break;}
} else {
ia++;
ib++;
if (ia > na) {ok = kTRUE; break;}
if (ib > nb) {ok = kTRUE; break;}
}
rdmax = TMath::Max(rdmax,TMath::Abs(rdiff));
}
// Should never terminate this loop with ok = kFALSE!
if (ok) {
rdmax = TMath::Max(rdmax,TMath::Abs(rdiff));
Double_t z = rdmax * TMath::Sqrt(rna*rnb/(rna+rnb));
prob = TMath::KolmogorovProb(z);
}
// debug printout
if (opt.Contains("D")) {
printf(" Kolmogorov Probability = %g, Max Dist = %g\n",prob,rdmax);
}
if(opt.Contains("M")) return rdmax;
else return prob;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::Voigt(Double_t xx, Double_t sigma, Double_t lg, Int_t r)
{
// Computation of Voigt function (normalised).
// Voigt is a convolution of
// gauss(xx) = 1/(sqrt(2*pi)*sigma) * exp(xx*xx/(2*sigma*sigma)
// and
// lorentz(xx) = (1/pi) * (lg/2) / (xx*xx + g*g/4)
// functions.
//
// The Voigt function is known to be the real part of Faddeeva function also
// called complex error function [2].
//
// The algoritm was developed by J. Humlicek [1].
// This code is based on fortran code presented by R. J. Wells [2].
// Translated and adapted by Miha D. Puc
//
// To calculate the Faddeeva function with relative error less than 10^(-r).
// r can be set by the the user subject to the constraints 2 <= r <= 5.
//
// [1] J. Humlicek, JQSRT, 21, 437 (1982).
// [2] R.J. Wells "Rapid Approximation to the Voigt/Faddeeva Function and its
// Derivatives" JQSRT 62 (1999), pp 29-48.
// http://www-atm.physics.ox.ac.uk/user/wells/voigt.html
if ((sigma < 0 || lg < 0) || (sigma==0 && lg==0)) {
return 0; // Not meant to be for those who want to be thinner than 0
}
if (sigma == 0) {
return lg * 0.159154943 / (xx*xx + lg*lg /4); //pure Lorentz
}
if (lg == 0) { //pure gauss
return 0.39894228 / sigma * TMath::Exp(-xx*xx / (2*sigma*sigma));
}
Double_t x, y, k;
x = xx / sigma / 1.41421356;
y = lg / 2 / sigma / 1.41421356;
Double_t r0, r1;
if (r < 2) r = 2;
if (r > 5) r = 5;
r0=1.51 * exp(1.144 * (Double_t)r);
r1=1.60 * exp(0.554 * (Double_t)r);
// Constants
const Double_t rrtpi = 0.56418958; // 1/SQRT(pi)
Double_t y0, y0py0, y0q; // for CPF12 algorithm
y0 = 1.5;
y0py0 = y0 + y0;
y0q = y0 * y0;
Double_t c[6] = { 1.0117281, -0.75197147, 0.012557727, 0.010022008, -0.00024206814, 0.00000050084806};
Double_t s[6] = { 1.393237, 0.23115241, -0.15535147, 0.0062183662, 0.000091908299, -0.00000062752596};
Double_t t[6] = { 0.31424038, 0.94778839, 1.5976826, 2.2795071, 3.0206370, 3.8897249};
// Local variables
int j; // Loop variables
int rg1, rg2, rg3; // y polynomial flags
Double_t abx, xq, yq, yrrtpi; // --x--, x^2, y^2, y/SQRT(pi)
Double_t xlim0, xlim1, xlim2, xlim3, xlim4; // --x-- on region boundaries
Double_t a0=0, d0=0, d2=0, e0=0, e2=0, e4=0, h0=0, h2=0, h4=0, h6=0;// W4 temporary variables
Double_t p0=0, p2=0, p4=0, p6=0, p8=0, z0=0, z2=0, z4=0, z6=0, z8=0;
Double_t xp[6], xm[6], yp[6], ym[6]; // CPF12 temporary values
Double_t mq[6], pq[6], mf[6], pf[6];
Double_t d, yf, ypy0, ypy0q;
//***** Start of executable code *****************************************
rg1 = 1; // Set flags
rg2 = 1;
rg3 = 1;
yq = y * y; // y^2
yrrtpi = y * rrtpi; // y/SQRT(pi)
// Region boundaries when both k and L are required or when R<>4
xlim0 = r0 - y;
xlim1 = r1 - y;
xlim3 = 3.097 * y - 0.45;
xlim2 = 6.8 - y;
xlim4 = 18.1 * y + 1.65;
if ( y <= 1e-6 ) { // When y<10^-6 avoid W4 algorithm
xlim1 = xlim0;
xlim2 = xlim0;
}
abx = fabs(x); // |x|
xq = abx * abx; // x^2
if ( abx > xlim0 ) { // Region 0 algorithm
k = yrrtpi / (xq + yq);
} else if ( abx > xlim1 ) { // Humlicek W4 Region 1
if ( rg1 != 0 ) { // First point in Region 1
rg1 = 0;
a0 = yq + 0.5; // Region 1 y-dependents
d0 = a0*a0;
d2 = yq + yq - 1.0;
}
d = rrtpi / (d0 + xq*(d2 + xq));
k = d * y * (a0 + xq);
} else if ( abx > xlim2 ) { // Humlicek W4 Region 2
if ( rg2 != 0 ) { // First point in Region 2
rg2 = 0;
h0 = 0.5625 + yq * (4.5 + yq * (10.5 + yq * (6.0 + yq)));
// Region 2 y-dependents
h2 = -4.5 + yq * (9.0 + yq * ( 6.0 + yq * 4.0));
h4 = 10.5 - yq * (6.0 - yq * 6.0);
h6 = -6.0 + yq * 4.0;
e0 = 1.875 + yq * (8.25 + yq * (5.5 + yq));
e2 = 5.25 + yq * (1.0 + yq * 3.0);
e4 = 0.75 * h6;
}
d = rrtpi / (h0 + xq * (h2 + xq * (h4 + xq * (h6 + xq))));
k = d * y * (e0 + xq * (e2 + xq * (e4 + xq)));
} else if ( abx < xlim3 ) { // Humlicek W4 Region 3
if ( rg3 != 0 ) { // First point in Region 3
rg3 = 0;
z0 = 272.1014 + y * (1280.829 + y *
(2802.870 + y *
(3764.966 + y *
(3447.629 + y *
(2256.981 + y *
(1074.409 + y *
(369.1989 + y *
(88.26741 + y *
(13.39880 + y)
)))))))); // Region 3 y-dependents
z2 = 211.678 + y * (902.3066 + y *
(1758.336 + y *
(2037.310 + y *
(1549.675 + y *
(793.4273 + y *
(266.2987 + y *
(53.59518 + y * 5.0)
))))));
z4 = 78.86585 + y * (308.1852 + y *
(497.3014 + y *
(479.2576 + y *
(269.2916 + y *
(80.39278 + y * 10.0)
))));
z6 = 22.03523 + y * (55.02933 + y *
(92.75679 + y *
(53.59518 + y * 10.0)
));
z8 = 1.496460 + y * (13.39880 + y * 5.0);
p0 = 153.5168 + y * (549.3954 + y *
(919.4955 + y *
(946.8970 + y *
(662.8097 + y *
(328.2151 + y *
(115.3772 + y *
(27.93941 + y *
(4.264678 + y * 0.3183291)
)))))));
p2 = -34.16955 + y * (-1.322256+ y *
(124.5975 + y *
(189.7730 + y *
(139.4665 + y *
(56.81652 + y *
(12.79458 + y * 1.2733163)
)))));
p4 = 2.584042 + y * (10.46332 + y *
(24.01655 + y *
(29.81482 + y *
(12.79568 + y * 1.9099744)
)));
p6 = -0.07272979 + y * (0.9377051 + y *
(4.266322 + y * 1.273316));
p8 = 0.0005480304 + y * 0.3183291;
}
d = 1.7724538 / (z0 + xq * (z2 + xq * (z4 + xq * (z6 + xq * (z8 + xq)))));
k = d * (p0 + xq * (p2 + xq * (p4 + xq * (p6 + xq * p8))));
} else { // Humlicek CPF12 algorithm
ypy0 = y + y0;
ypy0q = ypy0 * ypy0;
k = 0.0;
for (j = 0; j <= 5; j++) {
d = x - t[j];
mq[j] = d * d;
mf[j] = 1.0 / (mq[j] + ypy0q);
xm[j] = mf[j] * d;
ym[j] = mf[j] * ypy0;
d = x + t[j];
pq[j] = d * d;
pf[j] = 1.0 / (pq[j] + ypy0q);
xp[j] = pf[j] * d;
yp[j] = pf[j] * ypy0;
}
if ( abx <= xlim4 ) { // Humlicek CPF12 Region I
for (j = 0; j <= 5; j++) {
k = k + c[j]*(ym[j]+yp[j]) - s[j]*(xm[j]-xp[j]) ;
}
} else { // Humlicek CPF12 Region II
yf = y + y0py0;
for ( j = 0; j <= 5; j++) {
k = k + (c[j] *
(mq[j] * mf[j] - y0 * ym[j])
+ s[j] * yf * xm[j]) / (mq[j]+y0q)
+ (c[j] * (pq[j] * pf[j] - y0 * yp[j])
- s[j] * yf * xp[j]) / (pq[j]+y0q);
}
k = y * k + exp( -xq );
}
}
return k / 2.506628 / sigma; // Normalize by dividing by sqrt(2*pi)*sigma.
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TMath::RootsCubic(const Double_t coef[4],Double_t &a, Double_t &b, Double_t &c)
{
// Computes the roots of a cubic polynomial
// coef: Coefficients
// a,b,c: references to the roots
// Author: Jan Conrad
Double_t pi= TMath::Pi();
Int_t threeroots = 0;
Double_t phi,q,r,s,t,p,d,r1,x,temp;
a = 0.0;
b = 0.0;
c = 0.0;
if (coef[3] == 0) return;
r = coef[2]/coef[3];
s = coef[1]/coef[3];
t = coef[0]/coef[3];
p = (3 * s - r*r)/3;
q = (2 * r*r*r)/27 - (r * s)/3 + t;
d = (p/3)*(p/3)*(p/3) + (q/2)*(q/2);
r1 = q/TMath::Abs(q) * TMath::Sqrt(TMath::Abs(p)/3);
if (p==0) {
q = 8.0;
a = TMath::Power(q,1./3.);
goto done;
}
if ( p < 0) {
if (d <= 0) {
threeroots=1;
phi = TMath::ACos(q/2/(r1*r1*r1));
a = TMath::Cos(phi/3);
b = TMath::Cos(phi/3 + (2 * pi)/3);
c = TMath::Cos(phi/3 + (4 * pi)/3);
} else {
x = q/2/(r1*r1*r1);
phi = TMath::Log(x+TMath::Sqrt(x*x-1));
b = TMath::CosH(phi/3);
}
} else {
x = q/2/(r1*r1*r1);
phi = TMath::Log(x+TMath::Sqrt(x*x+1));
b = TMath::SinH(phi/3);
}
a = (-2*r1)*a-r/3;
b = (-2*r1)*b-r/3;
c = (-2*r1)*c-r/3;
done:
if (threeroots == 1) {
if (a > b){
temp=a;
a=b;
b=temp;
}
if (b > c) {
temp=b;
b=c;
c=temp;
}
if (a > b) {
temp=a;
a=b;
b=temp;
}
}
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Short_t TMath::MinElement(Long64_t n, const Short_t *a)
{
// Return minimum of array a of length n.
return *min_element(a,a+n);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TMath::MinElement(Long64_t n, const Int_t *a)
{
// Return minimum of array a of length n.
return *min_element(a,a+n);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Float_t TMath::MinElement(Long64_t n, const Float_t *a)
{
// Return minimum of array a of length n.
return *min_element(a,a+n);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::MinElement(Long64_t n, const Double_t *a)
{
// Return minimum of array a of length n.
return *min_element(a,a+n);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long_t TMath::MinElement(Long64_t n, const Long_t *a)
{
// Return minimum of array a of length n.
return *min_element(a,a+n);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long64_t TMath::MinElement(Long64_t n, const Long64_t *a)
{
// Return minimum of array a of length n.
return *min_element(a,a+n);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Short_t TMath::MaxElement(Long64_t n, const Short_t *a)
{
// Return maximum of array a of length n.
return *max_element(a,a+n);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TMath::MaxElement(Long64_t n, const Int_t *a)
{
// Return maximum of array a of length n.
return *max_element(a,a+n);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Float_t TMath::MaxElement(Long64_t n, const Float_t *a)
{
// Return maximum of array a of length n.
return *max_element(a,a+n);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::MaxElement(Long64_t n, const Double_t *a)
{
// Return maximum of array a of length n.
return *max_element(a,a+n);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long_t TMath::MaxElement(Long64_t n, const Long_t *a)
{
// Return maximum of array a of length n.
return *max_element(a,a+n);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long64_t TMath::MaxElement(Long64_t n, const Long64_t *a)
{
// Return maximum of array a of length n.
return *max_element(a,a+n);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long64_t TMath::LocMin(Long64_t n, const Short_t *a)
{
// Return index of array with the minimum element.
// If more than one element is minimum returns first found.
if (n <= 0 || !a) return -1;
Short_t xmin = a[0];
Long64_t loc = 0;
for (Long64_t i = 1; i < n; i++) {
if (xmin > a[i]) {
xmin = a[i];
loc = i;
}
}
return loc;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long64_t TMath::LocMin(Long64_t n, const Int_t *a)
{
// Return index of array with the minimum element.
// If more than one element is minimum returns first found.
if (n <= 0 || !a) return -1;
Int_t xmin = a[0];
Long64_t loc = 0;
for (Long64_t i = 1; i < n; i++) {
if (xmin > a[i]) {
xmin = a[i];
loc = i;
}
}
return loc;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long64_t TMath::LocMin(Long64_t n, const Float_t *a)
{
// Return index of array with the minimum element.
// If more than one element is minimum returns first found.
if (n <= 0 || !a) return -1;
Float_t xmin = a[0];
Long64_t loc = 0;
for (Long64_t i = 1; i < n; i++) {
if (xmin > a[i]) {
xmin = a[i];
loc = i;
}
}
return loc;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long64_t TMath::LocMin(Long64_t n, const Double_t *a)
{
// Return index of array with the minimum element.
// If more than one element is minimum returns first found.
if (n <= 0 || !a) return -1;
Double_t xmin = a[0];
Long64_t loc = 0;
for (Long64_t i = 1; i < n; i++) {
if (xmin > a[i]) {
xmin = a[i];
loc = i;
}
}
return loc;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long64_t TMath::LocMin(Long64_t n, const Long_t *a)
{
// Return index of array with the minimum element.
// If more than one element is minimum returns first found.
if (n <= 0 || !a) return -1;
Long_t xmin = a[0];
Long64_t loc = 0;
for (Int_t i = 1; i < n; i++) {
if (xmin > a[i]) {
xmin = a[i];
loc = i;
}
}
return loc;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long64_t TMath::LocMin(Long64_t n, const Long64_t *a)
{
// Return index of array with the minimum element.
// If more than one element is minimum returns first found.
if (n <= 0 || !a) return -1;
Long64_t xmin = a[0];
Long64_t loc = 0;
for (Int_t i = 1; i < n; i++) {
if (xmin > a[i]) {
xmin = a[i];
loc = i;
}
}
return loc;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long64_t TMath::LocMax(Long64_t n, const Short_t *a)
{
// Return index of array with the maximum element.
// If more than one element is maximum returns first found.
if (n <= 0 || !a) return -1;
Short_t xmax = a[0];
Long64_t loc = 0;
for (Long64_t i = 1; i < n; i++) {
if (xmax < a[i]) {
xmax = a[i];
loc = i;
}
}
return loc;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long64_t TMath::LocMax(Long64_t n, const Int_t *a)
{
// Return index of array with the maximum element.
// If more than one element is maximum returns first found.
if (n <= 0 || !a) return -1;
Int_t xmax = a[0];
Long64_t loc = 0;
for (Long64_t i = 1; i < n; i++) {
if (xmax < a[i]) {
xmax = a[i];
loc = i;
}
}
return loc;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long64_t TMath::LocMax(Long64_t n, const Float_t *a)
{
// Return index of array with the maximum element.
// If more than one element is maximum returns first found.
if (n <= 0 || !a) return -1;
Float_t xmax = a[0];
Long64_t loc = 0;
for (Long64_t i = 1; i < n; i++) {
if (xmax < a[i]) {
xmax = a[i];
loc = i;
}
}
return loc;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long64_t TMath::LocMax(Long64_t n, const Double_t *a)
{
// Return index of array with the maximum element.
// If more than one element is maximum returns first found.
if (n <= 0 || !a) return -1;
Double_t xmax = a[0];
Long64_t loc = 0;
for (Long64_t i = 1; i < n; i++) {
if (xmax < a[i]) {
xmax = a[i];
loc = i;
}
}
return loc;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long64_t TMath::LocMax(Long64_t n, const Long64_t *a)
{
// Return index of array with the maximum element.
// If more than one element is maximum returns first found.
if (n <= 0 || !a) return -1;
Long64_t xmax = a[0];
Long64_t loc = 0;
for (Long64_t i = 1; i < n; i++) {
if (xmax < a[i]) {
xmax = a[i];
loc = i;
}
}
return loc;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long64_t TMath::LocMax(Long64_t n, const Long_t *a)
{
// Return index of array with the maximum element.
// If more than one element is maximum returns first found.
if (n <= 0 || !a) return -1;
Long_t xmax = a[0];
Long64_t loc = 0;
for (Long64_t i = 1; i < n; i++) {
if (xmax < a[i]) {
xmax = a[i];
loc = i;
}
}
return loc;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::Mean(Long64_t n, const Short_t *a, const Double_t *w)
{
// Return the weighted mean of an array a with length n.
if (n <= 0 || !a) return 0;
Double_t sum = 0;
Double_t sumw = 0;
if (w) {
for (Long64_t i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (w[i] < 0) {
::Error("TMath::Mean","w[%d] = %.4e < 0 ?!",i,w[i]);
return 0;
}
sum += w[i]*a[i];
sumw += w[i];
}
if (sumw <= 0) {
::Error("TMath::Mean","sum of weights == 0 ?!");
return 0;
}
} else {
sumw = n;
for (Long64_t i = 0; i < n; i++)
sum += a[i];
}
return sum/sumw;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::Mean(Long64_t n, const Int_t *a, const Double_t *w)
{
// Return the weighted mean of an array a with length n.
if (n <= 0 || !a) return 0;
Double_t sum = 0;
Double_t sumw = 0;
if (w) {
for (Long64_t i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (w[i] < 0) {
::Error("TMath::Mean","w[%d] = %.4e < 0 ?!",i,w[i]);
return 0;
}
sum += w[i]*a[i];
sumw += w[i];
}
if (sumw <= 0) {
::Error("TMath::Mean","sum of weights == 0 ?!");
return 0;
}
} else {
sumw = n;
for (Long64_t i = 0; i < n; i++)
sum += a[i];
}
return sum/sumw;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::Mean(Long64_t n, const Float_t *a, const Double_t *w)
{
// Return the weighted mean of an array a with length n.
if (n <= 0 || !a) return 0;
Double_t sum = 0;
Double_t sumw = 0;
if (w) {
for (Long64_t i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (w[i] < 0) {
::Error("TMath::Mean","w[%d] = %.4e < 0 ?!",i,w[i]);
return 0;
}
sum += w[i]*a[i];
sumw += w[i];
}
if (sumw <= 0) {
::Error("TMath::Mean","sum of weights == 0 ?!");
return 0;
}
} else {
sumw = n;
for (Long64_t i = 0; i < n; i++)
sum += a[i];
}
return sum/sumw;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::Mean(Long64_t n, const Double_t *a, const Double_t *w)
{
// Return the weighted mean of an array a with length n.
if (n <= 0 || !a) return 0;
Double_t sum = 0;
Double_t sumw = 0;
if (w) {
for (Long64_t i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (w[i] < 0) {
::Error("TMath::Mean","w[%d] = %.4e < 0 ?!",i,w[i]);
return 0;
}
sum += w[i]*a[i];
sumw += w[i];
}
if (sumw <= 0) {
::Error("TMath::Mean","sum of weights == 0 ?!");
return 0;
}
} else {
sumw = n;
for (Long64_t i = 0; i < n; i++)
sum += a[i];
}
return sum/sumw;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::Mean(Long64_t n, const Long_t *a, const Double_t *w)
{
// Return the weighted mean of an array a with length n.
if (n <= 0 || !a) return 0;
Double_t sum = 0;
Double_t sumw = 0;
if (w) {
for (Long64_t i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (w[i] < 0) {
::Error("TMath::Mean","w[%d] = %.4e < 0 ?!",i,w[i]);
return 0;
}
sum += w[i]*a[i];
sumw += w[i];
}
if (sumw <= 0) {
::Error("TMath::Mean","sum of weights == 0 ?!");
return 0;
}
} else {
sumw = n;
for (Long64_t i = 0; i < n; i++)
sum += a[i];
}
return sum/sumw;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::Mean(Long64_t n, const Long64_t *a, const Double_t *w)
{
// Return the weighted mean of an array a with length n.
if (n <= 0 || !a) return 0;
Double_t sum = 0;
Double_t sumw = 0;
if (w) {
for (Long64_t i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (w[i] < 0) {
::Error("TMath::Mean","w[%d] = %.4e < 0 ?!",i,w[i]);
return 0;
}
sum += w[i]*a[i];
sumw += w[i];
}
if (sumw <= 0) {
::Error("TMath::Mean","sum of weights == 0 ?!");
return 0;
}
} else {
sumw = n;
for (Long64_t i = 0; i < n; i++)
sum += a[i];
}
return sum/sumw;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::GeomMean(Long64_t n, const Short_t *a)
{
// Return the geometric mean of an array a with length n.
// geometric_mean = (Prod_i=0,n-1 |a[i]|)^1/n
if (n <= 0 || !a) return 0;
Double_t logsum = 0.;
for (Long64_t i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (a[i] == 0) return 0.;
Double_t absa = (Double_t) TMath::Abs(a[i]);
logsum += TMath::Log(absa);
}
return TMath::Exp(logsum/n);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::GeomMean(Long64_t n, const Int_t *a)
{
// Return the geometric mean of an array a with length n.
// geometric_mean = (Prod_i=0,n-1 |a[i]|)^1/n
if (n <= 0 || !a) return 0;
Double_t logsum = 0.;
for (Long64_t i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (a[i] == 0) return 0.;
Double_t absa = (Double_t) TMath::Abs(a[i]);
logsum += TMath::Log(absa);
}
return TMath::Exp(logsum/n);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::GeomMean(Long64_t n, const Float_t *a)
{
// Return the geometric mean of an array a with length n.
// geometric_mean = (Prod_i=0,n-1 |a[i]|)^1/n
if (n <= 0 || !a) return 0;
Double_t logsum = 0.;
for (Long64_t i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (a[i] == 0) return 0.;
Double_t absa = (Double_t) TMath::Abs(a[i]);
logsum += TMath::Log(absa);
}
return TMath::Exp(logsum/n);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::GeomMean(Long64_t n, const Double_t *a)
{
// Return the geometric mean of an array a with length n.
// geometric_mean = (Prod_i=0,n-1 |a[i]|)^1/n
if (n <= 0 || !a) return 0;
Double_t logsum = 0.;
for (Long64_t i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (a[i] == 0) return 0.;
Double_t absa = (Double_t) TMath::Abs(a[i]);
logsum += TMath::Log(absa);
}
return TMath::Exp(logsum/n);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::GeomMean(Long64_t n, const Long64_t *a)
{
// Return the geometric mean of an array a with length n.
// geometric_mean = (Prod_i=0,n-1 |a[i]|)^1/n
if (n <= 0 || !a) return 0;
Double_t logsum = 0.;
for (Long64_t i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (a[i] == 0) return 0.;
Double_t absa = (Double_t) TMath::Abs(a[i]);
logsum += TMath::Log(absa);
}
return TMath::Exp(logsum/n);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::GeomMean(Long64_t n, const Long_t *a)
{
// Return the geometric mean of an array a with length n.
// geometric_mean = (Prod_i=0,n-1 |a[i]|)^1/n
if (n <= 0 || !a) return 0;
Double_t logsum = 0.;
for (Long64_t i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (a[i] == 0) return 0.;
Double_t absa = (Double_t) TMath::Abs(a[i]);
logsum += TMath::Log(absa);
}
return TMath::Exp(logsum/n);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
#if defined(_MSC_VER) && (_MSC_VER<1300)
// See also the declarations at the top of this file
template <class Element, class Index, class Size>
Double_t MedianImpStandalone(Size n, const Element *a, const Double_t *w, Index *work)
#else
template <class Element, class Index, class Size>
Double_t TMath::MedianImp(Size n, const Element *a,const Double_t *w, Index *work)
#endif
{
// Return the median of the array a where each entry i has weight w[i] .
// Both arrays have a length of at least n . The median is a number obtained
// from the sorted array a through
//
// median = (a[jl]+a[jh])/2. where (using also the sorted index on the array w)
//
// sum_i=0,jl w[i] <= sumTot/2
// sum_i=0,jh w[i] >= sumTot/2
// sumTot = sum_i=0,n w[i]
//
// If w=0, the algorithm defaults to the median definition where it is
// a number that divides the sorted sequence into 2 halves.
// When n is odd or n > 1000, the median is kth element k = (n + 1) / 2.
// when n is even and n < 1000the median is a mean of the elements k = n/2 and k = n/2 + 1.
//
// If work is supplied, it is used to store the sorting index and assumed to be
// >= n . If work=0, local storage is used, either on the stack if n < kWorkMax
// or on the heap for n >= kWorkMax .
if (n <= 0 || !a) return 0;
Bool_t isAllocated = kFALSE;
Double_t median;
Index *ind;
Index workLocal[kWorkMax];
if (work) {
ind = work;
} else {
ind = workLocal;
if (n > kWorkMax) {
isAllocated = kTRUE;
ind = new Index[n];
}
}
if (w) {
Double_t sumTot2 = 0;
for (Int_t j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (w[j] < 0) {
::Error("TMath::Median","w[%d] = %.4e < 0 ?!",j,w[j]);
return 0;
}
sumTot2 += w[j];
}
sumTot2 /= 2.;
SortImp(n, a, ind, kFALSE);
Double_t sum = 0.;
Int_t jl;
for (jl = 0; jl < n; jl++) {
sum += w[ind[jl]];
if (sum >= sumTot2) break;
}
Int_t jh;
sum = 2.*sumTot2;
for (jh = n-1; jh >= 0; jh--) {
sum -= w[ind[jh]];
if (sum <= sumTot2) break;
}
median = 0.5*(a[ind[jl]]+a[ind[jh]]);
} else {
if (n%2 == 1)
median = KOrdStatImp(n, a,n/2, ind);
else {
median = 0.5*(KOrdStatImp(n, a, n/2 -1, ind)+KOrdStatImp(n, a, n/2, ind));
}
}
if (isAllocated)
delete [] ind;
return median;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::Median(Long64_t n, const Short_t *a, const Double_t *w, Long64_t *work)
{
// Return the median of the array a where each entry i has weight w[i] .
// Both arrays have a length of at least n . The median is a number obtained
// from the sorted array a through
//
// median = (a[jl]+a[jh])/2. where (using also the sorted index on the array w)
//
// sum_i=0,jl w[i] <= sumTot/2
// sum_i=0,jh w[i] >= sumTot/2
// sumTot = sum_i=0,n w[i]
//
// If w=0, the algorithm defaults to the median definition where it is
// a number that divides the sorted sequence into 2 halves.
// When n is odd or n > 1000, the median is kth element k = (n + 1) / 2.
// when n is even and n < 1000the median is a mean of the elements k = n/2 and k = n/2 + 1.
//
// If work is supplied, it is used to store the sorting index and assumed to be
// >= n . If work=0, local storage is used, either on the stack if n < kWorkMax
// or on the heap for n >= kWorkMax .
return MedianImp(n, a, w, work);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::Median(Long64_t n, const Int_t *a, const Double_t *w, Long64_t *work)
{
// Return the median of the array a where each entry i has weight w[i] .
// Both arrays have a length of at least n . The median is a number obtained
// from the sorted array a through
//
// median = (a[jl]+a[jh])/2. where (using also the sorted index on the array w)
//
// sum_i=0,jl w[i] <= sumTot/2
// sum_i=0,jh w[i] >= sumTot/2
// sumTot = sum_i=0,n w[i]
//
// If w=0, the algorithm defaults to the median definition where it is
// a number that divides the sorted sequence into 2 halves.
// When n is odd or n > 1000, the median is kth element k = (n + 1) / 2.
// when n is even and n < 1000the median is a mean of the elements k = n/2 and k = n/2 + 1.
//
// If work is supplied, it is used to store the sorting index and assumed to be
// >= n . If work=0, local storage is used, either on the stack if n < kWorkMax
// or on the heap for n >= kWorkMax .
return MedianImp(n, a, w, work);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::Median(Long64_t n, const Float_t *a, const Double_t *w, Long64_t *work)
{
// Return the median of the array a where each entry i has weight w[i] .
// Both arrays have a length of at least n . The median is a number obtained
// from the sorted array a through
//
// median = (a[jl]+a[jh])/2. where (using also the sorted index on the array w)
//
// sum_i=0,jl w[i] <= sumTot/2
// sum_i=0,jh w[i] >= sumTot/2
// sumTot = sum_i=0,n w[i]
//
// If w=0, the algorithm defaults to the median definition where it is
// a number that divides the sorted sequence into 2 halves.
// When n is odd or n > 1000, the median is kth element k = (n + 1) / 2.
// when n is even and n < 1000the median is a mean of the elements k = n/2 and k = n/2 + 1.
//
// If work is supplied, it is used to store the sorting index and assumed to be
// >= n . If work=0, local storage is used, either on the stack if n < kWorkMax
// or on the heap for n >= kWorkMax .
return MedianImp(n, a, w, work);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::Median(Long64_t n, const Double_t *a, const Double_t *w, Long64_t *work)
{
// Return the median of the array a where each entry i has weight w[i] .
// Both arrays have a length of at least n . The median is a number obtained
// from the sorted array a through
//
// median = (a[jl]+a[jh])/2. where (using also the sorted index on the array w)
//
// sum_i=0,jl w[i] <= sumTot/2
// sum_i=0,jh w[i] >= sumTot/2
// sumTot = sum_i=0,n w[i]
//
// If w=0, the algorithm defaults to the median definition where it is
// a number that divides the sorted sequence into 2 halves.
// When n is odd or n > 1000, the median is kth element k = (n + 1) / 2.
// when n is even and n < 1000the median is a mean of the elements k = n/2 and k = n/2 + 1.
//
// If work is supplied, it is used to store the sorting index and assumed to be
// >= n . If work=0, local storage is used, either on the stack if n < kWorkMax
// or on the heap for n >= kWorkMax .
return MedianImp(n, a, w, work);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::Median(Long64_t n, const Long_t *a, const Double_t *w, Long64_t *work)
{
// Return the median of the array a where each entry i has weight w[i] .
// Both arrays have a length of at least n . The median is a number obtained
// from the sorted array a through
//
// median = (a[jl]+a[jh])/2. where (using also the sorted index on the array w)
//
// sum_i=0,jl w[i] <= sumTot/2
// sum_i=0,jh w[i] >= sumTot/2
// sumTot = sum_i=0,n w[i]
//
// If w=0, the algorithm defaults to the median definition where it is
// a number that divides the sorted sequence into 2 halves.
// When n is odd or n > 1000, the median is kth element k = (n + 1) / 2.
// when n is even and n < 1000the median is a mean of the elements k = n/2 and k = n/2 + 1.
//
// If work is supplied, it is used to store the sorting index and assumed to be
// >= n . If work=0, local storage is used, either on the stack if n < kWorkMax
// or on the heap for n >= kWorkMax .
return MedianImp(n, a, w, work);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::Median(Long64_t n, const Long64_t *a, const Double_t *w, Long64_t *work)
{
// Return the median of the array a where each entry i has weight w[i] .
// Both arrays have a length of at least n . The median is a number obtained
// from the sorted array a through
//
// median = (a[jl]+a[jh])/2. where (using also the sorted index on the array w)
//
// sum_i=0,jl w[i] <= sumTot/2
// sum_i=0,jh w[i] >= sumTot/2
// sumTot = sum_i=0,n w[i]
//
// If w=0, the algorithm defaults to the median definition where it is
// a number that divides the sorted sequence into 2 halves.
// When n is odd or n > 1000, the median is kth element k = (n + 1) / 2.
// when n is even and n < 1000the median is a mean of the elements k = n/2 and k = n/2 + 1.
//
// If work is supplied, it is used to store the sorting index and assumed to be
// >= n . If work=0, local storage is used, either on the stack if n < kWorkMax
// or on the heap for n >= kWorkMax .
return MedianImp(n, a, w, work);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
#if defined(_MSC_VER) && (_MSC_VER<1300)
template <class Element, class Index, class Size>
Element KOrdStatImpStandalone(Size n, const Element *a, Size k, Index *work)
#else
template <class Element, class Index, class Size>
Element TMath::KOrdStatImp(Size n, const Element *a, Size k, Index *work)
#endif
{
// Returns k_th order statistic of the array a of size n
// (k_th smallest element out of n elements).
//
// C-convention is used for array indexing, so if you want
// the second smallest element, call KOrdStat(n, a, 1).
//
// If work is supplied, it is used to store the sorting index and
// assumed to be >= n. If work=0, local storage is used, either on
// the stack if n < kWorkMax or on the heap for n >= kWorkMax.
//
// Taken from "Numerical Recipes in C++" without the index array
// implemented by Anna Khreshuk.
//
// See also the declarations at the top of this file
Bool_t isAllocated = kFALSE;
Size i, ir, j, l, mid;
Index arr;
Index *ind;
Index workLocal[kWorkMax];
Index temp;
if (work) {
ind = work;
} else {
ind = workLocal;
if (n > kWorkMax) {
isAllocated = kTRUE;
ind = new Index[n];
}
}
for (Size ii=0; ii<n; ii++) {
ind[ii]=ii;
}
Size rk = k;
l=0;
ir = n-1;
for(;;) {
if (ir<=l+1) { //active partition contains 1 or 2 elements
if (ir == l+1 && a[ind[ir]]<a[ind[l]])
{temp = ind[l]; ind[l]=ind[ir]; ind[ir]=temp;}
Element tmp = a[ind[rk]];
if (isAllocated)
delete [] ind;
return tmp;
} else {
mid = (l+ir) >> 1; //choose median of left, center and right
{temp = ind[mid]; ind[mid]=ind[l+1]; ind[l+1]=temp;}//elements as partitioning element arr.
if (a[ind[l]]>a[ind[ir]]) //also rearrange so that a[l]<=a[l+1]
{temp = ind[l]; ind[l]=ind[ir]; ind[ir]=temp;}
if (a[ind[l+1]]>a[ind[ir]])
{temp=ind[l+1]; ind[l+1]=ind[ir]; ind[ir]=temp;}
if (a[ind[l]]>a[ind[l+1]])
{temp = ind[l]; ind[l]=ind[l+1]; ind[l+1]=temp;}
i=l+1; //initialize pointers for partitioning
j=ir;
arr = ind[l+1];
for (;;){
do i++; while (a[ind[i]]<a[arr]);
do j--; while (a[ind[j]]>a[arr]);
if (j<i) break; //pointers crossed, partitioning complete
{temp=ind[i]; ind[i]=ind[j]; ind[j]=temp;}
}
ind[l+1]=ind[j];
ind[j]=arr;
if (j>=rk) ir = j-1; //keep active the partition that
if (j<=rk) l=i; //contains the k_th element
}
}
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::KOrdStat(Long64_t n, const Double_t *a, Long64_t k, Long64_t *work)
{
// Returns k_th order statistic of the array a of size n
// (k_th smallest element out of n elements).
//
// C-convention is used for array indexing, so if you want
// the second smallest element, call KOrdStat(n, a, 1).
//
// If work is supplied, it is used to store the sorting index and
// assumed to be >= n. If work=0, local storage is used, either on
// the stack if n < kWorkMax or on the heap for n >= kWorkMax.
return KOrdStatImp(n, a, k, work);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Float_t TMath::KOrdStat(Long64_t n, const Float_t *a, Long64_t k, Long64_t *work)
{
// Returns k_th order statistic of the array a of size n
// (k_th smallest element out of n elements).
//
// C-convention is used for array indexing, so if you want
// the second smallest element, call KOrdStat(n, a, 1).
//
// If work is supplied, it is used to store the sorting index and
// assumed to be >= n. If work=0, local storage is used, either on
// the stack if n < kWorkMax or on the heap for n >= kWorkMax.
return KOrdStatImp(n, a, k, work);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TMath::KOrdStat(Long64_t n, const Int_t *a, Long64_t k, Long64_t *work)
{
// Returns k_th order statistic of the array a of size n
// (k_th smallest element out of n elements).
//
// C-convention is used for array indexing, so if you want
// the second smallest element, call KOrdStat(n, a, 1).
//
// If work is supplied, it is used to store the sorting index and
// assumed to be >= n. If work=0, local storage is used, either on
// the stack if n < kWorkMax or on the heap for n >= kWorkMax.
return KOrdStatImp(n, a, k, work);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Short_t TMath::KOrdStat(Long64_t n, const Short_t *a, Long64_t k, Long64_t *work)
{
// Returns k_th order statistic of the array a of size n
// (k_th smallest element out of n elements).
//
// C-convention is used for array indexing, so if you want
// the second smallest element, call KOrdStat(n, a, 1).
//
// If work is supplied, it is used to store the sorting index and
// assumed to be >= n . If work=0, local storage is used, either on
// the stack if n < kWorkMax or on the heap for n >= kWorkMax.
return KOrdStatImp(n, a, k, work);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long64_t TMath::KOrdStat(Long64_t n, const Long_t *a, Long64_t k, Long64_t *work)
{
// Returns k_th order statistic of the array a of size n
// (k_th smallest element out of n elements).
//
// C-convention is used for array indexing, so if you want
// the second smallest element, call KOrdStat(n, a, 1).
//
// If work is supplied, it is used to store the sorting index and
// assumed to be >= n. If work=0, local storage is used, either on
// the stack if n < kWorkMax or on the heap for n >= kWorkMax.
return KOrdStatImp(n, a, k, work);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long64_t TMath::KOrdStat(Long64_t n, const Long64_t *a, Long64_t k, Long64_t *work)
{
// Returns k_th order statistic of the array a of size n
// (k_th smallest element out of n elements).
//
// C-convention is used for array indexing, so if you want
// the second smallest element, call KOrdStat(n, a, 1).
//
// If work is supplied, it is used to store the sorting index and
// assumed to be >= n. If work=0, local storage is used, either on
// the stack if n < kWorkMax or on the heap for n >= kWorkMax.
return KOrdStatImp(n, a, k, work);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::RMS(Long64_t n, const Short_t *a)
{
// Return the RMS of an array a with length n.
if (n <= 0 || !a) return 0;
Double_t tot = 0, tot2 =0, adouble;
for (Long64_t i=0;i<n;i++) {
adouble=Double_t(a[i]);
tot += adouble; tot2 += adouble*adouble;
}
Double_t n1 = 1./n;
Double_t mean = tot*n1;
Double_t rms = TMath::Sqrt(TMath::Abs(tot2*n1 -mean*mean));
return rms;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::RMS(Long64_t n, const Int_t *a)
{
// Return the RMS of an array a with length n.
if (n <= 0 || !a) return 0;
Double_t tot = 0, tot2 =0, adouble;
for (Long64_t i=0;i<n;i++) {
adouble=Double_t(a[i]);
tot += adouble; tot2 += adouble*adouble;
}
Double_t n1 = 1./n;
Double_t mean = tot*n1;
Double_t rms = TMath::Sqrt(TMath::Abs(tot2*n1 -mean*mean));
return rms;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::RMS(Long64_t n, const Float_t *a)
{
// Return the RMS of an array a with length n.
if (n <= 0 || !a) return 0;
Double_t tot = 0, tot2 =0, adouble;
for (Long64_t i=0;i<n;i++) {
adouble=Double_t(a[i]);
tot += adouble; tot2 += adouble*adouble;
}
Double_t n1 = 1./n;
Double_t mean = tot*n1;
Double_t rms = TMath::Sqrt(TMath::Abs(tot2*n1 -mean*mean));
return rms;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::RMS(Long64_t n, const Double_t *a)
{
// Return the RMS of an array a with length n.
if (n <= 0 || !a) return 0;
Double_t tot = 0, tot2 =0;
for (Long64_t i=0;i<n;i++) {tot += a[i]; tot2 += a[i]*a[i]; }
Double_t n1 = 1./n;
Double_t mean = tot*n1;
Double_t rms = TMath::Sqrt(TMath::Abs(tot2*n1 -mean*mean));
return rms;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::RMS(Long64_t n, const Long_t *a)
{
// Return the RMS of an array a with length n.
if (n <= 0 || !a) return 0;
Double_t tot = 0, tot2 =0, adouble;
for (Long64_t i=0;i<n;i++) {
adouble=Double_t(a[i]);
tot += adouble; tot2 += adouble*adouble;
}
Double_t n1 = 1./n;
Double_t mean = tot*n1;
Double_t rms = TMath::Sqrt(TMath::Abs(tot2*n1 -mean*mean));
return rms;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::RMS(Long64_t n, const Long64_t *a)
{
// Return the RMS of an array a with length n.
if (n <= 0 || !a) return 0;
Double_t tot = 0, tot2 =0, adouble;
for (Long64_t i=0;i<n;i++) {
adouble=Double_t(a[i]);
tot += adouble; tot2 += adouble*adouble;
}
Double_t n1 = 1./n;
Double_t mean = tot*n1;
Double_t rms = TMath::Sqrt(TMath::Abs(tot2*n1 -mean*mean));
return rms;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long64_t TMath::BinarySearch(Long64_t n, const Short_t *array, Short_t value)
{
// Binary search in an array of n values to locate value.
//
// Array is supposed to be sorted prior to this call.
// If match is found, function returns position of element.
// If no match found, function gives nearest element smaller than value.
Long64_t nabove, nbelow, middle;
nabove = n+1;
nbelow = 0;
while(nabove-nbelow > 1) {
middle = (nabove+nbelow)/2;
if (value == array[middle-1]) return middle-1;
if (value < array[middle-1]) nabove = middle;
else nbelow = middle;
}
return nbelow-1;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long64_t TMath::BinarySearch(Long64_t n, const Short_t **array, Short_t value)
{
// Binary search in an array of n values to locate value.
//
// Array is supposed to be sorted prior to this call.
// If match is found, function returns position of element.
// If no match found, function gives nearest element smaller than value.
Long64_t nabove, nbelow, middle;
nabove = n+1;
nbelow = 0;
while(nabove-nbelow > 1) {
middle = (nabove+nbelow)/2;
if (value == *array[middle-1]) return middle-1;
if (value < *array[middle-1]) nabove = middle;
else nbelow = middle;
}
return nbelow-1;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long64_t TMath::BinarySearch(Long64_t n, const Int_t *array, Int_t value)
{
// Binary search in an array of n values to locate value.
//
// Array is supposed to be sorted prior to this call.
// If match is found, function returns position of element.
// If no match found, function gives nearest element smaller than value.
Long64_t nabove, nbelow, middle;
nabove = n+1;
nbelow = 0;
while(nabove-nbelow > 1) {
middle = (nabove+nbelow)/2;
if (value == array[middle-1]) return middle-1;
if (value < array[middle-1]) nabove = middle;
else nbelow = middle;
}
return nbelow-1;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long64_t TMath::BinarySearch(Long64_t n, const Int_t **array, Int_t value)
{
// Binary search in an array of n values to locate value.
//
// Array is supposed to be sorted prior to this call.
// If match is found, function returns position of element.
// If no match found, function gives nearest element smaller than value.
Long64_t nabove, nbelow, middle;
nabove = n+1;
nbelow = 0;
while(nabove-nbelow > 1) {
middle = (nabove+nbelow)/2;
if (value == *array[middle-1]) return middle-1;
if (value < *array[middle-1]) nabove = middle;
else nbelow = middle;
}
return nbelow-1;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long64_t TMath::BinarySearch(Long64_t n, const Float_t *array, Float_t value)
{
// Binary search in an array of n values to locate value.
//
// Array is supposed to be sorted prior to this call.
// If match is found, function returns position of element.
// If no match found, function gives nearest element smaller than value.
Long64_t nabove, nbelow, middle;
nabove = n+1;
nbelow = 0;
while(nabove-nbelow > 1) {
middle = (nabove+nbelow)/2;
if (value == array[middle-1]) return middle-1;
if (value < array[middle-1]) nabove = middle;
else nbelow = middle;
}
return nbelow-1;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long64_t TMath::BinarySearch(Long64_t n, const Float_t **array, Float_t value)
{
// Binary search in an array of n values to locate value.
//
// Array is supposed to be sorted prior to this call.
// If match is found, function returns position of element.
// If no match found, function gives nearest element smaller than value.
Long64_t nabove, nbelow, middle;
nabove = n+1;
nbelow = 0;
while(nabove-nbelow > 1) {
middle = (nabove+nbelow)/2;
if (value == *array[middle-1]) return middle-1;
if (value < *array[middle-1]) nabove = middle;
else nbelow = middle;
}
return nbelow-1;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long64_t TMath::BinarySearch(Long64_t n, const Double_t *array, Double_t value)
{
// Binary search in an array of n values to locate value.
//
// Array is supposed to be sorted prior to this call.
// If match is found, function returns position of element.
// If no match found, function gives nearest element smaller than value.
Long64_t nabove, nbelow, middle;
nabove = n+1;
nbelow = 0;
while(nabove-nbelow > 1) {
middle = (nabove+nbelow)/2;
if (value == array[middle-1]) return middle-1;
if (value < array[middle-1]) nabove = middle;
else nbelow = middle;
}
return nbelow-1;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long64_t TMath::BinarySearch(Long64_t n, const Double_t **array, Double_t value)
{
// Binary search in an array of n values to locate value.
//
// Array is supposed to be sorted prior to this call.
// If match is found, function returns position of element.
// If no match found, function gives nearest element smaller than value.
Long64_t nabove, nbelow, middle;
nabove = n+1;
nbelow = 0;
while(nabove-nbelow > 1) {
middle = (nabove+nbelow)/2;
if (value == *array[middle-1]) return middle-1;
if (value < *array[middle-1]) nabove = middle;
else nbelow = middle;
}
return nbelow-1;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long64_t TMath::BinarySearch(Long64_t n, const Long_t *array, Long_t value)
{
// Binary search in an array of n values to locate value.
//
// Array is supposed to be sorted prior to this call.
// If match is found, function returns position of element.
// If no match found, function gives nearest element smaller than value.
Long64_t nabove, nbelow, middle;
nabove = n+1;
nbelow = 0;
while(nabove-nbelow > 1) {
middle = (nabove+nbelow)/2;
if (value == array[middle-1]) return middle-1;
if (value < array[middle-1]) nabove = middle;
else nbelow = middle;
}
return nbelow-1;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long64_t TMath::BinarySearch(Long64_t n, const Long_t **array, Long_t value)
{
// Binary search in an array of n values to locate value.
//
// Array is supposed to be sorted prior to this call.
// If match is found, function returns position of element.
// If no match found, function gives nearest element smaller than value.
Long64_t nabove, nbelow, middle;
nabove = n+1;
nbelow = 0;
while(nabove-nbelow > 1) {
middle = (nabove+nbelow)/2;
if (value == *array[middle-1]) return middle-1;
if (value < *array[middle-1]) nabove = middle;
else nbelow = middle;
}
return nbelow-1;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long64_t TMath::BinarySearch(Long64_t n, const Long64_t *array, Long64_t value)
{
// Binary search in an array of n values to locate value.
//
// Array is supposed to be sorted prior to this call.
// If match is found, function returns position of element.
// If no match found, function gives nearest element smaller than value.
Long64_t nabove, nbelow, middle;
nabove = n+1;
nbelow = 0;
while(nabove-nbelow > 1) {
middle = (nabove+nbelow)/2;
if (value == array[middle-1]) return middle-1;
if (value < array[middle-1]) nabove = middle;
else nbelow = middle;
}
return nbelow-1;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long64_t TMath::BinarySearch(Long64_t n, const Long64_t **array, Long64_t value)
{
// Binary search in an array of n values to locate value.
//
// Array is supposed to be sorted prior to this call.
// If match is found, function returns position of element.
// If no match found, function gives nearest element smaller than value.
Long64_t nabove, nbelow, middle;
nabove = n+1;
nbelow = 0;
while(nabove-nbelow > 1) {
middle = (nabove+nbelow)/2;
if (value == *array[middle-1]) return middle-1;
if (value < *array[middle-1]) nabove = middle;
else nbelow = middle;
}
return nbelow-1;
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
Bool_t TMath::IsInside(Double_t xp, Double_t yp, Int_t np, Double_t *x, Double_t *y)
{
// Function which returns kTRUE if point xp,yp lies inside the
// polygon defined by the np points in arrays x and y, kFALSE otherwise
// NOTE that the polygon must be a closed polygon (1st and last point
// must be identical).
Double_t xint;
Int_t i;
Int_t inter = 0;
for (i=0;i<np-1;i++) {
if (y[i] == y[i+1]) continue;
if (yp <= y[i] && yp <= y[i+1]) continue;
if (y[i] < yp && y[i+1] < yp) continue;
xint = x[i] + (yp-y[i])*(x[i+1]-x[i])/(y[i+1]-y[i]);
if (xp < xint) inter++;
}
if (inter%2) return kTRUE;
return kFALSE;
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
Bool_t TMath::IsInside(Float_t xp, Float_t yp, Int_t np, Float_t *x, Float_t *y)
{
// Function which returns kTRUE if point xp,yp lies inside the
// polygon defined by the np points in arrays x and y, kFALSE otherwise
// NOTE that the polygon must be a closed polygon (1st and last point
// must be identical).
Double_t xint;
Int_t i;
Int_t inter = 0;
for (i=0;i<np-1;i++) {
if (y[i] == y[i+1]) continue;
if (yp <= y[i] && yp <= y[i+1]) continue;
if (y[i] < yp && y[i+1] < yp) continue;
xint = x[i] + (yp-y[i])*(x[i+1]-x[i])/(y[i+1]-y[i]);
if ((Double_t)xp < xint) inter++;
}
if (inter%2) return kTRUE;
return kFALSE;
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
Bool_t TMath::IsInside(Int_t xp, Int_t yp, Int_t np, Int_t *x, Int_t *y)
{
// Function which returns kTRUE if point xp,yp lies inside the
// polygon defined by the np points in arrays x and y, kFALSE otherwise
// NOTE that the polygon must be a closed polygon (1st and last point
// must be identical).
Double_t xint;
Int_t i;
Int_t inter = 0;
for (i=0;i<np-1;i++) {
if (y[i] == y[i+1]) continue;
if (yp <= y[i] && yp <= y[i+1]) continue;
if (y[i] < yp && y[i+1] < yp) continue;
xint = x[i] + (yp-y[i])*(x[i+1]-x[i])/(y[i+1]-y[i]);
if ((Double_t)xp < xint) inter++;
}
if (inter%2) return kTRUE;
return kFALSE;
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
#if defined(_MSC_VER) && (_MSC_VER<1300)
template <class Element, class Index, class Size>
void SortImpStandalone(Size n1, const Element *a,
Index *index, Bool_t down)
#else
template <class Element, class Index, class Size>
void TMath::SortImp(Size n1, const Element *a,
Index *index, Bool_t down)
#endif
{
// Templated version of the Sort.
//
// Sort the n1 elements of the array a.of Element
// In output the array index contains the indices of the sorted array.
// If down is false sort in increasing order (default is decreasing order).
// This is a translation of the CERNLIB routine sortzv (M101)
// based on the quicksort algorithm.
// NOTE that the array index must be created with a length >= n1
// before calling this function.
//
// See also the declarations at the top of this file.
Size i,i1,n,i2,i3,i33,i222,iswap,n2;
Size i22 = 0;
Element ai;
n = n1;
if (n <= 0 || !a) return;
if (n == 1) {index[0] = 0; return;}
for (i=0;i<n;i++) index[i] = i+1;
for (i1=2;i1<=n;i1++) {
i3 = i1;
i33 = index[i3-1];
ai = a[i33-1];
while(1) {
i2 = i3/2;
if (i2 <= 0) break;
i22 = index[i2-1];
if (ai <= a[i22-1]) break;
index[i3-1] = i22;
i3 = i2;
}
index[i3-1] = i33;
}
while(1) {
i3 = index[n-1];
index[n-1] = index[0];
ai = a[i3-1];
n--;
if(n-1 < 0) {index[0] = i3; break;}
i1 = 1;
while(2) {
i2 = i1+i1;
if (i2 <= n) i22 = index[i2-1];
if (i2-n > 0) {index[i1-1] = i3; break;}
if (i2-n < 0) {
i222 = index[i2];
if (a[i22-1] - a[i222-1] < 0) {
i2++;
i22 = i222;
}
}
if (ai - a[i22-1] > 0) {index[i1-1] = i3; break;}
index[i1-1] = i22;
i1 = i2;
}
}
for (i=0;i<n1;i++) index[i]--;
if (!down) return;
n2 = n1/2;
for (i=0;i<n2;i++) {
iswap = index[i];
index[i] = index[n1-i-1];
index[n1-i-1] = iswap;
}
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
void TMath::Sort(Int_t n1, const Short_t *a, Int_t *index, Bool_t down)
{
// Sort the n1 elements of the Short_t array a.
// In output the array index contains the indices of the sorted array.
// If down is false sort in increasing order (default is decreasing order).
// This is a translation of the CERNLIB routine sortzv (M101)
// based on the quicksort algorithm.
// NOTE that the array index must be created with a length >= n1
// before calling this function.
SortImp(n1,a,index,down);
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
void TMath::Sort(Int_t n1, const Int_t *a, Int_t *index, Bool_t down)
{
// Sort the n1 elements of the Int_t array a.
// In output the array index contains the indices of the sorted array.
// If down is false sort in increasing order (default is decreasing order).
// This is a translation of the CERNLIB routine sortzv (M101)
// based on the quicksort algorithm.
// NOTE that the array index must be created with a length >= n1
// before calling this function.
SortImp(n1,a,index,down);
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
void TMath::Sort(Int_t n1, const Float_t *a, Int_t *index, Bool_t down)
{
// Sort the n1 elements of the Float_t array a.
// In output the array index contains the indices of the sorted array.
// If down is false sort in increasing order (default is decreasing order).
// This is a translation of the CERNLIB routine sortzv (M101)
// based on the quicksort algorithm.
// NOTE that the array index must be created with a length >= n1
// before calling this function.
SortImp(n1,a,index,down);
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
void TMath::Sort(Int_t n1, const Double_t *a, Int_t *index, Bool_t down)
{
// Sort the n1 elements of the Double_t array a.
// In output the array index contains the indices of the sorted array.
// If down is false sort in increasing order (default is decreasing order).
// This is a translation of the CERNLIB routine sortzv (M101)
// based on the quicksort algorithm.
// NOTE that the array index must be created with a length >= n1
// before calling this function.
SortImp(n1,a,index,down);
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
void TMath::Sort(Int_t n1, const Long_t *a, Int_t *index, Bool_t down)
{
// Sort the n1 elements of the Long64_t array a.
// In output the array index contains the indices of the sorted array.
// If down is false sort in increasing order (default is decreasing order).
// This is a translation of the CERNLIB routine sortzv (M101)
// based on the quicksort algorithm.
// NOTE that the array index must be created with a length >= n1
// before calling this function.
SortImp(n1,a,index,down);
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
void TMath::Sort(Int_t n1, const Long64_t *a, Int_t *index, Bool_t down)
{
// Sort the n1 elements of the Long64_t array a.
// In output the array index contains the indices of the sorted array.
// If down is false sort in increasing order (default is decreasing order).
// This is a translation of the CERNLIB routine sortzv (M101)
// based on the quicksort algorithm.
// NOTE that the array index must be created with a length >= n1
// before calling this function.
SortImp(n1,a,index,down);
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
void TMath::Sort(Long64_t n1, const Short_t *a, Long64_t *index, Bool_t down)
{
// Sort the n1 elements of the Short_t array a.
// In output the array index contains the indices of the sorted array.
// If down is false sort in increasing order (default is decreasing order).
// This is a translation of the CERNLIB routine sortzv (M101)
// based on the quicksort algorithm.
// NOTE that the array index must be created with a length >= n1
// before calling this function.
SortImp(n1,a,index,down);
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
void TMath::Sort(Long64_t n1, const Int_t *a, Long64_t *index, Bool_t down)
{
// Sort the n1 elements of the Int_t array a.
// In output the array index contains the indices of the sorted array.
// If down is false sort in increasing order (default is decreasing order).
// This is a translation of the CERNLIB routine sortzv (M101)
// based on the quicksort algorithm.
// NOTE that the array index must be created with a length >= n1
// before calling this function.
SortImp(n1,a,index,down);
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
void TMath::Sort(Long64_t n1, const Float_t *a, Long64_t *index, Bool_t down)
{
// Sort the n1 elements of the Float_t array a.
// In output the array index contains the indices of the sorted array.
// If down is false sort in increasing order (default is decreasing order).
// This is a translation of the CERNLIB routine sortzv (M101)
// based on the quicksort algorithm.
// NOTE that the array index must be created with a length >= n1
// before calling this function.
SortImp(n1,a,index,down);
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
void TMath::Sort(Long64_t n1, const Double_t *a, Long64_t *index, Bool_t down)
{
// Sort the n1 elements of the Double_t array a.
// In output the array index contains the indices of the sorted array.
// If down is false sort in increasing order (default is decreasing order).
// This is a translation of the CERNLIB routine sortzv (M101)
// based on the quicksort algorithm.
// NOTE that the array index must be created with a length >= n1
// before calling this function.
SortImp(n1,a,index,down);
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
void TMath::Sort(Long64_t n1, const Long_t *a, Long64_t *index, Bool_t down)
{
// Sort the n1 elements of the Long64_t array a.
// In output the array index contains the indices of the sorted array.
// If down is false sort in increasing order (default is decreasing order).
// This is a translation of the CERNLIB routine sortzv (M101)
// based on the quicksort algorithm.
// NOTE that the array index must be created with a length >= n1
// before calling this function.
SortImp(n1,a,index,down);
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
void TMath::Sort(Long64_t n1, const Long64_t *a, Long64_t *index, Bool_t down)
{
// Sort the n1 elements of the Long64_t array a.
// In output the array index contains the indices of the sorted array.
// If down is false sort in increasing order (default is decreasing order).
// This is a translation of the CERNLIB routine sortzv (M101)
// based on the quicksort algorithm.
// NOTE that the array index must be created with a length >= n1
// before calling this function.
SortImp(n1,a,index,down);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TMath::BubbleHigh(Int_t Narr, Double_t *arr1, Int_t *arr2)
{
// Bubble sort variant to obtain the order of an array's elements into
// an index in order to do more useful things than the standard built
// in functions.
// *arr1 is unchanged;
// *arr2 is the array of indicies corresponding to the decending value
// of arr1 with arr2[0] corresponding to the largest arr1 value and
// arr2[Narr] the smallest.
//
// Author: Adrian Bevan (bevan@slac.stanford.edu)
// Copyright: Liverpool University, July 2001
if (Narr <= 0) return;
double *localArr1 = new double[Narr];
int *localArr2 = new int[Narr];
int iEl;
int iEl2;
for(iEl = 0; iEl < Narr; iEl++) {
localArr1[iEl] = arr1[iEl];
localArr2[iEl] = iEl;
}
for (iEl = 0; iEl < Narr; iEl++) {
for (iEl2 = Narr-1; iEl2 > iEl; --iEl2) {
if (localArr1[iEl2-1] < localArr1[iEl2]) {
double tmp = localArr1[iEl2-1];
localArr1[iEl2-1] = localArr1[iEl2];
localArr1[iEl2] = tmp;
int tmp2 = localArr2[iEl2-1];
localArr2[iEl2-1] = localArr2[iEl2];
localArr2[iEl2] = tmp2;
}
}
}
for (iEl = 0; iEl < Narr; iEl++) {
arr2[iEl] = localArr2[iEl];
}
delete [] localArr2;
delete [] localArr1;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TMath::BubbleLow(Int_t Narr, Double_t *arr1, Int_t *arr2)
{
// Opposite ordering of the array arr2[] to that of BubbleHigh.
//
// Author: Adrian Bevan (bevan@slac.stanford.edu)
// Copyright: Liverpool University, July 2001
if (Narr <= 0) return;
double *localArr1 = new double[Narr];
int *localArr2 = new int[Narr];
int iEl;
int iEl2;
for (iEl = 0; iEl < Narr; iEl++) {
localArr1[iEl] = arr1[iEl];
localArr2[iEl] = iEl;
}
for (iEl = 0; iEl < Narr; iEl++) {
for (iEl2 = Narr-1; iEl2 > iEl; --iEl2) {
if (localArr1[iEl2-1] > localArr1[iEl2]) {
double tmp = localArr1[iEl2-1];
localArr1[iEl2-1] = localArr1[iEl2];
localArr1[iEl2] = tmp;
int tmp2 = localArr2[iEl2-1];
localArr2[iEl2-1] = localArr2[iEl2];
localArr2[iEl2] = tmp2;
}
}
}
for (iEl = 0; iEl < Narr; iEl++) {
arr2[iEl] = localArr2[iEl];
}
delete [] localArr2;
delete [] localArr1;
}
#ifdef OLD_HASH
//______________________________________________________________________________
ULong_t TMath::Hash(const void *txt, Int_t ntxt)
{
// Calculates hash index from any char string.
// Based on precalculated table of 256 specially selected random numbers.
//
// For string: i = TMath::Hash(string,nstring);
// For int: i = TMath::Hash(&intword,sizeof(int));
// For pointer: i = TMath::Hash(&pointer,sizeof(void*));
//
// Limitation: for ntxt>256 calculates hash only from first 256 bytes
//
// V.Perev
const UChar_t *uc = (const UChar_t*) txt;
ULong_t u = 0, uu = 0;
static ULong_t utab[256] =
{0xb93f6fc0,0x553dfc51,0xb22c1e8c,0x638462c0,0x13e81418,0x2836e171,0x7c4abb90,0xda1a4f39
,0x38f211d1,0x8c804829,0x95a6602d,0x4c590993,0x1810580a,0x721057d4,0x0f587215,0x9f49ce2a
,0xcd5ab255,0xab923a99,0x80890f39,0xbcfa2290,0x16587b52,0x6b6d3f0d,0xea8ff307,0x51542d5c
,0x189bf223,0x39643037,0x0e4a326a,0x214eca01,0x47645a9b,0x0f364260,0x8e9b2da4,0x5563ebd9
,0x57a31c1c,0xab365854,0xdd63ab1f,0x0b89acbd,0x23d57d33,0x1800a0fd,0x225ac60a,0xd0e51943
,0x6c65f669,0xcb966ea0,0xcbafda95,0x2e5c0c5f,0x2988e87e,0xc781cbab,0x3add3dc7,0x693a2c30
,0x42d6c23c,0xebf85f26,0x2544987e,0x2e315e3f,0xac88b5b5,0x7ebd2bbb,0xda07c87b,0x20d460f1
,0xc61c3f40,0x182046e7,0x3b6c3b66,0x2fc10d4a,0x0780dfbb,0xc437280c,0x0988dd07,0xe1498606
,0x8e61d728,0x4f1f3909,0x040a9682,0x49411b29,0x391b0e1c,0xd7905241,0xdd77d95b,0x88426c13
,0x33033e58,0xe158e30e,0x7e342647,0x1e09544b,0x4637353d,0x18ea0924,0x39212b08,0x12580ae8
,0x269a6f06,0x3e10b73b,0x123db33b,0x085412da,0x3bb5f464,0xd9b2d442,0x103d26bb,0xd0038bab
,0x45b6177f,0xfb48f1fe,0x99074c55,0xb545e82e,0x5f79fd0d,0x570f3ae4,0x57e43255,0x037a12ae
,0x4357bdb2,0x337c2c4d,0x2982499d,0x2ab72793,0x3900e7d1,0x57a6bb81,0x7503609b,0x3f39c0d0
,0x717b389d,0x5748034f,0x4698162b,0x5801b97c,0x1dfd5d7e,0xc1386d1c,0xa387a72a,0x084547e4
,0x2e54d8e9,0x2e2f384c,0xe09ccc20,0x8904b71e,0x3e24edc5,0x06a22e16,0x8a2be1df,0x9e5058b2
,0xe01a2f16,0x03325eed,0x587ecfe6,0x584d9cd3,0x32926930,0xe943d68c,0xa9442da8,0xf9650560
,0xf003871e,0x1109c663,0x7a2f2f89,0x1c2210bb,0x37335787,0xb92b382f,0xea605cb5,0x336bbe38
,0x08126bd3,0x1f8c2bd6,0xba6c46f2,0x1a4d1b83,0xc988180d,0xe2582505,0xa8a1b375,0x59a08c49
,0x3db54b48,0x44400f35,0x272d4e7f,0x5579f733,0x98eb590e,0x8ee09813,0x12cc9301,0xc85c402d
,0x135c1039,0x22318128,0x4063c705,0x87a8a3fa,0xfc14431f,0x6e27bf47,0x2d080a19,0x01dba174
,0xe343530b,0xaa1bfced,0x283bb2c8,0x5df250c8,0x4ff9140b,0x045039c1,0xa377780d,0x750f2661
,0x2b108918,0x0b152120,0x3cbc251f,0x5e87b350,0x060625bb,0xe068ba3b,0xdb73ebd7,0x66014ff3
,0xdb003000,0x161a3a0b,0xdc24e142,0x97ea5575,0x635a3cab,0xa719100a,0x256084db,0xc1f4a1e7
,0xe13388f2,0xb8199fc9,0x50c70dc9,0x08154211,0xd60e5220,0xe52c6592,0x584c5fe1,0xfe5e0875
,0x21072b30,0x3370d773,0x92608fe2,0x2d013d93,0x53414b3c,0x2c066142,0x64676644,0x0420887c
,0x35c01187,0x6822119b,0xf9bfe6df,0x273f4ee4,0x87973149,0x7b41282d,0x635d0d1f,0x5f7ecc1e
,0x14c3608a,0x462dfdab,0xc33d8808,0x1dcd995e,0x0fcb11ba,0x11755914,0x5a62044b,0x37f76755
,0x345bd058,0x8831c2b5,0x204a8468,0x3b0b1cd2,0x444e56f4,0x97a93e2c,0xd5f15067,0x266a95fa
,0xff4f8036,0x6160060d,0x930c472f,0xed922184,0x37120251,0xc0add74f,0x1c0bc89d,0x018d47f2
,0xff59ef66,0xd1901a17,0x91f6701b,0x0960082f,0x86f6a8f3,0x1154fecd,0x9867d1de,0x0945482f
,0x790ffcac,0xe5610011,0x4765637e,0xa745dbff,0x841fdcb3,0x4f7372a0,0x3c05013d,0xf1ac4ab7
,0x3bc5b5cc,0x49a73349,0x356a7f67,0x1174f031,0x11d32634,0x4413d301,0x1dd285c4,0x3fae4800
};
if (ntxt > 255) ntxt = 255;
for ( ; ntxt--; uc++) {
uu = uu<<1 ^ utab[(*uc) ^ ntxt];
u ^= uu;
}
return u;
}
#else
//______________________________________________________________________________
ULong_t TMath::Hash(const void *txt, Int_t ntxt)
{
// Calculates hash index from any char string.
// Based on precalculated table of 256 specially selected numbers.
// These numbers are selected in such a way, that for string
// length == 4 (integer number) the hash is unambigous, i.e.
// from hash value we can recalculate input (no degeneration).
//
// The quality of hash method is good enough, that
// "random" numbers made as R = Hash(1), Hash(2), ...Hash(N)
// tested by <R>, <R*R>, <Ri*Ri+1> gives the same result
// as for libc rand().
//
// For string: i = TMath::Hash(string,nstring);
// For int: i = TMath::Hash(&intword,sizeof(int));
// For pointer: i = TMath::Hash(&pointer,sizeof(void*));
//
// V.Perev
static const ULong_t utab[] = {
0xdd367647,0x9caf993f,0x3f3cc5ff,0xfde25082,0x4c764b21,0x89affca7,0x5431965c,0xce22eeec
,0xc61ab4dc,0x59cc93bd,0xed3107e3,0x0b0a287a,0x4712475a,0xce4a4c71,0x352c8403,0x94cb3cee
,0xc3ac509b,0x09f827a2,0xce02e37e,0x7b20bbba,0x76adcedc,0x18c52663,0x19f74103,0x6f30e47b
,0x132ea5a1,0xfdd279e0,0xa3d57d00,0xcff9cb40,0x9617f384,0x6411acfa,0xff908678,0x5c796b2c
,0x4471b62d,0xd38e3275,0xdb57912d,0x26bf953f,0xfc41b2a5,0xe64bcebd,0x190b7839,0x7e8e6a56
,0x9ca22311,0xef28aa60,0xe6b9208e,0xd257fb65,0x45781c2c,0x9a558ac3,0x2743e74d,0x839417a8
,0x06b54d5d,0x1a82bcb4,0x06e97a66,0x70abdd03,0xd163f30d,0x222ed322,0x777bfeda,0xab7a2e83
,0x8494e0cf,0x2dca2d4f,0x78f94278,0x33f04a09,0x402b6452,0x0cd8b709,0xdb72a39e,0x170e00a2
,0x26354faa,0x80e57453,0xcfe8d4e1,0x19e45254,0x04c291c3,0xeb503738,0x425af3bc,0x67836f2a
,0xfac22add,0xfafc2b8c,0x59b8c2a0,0x03e806f9,0xcb4938b9,0xccc942af,0xcee3ae2e,0xfbe748fa
,0xb223a075,0x85c49b5d,0xe4576ac9,0x0fbd46e2,0xb49f9cf5,0xf3e1e86a,0x7d7927fb,0x711afe12
,0xbf61c346,0x157c9956,0x86b6b046,0x2e402146,0xb2a57d8a,0x0d064bb1,0x30ce390c,0x3a3e1eb1
,0xbe7f6f8f,0xd8e30f87,0x5be2813c,0x73a3a901,0xa3aaf967,0x59ff092c,0x1705c798,0xf610dd66
,0xb17da91e,0x8e59534e,0x2211ea5b,0xa804ba03,0xd890efbb,0xb8b48110,0xff390068,0xc8c325b4
,0xf7289c07,0x787e104f,0x3d0df3d0,0x3526796d,0x10548055,0x1d59a42b,0xed1cc5a3,0xdd45372a
,0x31c50d57,0x65757cb7,0x3cfb85be,0xa329910d,0x6ad8ce39,0xa2de44de,0x0dd32432,0xd4a5b617
,0x8f3107fc,0x96485175,0x7f94d4f3,0x35097634,0xdb3ca782,0x2c0290b8,0x2045300b,0xe0f5d15a
,0x0e8cbffa,0xaa1cc38a,0x84008d6f,0xe9a9e794,0x5c602c25,0xfa3658fa,0x98d9d82b,0x3f1497e7
,0x84b6f031,0xe381eff9,0xfc7ae252,0xb239e05d,0xe3723d1f,0xcc3bda82,0xe21b1ad3,0x9104f7c8
,0x4bb2dfcd,0x4d14a8bc,0x6ba7f28c,0x8f89886c,0xad44c97e,0xb30fd975,0x633cdab1,0xf6c2d514
,0x067a49d2,0xdc461ad9,0xebaf9f3f,0x8dc6cac3,0x7a060f16,0xbab063ad,0xf42e25e6,0x60724ca6
,0xc7245c2e,0x4e48ea3c,0x9f89a609,0xa1c49890,0x4bb7f116,0xd722865c,0xa8ee3995,0x0ee070b1
,0xd9bffcc2,0xe55b64f9,0x25507a5a,0xc7a3e2b5,0x5f395f7e,0xe7957652,0x7381ba6a,0xde3d21f1
,0xdf1708dd,0xad0c9d0c,0x00cbc9e5,0x1160e833,0x6779582c,0x29d5d393,0x3f11d7d7,0x826a6b9b
,0xe73ff12f,0x8bad3d86,0xee41d3e5,0x7f0c8917,0x8089ef24,0x90c5cb28,0x2f7f8e6b,0x6966418a
,0x345453fb,0x7a2f8a68,0xf198593d,0xc079a532,0xc1971e81,0x1ab74e26,0x329ef347,0x7423d3d0
,0x942c510b,0x7f6c6382,0x14ae6acc,0x64b59da7,0x2356fa47,0xb6749d9c,0x499de1bb,0x92ffd191
,0xe8f2fb75,0x848dc913,0x3e8727d3,0x1dcffe61,0xb6e45245,0x49055738,0x827a6b55,0xb4788887
,0x7e680125,0xd19ce7ed,0x6b4b8e30,0xa8cadea2,0x216035d8,0x1c63bc3c,0xe1299056,0x1ad3dff4
,0x0aefd13c,0x0e7b921c,0xca0173c6,0x9995782d,0xcccfd494,0xd4b0ac88,0x53d552b1,0x630dae8b
,0xa8332dad,0x7139d9a2,0x5d76f2c4,0x7a4f8f1e,0x8d1aef97,0xd1cf285d,0xc8239153,0xce2608a9
,0x7b562475,0xe4b4bc83,0xf3db0c3a,0x70a65e48,0x6016b302,0xdebd5046,0x707e786a,0x6f10200c
};
static const ULong_t msk[] = { 0x11111111, 0x33333333, 0x77777777, 0xffffffff };
const UChar_t *uc = (const UChar_t *) txt;
ULong_t uu = 0;
union {
ULong_t u;
UShort_t s[2];
} u;
u.u = 0;
Int_t i, idx;
for (i = 0; i < ntxt; i++) {
idx = (uc[i] ^ i) & 255;
uu = (uu << 1) ^ (utab[idx] & msk[i & 3]);
if ((i & 3) == 3) u.u ^= uu;
}
if (i & 3) u.u ^= uu;
u.u *= 1879048201; // prime number
u.s[0] += u.s[1];
u.u *= 1979048191; // prime number
u.s[1] ^= u.s[0];
u.u *= 2079048197; // prime number
return u.u;
}
#endif
//______________________________________________________________________________
ULong_t TMath::Hash(const char *txt)
{
return Hash(txt, Int_t(strlen(txt)));
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::BesselI0(Double_t x)
{
// Compute the modified Bessel function I_0(x) for any real x.
//
//--- NvE 12-mar-2000 UU-SAP Utrecht
// Parameters of the polynomial approximation
const Double_t p1=1.0, p2=3.5156229, p3=3.0899424,
p4=1.2067492, p5=0.2659732, p6=3.60768e-2, p7=4.5813e-3;
const Double_t q1= 0.39894228, q2= 1.328592e-2, q3= 2.25319e-3,
q4=-1.57565e-3, q5= 9.16281e-3, q6=-2.057706e-2,
q7= 2.635537e-2, q8=-1.647633e-2, q9= 3.92377e-3;
const Double_t k1 = 3.75;
Double_t ax = TMath::Abs(x);
Double_t y=0, result=0;
if (ax < k1) {
Double_t xx = x/k1;
y = xx*xx;
result = p1+y*(p2+y*(p3+y*(p4+y*(p5+y*(p6+y*p7)))));
} else {
y = k1/ax;
result = (TMath::Exp(ax)/TMath::Sqrt(ax))*(q1+y*(q2+y*(q3+y*(q4+y*(q5+y*(q6+y*(q7+y*(q8+y*q9))))))));
}
return result;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::BesselK0(Double_t x)
{
// Compute the modified Bessel function K_0(x) for positive real x.
//
// M.Abramowitz and I.A.Stegun, Handbook of Mathematical Functions,
// Applied Mathematics Series vol. 55 (1964), Washington.
//
//--- NvE 12-mar-2000 UU-SAP Utrecht
// Parameters of the polynomial approximation
const Double_t p1=-0.57721566, p2=0.42278420, p3=0.23069756,
p4= 3.488590e-2, p5=2.62698e-3, p6=1.0750e-4, p7=7.4e-6;
const Double_t q1= 1.25331414, q2=-7.832358e-2, q3= 2.189568e-2,
q4=-1.062446e-2, q5= 5.87872e-3, q6=-2.51540e-3, q7=5.3208e-4;
if (x <= 0) {
Error("TMath::BesselK0", "*K0* Invalid argument x = %g\n",x);
return 0;
}
Double_t y=0, result=0;
if (x <= 2) {
y = x*x/4;
result = (-log(x/2.)*TMath::BesselI0(x))+(p1+y*(p2+y*(p3+y*(p4+y*(p5+y*(p6+y*p7))))));
} else {
y = 2/x;
result = (exp(-x)/sqrt(x))*(q1+y*(q2+y*(q3+y*(q4+y*(q5+y*(q6+y*q7))))));
}
return result;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::BesselI1(Double_t x)
{
// Compute the modified Bessel function I_1(x) for any real x.
//
// M.Abramowitz and I.A.Stegun, Handbook of Mathematical Functions,
// Applied Mathematics Series vol. 55 (1964), Washington.
//
//--- NvE 12-mar-2000 UU-SAP Utrecht
// Parameters of the polynomial approximation
const Double_t p1=0.5, p2=0.87890594, p3=0.51498869,
p4=0.15084934, p5=2.658733e-2, p6=3.01532e-3, p7=3.2411e-4;
const Double_t q1= 0.39894228, q2=-3.988024e-2, q3=-3.62018e-3,
q4= 1.63801e-3, q5=-1.031555e-2, q6= 2.282967e-2,
q7=-2.895312e-2, q8= 1.787654e-2, q9=-4.20059e-3;
const Double_t k1 = 3.75;
Double_t ax = TMath::Abs(x);
Double_t y=0, result=0;
if (ax < k1) {
Double_t xx = x/k1;
y = xx*xx;
result = x*(p1+y*(p2+y*(p3+y*(p4+y*(p5+y*(p6+y*p7))))));
} else {
y = k1/ax;
result = (exp(ax)/sqrt(ax))*(q1+y*(q2+y*(q3+y*(q4+y*(q5+y*(q6+y*(q7+y*(q8+y*q9))))))));
if (x < 0) result = -result;
}
return result;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::BesselK1(Double_t x)
{
// Compute the modified Bessel function K_1(x) for positive real x.
//
// M.Abramowitz and I.A.Stegun, Handbook of Mathematical Functions,
// Applied Mathematics Series vol. 55 (1964), Washington.
//
//--- NvE 12-mar-2000 UU-SAP Utrecht
// Parameters of the polynomial approximation
const Double_t p1= 1., p2= 0.15443144, p3=-0.67278579,
p4=-0.18156897, p5=-1.919402e-2, p6=-1.10404e-3, p7=-4.686e-5;
const Double_t q1= 1.25331414, q2= 0.23498619, q3=-3.655620e-2,
q4= 1.504268e-2, q5=-7.80353e-3, q6= 3.25614e-3, q7=-6.8245e-4;
if (x <= 0) {
Error("TMath::BesselK1", "*K1* Invalid argument x = %g\n",x);
return 0;
}
Double_t y=0,result=0;
if (x <= 2) {
y = x*x/4;
result = (log(x/2.)*TMath::BesselI1(x))+(1./x)*(p1+y*(p2+y*(p3+y*(p4+y*(p5+y*(p6+y*p7))))));
} else {
y = 2/x;
result = (exp(-x)/sqrt(x))*(q1+y*(q2+y*(q3+y*(q4+y*(q5+y*(q6+y*q7))))));
}
return result;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::BesselK(Int_t n,Double_t x)
{
// Compute the Integer Order Modified Bessel function K_n(x)
// for n=0,1,2,... and positive real x.
//
//--- NvE 12-mar-2000 UU-SAP Utrecht
if (x <= 0 || n < 0) {
Error("TMath::BesselK", "*K* Invalid argument(s) (n,x) = (%d, %g)\n",n,x);
return 0;
}
if (n==0) return TMath::BesselK0(x);
if (n==1) return TMath::BesselK1(x);
// Perform upward recurrence for all x
Double_t tox = 2/x;
Double_t bkm = TMath::BesselK0(x);
Double_t bk = TMath::BesselK1(x);
Double_t bkp = 0;
for (Int_t j=1; j<n; j++) {
bkp = bkm+Double_t(j)*tox*bk;
bkm = bk;
bk = bkp;
}
return bk;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::BesselI(Int_t n,Double_t x)
{
// Compute the Integer Order Modified Bessel function I_n(x)
// for n=0,1,2,... and any real x.
//
//--- NvE 12-mar-2000 UU-SAP Utrecht
Int_t iacc = 40; // Increase to enhance accuracy
const Double_t kBigPositive = 1.e10;
const Double_t kBigNegative = 1.e-10;
if (n < 0) {
Error("TMath::BesselI", "*I* Invalid argument (n,x) = (%d, %g)\n",n,x);
return 0;
}
if (n==0) return TMath::BesselI0(x);
if (n==1) return TMath::BesselI1(x);
if (x == 0) return 0;
if (TMath::Abs(x) > kBigPositive) return 0;
Double_t tox = 2/TMath::Abs(x);
Double_t bip = 0, bim = 0;
Double_t bi = 1;
Double_t result = 0;
Int_t m = 2*((n+Int_t(sqrt(Float_t(iacc*n)))));
for (Int_t j=m; j>=1; j--) {
bim = bip+Double_t(j)*tox*bi;
bip = bi;
bi = bim;
// Renormalise to prevent overflows
if (TMath::Abs(bi) > kBigPositive) {
result *= kBigNegative;
bi *= kBigNegative;
bip *= kBigNegative;
}
if (j==n) result=bip;
}
result *= TMath::BesselI0(x)/bi; // Normalise with BesselI0(x)
if ((x < 0) && (n%2 == 1)) result = -result;
return result;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::BesselJ0(Double_t x)
{
// Returns the Bessel function J0(x) for any real x.
Double_t ax,z;
Double_t xx,y,result,result1,result2;
const Double_t p1 = 57568490574.0, p2 = -13362590354.0, p3 = 651619640.7;
const Double_t p4 = -11214424.18, p5 = 77392.33017, p6 = -184.9052456;
const Double_t p7 = 57568490411.0, p8 = 1029532985.0, p9 = 9494680.718;
const Double_t p10 = 59272.64853, p11 = 267.8532712;
const Double_t q1 = 0.785398164;
const Double_t q2 = -0.1098628627e-2, q3 = 0.2734510407e-4;
const Double_t q4 = -0.2073370639e-5, q5 = 0.2093887211e-6;
const Double_t q6 = -0.1562499995e-1, q7 = 0.1430488765e-3;
const Double_t q8 = -0.6911147651e-5, q9 = 0.7621095161e-6;
const Double_t q10 = 0.934935152e-7, q11 = 0.636619772;
if ((ax=fabs(x)) < 8) {
y=x*x;
result1 = p1 + y*(p2 + y*(p3 + y*(p4 + y*(p5 + y*p6))));
result2 = p7 + y*(p8 + y*(p9 + y*(p10 + y*(p11 + y))));
result = result1/result2;
} else {
z = 8/ax;
y = z*z;
xx = ax-q1;
result1 = 1 + y*(q2 + y*(q3 + y*(q4 + y*q5)));
result2 = q6 + y*(q7 + y*(q8 + y*(q9 - y*q10)));
result = sqrt(q11/ax)*(cos(xx)*result1-z*sin(xx)*result2);
}
return result;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::BesselJ1(Double_t x)
{
// Returns the Bessel function J1(x) for any real x.
Double_t ax,z;
Double_t xx,y,result,result1,result2;
const Double_t p1 = 72362614232.0, p2 = -7895059235.0, p3 = 242396853.1;
const Double_t p4 = -2972611.439, p5 = 15704.48260, p6 = -30.16036606;
const Double_t p7 = 144725228442.0, p8 = 2300535178.0, p9 = 18583304.74;
const Double_t p10 = 99447.43394, p11 = 376.9991397;
const Double_t q1 = 2.356194491;
const Double_t q2 = 0.183105e-2, q3 = -0.3516396496e-4;
const Double_t q4 = 0.2457520174e-5, q5 = -0.240337019e-6;
const Double_t q6 = 0.04687499995, q7 = -0.2002690873e-3;
const Double_t q8 = 0.8449199096e-5, q9 = -0.88228987e-6;
const Double_t q10 = 0.105787412e-6, q11 = 0.636619772;
if ((ax=fabs(x)) < 8) {
y=x*x;
result1 = x*(p1 + y*(p2 + y*(p3 + y*(p4 + y*(p5 + y*p6)))));
result2 = p7 + y*(p8 + y*(p9 + y*(p10 + y*(p11 + y))));
result = result1/result2;
} else {
z = 8/ax;
y = z*z;
xx = ax-q1;
result1 = 1 + y*(q2 + y*(q3 + y*(q4 + y*q5)));
result2 = q6 + y*(q7 + y*(q8 + y*(q9 + y*q10)));
result = sqrt(q11/ax)*(cos(xx)*result1-z*sin(xx)*result2);
if (x < 0) result = -result;
}
return result;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::BesselY0(Double_t x)
{
// Returns the Bessel function Y0(x) for positive x.
Double_t z,xx,y,result,result1,result2;
const Double_t p1 = -2957821389., p2 = 7062834065.0, p3 = -512359803.6;
const Double_t p4 = 10879881.29, p5 = -86327.92757, p6 = 228.4622733;
const Double_t p7 = 40076544269., p8 = 745249964.8, p9 = 7189466.438;
const Double_t p10 = 47447.26470, p11 = 226.1030244, p12 = 0.636619772;
const Double_t q1 = 0.785398164;
const Double_t q2 = -0.1098628627e-2, q3 = 0.2734510407e-4;
const Double_t q4 = -0.2073370639e-5, q5 = 0.2093887211e-6;
const Double_t q6 = -0.1562499995e-1, q7 = 0.1430488765e-3;
const Double_t q8 = -0.6911147651e-5, q9 = 0.7621095161e-6;
const Double_t q10 = -0.934945152e-7, q11 = 0.636619772;
if (x < 8) {
y = x*x;
result1 = p1 + y*(p2 + y*(p3 + y*(p4 + y*(p5 + y*p6))));
result2 = p7 + y*(p8 + y*(p9 + y*(p10 + y*(p11 + y))));
result = (result1/result2) + p12*TMath::BesselJ0(x)*log(x);
} else {
z = 8/x;
y = z*z;
xx = x-q1;
result1 = 1 + y*(q2 + y*(q3 + y*(q4 + y*q5)));
result2 = q6 + y*(q7 + y*(q8 + y*(q9 + y*q10)));
result = sqrt(q11/x)*(sin(xx)*result1+z*cos(xx)*result2);
}
return result;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::BesselY1(Double_t x)
{
// Returns the Bessel function Y1(x) for positive x.
Double_t z,xx,y,result,result1,result2;
const Double_t p1 = -0.4900604943e13, p2 = 0.1275274390e13;
const Double_t p3 = -0.5153438139e11, p4 = 0.7349264551e9;
const Double_t p5 = -0.4237922726e7, p6 = 0.8511937935e4;
const Double_t p7 = 0.2499580570e14, p8 = 0.4244419664e12;
const Double_t p9 = 0.3733650367e10, p10 = 0.2245904002e8;
const Double_t p11 = 0.1020426050e6, p12 = 0.3549632885e3;
const Double_t p13 = 0.636619772;
const Double_t q1 = 2.356194491;
const Double_t q2 = 0.183105e-2, q3 = -0.3516396496e-4;
const Double_t q4 = 0.2457520174e-5, q5 = -0.240337019e-6;
const Double_t q6 = 0.04687499995, q7 = -0.2002690873e-3;
const Double_t q8 = 0.8449199096e-5, q9 = -0.88228987e-6;
const Double_t q10 = 0.105787412e-6, q11 = 0.636619772;
if (x < 8) {
y=x*x;
result1 = x*(p1 + y*(p2 + y*(p3 + y*(p4 + y*(p5 + y*p6)))));
result2 = p7 + y*(p8 + y*(p9 + y*(p10 + y*(p11 + y*(p12+y)))));
result = (result1/result2) + p13*(TMath::BesselJ1(x)*log(x)-1/x);
} else {
z = 8/x;
y = z*z;
xx = x-q1;
result1 = 1 + y*(q2 + y*(q3 + y*(q4 + y*q5)));
result2 = q6 + y*(q7 + y*(q8 + y*(q9 + y*q10)));
result = sqrt(q11/x)*(sin(xx)*result1+z*cos(xx)*result2);
}
return result;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::StruveH0(Double_t x)
{
// Struve Functions of Order 0
//
// Converted from CERNLIB M342 by Rene Brun.
const Int_t n1 = 15;
const Int_t n2 = 25;
const Double_t c1[16] = { 1.00215845609911981, -1.63969292681309147,
1.50236939618292819, -.72485115302121872,
.18955327371093136, -.03067052022988,
.00337561447375194, -2.6965014312602e-4,
1.637461692612e-5, -7.8244408508e-7,
3.021593188e-8, -9.6326645e-10,
2.579337e-11, -5.8854e-13,
1.158e-14, -2e-16 };
const Double_t c2[26] = { .99283727576423943, -.00696891281138625,
1.8205103787037e-4, -1.063258252844e-5,
9.8198294287e-7, -1.2250645445e-7,
1.894083312e-8, -3.44358226e-9,
7.1119102e-10, -1.6288744e-10,
4.065681e-11, -1.091505e-11,
3.12005e-12, -9.4202e-13,
2.9848e-13, -9.872e-14,
3.394e-14, -1.208e-14,
4.44e-15, -1.68e-15,
6.5e-16, -2.6e-16,
1.1e-16, -4e-17,
2e-17, -1e-17 };
const Double_t c0 = 2/TMath::Pi();
Int_t i;
Double_t alfa, h, r, y, b0, b1, b2;
Double_t v = TMath::Abs(x);
v = TMath::Abs(x);
if (v < 8) {
y = v/8;
h = 2*y*y -1;
alfa = h + h;
b0 = 0;
b1 = 0;
b2 = 0;
for (i = n1; i >= 0; --i) {
b0 = c1[i] + alfa*b1 - b2;
b2 = b1;
b1 = b0;
}
h = y*(b0 - h*b2);
} else {
r = 1/v;
h = 128*r*r -1;
alfa = h + h;
b0 = 0;
b1 = 0;
b2 = 0;
for (i = n2; i >= 0; --i) {
b0 = c2[i] + alfa*b1 - b2;
b2 = b1;
b1 = b0;
}
h = TMath::BesselY0(v) + r*c0*(b0 - h*b2);
}
if (x < 0) h = -h;
return h;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::StruveH1(Double_t x)
{
// Struve Functions of Order 1
//
// Converted from CERNLIB M342 by Rene Brun.
const Int_t n3 = 16;
const Int_t n4 = 22;
const Double_t c3[17] = { .5578891446481605, -.11188325726569816,
-.16337958125200939, .32256932072405902,
-.14581632367244242, .03292677399374035,
-.00460372142093573, 4.434706163314e-4,
-3.142099529341e-5, 1.7123719938e-6,
-7.416987005e-8, 2.61837671e-9,
-7.685839e-11, 1.9067e-12,
-4.052e-14, 7.5e-16,
-1e-17 };
const Double_t c4[23] = { 1.00757647293865641, .00750316051248257,
-7.043933264519e-5, 2.66205393382e-6,
-1.8841157753e-7, 1.949014958e-8,
-2.6126199e-9, 4.236269e-10,
-7.955156e-11, 1.679973e-11,
-3.9072e-12, 9.8543e-13,
-2.6636e-13, 7.645e-14,
-2.313e-14, 7.33e-15,
-2.42e-15, 8.3e-16,
-3e-16, 1.1e-16,
-4e-17, 2e-17,-1e-17 };
const Double_t c0 = 2/TMath::Pi();
const Double_t cc = 2/(3*TMath::Pi());
Int_t i, i1;
Double_t alfa, h, r, y, b0, b1, b2;
Double_t v = TMath::Abs(x);
if (v == 0) {
h = 0;
} else if (v <= 0.3) {
y = v*v;
r = 1;
h = 1;
i1 = (Int_t)(-8. / TMath::Log10(v));
for (i = 1; i <= i1; ++i) {
h = -h*y / ((2*i+ 1)*(2*i + 3));
r += h;
}
h = cc*y*r;
} else if (v < 8) {
h = v*v/32 -1;
alfa = h + h;
b0 = 0;
b1 = 0;
b2 = 0;
for (i = n3; i >= 0; --i) {
b0 = c3[i] + alfa*b1 - b2;
b2 = b1;
b1 = b0;
}
h = b0 - h*b2;
} else {
h = 128/(v*v) -1;
alfa = h + h;
b0 = 0;
b1 = 0;
b2 = 0;
for (i = n4; i >= 0; --i) {
b0 = c4[i] + alfa*b1 - b2;
b2 = b1;
b1 = b0;
}
h = TMath::BesselY1(v) + c0*(b0 - h*b2);
}
return h;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::StruveL0(Double_t x)
{
// Modified Struve Function of Order 0.
// By Kirill Filimonov.
const Double_t pi=TMath::Pi();
Double_t s=1.0;
Double_t r=1.0;
Double_t a0,sl0,a1,bi0;
Int_t km,i;
if (x<=20.) {
a0=2.0*x/pi;
for (int i=1; i<=60;i++) {
r*=(x/(2*i+1))*(x/(2*i+1));
s+=r;
if(TMath::Abs(r/s)<1.e-12) break;
}
sl0=a0*s;
} else {
km=int(5*(x+1.0));
if(x>=50.0)km=25;
for (i=1; i<=km; i++) {
r*=(2*i-1)*(2*i-1)/x/x;
s+=r;
if(TMath::Abs(r/s)<1.0e-12) break;
}
a1=TMath::Exp(x)/TMath::Sqrt(2*pi*x);
r=1.0;
bi0=1.0;
for (i=1; i<=16; i++) {
r=0.125*r*(2.0*i-1.0)*(2.0*i-1.0)/(i*x);
bi0+=r;
if(TMath::Abs(r/bi0)<1.0e-12) break;
}
bi0=a1*bi0;
sl0=-2.0/(pi*x)*s+bi0;
}
return sl0;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::StruveL1(Double_t x)
{
// Modified Struve Function of Order 1.
// By Kirill Filimonov.
const Double_t pi=TMath::Pi();
Double_t a1,sl1,bi1,s;
Double_t r=1.0;
Int_t km,i;
if (x<=20.) {
s=0.0;
for (i=1; i<=60;i++) {
r*=x*x/(4.0*i*i-1.0);
s+=r;
if(TMath::Abs(r)<TMath::Abs(s)*1.e-12) break;
}
sl1=2.0/pi*s;
} else {
s=1.0;
km=int(0.5*x);
if(x>50.0)km=25;
for (i=1; i<=km; i++) {
r*=(2*i+3)*(2*i+1)/x/x;
s+=r;
if(TMath::Abs(r/s)<1.0e-12) break;
}
sl1=2.0/pi*(-1.0+1.0/(x*x)+3.0*s/(x*x*x*x));
a1=TMath::Exp(x)/TMath::Sqrt(2*pi*x);
r=1.0;
bi1=1.0;
for (i=1; i<=16; i++) {
r=-0.125*r*(4.0-(2.0*i-1.0)*(2.0*i-1.0))/(i*x);
bi1+=r;
if(TMath::Abs(r/bi1)<1.0e-12) break;
}
sl1+=a1*bi1;
}
return sl1;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::Beta(Double_t p, Double_t q)
{
// Calculates Beta-function Gamma(p)*Gamma(q)/Gamma(p+q).
return TMath::Exp(TMath::LnGamma(p)+TMath::LnGamma(q)-TMath::LnGamma(p+q));
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::BetaCf(Double_t x, Double_t a, Double_t b)
{
// Continued fraction evaluation by modified Lentz's method
// used in calculation of incomplete Beta function.
Int_t itmax = 500;
Double_t eps = 3.e-14;
Double_t fpmin = 1.e-30;
Int_t m, m2;
Double_t aa, c, d, del, qab, qam, qap;
Double_t h;
qab = a+b;
qap = a+1.0;
qam = a-1.0;
c = 1.0;
d = 1.0 - qab*x/qap;
if (TMath::Abs(d)<fpmin) d=fpmin;
d=1.0/d;
h=d;
for (m=1; m<=itmax; m++) {
m2=m*2;
aa = m*(b-m)*x/((qam+ m2)*(a+m2));
d = 1.0 +aa*d;
if(TMath::Abs(d)<fpmin) d = fpmin;
c = 1 +aa/c;
if (TMath::Abs(c)<fpmin) c = fpmin;
d=1.0/d;
h*=d*c;
aa = -(a+m)*(qab +m)*x/((a+m2)*(qap+m2));
d=1.0+aa*d;
if(TMath::Abs(d)<fpmin) d = fpmin;
c = 1.0 +aa/c;
if (TMath::Abs(c)<fpmin) c = fpmin;
d=1.0/d;
del = d*c;
h*=del;
if (TMath::Abs(del-1)<=eps) break;
}
if (m>itmax) {
Info("TMath::BetaCf", "a or b too big, or itmax too small, a=%g, b=%g, x=%g, h=%g, itmax=%d",
a,b,x,h,itmax);
}
return h;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::BetaDist(Double_t x, Double_t p, Double_t q)
{
// Computes the probability density function of the Beta distribution
// (the distribution function is computed in BetaDistI).
// The first argument is the point, where the function will be
// computed, second and third are the function parameters.
// Since the Beta distribution is bounded on both sides, it's often
// used to represent processes with natural lower and upper limits.
if ((x<0) || (x>1) || (p<=0) || (q<=0)){
Error("TMath::BetaDist", "parameter value outside allowed range");
return 0;
}
Double_t beta = TMath::Beta(p, q);
Double_t r = TMath::Power(x, p-1)*TMath::Power(1-x, q-1)/beta;
return r;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::BetaDistI(Double_t x, Double_t p, Double_t q)
{
// Computes the distribution function of the Beta distribution.
// The first argument is the point, where the function will be
// computed, second and third are the function parameters.
// Since the Beta distribution is bounded on both sides, it's often
// used to represent processes with natural lower and upper limits.
if ((x<0) || (x>1) || (p<=0) || (q<=0)){
Error("TMath::BetaDistI", "parameter value outside allowed range");
return 0;
}
Double_t betai = TMath::BetaIncomplete(x, p, q);
return betai;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::BetaIncomplete(Double_t x, Double_t a, Double_t b)
{
// Calculates the incomplete Beta-function.
// -- implementation by Anna Kreshuk
Double_t bt;
if ((x<0.0)||(x>1.0)) {
Error("TMath::BetaIncomplete", "X must between 0 and 1");
return 0.0;
}
if ((x==0.0)||(x==1.0)) {
bt=0.0;
} else {
bt = TMath::Power(x, a)*TMath::Power(1-x, b)/Beta(a, b);
}
if (x<(a+1)/(a+b+2)) {
return bt*BetaCf(x, a, b)/a;
}
else {
return (1 - bt*BetaCf(1-x, b, a)/b);
}
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::Binomial(Int_t n,Int_t k)
{
// Calculate the binomial coefficient n over k.
if (k==0 || n==k) return 1;
if (n<=0 || k<0 || n<k) return 0;
Int_t k1=TMath::Min(k,n-k);
Int_t k2=n-k1;
Double_t fact=k2+1;
for (Int_t i=k1;i>1;i--)
fact*=static_cast<Double_t>(k2+i)/i;
return fact;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::BinomialI(Double_t p, Int_t n, Int_t k)
{
// Suppose an event occurs with probability _p_ per trial
// Then the probability P of its occuring _k_ or more times
// in _n_ trials is termed a cumulative binomial probability
// the formula is P = sum_from_j=k_to_n(TMath::Binomial(n, j)*
// *TMath::Power(p, j)*TMath::Power(1-p, n-j)
// For _n_ larger than 12 BetaIncomplete is a much better way
// to evaluate the sum than would be the straightforward sum calculation
// for _n_ smaller than 12 either method is acceptable
// ("Numerical Recipes")
// --implementation by Anna Kreshuk
return BetaIncomplete(p, Double_t(k), Double_t(n-k+1));
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::CauchyDist(Double_t x, Double_t t, Double_t s)
{
// Computes the density of Cauchy distribution at point x
// by default, standard Cauchy distribution is used (t=0, s=1)
// t is the location parameter
// s is the scale parameter
// The Cauchy distribution, also called Lorentzian distribution,
// is a continuous distribution describing resonance behavior
// The mean and standard deviation of the Cauchy distribution are undefined.
// The practical meaning of this is that collecting 1,000 data points gives
// no more accurate an estimate of the mean and standard deviation than
// does a single point.
// The formula was taken from "Engineering Statistics Handbook" on site
// http://www.itl.nist.gov/div898/handbook/eda/section3/eda3663.htm
// Implementation by Anna Kreshuk.
// Example:
// TF1* fc = new TF1("fc", "TMath::CauchyDist(x, [0], [1])", -5, 5);
// fc->SetParameters(0, 1);
// fc->Draw();
Double_t temp= (x-t)*(x-t)/(s*s);
Double_t result = 1/(s*TMath::Pi()*(1+temp));
return result;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::ChisquareQuantile(Double_t p, Double_t ndf)
{
// Evaluate the quantiles of the chi-squared probability distribution function.
// Algorithm AS 91 Appl. Statist. (1975) Vol.24, P.35
// implemented by Anna Kreshuk.
// Incorporates the suggested changes in AS R85 (vol.40(1), pp.233-5, 1991)
// Parameters:
// p - the probability value, at which the quantile is computed
// ndf - number of degrees of freedom
Double_t c[]={0, 0.01, 0.222222, 0.32, 0.4, 1.24, 2.2,
4.67, 6.66, 6.73, 13.32, 60.0, 70.0,
84.0, 105.0, 120.0, 127.0, 140.0, 175.0,
210.0, 252.0, 264.0, 294.0, 346.0, 420.0,
462.0, 606.0, 672.0, 707.0, 735.0, 889.0,
932.0, 966.0, 1141.0, 1182.0, 1278.0, 1740.0,
2520.0, 5040.0};
Double_t e = 5e-7;
Double_t aa = 0.6931471806;
Int_t maxit = 20;
Double_t ch, p1, p2, q, t, a, b, x;
Double_t s1, s2, s3, s4, s5, s6;
if (ndf <= 0) return 0;
Double_t g = TMath::LnGamma(0.5*ndf);
Double_t xx = 0.5 * ndf;
Double_t cp = xx - 1;
if (ndf >= TMath::Log(p)*(-c[5])){
//starting approximation for ndf less than or equal to 0.32
if (ndf > c[3]) {
x = TMath::NormQuantile(p);
//starting approximation using Wilson and Hilferty estimate
p1=c[2]/ndf;
ch = ndf*TMath::Power((x*TMath::Sqrt(p1) + 1 - p1), 3);
if (ch > c[6]*ndf + 6)
ch = -2 * (TMath::Log(1-p) - cp * TMath::Log(0.5 * ch) + g);
} else {
ch = c[4];
a = TMath::Log(1-p);
do{
q = ch;
p1 = 1 + ch * (c[7]+ch);
p2 = ch * (c[9] + ch * (c[8] + ch));
t = -0.5 + (c[7] + 2 * ch) / p1 - (c[9] + ch * (c[10] + 3 * ch)) / p2;
ch = ch - (1 - TMath::Exp(a + g + 0.5 * ch + cp * aa) *p2 / p1) / t;
}while (TMath::Abs(q/ch - 1) > c[1]);
}
} else {
ch = TMath::Power((p * xx * TMath::Exp(g + xx * aa)),(1./xx));
if (ch < e) return ch;
}
//call to algorithm AS 239 and calculation of seven term Taylor series
for (Int_t i=0; i<maxit; i++){
q = ch;
p1 = 0.5 * ch;
p2 = p - TMath::Gamma(xx, p1);
t = p2 * TMath::Exp(xx * aa + g + p1 - cp * TMath::Log(ch));
b = t / ch;
a = 0.5 * t - b * cp;
s1 = (c[19] + a * (c[17] + a * (c[14] + a * (c[13] + a * (c[12] +c[11] * a))))) / c[24];
s2 = (c[24] + a * (c[29] + a * (c[32] + a * (c[33] + c[35] * a)))) / c[37];
s3 = (c[19] + a * (c[25] + a * (c[28] + c[31] * a))) / c[37];
s4 = (c[20] + a * (c[27] + c[34] * a) + cp * (c[22] + a * (c[30] + c[36] * a))) / c[38];
s5 = (c[13] + c[21] * a + cp * (c[18] + c[26] * a)) / c[37];
s6 = (c[15] + cp * (c[23] + c[16] * cp)) / c[38];
ch = ch + t * (1 + 0.5 * t * s1 - b * cp * (s1 - b * (s2 - b * (s3 - b * (s4 - b * (s5 - b * s6))))));
if (TMath::Abs(q / ch - 1) > e) break;
}
return ch;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::FDist(Double_t F, Double_t N, Double_t M)
{
// Computes the density function of F-distribution
// (probability function, integral of density, is computed in FDistI).
//
// Parameters N and M stand for degrees of freedom of chi-squares
// mentioned above parameter F is the actual variable x of the
// density function p(x) and the point at which the density function
// is calculated.
//
// About F distribution:
// F-distribution arises in testing whether two random samples
// have the same variance. It is the ratio of two chi-square
// distributions, with N and M degrees of freedom respectively,
// where each chi-square is first divided by it's number of degrees
// of freedom.
// Implementation by Anna Kreshuk.
if ((F<0)||(N<1)||(M<1)){
return 0;
} else {
Double_t denom = TMath::Gamma(N/2)*TMath::Gamma(M/2)*TMath::Power(M+N*F, (N+M)/2);
Double_t div = TMath::Gamma((N+M)/2)*TMath::Power(N, N/2)*TMath::Power(M, M/2)*TMath::Power(F, 0.5*N-1);
return div/denom;
}
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::FDistI(Double_t F, Double_t N, Double_t M)
{
// Calculates the cumulative distribution function of F-distribution,
// this function occurs in the statistical test of whether two observed
// samples have the same variance. For this test a certain statistic F,
// the ratio of observed dispersion of the first sample to that of the
// second sample, is calculated. N and M stand for numbers of degrees
// of freedom in the samples 1-FDistI() is the significance level at
// which the hypothesis "1 has smaller variance than 2" can be rejected.
// A small numerical value of 1 - FDistI() implies a very significant
// rejection, in turn implying high confidence in the hypothesis
// "1 has variance greater than 2".
// Implementation by Anna Kreshuk.
Double_t fi = 1 - BetaIncomplete((M/(M+N*F)), M*0.5, N*0.5);
return fi;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::GammaDist(Double_t x, Double_t gamma, Double_t mu, Double_t beta)
{
// Computes the density function of Gamma distribution at point x.
// gamma - shape parameter
// mu - location parameter
// beta - scale parameter
// The formula was taken from "Engineering Statistics Handbook" on site
// http://www.itl.nist.gov/div898/handbook/eda/section3/eda366b.htm
// Implementation by Anna Kreshuk.
//
/*
*/
//
// which gives the probability that Kolmogorov's test statistic will exceed
// the value z assuming the null hypothesis. This gives a very powerful
// test for comparing two one-dimensional distributions.
// see, for example, Eadie et al, "statistocal Methods in Experimental
// Physics', pp 269-270).
//
// This function returns the confidence level for the null hypothesis, where:
// z = dn*sqrt(n), and
// dn is the maximum deviation between a hypothetical distribution
// function and an experimental distribution with
// n events
//
// NOTE: To compare two experimental distributions with m and n events,
// use z = sqrt(m*n/(m+n))*dn
//
// Accuracy: The function is far too accurate for any imaginable application.
// Probabilities less than 10^-15 are returned as zero.
// However, remember that the formula is only valid for "large" n.
// Theta function inversion formula is used for z <= 1
//
// This function was translated by Rene Brun from PROBKL in CERNLIB.
Double_t fj[4] = {-2,-8,-18,-32}, r[4];
const Double_t w = 2.50662827;
// c1 - -pi**2/8, c2 = 9*c1, c3 = 25*c1
const Double_t c1 = -1.2337005501361697;
const Double_t c2 = -11.103304951225528;
const Double_t c3 = -30.842513753404244;
Double_t u = TMath::Abs(z);
Double_t p;
if (u < 0.2) {
p = 1;
} else if (u < 0.755) {
Double_t v = 1./(u*u);
p = 1 - w*(TMath::Exp(c1*v) + TMath::Exp(c2*v) + TMath::Exp(c3*v))/u;
} else if (u < 6.8116) {
r[1] = 0;
r[2] = 0;
r[3] = 0;
Double_t v = u*u;
Int_t maxj = TMath::Max(1,TMath::Nint(3./u));
for (Int_t j=0; j<maxj;j++) {
r[j] = TMath::Exp(fj[j]*v);
}
p = 2*(r[0] - r[1] +r[2] - r[3]);
} else {
p = 0;
}
return p;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::KolmogorovTest(Int_t na, const Double_t *a, Int_t nb, const Double_t *b, Option_t *option)
{
// Statistical test whether two one-dimensional sets of points are compatible
// with coming from the same parent distribution, using the Kolmogorov test.
// That is, it is used to compare two experimental distributions of unbinned data.
//
// Input:
// a,b: One-dimensional arrays of length na, nb, respectively.
// The elements of a and b must be given in ascending order.
// option is a character string to specify options
// "D" Put out a line of "Debug" printout
// "M" Return the Maximum Kolmogorov distance instead of prob
//
// Output:
// The returned value prob is a calculated confidence level which gives a
// statistical test for compatibility of a and b.
// Values of prob close to zero are taken as indicating a small probability
// of compatibility. For two point sets drawn randomly from the same parent
// distribution, the value of prob should be uniformly distributed between
// zero and one.
// in case of error the function return -1
// If the 2 sets have a different number of points, the minimum of
// the two sets is used.
//
// Method:
// The Kolmogorov test is used. The test statistic is the maximum deviation
// between the two integrated distribution functions, multiplied by the
// normalizing factor (rdmax*sqrt(na*nb/(na+nb)).
//
// Code adapted by Rene Brun from CERNLIB routine TKOLMO (Fred James)
// (W.T. Eadie, D. Drijard, F.E. James, M. Roos and B. Sadoulet,
// Statistical Methods in Experimental Physics, (North-Holland,
// Amsterdam 1971) 269-271)
//
// NOTE1
// A good description of the Kolmogorov test can be seen at:
// http://www.itl.nist.gov/div898/handbook/eda/section3/eda35g.htm
TString opt = option;
opt.ToUpper();
Double_t prob = -1;
// Require at least two points in each graph
if (!a || !b || na <= 2 || nb <= 2) {
Error("KolmogorovTest","Sets must have more than 2 points");
return prob;
}
// Constants needed
Double_t rna = na;
Double_t rnb = nb;
Double_t sa = 1./rna;
Double_t sb = 1./rnb;
Double_t rdiff;
Int_t ia,ib;
// Starting values for main loop
if (a[0] < b[0]) {
rdiff = -sa;
ia = 2;
ib = 1;
} else {
rdiff = sb;
ib = 2;
ia = 1;
}
Double_t rdmax = TMath::Abs(rdiff);
// Main loop over point sets to find max distance
// rdiff is the running difference, and rdmax the max.
Bool_t ok = kFALSE;
for (Int_t i=0;i<na+nb;i++) {
if (a[ia-1] < b[ib-1]) {
rdiff -= sa;
ia++;
if (ia > na) {ok = kTRUE; break;}
} else if (a[ia-1] > b[ib-1]) {
rdiff += sb;
ib++;
if (ib > nb) {ok = kTRUE; break;}
} else {
ia++;
ib++;
if (ia > na) {ok = kTRUE; break;}
if (ib > nb) {ok = kTRUE; break;}
}
rdmax = TMath::Max(rdmax,TMath::Abs(rdiff));
}
// Should never terminate this loop with ok = kFALSE!
if (ok) {
rdmax = TMath::Max(rdmax,TMath::Abs(rdiff));
Double_t z = rdmax * TMath::Sqrt(rna*rnb/(rna+rnb));
prob = TMath::KolmogorovProb(z);
}
// debug printout
if (opt.Contains("D")) {
printf(" Kolmogorov Probability = %g, Max Dist = %g\n",prob,rdmax);
}
if(opt.Contains("M")) return rdmax;
else return prob;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::Voigt(Double_t xx, Double_t sigma, Double_t lg, Int_t r)
{
// Computation of Voigt function (normalised).
// Voigt is a convolution of
// gauss(xx) = 1/(sqrt(2*pi)*sigma) * exp(xx*xx/(2*sigma*sigma)
// and
// lorentz(xx) = (1/pi) * (lg/2) / (xx*xx + g*g/4)
// functions.
//
// The Voigt function is known to be the real part of Faddeeva function also
// called complex error function [2].
//
// The algoritm was developed by J. Humlicek [1].
// This code is based on fortran code presented by R. J. Wells [2].
// Translated and adapted by Miha D. Puc
//
// To calculate the Faddeeva function with relative error less than 10^(-r).
// r can be set by the the user subject to the constraints 2 <= r <= 5.
//
// [1] J. Humlicek, JQSRT, 21, 437 (1982).
// [2] R.J. Wells "Rapid Approximation to the Voigt/Faddeeva Function and its
// Derivatives" JQSRT 62 (1999), pp 29-48.
// http://www-atm.physics.ox.ac.uk/user/wells/voigt.html
if ((sigma < 0 || lg < 0) || (sigma==0 && lg==0)) {
return 0; // Not meant to be for those who want to be thinner than 0
}
if (sigma == 0) {
return lg * 0.159154943 / (xx*xx + lg*lg /4); //pure Lorentz
}
if (lg == 0) { //pure gauss
return 0.39894228 / sigma * TMath::Exp(-xx*xx / (2*sigma*sigma));
}
Double_t x, y, k;
x = xx / sigma / 1.41421356;
y = lg / 2 / sigma / 1.41421356;
Double_t r0, r1;
if (r < 2) r = 2;
if (r > 5) r = 5;
r0=1.51 * exp(1.144 * (Double_t)r);
r1=1.60 * exp(0.554 * (Double_t)r);
// Constants
const Double_t rrtpi = 0.56418958; // 1/SQRT(pi)
Double_t y0, y0py0, y0q; // for CPF12 algorithm
y0 = 1.5;
y0py0 = y0 + y0;
y0q = y0 * y0;
Double_t c[6] = { 1.0117281, -0.75197147, 0.012557727, 0.010022008, -0.00024206814, 0.00000050084806};
Double_t s[6] = { 1.393237, 0.23115241, -0.15535147, 0.0062183662, 0.000091908299, -0.00000062752596};
Double_t t[6] = { 0.31424038, 0.94778839, 1.5976826, 2.2795071, 3.0206370, 3.8897249};
// Local variables
int j; // Loop variables
int rg1, rg2, rg3; // y polynomial flags
Double_t abx, xq, yq, yrrtpi; // --x--, x^2, y^2, y/SQRT(pi)
Double_t xlim0, xlim1, xlim2, xlim3, xlim4; // --x-- on region boundaries
Double_t a0=0, d0=0, d2=0, e0=0, e2=0, e4=0, h0=0, h2=0, h4=0, h6=0;// W4 temporary variables
Double_t p0=0, p2=0, p4=0, p6=0, p8=0, z0=0, z2=0, z4=0, z6=0, z8=0;
Double_t xp[6], xm[6], yp[6], ym[6]; // CPF12 temporary values
Double_t mq[6], pq[6], mf[6], pf[6];
Double_t d, yf, ypy0, ypy0q;
//***** Start of executable code *****************************************
rg1 = 1; // Set flags
rg2 = 1;
rg3 = 1;
yq = y * y; // y^2
yrrtpi = y * rrtpi; // y/SQRT(pi)
// Region boundaries when both k and L are required or when R<>4
xlim0 = r0 - y;
xlim1 = r1 - y;
xlim3 = 3.097 * y - 0.45;
xlim2 = 6.8 - y;
xlim4 = 18.1 * y + 1.65;
if ( y <= 1e-6 ) { // When y<10^-6 avoid W4 algorithm
xlim1 = xlim0;
xlim2 = xlim0;
}
abx = fabs(x); // |x|
xq = abx * abx; // x^2
if ( abx > xlim0 ) { // Region 0 algorithm
k = yrrtpi / (xq + yq);
} else if ( abx > xlim1 ) { // Humlicek W4 Region 1
if ( rg1 != 0 ) { // First point in Region 1
rg1 = 0;
a0 = yq + 0.5; // Region 1 y-dependents
d0 = a0*a0;
d2 = yq + yq - 1.0;
}
d = rrtpi / (d0 + xq*(d2 + xq));
k = d * y * (a0 + xq);
} else if ( abx > xlim2 ) { // Humlicek W4 Region 2
if ( rg2 != 0 ) { // First point in Region 2
rg2 = 0;
h0 = 0.5625 + yq * (4.5 + yq * (10.5 + yq * (6.0 + yq)));
// Region 2 y-dependents
h2 = -4.5 + yq * (9.0 + yq * ( 6.0 + yq * 4.0));
h4 = 10.5 - yq * (6.0 - yq * 6.0);
h6 = -6.0 + yq * 4.0;
e0 = 1.875 + yq * (8.25 + yq * (5.5 + yq));
e2 = 5.25 + yq * (1.0 + yq * 3.0);
e4 = 0.75 * h6;
}
d = rrtpi / (h0 + xq * (h2 + xq * (h4 + xq * (h6 + xq))));
k = d * y * (e0 + xq * (e2 + xq * (e4 + xq)));
} else if ( abx < xlim3 ) { // Humlicek W4 Region 3
if ( rg3 != 0 ) { // First point in Region 3
rg3 = 0;
z0 = 272.1014 + y * (1280.829 + y *
(2802.870 + y *
(3764.966 + y *
(3447.629 + y *
(2256.981 + y *
(1074.409 + y *
(369.1989 + y *
(88.26741 + y *
(13.39880 + y)
)))))))); // Region 3 y-dependents
z2 = 211.678 + y * (902.3066 + y *
(1758.336 + y *
(2037.310 + y *
(1549.675 + y *
(793.4273 + y *
(266.2987 + y *
(53.59518 + y * 5.0)
))))));
z4 = 78.86585 + y * (308.1852 + y *
(497.3014 + y *
(479.2576 + y *
(269.2916 + y *
(80.39278 + y * 10.0)
))));
z6 = 22.03523 + y * (55.02933 + y *
(92.75679 + y *
(53.59518 + y * 10.0)
));
z8 = 1.496460 + y * (13.39880 + y * 5.0);
p0 = 153.5168 + y * (549.3954 + y *
(919.4955 + y *
(946.8970 + y *
(662.8097 + y *
(328.2151 + y *
(115.3772 + y *
(27.93941 + y *
(4.264678 + y * 0.3183291)
)))))));
p2 = -34.16955 + y * (-1.322256+ y *
(124.5975 + y *
(189.7730 + y *
(139.4665 + y *
(56.81652 + y *
(12.79458 + y * 1.2733163)
)))));
p4 = 2.584042 + y * (10.46332 + y *
(24.01655 + y *
(29.81482 + y *
(12.79568 + y * 1.9099744)
)));
p6 = -0.07272979 + y * (0.9377051 + y *
(4.266322 + y * 1.273316));
p8 = 0.0005480304 + y * 0.3183291;
}
d = 1.7724538 / (z0 + xq * (z2 + xq * (z4 + xq * (z6 + xq * (z8 + xq)))));
k = d * (p0 + xq * (p2 + xq * (p4 + xq * (p6 + xq * p8))));
} else { // Humlicek CPF12 algorithm
ypy0 = y + y0;
ypy0q = ypy0 * ypy0;
k = 0.0;
for (j = 0; j <= 5; j++) {
d = x - t[j];
mq[j] = d * d;
mf[j] = 1.0 / (mq[j] + ypy0q);
xm[j] = mf[j] * d;
ym[j] = mf[j] * ypy0;
d = x + t[j];
pq[j] = d * d;
pf[j] = 1.0 / (pq[j] + ypy0q);
xp[j] = pf[j] * d;
yp[j] = pf[j] * ypy0;
}
if ( abx <= xlim4 ) { // Humlicek CPF12 Region I
for (j = 0; j <= 5; j++) {
k = k + c[j]*(ym[j]+yp[j]) - s[j]*(xm[j]-xp[j]) ;
}
} else { // Humlicek CPF12 Region II
yf = y + y0py0;
for ( j = 0; j <= 5; j++) {
k = k + (c[j] *
(mq[j] * mf[j] - y0 * ym[j])
+ s[j] * yf * xm[j]) / (mq[j]+y0q)
+ (c[j] * (pq[j] * pf[j] - y0 * yp[j])
- s[j] * yf * xp[j]) / (pq[j]+y0q);
}
k = y * k + exp( -xq );
}
}
return k / 2.506628 / sigma; // Normalize by dividing by sqrt(2*pi)*sigma.
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TMath::RootsCubic(const Double_t coef[4],Double_t &a, Double_t &b, Double_t &c)
{
// Computes the roots of a cubic polynomial
// coef: Coefficients
// a,b,c: references to the roots
// Author: Jan Conrad
Double_t pi= TMath::Pi();
Int_t threeroots = 0;
Double_t phi,q,r,s,t,p,d,r1,x,temp;
a = 0.0;
b = 0.0;
c = 0.0;
if (coef[3] == 0) return;
r = coef[2]/coef[3];
s = coef[1]/coef[3];
t = coef[0]/coef[3];
p = (3 * s - r*r)/3;
q = (2 * r*r*r)/27 - (r * s)/3 + t;
d = (p/3)*(p/3)*(p/3) + (q/2)*(q/2);
r1 = q/TMath::Abs(q) * TMath::Sqrt(TMath::Abs(p)/3);
if (p==0) {
q = 8.0;
a = TMath::Power(q,1./3.);
goto done;
}
if ( p < 0) {
if (d <= 0) {
threeroots=1;
phi = TMath::ACos(q/2/(r1*r1*r1));
a = TMath::Cos(phi/3);
b = TMath::Cos(phi/3 + (2 * pi)/3);
c = TMath::Cos(phi/3 + (4 * pi)/3);
} else {
x = q/2/(r1*r1*r1);
phi = TMath::Log(x+TMath::Sqrt(x*x-1));
b = TMath::CosH(phi/3);
}
} else {
x = q/2/(r1*r1*r1);
phi = TMath::Log(x+TMath::Sqrt(x*x+1));
b = TMath::SinH(phi/3);
}
a = (-2*r1)*a-r/3;
b = (-2*r1)*b-r/3;
c = (-2*r1)*c-r/3;
done:
if (threeroots == 1) {
if (a > b){
temp=a;
a=b;
b=temp;
}
if (b > c) {
temp=b;
b=c;
c=temp;
}
if (a > b) {
temp=a;
a=b;
b=temp;
}
}
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Short_t TMath::MinElement(Long64_t n, const Short_t *a)
{
// Return minimum of array a of length n.
return *min_element(a,a+n);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TMath::MinElement(Long64_t n, const Int_t *a)
{
// Return minimum of array a of length n.
return *min_element(a,a+n);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Float_t TMath::MinElement(Long64_t n, const Float_t *a)
{
// Return minimum of array a of length n.
return *min_element(a,a+n);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::MinElement(Long64_t n, const Double_t *a)
{
// Return minimum of array a of length n.
return *min_element(a,a+n);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long_t TMath::MinElement(Long64_t n, const Long_t *a)
{
// Return minimum of array a of length n.
return *min_element(a,a+n);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long64_t TMath::MinElement(Long64_t n, const Long64_t *a)
{
// Return minimum of array a of length n.
return *min_element(a,a+n);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Short_t TMath::MaxElement(Long64_t n, const Short_t *a)
{
// Return maximum of array a of length n.
return *max_element(a,a+n);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TMath::MaxElement(Long64_t n, const Int_t *a)
{
// Return maximum of array a of length n.
return *max_element(a,a+n);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Float_t TMath::MaxElement(Long64_t n, const Float_t *a)
{
// Return maximum of array a of length n.
return *max_element(a,a+n);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::MaxElement(Long64_t n, const Double_t *a)
{
// Return maximum of array a of length n.
return *max_element(a,a+n);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long_t TMath::MaxElement(Long64_t n, const Long_t *a)
{
// Return maximum of array a of length n.
return *max_element(a,a+n);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long64_t TMath::MaxElement(Long64_t n, const Long64_t *a)
{
// Return maximum of array a of length n.
return *max_element(a,a+n);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long64_t TMath::LocMin(Long64_t n, const Short_t *a)
{
// Return index of array with the minimum element.
// If more than one element is minimum returns first found.
if (n <= 0 || !a) return -1;
Short_t xmin = a[0];
Long64_t loc = 0;
for (Long64_t i = 1; i < n; i++) {
if (xmin > a[i]) {
xmin = a[i];
loc = i;
}
}
return loc;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long64_t TMath::LocMin(Long64_t n, const Int_t *a)
{
// Return index of array with the minimum element.
// If more than one element is minimum returns first found.
if (n <= 0 || !a) return -1;
Int_t xmin = a[0];
Long64_t loc = 0;
for (Long64_t i = 1; i < n; i++) {
if (xmin > a[i]) {
xmin = a[i];
loc = i;
}
}
return loc;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long64_t TMath::LocMin(Long64_t n, const Float_t *a)
{
// Return index of array with the minimum element.
// If more than one element is minimum returns first found.
if (n <= 0 || !a) return -1;
Float_t xmin = a[0];
Long64_t loc = 0;
for (Long64_t i = 1; i < n; i++) {
if (xmin > a[i]) {
xmin = a[i];
loc = i;
}
}
return loc;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long64_t TMath::LocMin(Long64_t n, const Double_t *a)
{
// Return index of array with the minimum element.
// If more than one element is minimum returns first found.
if (n <= 0 || !a) return -1;
Double_t xmin = a[0];
Long64_t loc = 0;
for (Long64_t i = 1; i < n; i++) {
if (xmin > a[i]) {
xmin = a[i];
loc = i;
}
}
return loc;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long64_t TMath::LocMin(Long64_t n, const Long_t *a)
{
// Return index of array with the minimum element.
// If more than one element is minimum returns first found.
if (n <= 0 || !a) return -1;
Long_t xmin = a[0];
Long64_t loc = 0;
for (Int_t i = 1; i < n; i++) {
if (xmin > a[i]) {
xmin = a[i];
loc = i;
}
}
return loc;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long64_t TMath::LocMin(Long64_t n, const Long64_t *a)
{
// Return index of array with the minimum element.
// If more than one element is minimum returns first found.
if (n <= 0 || !a) return -1;
Long64_t xmin = a[0];
Long64_t loc = 0;
for (Int_t i = 1; i < n; i++) {
if (xmin > a[i]) {
xmin = a[i];
loc = i;
}
}
return loc;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long64_t TMath::LocMax(Long64_t n, const Short_t *a)
{
// Return index of array with the maximum element.
// If more than one element is maximum returns first found.
if (n <= 0 || !a) return -1;
Short_t xmax = a[0];
Long64_t loc = 0;
for (Long64_t i = 1; i < n; i++) {
if (xmax < a[i]) {
xmax = a[i];
loc = i;
}
}
return loc;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long64_t TMath::LocMax(Long64_t n, const Int_t *a)
{
// Return index of array with the maximum element.
// If more than one element is maximum returns first found.
if (n <= 0 || !a) return -1;
Int_t xmax = a[0];
Long64_t loc = 0;
for (Long64_t i = 1; i < n; i++) {
if (xmax < a[i]) {
xmax = a[i];
loc = i;
}
}
return loc;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long64_t TMath::LocMax(Long64_t n, const Float_t *a)
{
// Return index of array with the maximum element.
// If more than one element is maximum returns first found.
if (n <= 0 || !a) return -1;
Float_t xmax = a[0];
Long64_t loc = 0;
for (Long64_t i = 1; i < n; i++) {
if (xmax < a[i]) {
xmax = a[i];
loc = i;
}
}
return loc;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long64_t TMath::LocMax(Long64_t n, const Double_t *a)
{
// Return index of array with the maximum element.
// If more than one element is maximum returns first found.
if (n <= 0 || !a) return -1;
Double_t xmax = a[0];
Long64_t loc = 0;
for (Long64_t i = 1; i < n; i++) {
if (xmax < a[i]) {
xmax = a[i];
loc = i;
}
}
return loc;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long64_t TMath::LocMax(Long64_t n, const Long64_t *a)
{
// Return index of array with the maximum element.
// If more than one element is maximum returns first found.
if (n <= 0 || !a) return -1;
Long64_t xmax = a[0];
Long64_t loc = 0;
for (Long64_t i = 1; i < n; i++) {
if (xmax < a[i]) {
xmax = a[i];
loc = i;
}
}
return loc;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long64_t TMath::LocMax(Long64_t n, const Long_t *a)
{
// Return index of array with the maximum element.
// If more than one element is maximum returns first found.
if (n <= 0 || !a) return -1;
Long_t xmax = a[0];
Long64_t loc = 0;
for (Long64_t i = 1; i < n; i++) {
if (xmax < a[i]) {
xmax = a[i];
loc = i;
}
}
return loc;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::Mean(Long64_t n, const Short_t *a, const Double_t *w)
{
// Return the weighted mean of an array a with length n.
if (n <= 0 || !a) return 0;
Double_t sum = 0;
Double_t sumw = 0;
if (w) {
for (Long64_t i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (w[i] < 0) {
::Error("TMath::Mean","w[%d] = %.4e < 0 ?!",i,w[i]);
return 0;
}
sum += w[i]*a[i];
sumw += w[i];
}
if (sumw <= 0) {
::Error("TMath::Mean","sum of weights == 0 ?!");
return 0;
}
} else {
sumw = n;
for (Long64_t i = 0; i < n; i++)
sum += a[i];
}
return sum/sumw;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::Mean(Long64_t n, const Int_t *a, const Double_t *w)
{
// Return the weighted mean of an array a with length n.
if (n <= 0 || !a) return 0;
Double_t sum = 0;
Double_t sumw = 0;
if (w) {
for (Long64_t i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (w[i] < 0) {
::Error("TMath::Mean","w[%d] = %.4e < 0 ?!",i,w[i]);
return 0;
}
sum += w[i]*a[i];
sumw += w[i];
}
if (sumw <= 0) {
::Error("TMath::Mean","sum of weights == 0 ?!");
return 0;
}
} else {
sumw = n;
for (Long64_t i = 0; i < n; i++)
sum += a[i];
}
return sum/sumw;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::Mean(Long64_t n, const Float_t *a, const Double_t *w)
{
// Return the weighted mean of an array a with length n.
if (n <= 0 || !a) return 0;
Double_t sum = 0;
Double_t sumw = 0;
if (w) {
for (Long64_t i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (w[i] < 0) {
::Error("TMath::Mean","w[%d] = %.4e < 0 ?!",i,w[i]);
return 0;
}
sum += w[i]*a[i];
sumw += w[i];
}
if (sumw <= 0) {
::Error("TMath::Mean","sum of weights == 0 ?!");
return 0;
}
} else {
sumw = n;
for (Long64_t i = 0; i < n; i++)
sum += a[i];
}
return sum/sumw;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::Mean(Long64_t n, const Double_t *a, const Double_t *w)
{
// Return the weighted mean of an array a with length n.
if (n <= 0 || !a) return 0;
Double_t sum = 0;
Double_t sumw = 0;
if (w) {
for (Long64_t i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (w[i] < 0) {
::Error("TMath::Mean","w[%d] = %.4e < 0 ?!",i,w[i]);
return 0;
}
sum += w[i]*a[i];
sumw += w[i];
}
if (sumw <= 0) {
::Error("TMath::Mean","sum of weights == 0 ?!");
return 0;
}
} else {
sumw = n;
for (Long64_t i = 0; i < n; i++)
sum += a[i];
}
return sum/sumw;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::Mean(Long64_t n, const Long_t *a, const Double_t *w)
{
// Return the weighted mean of an array a with length n.
if (n <= 0 || !a) return 0;
Double_t sum = 0;
Double_t sumw = 0;
if (w) {
for (Long64_t i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (w[i] < 0) {
::Error("TMath::Mean","w[%d] = %.4e < 0 ?!",i,w[i]);
return 0;
}
sum += w[i]*a[i];
sumw += w[i];
}
if (sumw <= 0) {
::Error("TMath::Mean","sum of weights == 0 ?!");
return 0;
}
} else {
sumw = n;
for (Long64_t i = 0; i < n; i++)
sum += a[i];
}
return sum/sumw;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::Mean(Long64_t n, const Long64_t *a, const Double_t *w)
{
// Return the weighted mean of an array a with length n.
if (n <= 0 || !a) return 0;
Double_t sum = 0;
Double_t sumw = 0;
if (w) {
for (Long64_t i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (w[i] < 0) {
::Error("TMath::Mean","w[%d] = %.4e < 0 ?!",i,w[i]);
return 0;
}
sum += w[i]*a[i];
sumw += w[i];
}
if (sumw <= 0) {
::Error("TMath::Mean","sum of weights == 0 ?!");
return 0;
}
} else {
sumw = n;
for (Long64_t i = 0; i < n; i++)
sum += a[i];
}
return sum/sumw;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::GeomMean(Long64_t n, const Short_t *a)
{
// Return the geometric mean of an array a with length n.
// geometric_mean = (Prod_i=0,n-1 |a[i]|)^1/n
if (n <= 0 || !a) return 0;
Double_t logsum = 0.;
for (Long64_t i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (a[i] == 0) return 0.;
Double_t absa = (Double_t) TMath::Abs(a[i]);
logsum += TMath::Log(absa);
}
return TMath::Exp(logsum/n);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::GeomMean(Long64_t n, const Int_t *a)
{
// Return the geometric mean of an array a with length n.
// geometric_mean = (Prod_i=0,n-1 |a[i]|)^1/n
if (n <= 0 || !a) return 0;
Double_t logsum = 0.;
for (Long64_t i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (a[i] == 0) return 0.;
Double_t absa = (Double_t) TMath::Abs(a[i]);
logsum += TMath::Log(absa);
}
return TMath::Exp(logsum/n);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::GeomMean(Long64_t n, const Float_t *a)
{
// Return the geometric mean of an array a with length n.
// geometric_mean = (Prod_i=0,n-1 |a[i]|)^1/n
if (n <= 0 || !a) return 0;
Double_t logsum = 0.;
for (Long64_t i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (a[i] == 0) return 0.;
Double_t absa = (Double_t) TMath::Abs(a[i]);
logsum += TMath::Log(absa);
}
return TMath::Exp(logsum/n);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::GeomMean(Long64_t n, const Double_t *a)
{
// Return the geometric mean of an array a with length n.
// geometric_mean = (Prod_i=0,n-1 |a[i]|)^1/n
if (n <= 0 || !a) return 0;
Double_t logsum = 0.;
for (Long64_t i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (a[i] == 0) return 0.;
Double_t absa = (Double_t) TMath::Abs(a[i]);
logsum += TMath::Log(absa);
}
return TMath::Exp(logsum/n);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::GeomMean(Long64_t n, const Long64_t *a)
{
// Return the geometric mean of an array a with length n.
// geometric_mean = (Prod_i=0,n-1 |a[i]|)^1/n
if (n <= 0 || !a) return 0;
Double_t logsum = 0.;
for (Long64_t i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (a[i] == 0) return 0.;
Double_t absa = (Double_t) TMath::Abs(a[i]);
logsum += TMath::Log(absa);
}
return TMath::Exp(logsum/n);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::GeomMean(Long64_t n, const Long_t *a)
{
// Return the geometric mean of an array a with length n.
// geometric_mean = (Prod_i=0,n-1 |a[i]|)^1/n
if (n <= 0 || !a) return 0;
Double_t logsum = 0.;
for (Long64_t i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (a[i] == 0) return 0.;
Double_t absa = (Double_t) TMath::Abs(a[i]);
logsum += TMath::Log(absa);
}
return TMath::Exp(logsum/n);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
#if defined(_MSC_VER) && (_MSC_VER<1300)
// See also the declarations at the top of this file
template <class Element, class Index, class Size>
Double_t MedianImpStandalone(Size n, const Element *a, const Double_t *w, Index *work)
#else
template <class Element, class Index, class Size>
Double_t TMath::MedianImp(Size n, const Element *a,const Double_t *w, Index *work)
#endif
{
// Return the median of the array a where each entry i has weight w[i] .
// Both arrays have a length of at least n . The median is a number obtained
// from the sorted array a through
//
// median = (a[jl]+a[jh])/2. where (using also the sorted index on the array w)
//
// sum_i=0,jl w[i] <= sumTot/2
// sum_i=0,jh w[i] >= sumTot/2
// sumTot = sum_i=0,n w[i]
//
// If w=0, the algorithm defaults to the median definition where it is
// a number that divides the sorted sequence into 2 halves.
// When n is odd or n > 1000, the median is kth element k = (n + 1) / 2.
// when n is even and n < 1000the median is a mean of the elements k = n/2 and k = n/2 + 1.
//
// If work is supplied, it is used to store the sorting index and assumed to be
// >= n . If work=0, local storage is used, either on the stack if n < kWorkMax
// or on the heap for n >= kWorkMax .
if (n <= 0 || !a) return 0;
Bool_t isAllocated = kFALSE;
Double_t median;
Index *ind;
Index workLocal[kWorkMax];
if (work) {
ind = work;
} else {
ind = workLocal;
if (n > kWorkMax) {
isAllocated = kTRUE;
ind = new Index[n];
}
}
if (w) {
Double_t sumTot2 = 0;
for (Int_t j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (w[j] < 0) {
::Error("TMath::Median","w[%d] = %.4e < 0 ?!",j,w[j]);
return 0;
}
sumTot2 += w[j];
}
sumTot2 /= 2.;
SortImp(n, a, ind, kFALSE);
Double_t sum = 0.;
Int_t jl;
for (jl = 0; jl < n; jl++) {
sum += w[ind[jl]];
if (sum >= sumTot2) break;
}
Int_t jh;
sum = 2.*sumTot2;
for (jh = n-1; jh >= 0; jh--) {
sum -= w[ind[jh]];
if (sum <= sumTot2) break;
}
median = 0.5*(a[ind[jl]]+a[ind[jh]]);
} else {
if (n%2 == 1)
median = KOrdStatImp(n, a,n/2, ind);
else {
median = 0.5*(KOrdStatImp(n, a, n/2 -1, ind)+KOrdStatImp(n, a, n/2, ind));
}
}
if (isAllocated)
delete [] ind;
return median;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::Median(Long64_t n, const Short_t *a, const Double_t *w, Long64_t *work)
{
// Return the median of the array a where each entry i has weight w[i] .
// Both arrays have a length of at least n . The median is a number obtained
// from the sorted array a through
//
// median = (a[jl]+a[jh])/2. where (using also the sorted index on the array w)
//
// sum_i=0,jl w[i] <= sumTot/2
// sum_i=0,jh w[i] >= sumTot/2
// sumTot = sum_i=0,n w[i]
//
// If w=0, the algorithm defaults to the median definition where it is
// a number that divides the sorted sequence into 2 halves.
// When n is odd or n > 1000, the median is kth element k = (n + 1) / 2.
// when n is even and n < 1000the median is a mean of the elements k = n/2 and k = n/2 + 1.
//
// If work is supplied, it is used to store the sorting index and assumed to be
// >= n . If work=0, local storage is used, either on the stack if n < kWorkMax
// or on the heap for n >= kWorkMax .
return MedianImp(n, a, w, work);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::Median(Long64_t n, const Int_t *a, const Double_t *w, Long64_t *work)
{
// Return the median of the array a where each entry i has weight w[i] .
// Both arrays have a length of at least n . The median is a number obtained
// from the sorted array a through
//
// median = (a[jl]+a[jh])/2. where (using also the sorted index on the array w)
//
// sum_i=0,jl w[i] <= sumTot/2
// sum_i=0,jh w[i] >= sumTot/2
// sumTot = sum_i=0,n w[i]
//
// If w=0, the algorithm defaults to the median definition where it is
// a number that divides the sorted sequence into 2 halves.
// When n is odd or n > 1000, the median is kth element k = (n + 1) / 2.
// when n is even and n < 1000the median is a mean of the elements k = n/2 and k = n/2 + 1.
//
// If work is supplied, it is used to store the sorting index and assumed to be
// >= n . If work=0, local storage is used, either on the stack if n < kWorkMax
// or on the heap for n >= kWorkMax .
return MedianImp(n, a, w, work);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::Median(Long64_t n, const Float_t *a, const Double_t *w, Long64_t *work)
{
// Return the median of the array a where each entry i has weight w[i] .
// Both arrays have a length of at least n . The median is a number obtained
// from the sorted array a through
//
// median = (a[jl]+a[jh])/2. where (using also the sorted index on the array w)
//
// sum_i=0,jl w[i] <= sumTot/2
// sum_i=0,jh w[i] >= sumTot/2
// sumTot = sum_i=0,n w[i]
//
// If w=0, the algorithm defaults to the median definition where it is
// a number that divides the sorted sequence into 2 halves.
// When n is odd or n > 1000, the median is kth element k = (n + 1) / 2.
// when n is even and n < 1000the median is a mean of the elements k = n/2 and k = n/2 + 1.
//
// If work is supplied, it is used to store the sorting index and assumed to be
// >= n . If work=0, local storage is used, either on the stack if n < kWorkMax
// or on the heap for n >= kWorkMax .
return MedianImp(n, a, w, work);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::Median(Long64_t n, const Double_t *a, const Double_t *w, Long64_t *work)
{
// Return the median of the array a where each entry i has weight w[i] .
// Both arrays have a length of at least n . The median is a number obtained
// from the sorted array a through
//
// median = (a[jl]+a[jh])/2. where (using also the sorted index on the array w)
//
// sum_i=0,jl w[i] <= sumTot/2
// sum_i=0,jh w[i] >= sumTot/2
// sumTot = sum_i=0,n w[i]
//
// If w=0, the algorithm defaults to the median definition where it is
// a number that divides the sorted sequence into 2 halves.
// When n is odd or n > 1000, the median is kth element k = (n + 1) / 2.
// when n is even and n < 1000the median is a mean of the elements k = n/2 and k = n/2 + 1.
//
// If work is supplied, it is used to store the sorting index and assumed to be
// >= n . If work=0, local storage is used, either on the stack if n < kWorkMax
// or on the heap for n >= kWorkMax .
return MedianImp(n, a, w, work);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::Median(Long64_t n, const Long_t *a, const Double_t *w, Long64_t *work)
{
// Return the median of the array a where each entry i has weight w[i] .
// Both arrays have a length of at least n . The median is a number obtained
// from the sorted array a through
//
// median = (a[jl]+a[jh])/2. where (using also the sorted index on the array w)
//
// sum_i=0,jl w[i] <= sumTot/2
// sum_i=0,jh w[i] >= sumTot/2
// sumTot = sum_i=0,n w[i]
//
// If w=0, the algorithm defaults to the median definition where it is
// a number that divides the sorted sequence into 2 halves.
// When n is odd or n > 1000, the median is kth element k = (n + 1) / 2.
// when n is even and n < 1000the median is a mean of the elements k = n/2 and k = n/2 + 1.
//
// If work is supplied, it is used to store the sorting index and assumed to be
// >= n . If work=0, local storage is used, either on the stack if n < kWorkMax
// or on the heap for n >= kWorkMax .
return MedianImp(n, a, w, work);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::Median(Long64_t n, const Long64_t *a, const Double_t *w, Long64_t *work)
{
// Return the median of the array a where each entry i has weight w[i] .
// Both arrays have a length of at least n . The median is a number obtained
// from the sorted array a through
//
// median = (a[jl]+a[jh])/2. where (using also the sorted index on the array w)
//
// sum_i=0,jl w[i] <= sumTot/2
// sum_i=0,jh w[i] >= sumTot/2
// sumTot = sum_i=0,n w[i]
//
// If w=0, the algorithm defaults to the median definition where it is
// a number that divides the sorted sequence into 2 halves.
// When n is odd or n > 1000, the median is kth element k = (n + 1) / 2.
// when n is even and n < 1000the median is a mean of the elements k = n/2 and k = n/2 + 1.
//
// If work is supplied, it is used to store the sorting index and assumed to be
// >= n . If work=0, local storage is used, either on the stack if n < kWorkMax
// or on the heap for n >= kWorkMax .
return MedianImp(n, a, w, work);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
#if defined(_MSC_VER) && (_MSC_VER<1300)
template <class Element, class Index, class Size>
Element KOrdStatImpStandalone(Size n, const Element *a, Size k, Index *work)
#else
template <class Element, class Index, class Size>
Element TMath::KOrdStatImp(Size n, const Element *a, Size k, Index *work)
#endif
{
// Returns k_th order statistic of the array a of size n
// (k_th smallest element out of n elements).
//
// C-convention is used for array indexing, so if you want
// the second smallest element, call KOrdStat(n, a, 1).
//
// If work is supplied, it is used to store the sorting index and
// assumed to be >= n. If work=0, local storage is used, either on
// the stack if n < kWorkMax or on the heap for n >= kWorkMax.
//
// Taken from "Numerical Recipes in C++" without the index array
// implemented by Anna Khreshuk.
//
// See also the declarations at the top of this file
Bool_t isAllocated = kFALSE;
Size i, ir, j, l, mid;
Index arr;
Index *ind;
Index workLocal[kWorkMax];
Index temp;
if (work) {
ind = work;
} else {
ind = workLocal;
if (n > kWorkMax) {
isAllocated = kTRUE;
ind = new Index[n];
}
}
for (Size ii=0; ii<n; ii++) {
ind[ii]=ii;
}
Size rk = k;
l=0;
ir = n-1;
for(;;) {
if (ir<=l+1) { //active partition contains 1 or 2 elements
if (ir == l+1 && a[ind[ir]]<a[ind[l]])
{temp = ind[l]; ind[l]=ind[ir]; ind[ir]=temp;}
Element tmp = a[ind[rk]];
if (isAllocated)
delete [] ind;
return tmp;
} else {
mid = (l+ir) >> 1; //choose median of left, center and right
{temp = ind[mid]; ind[mid]=ind[l+1]; ind[l+1]=temp;}//elements as partitioning element arr.
if (a[ind[l]]>a[ind[ir]]) //also rearrange so that a[l]<=a[l+1]
{temp = ind[l]; ind[l]=ind[ir]; ind[ir]=temp;}
if (a[ind[l+1]]>a[ind[ir]])
{temp=ind[l+1]; ind[l+1]=ind[ir]; ind[ir]=temp;}
if (a[ind[l]]>a[ind[l+1]])
{temp = ind[l]; ind[l]=ind[l+1]; ind[l+1]=temp;}
i=l+1; //initialize pointers for partitioning
j=ir;
arr = ind[l+1];
for (;;){
do i++; while (a[ind[i]]<a[arr]);
do j--; while (a[ind[j]]>a[arr]);
if (j<i) break; //pointers crossed, partitioning complete
{temp=ind[i]; ind[i]=ind[j]; ind[j]=temp;}
}
ind[l+1]=ind[j];
ind[j]=arr;
if (j>=rk) ir = j-1; //keep active the partition that
if (j<=rk) l=i; //contains the k_th element
}
}
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::KOrdStat(Long64_t n, const Double_t *a, Long64_t k, Long64_t *work)
{
// Returns k_th order statistic of the array a of size n
// (k_th smallest element out of n elements).
//
// C-convention is used for array indexing, so if you want
// the second smallest element, call KOrdStat(n, a, 1).
//
// If work is supplied, it is used to store the sorting index and
// assumed to be >= n. If work=0, local storage is used, either on
// the stack if n < kWorkMax or on the heap for n >= kWorkMax.
return KOrdStatImp(n, a, k, work);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Float_t TMath::KOrdStat(Long64_t n, const Float_t *a, Long64_t k, Long64_t *work)
{
// Returns k_th order statistic of the array a of size n
// (k_th smallest element out of n elements).
//
// C-convention is used for array indexing, so if you want
// the second smallest element, call KOrdStat(n, a, 1).
//
// If work is supplied, it is used to store the sorting index and
// assumed to be >= n. If work=0, local storage is used, either on
// the stack if n < kWorkMax or on the heap for n >= kWorkMax.
return KOrdStatImp(n, a, k, work);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TMath::KOrdStat(Long64_t n, const Int_t *a, Long64_t k, Long64_t *work)
{
// Returns k_th order statistic of the array a of size n
// (k_th smallest element out of n elements).
//
// C-convention is used for array indexing, so if you want
// the second smallest element, call KOrdStat(n, a, 1).
//
// If work is supplied, it is used to store the sorting index and
// assumed to be >= n. If work=0, local storage is used, either on
// the stack if n < kWorkMax or on the heap for n >= kWorkMax.
return KOrdStatImp(n, a, k, work);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Short_t TMath::KOrdStat(Long64_t n, const Short_t *a, Long64_t k, Long64_t *work)
{
// Returns k_th order statistic of the array a of size n
// (k_th smallest element out of n elements).
//
// C-convention is used for array indexing, so if you want
// the second smallest element, call KOrdStat(n, a, 1).
//
// If work is supplied, it is used to store the sorting index and
// assumed to be >= n . If work=0, local storage is used, either on
// the stack if n < kWorkMax or on the heap for n >= kWorkMax.
return KOrdStatImp(n, a, k, work);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long64_t TMath::KOrdStat(Long64_t n, const Long_t *a, Long64_t k, Long64_t *work)
{
// Returns k_th order statistic of the array a of size n
// (k_th smallest element out of n elements).
//
// C-convention is used for array indexing, so if you want
// the second smallest element, call KOrdStat(n, a, 1).
//
// If work is supplied, it is used to store the sorting index and
// assumed to be >= n. If work=0, local storage is used, either on
// the stack if n < kWorkMax or on the heap for n >= kWorkMax.
return KOrdStatImp(n, a, k, work);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long64_t TMath::KOrdStat(Long64_t n, const Long64_t *a, Long64_t k, Long64_t *work)
{
// Returns k_th order statistic of the array a of size n
// (k_th smallest element out of n elements).
//
// C-convention is used for array indexing, so if you want
// the second smallest element, call KOrdStat(n, a, 1).
//
// If work is supplied, it is used to store the sorting index and
// assumed to be >= n. If work=0, local storage is used, either on
// the stack if n < kWorkMax or on the heap for n >= kWorkMax.
return KOrdStatImp(n, a, k, work);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::RMS(Long64_t n, const Short_t *a)
{
// Return the RMS of an array a with length n.
if (n <= 0 || !a) return 0;
Double_t tot = 0, tot2 =0, adouble;
for (Long64_t i=0;i<n;i++) {
adouble=Double_t(a[i]);
tot += adouble; tot2 += adouble*adouble;
}
Double_t n1 = 1./n;
Double_t mean = tot*n1;
Double_t rms = TMath::Sqrt(TMath::Abs(tot2*n1 -mean*mean));
return rms;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::RMS(Long64_t n, const Int_t *a)
{
// Return the RMS of an array a with length n.
if (n <= 0 || !a) return 0;
Double_t tot = 0, tot2 =0, adouble;
for (Long64_t i=0;i<n;i++) {
adouble=Double_t(a[i]);
tot += adouble; tot2 += adouble*adouble;
}
Double_t n1 = 1./n;
Double_t mean = tot*n1;
Double_t rms = TMath::Sqrt(TMath::Abs(tot2*n1 -mean*mean));
return rms;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::RMS(Long64_t n, const Float_t *a)
{
// Return the RMS of an array a with length n.
if (n <= 0 || !a) return 0;
Double_t tot = 0, tot2 =0, adouble;
for (Long64_t i=0;i<n;i++) {
adouble=Double_t(a[i]);
tot += adouble; tot2 += adouble*adouble;
}
Double_t n1 = 1./n;
Double_t mean = tot*n1;
Double_t rms = TMath::Sqrt(TMath::Abs(tot2*n1 -mean*mean));
return rms;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::RMS(Long64_t n, const Double_t *a)
{
// Return the RMS of an array a with length n.
if (n <= 0 || !a) return 0;
Double_t tot = 0, tot2 =0;
for (Long64_t i=0;i<n;i++) {tot += a[i]; tot2 += a[i]*a[i]; }
Double_t n1 = 1./n;
Double_t mean = tot*n1;
Double_t rms = TMath::Sqrt(TMath::Abs(tot2*n1 -mean*mean));
return rms;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::RMS(Long64_t n, const Long_t *a)
{
// Return the RMS of an array a with length n.
if (n <= 0 || !a) return 0;
Double_t tot = 0, tot2 =0, adouble;
for (Long64_t i=0;i<n;i++) {
adouble=Double_t(a[i]);
tot += adouble; tot2 += adouble*adouble;
}
Double_t n1 = 1./n;
Double_t mean = tot*n1;
Double_t rms = TMath::Sqrt(TMath::Abs(tot2*n1 -mean*mean));
return rms;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::RMS(Long64_t n, const Long64_t *a)
{
// Return the RMS of an array a with length n.
if (n <= 0 || !a) return 0;
Double_t tot = 0, tot2 =0, adouble;
for (Long64_t i=0;i<n;i++) {
adouble=Double_t(a[i]);
tot += adouble; tot2 += adouble*adouble;
}
Double_t n1 = 1./n;
Double_t mean = tot*n1;
Double_t rms = TMath::Sqrt(TMath::Abs(tot2*n1 -mean*mean));
return rms;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long64_t TMath::BinarySearch(Long64_t n, const Short_t *array, Short_t value)
{
// Binary search in an array of n values to locate value.
//
// Array is supposed to be sorted prior to this call.
// If match is found, function returns position of element.
// If no match found, function gives nearest element smaller than value.
Long64_t nabove, nbelow, middle;
nabove = n+1;
nbelow = 0;
while(nabove-nbelow > 1) {
middle = (nabove+nbelow)/2;
if (value == array[middle-1]) return middle-1;
if (value < array[middle-1]) nabove = middle;
else nbelow = middle;
}
return nbelow-1;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long64_t TMath::BinarySearch(Long64_t n, const Short_t **array, Short_t value)
{
// Binary search in an array of n values to locate value.
//
// Array is supposed to be sorted prior to this call.
// If match is found, function returns position of element.
// If no match found, function gives nearest element smaller than value.
Long64_t nabove, nbelow, middle;
nabove = n+1;
nbelow = 0;
while(nabove-nbelow > 1) {
middle = (nabove+nbelow)/2;
if (value == *array[middle-1]) return middle-1;
if (value < *array[middle-1]) nabove = middle;
else nbelow = middle;
}
return nbelow-1;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long64_t TMath::BinarySearch(Long64_t n, const Int_t *array, Int_t value)
{
// Binary search in an array of n values to locate value.
//
// Array is supposed to be sorted prior to this call.
// If match is found, function returns position of element.
// If no match found, function gives nearest element smaller than value.
Long64_t nabove, nbelow, middle;
nabove = n+1;
nbelow = 0;
while(nabove-nbelow > 1) {
middle = (nabove+nbelow)/2;
if (value == array[middle-1]) return middle-1;
if (value < array[middle-1]) nabove = middle;
else nbelow = middle;
}
return nbelow-1;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long64_t TMath::BinarySearch(Long64_t n, const Int_t **array, Int_t value)
{
// Binary search in an array of n values to locate value.
//
// Array is supposed to be sorted prior to this call.
// If match is found, function returns position of element.
// If no match found, function gives nearest element smaller than value.
Long64_t nabove, nbelow, middle;
nabove = n+1;
nbelow = 0;
while(nabove-nbelow > 1) {
middle = (nabove+nbelow)/2;
if (value == *array[middle-1]) return middle-1;
if (value < *array[middle-1]) nabove = middle;
else nbelow = middle;
}
return nbelow-1;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long64_t TMath::BinarySearch(Long64_t n, const Float_t *array, Float_t value)
{
// Binary search in an array of n values to locate value.
//
// Array is supposed to be sorted prior to this call.
// If match is found, function returns position of element.
// If no match found, function gives nearest element smaller than value.
Long64_t nabove, nbelow, middle;
nabove = n+1;
nbelow = 0;
while(nabove-nbelow > 1) {
middle = (nabove+nbelow)/2;
if (value == array[middle-1]) return middle-1;
if (value < array[middle-1]) nabove = middle;
else nbelow = middle;
}
return nbelow-1;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long64_t TMath::BinarySearch(Long64_t n, const Float_t **array, Float_t value)
{
// Binary search in an array of n values to locate value.
//
// Array is supposed to be sorted prior to this call.
// If match is found, function returns position of element.
// If no match found, function gives nearest element smaller than value.
Long64_t nabove, nbelow, middle;
nabove = n+1;
nbelow = 0;
while(nabove-nbelow > 1) {
middle = (nabove+nbelow)/2;
if (value == *array[middle-1]) return middle-1;
if (value < *array[middle-1]) nabove = middle;
else nbelow = middle;
}
return nbelow-1;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long64_t TMath::BinarySearch(Long64_t n, const Double_t *array, Double_t value)
{
// Binary search in an array of n values to locate value.
//
// Array is supposed to be sorted prior to this call.
// If match is found, function returns position of element.
// If no match found, function gives nearest element smaller than value.
Long64_t nabove, nbelow, middle;
nabove = n+1;
nbelow = 0;
while(nabove-nbelow > 1) {
middle = (nabove+nbelow)/2;
if (value == array[middle-1]) return middle-1;
if (value < array[middle-1]) nabove = middle;
else nbelow = middle;
}
return nbelow-1;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long64_t TMath::BinarySearch(Long64_t n, const Double_t **array, Double_t value)
{
// Binary search in an array of n values to locate value.
//
// Array is supposed to be sorted prior to this call.
// If match is found, function returns position of element.
// If no match found, function gives nearest element smaller than value.
Long64_t nabove, nbelow, middle;
nabove = n+1;
nbelow = 0;
while(nabove-nbelow > 1) {
middle = (nabove+nbelow)/2;
if (value == *array[middle-1]) return middle-1;
if (value < *array[middle-1]) nabove = middle;
else nbelow = middle;
}
return nbelow-1;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long64_t TMath::BinarySearch(Long64_t n, const Long_t *array, Long_t value)
{
// Binary search in an array of n values to locate value.
//
// Array is supposed to be sorted prior to this call.
// If match is found, function returns position of element.
// If no match found, function gives nearest element smaller than value.
Long64_t nabove, nbelow, middle;
nabove = n+1;
nbelow = 0;
while(nabove-nbelow > 1) {
middle = (nabove+nbelow)/2;
if (value == array[middle-1]) return middle-1;
if (value < array[middle-1]) nabove = middle;
else nbelow = middle;
}
return nbelow-1;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long64_t TMath::BinarySearch(Long64_t n, const Long_t **array, Long_t value)
{
// Binary search in an array of n values to locate value.
//
// Array is supposed to be sorted prior to this call.
// If match is found, function returns position of element.
// If no match found, function gives nearest element smaller than value.
Long64_t nabove, nbelow, middle;
nabove = n+1;
nbelow = 0;
while(nabove-nbelow > 1) {
middle = (nabove+nbelow)/2;
if (value == *array[middle-1]) return middle-1;
if (value < *array[middle-1]) nabove = middle;
else nbelow = middle;
}
return nbelow-1;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long64_t TMath::BinarySearch(Long64_t n, const Long64_t *array, Long64_t value)
{
// Binary search in an array of n values to locate value.
//
// Array is supposed to be sorted prior to this call.
// If match is found, function returns position of element.
// If no match found, function gives nearest element smaller than value.
Long64_t nabove, nbelow, middle;
nabove = n+1;
nbelow = 0;
while(nabove-nbelow > 1) {
middle = (nabove+nbelow)/2;
if (value == array[middle-1]) return middle-1;
if (value < array[middle-1]) nabove = middle;
else nbelow = middle;
}
return nbelow-1;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Long64_t TMath::BinarySearch(Long64_t n, const Long64_t **array, Long64_t value)
{
// Binary search in an array of n values to locate value.
//
// Array is supposed to be sorted prior to this call.
// If match is found, function returns position of element.
// If no match found, function gives nearest element smaller than value.
Long64_t nabove, nbelow, middle;
nabove = n+1;
nbelow = 0;
while(nabove-nbelow > 1) {
middle = (nabove+nbelow)/2;
if (value == *array[middle-1]) return middle-1;
if (value < *array[middle-1]) nabove = middle;
else nbelow = middle;
}
return nbelow-1;
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
Bool_t TMath::IsInside(Double_t xp, Double_t yp, Int_t np, Double_t *x, Double_t *y)
{
// Function which returns kTRUE if point xp,yp lies inside the
// polygon defined by the np points in arrays x and y, kFALSE otherwise
// NOTE that the polygon must be a closed polygon (1st and last point
// must be identical).
Double_t xint;
Int_t i;
Int_t inter = 0;
for (i=0;i<np-1;i++) {
if (y[i] == y[i+1]) continue;
if (yp <= y[i] && yp <= y[i+1]) continue;
if (y[i] < yp && y[i+1] < yp) continue;
xint = x[i] + (yp-y[i])*(x[i+1]-x[i])/(y[i+1]-y[i]);
if (xp < xint) inter++;
}
if (inter%2) return kTRUE;
return kFALSE;
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
Bool_t TMath::IsInside(Float_t xp, Float_t yp, Int_t np, Float_t *x, Float_t *y)
{
// Function which returns kTRUE if point xp,yp lies inside the
// polygon defined by the np points in arrays x and y, kFALSE otherwise
// NOTE that the polygon must be a closed polygon (1st and last point
// must be identical).
Double_t xint;
Int_t i;
Int_t inter = 0;
for (i=0;i<np-1;i++) {
if (y[i] == y[i+1]) continue;
if (yp <= y[i] && yp <= y[i+1]) continue;
if (y[i] < yp && y[i+1] < yp) continue;
xint = x[i] + (yp-y[i])*(x[i+1]-x[i])/(y[i+1]-y[i]);
if ((Double_t)xp < xint) inter++;
}
if (inter%2) return kTRUE;
return kFALSE;
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
Bool_t TMath::IsInside(Int_t xp, Int_t yp, Int_t np, Int_t *x, Int_t *y)
{
// Function which returns kTRUE if point xp,yp lies inside the
// polygon defined by the np points in arrays x and y, kFALSE otherwise
// NOTE that the polygon must be a closed polygon (1st and last point
// must be identical).
Double_t xint;
Int_t i;
Int_t inter = 0;
for (i=0;i<np-1;i++) {
if (y[i] == y[i+1]) continue;
if (yp <= y[i] && yp <= y[i+1]) continue;
if (y[i] < yp && y[i+1] < yp) continue;
xint = x[i] + (yp-y[i])*(x[i+1]-x[i])/(y[i+1]-y[i]);
if ((Double_t)xp < xint) inter++;
}
if (inter%2) return kTRUE;
return kFALSE;
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
#if defined(_MSC_VER) && (_MSC_VER<1300)
template <class Element, class Index, class Size>
void SortImpStandalone(Size n1, const Element *a,
Index *index, Bool_t down)
#else
template <class Element, class Index, class Size>
void TMath::SortImp(Size n1, const Element *a,
Index *index, Bool_t down)
#endif
{
// Templated version of the Sort.
//
// Sort the n1 elements of the array a.of Element
// In output the array index contains the indices of the sorted array.
// If down is false sort in increasing order (default is decreasing order).
// This is a translation of the CERNLIB routine sortzv (M101)
// based on the quicksort algorithm.
// NOTE that the array index must be created with a length >= n1
// before calling this function.
//
// See also the declarations at the top of this file.
Size i,i1,n,i2,i3,i33,i222,iswap,n2;
Size i22 = 0;
Element ai;
n = n1;
if (n <= 0 || !a) return;
if (n == 1) {index[0] = 0; return;}
for (i=0;i<n;i++) index[i] = i+1;
for (i1=2;i1<=n;i1++) {
i3 = i1;
i33 = index[i3-1];
ai = a[i33-1];
while(1) {
i2 = i3/2;
if (i2 <= 0) break;
i22 = index[i2-1];
if (ai <= a[i22-1]) break;
index[i3-1] = i22;
i3 = i2;
}
index[i3-1] = i33;
}
while(1) {
i3 = index[n-1];
index[n-1] = index[0];
ai = a[i3-1];
n--;
if(n-1 < 0) {index[0] = i3; break;}
i1 = 1;
while(2) {
i2 = i1+i1;
if (i2 <= n) i22 = index[i2-1];
if (i2-n > 0) {index[i1-1] = i3; break;}
if (i2-n < 0) {
i222 = index[i2];
if (a[i22-1] - a[i222-1] < 0) {
i2++;
i22 = i222;
}
}
if (ai - a[i22-1] > 0) {index[i1-1] = i3; break;}
index[i1-1] = i22;
i1 = i2;
}
}
for (i=0;i<n1;i++) index[i]--;
if (!down) return;
n2 = n1/2;
for (i=0;i<n2;i++) {
iswap = index[i];
index[i] = index[n1-i-1];
index[n1-i-1] = iswap;
}
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
void TMath::Sort(Int_t n1, const Short_t *a, Int_t *index, Bool_t down)
{
// Sort the n1 elements of the Short_t array a.
// In output the array index contains the indices of the sorted array.
// If down is false sort in increasing order (default is decreasing order).
// This is a translation of the CERNLIB routine sortzv (M101)
// based on the quicksort algorithm.
// NOTE that the array index must be created with a length >= n1
// before calling this function.
SortImp(n1,a,index,down);
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
void TMath::Sort(Int_t n1, const Int_t *a, Int_t *index, Bool_t down)
{
// Sort the n1 elements of the Int_t array a.
// In output the array index contains the indices of the sorted array.
// If down is false sort in increasing order (default is decreasing order).
// This is a translation of the CERNLIB routine sortzv (M101)
// based on the quicksort algorithm.
// NOTE that the array index must be created with a length >= n1
// before calling this function.
SortImp(n1,a,index,down);
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
void TMath::Sort(Int_t n1, const Float_t *a, Int_t *index, Bool_t down)
{
// Sort the n1 elements of the Float_t array a.
// In output the array index contains the indices of the sorted array.
// If down is false sort in increasing order (default is decreasing order).
// This is a translation of the CERNLIB routine sortzv (M101)
// based on the quicksort algorithm.
// NOTE that the array index must be created with a length >= n1
// before calling this function.
SortImp(n1,a,index,down);
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
void TMath::Sort(Int_t n1, const Double_t *a, Int_t *index, Bool_t down)
{
// Sort the n1 elements of the Double_t array a.
// In output the array index contains the indices of the sorted array.
// If down is false sort in increasing order (default is decreasing order).
// This is a translation of the CERNLIB routine sortzv (M101)
// based on the quicksort algorithm.
// NOTE that the array index must be created with a length >= n1
// before calling this function.
SortImp(n1,a,index,down);
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
void TMath::Sort(Int_t n1, const Long_t *a, Int_t *index, Bool_t down)
{
// Sort the n1 elements of the Long64_t array a.
// In output the array index contains the indices of the sorted array.
// If down is false sort in increasing order (default is decreasing order).
// This is a translation of the CERNLIB routine sortzv (M101)
// based on the quicksort algorithm.
// NOTE that the array index must be created with a length >= n1
// before calling this function.
SortImp(n1,a,index,down);
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
void TMath::Sort(Int_t n1, const Long64_t *a, Int_t *index, Bool_t down)
{
// Sort the n1 elements of the Long64_t array a.
// In output the array index contains the indices of the sorted array.
// If down is false sort in increasing order (default is decreasing order).
// This is a translation of the CERNLIB routine sortzv (M101)
// based on the quicksort algorithm.
// NOTE that the array index must be created with a length >= n1
// before calling this function.
SortImp(n1,a,index,down);
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
void TMath::Sort(Long64_t n1, const Short_t *a, Long64_t *index, Bool_t down)
{
// Sort the n1 elements of the Short_t array a.
// In output the array index contains the indices of the sorted array.
// If down is false sort in increasing order (default is decreasing order).
// This is a translation of the CERNLIB routine sortzv (M101)
// based on the quicksort algorithm.
// NOTE that the array index must be created with a length >= n1
// before calling this function.
SortImp(n1,a,index,down);
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
void TMath::Sort(Long64_t n1, const Int_t *a, Long64_t *index, Bool_t down)
{
// Sort the n1 elements of the Int_t array a.
// In output the array index contains the indices of the sorted array.
// If down is false sort in increasing order (default is decreasing order).
// This is a translation of the CERNLIB routine sortzv (M101)
// based on the quicksort algorithm.
// NOTE that the array index must be created with a length >= n1
// before calling this function.
SortImp(n1,a,index,down);
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
void TMath::Sort(Long64_t n1, const Float_t *a, Long64_t *index, Bool_t down)
{
// Sort the n1 elements of the Float_t array a.
// In output the array index contains the indices of the sorted array.
// If down is false sort in increasing order (default is decreasing order).
// This is a translation of the CERNLIB routine sortzv (M101)
// based on the quicksort algorithm.
// NOTE that the array index must be created with a length >= n1
// before calling this function.
SortImp(n1,a,index,down);
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
void TMath::Sort(Long64_t n1, const Double_t *a, Long64_t *index, Bool_t down)
{
// Sort the n1 elements of the Double_t array a.
// In output the array index contains the indices of the sorted array.
// If down is false sort in increasing order (default is decreasing order).
// This is a translation of the CERNLIB routine sortzv (M101)
// based on the quicksort algorithm.
// NOTE that the array index must be created with a length >= n1
// before calling this function.
SortImp(n1,a,index,down);
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
void TMath::Sort(Long64_t n1, const Long_t *a, Long64_t *index, Bool_t down)
{
// Sort the n1 elements of the Long64_t array a.
// In output the array index contains the indices of the sorted array.
// If down is false sort in increasing order (default is decreasing order).
// This is a translation of the CERNLIB routine sortzv (M101)
// based on the quicksort algorithm.
// NOTE that the array index must be created with a length >= n1
// before calling this function.
SortImp(n1,a,index,down);
}
//_____________________________________________________________________________
void TMath::Sort(Long64_t n1, const Long64_t *a, Long64_t *index, Bool_t down)
{
// Sort the n1 elements of the Long64_t array a.
// In output the array index contains the indices of the sorted array.
// If down is false sort in increasing order (default is decreasing order).
// This is a translation of the CERNLIB routine sortzv (M101)
// based on the quicksort algorithm.
// NOTE that the array index must be created with a length >= n1
// before calling this function.
SortImp(n1,a,index,down);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TMath::BubbleHigh(Int_t Narr, Double_t *arr1, Int_t *arr2)
{
// Bubble sort variant to obtain the order of an array's elements into
// an index in order to do more useful things than the standard built
// in functions.
// *arr1 is unchanged;
// *arr2 is the array of indicies corresponding to the decending value
// of arr1 with arr2[0] corresponding to the largest arr1 value and
// arr2[Narr] the smallest.
//
// Author: Adrian Bevan (bevan@slac.stanford.edu)
// Copyright: Liverpool University, July 2001
if (Narr <= 0) return;
double *localArr1 = new double[Narr];
int *localArr2 = new int[Narr];
int iEl;
int iEl2;
for(iEl = 0; iEl < Narr; iEl++) {
localArr1[iEl] = arr1[iEl];
localArr2[iEl] = iEl;
}
for (iEl = 0; iEl < Narr; iEl++) {
for (iEl2 = Narr-1; iEl2 > iEl; --iEl2) {
if (localArr1[iEl2-1] < localArr1[iEl2]) {
double tmp = localArr1[iEl2-1];
localArr1[iEl2-1] = localArr1[iEl2];
localArr1[iEl2] = tmp;
int tmp2 = localArr2[iEl2-1];
localArr2[iEl2-1] = localArr2[iEl2];
localArr2[iEl2] = tmp2;
}
}
}
for (iEl = 0; iEl < Narr; iEl++) {
arr2[iEl] = localArr2[iEl];
}
delete [] localArr2;
delete [] localArr1;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TMath::BubbleLow(Int_t Narr, Double_t *arr1, Int_t *arr2)
{
// Opposite ordering of the array arr2[] to that of BubbleHigh.
//
// Author: Adrian Bevan (bevan@slac.stanford.edu)
// Copyright: Liverpool University, July 2001
if (Narr <= 0) return;
double *localArr1 = new double[Narr];
int *localArr2 = new int[Narr];
int iEl;
int iEl2;
for (iEl = 0; iEl < Narr; iEl++) {
localArr1[iEl] = arr1[iEl];
localArr2[iEl] = iEl;
}
for (iEl = 0; iEl < Narr; iEl++) {
for (iEl2 = Narr-1; iEl2 > iEl; --iEl2) {
if (localArr1[iEl2-1] > localArr1[iEl2]) {
double tmp = localArr1[iEl2-1];
localArr1[iEl2-1] = localArr1[iEl2];
localArr1[iEl2] = tmp;
int tmp2 = localArr2[iEl2-1];
localArr2[iEl2-1] = localArr2[iEl2];
localArr2[iEl2] = tmp2;
}
}
}
for (iEl = 0; iEl < Narr; iEl++) {
arr2[iEl] = localArr2[iEl];
}
delete [] localArr2;
delete [] localArr1;
}
#ifdef OLD_HASH
//______________________________________________________________________________
ULong_t TMath::Hash(const void *txt, Int_t ntxt)
{
// Calculates hash index from any char string.
// Based on precalculated table of 256 specially selected random numbers.
//
// For string: i = TMath::Hash(string,nstring);
// For int: i = TMath::Hash(&intword,sizeof(int));
// For pointer: i = TMath::Hash(&pointer,sizeof(void*));
//
// Limitation: for ntxt>256 calculates hash only from first 256 bytes
//
// V.Perev
const UChar_t *uc = (const UChar_t*) txt;
ULong_t u = 0, uu = 0;
static ULong_t utab[256] =
{0xb93f6fc0,0x553dfc51,0xb22c1e8c,0x638462c0,0x13e81418,0x2836e171,0x7c4abb90,0xda1a4f39
,0x38f211d1,0x8c804829,0x95a6602d,0x4c590993,0x1810580a,0x721057d4,0x0f587215,0x9f49ce2a
,0xcd5ab255,0xab923a99,0x80890f39,0xbcfa2290,0x16587b52,0x6b6d3f0d,0xea8ff307,0x51542d5c
,0x189bf223,0x39643037,0x0e4a326a,0x214eca01,0x47645a9b,0x0f364260,0x8e9b2da4,0x5563ebd9
,0x57a31c1c,0xab365854,0xdd63ab1f,0x0b89acbd,0x23d57d33,0x1800a0fd,0x225ac60a,0xd0e51943
,0x6c65f669,0xcb966ea0,0xcbafda95,0x2e5c0c5f,0x2988e87e,0xc781cbab,0x3add3dc7,0x693a2c30
,0x42d6c23c,0xebf85f26,0x2544987e,0x2e315e3f,0xac88b5b5,0x7ebd2bbb,0xda07c87b,0x20d460f1
,0xc61c3f40,0x182046e7,0x3b6c3b66,0x2fc10d4a,0x0780dfbb,0xc437280c,0x0988dd07,0xe1498606
,0x8e61d728,0x4f1f3909,0x040a9682,0x49411b29,0x391b0e1c,0xd7905241,0xdd77d95b,0x88426c13
,0x33033e58,0xe158e30e,0x7e342647,0x1e09544b,0x4637353d,0x18ea0924,0x39212b08,0x12580ae8
,0x269a6f06,0x3e10b73b,0x123db33b,0x085412da,0x3bb5f464,0xd9b2d442,0x103d26bb,0xd0038bab
,0x45b6177f,0xfb48f1fe,0x99074c55,0xb545e82e,0x5f79fd0d,0x570f3ae4,0x57e43255,0x037a12ae
,0x4357bdb2,0x337c2c4d,0x2982499d,0x2ab72793,0x3900e7d1,0x57a6bb81,0x7503609b,0x3f39c0d0
,0x717b389d,0x5748034f,0x4698162b,0x5801b97c,0x1dfd5d7e,0xc1386d1c,0xa387a72a,0x084547e4
,0x2e54d8e9,0x2e2f384c,0xe09ccc20,0x8904b71e,0x3e24edc5,0x06a22e16,0x8a2be1df,0x9e5058b2
,0xe01a2f16,0x03325eed,0x587ecfe6,0x584d9cd3,0x32926930,0xe943d68c,0xa9442da8,0xf9650560
,0xf003871e,0x1109c663,0x7a2f2f89,0x1c2210bb,0x37335787,0xb92b382f,0xea605cb5,0x336bbe38
,0x08126bd3,0x1f8c2bd6,0xba6c46f2,0x1a4d1b83,0xc988180d,0xe2582505,0xa8a1b375,0x59a08c49
,0x3db54b48,0x44400f35,0x272d4e7f,0x5579f733,0x98eb590e,0x8ee09813,0x12cc9301,0xc85c402d
,0x135c1039,0x22318128,0x4063c705,0x87a8a3fa,0xfc14431f,0x6e27bf47,0x2d080a19,0x01dba174
,0xe343530b,0xaa1bfced,0x283bb2c8,0x5df250c8,0x4ff9140b,0x045039c1,0xa377780d,0x750f2661
,0x2b108918,0x0b152120,0x3cbc251f,0x5e87b350,0x060625bb,0xe068ba3b,0xdb73ebd7,0x66014ff3
,0xdb003000,0x161a3a0b,0xdc24e142,0x97ea5575,0x635a3cab,0xa719100a,0x256084db,0xc1f4a1e7
,0xe13388f2,0xb8199fc9,0x50c70dc9,0x08154211,0xd60e5220,0xe52c6592,0x584c5fe1,0xfe5e0875
,0x21072b30,0x3370d773,0x92608fe2,0x2d013d93,0x53414b3c,0x2c066142,0x64676644,0x0420887c
,0x35c01187,0x6822119b,0xf9bfe6df,0x273f4ee4,0x87973149,0x7b41282d,0x635d0d1f,0x5f7ecc1e
,0x14c3608a,0x462dfdab,0xc33d8808,0x1dcd995e,0x0fcb11ba,0x11755914,0x5a62044b,0x37f76755
,0x345bd058,0x8831c2b5,0x204a8468,0x3b0b1cd2,0x444e56f4,0x97a93e2c,0xd5f15067,0x266a95fa
,0xff4f8036,0x6160060d,0x930c472f,0xed922184,0x37120251,0xc0add74f,0x1c0bc89d,0x018d47f2
,0xff59ef66,0xd1901a17,0x91f6701b,0x0960082f,0x86f6a8f3,0x1154fecd,0x9867d1de,0x0945482f
,0x790ffcac,0xe5610011,0x4765637e,0xa745dbff,0x841fdcb3,0x4f7372a0,0x3c05013d,0xf1ac4ab7
,0x3bc5b5cc,0x49a73349,0x356a7f67,0x1174f031,0x11d32634,0x4413d301,0x1dd285c4,0x3fae4800
};
if (ntxt > 255) ntxt = 255;
for ( ; ntxt--; uc++) {
uu = uu<<1 ^ utab[(*uc) ^ ntxt];
u ^= uu;
}
return u;
}
#else
//______________________________________________________________________________
ULong_t TMath::Hash(const void *txt, Int_t ntxt)
{
// Calculates hash index from any char string.
// Based on precalculated table of 256 specially selected numbers.
// These numbers are selected in such a way, that for string
// length == 4 (integer number) the hash is unambigous, i.e.
// from hash value we can recalculate input (no degeneration).
//
// The quality of hash method is good enough, that
// "random" numbers made as R = Hash(1), Hash(2), ...Hash(N)
// tested by <R>, <R*R>, <Ri*Ri+1> gives the same result
// as for libc rand().
//
// For string: i = TMath::Hash(string,nstring);
// For int: i = TMath::Hash(&intword,sizeof(int));
// For pointer: i = TMath::Hash(&pointer,sizeof(void*));
//
// V.Perev
static const ULong_t utab[] = {
0xdd367647,0x9caf993f,0x3f3cc5ff,0xfde25082,0x4c764b21,0x89affca7,0x5431965c,0xce22eeec
,0xc61ab4dc,0x59cc93bd,0xed3107e3,0x0b0a287a,0x4712475a,0xce4a4c71,0x352c8403,0x94cb3cee
,0xc3ac509b,0x09f827a2,0xce02e37e,0x7b20bbba,0x76adcedc,0x18c52663,0x19f74103,0x6f30e47b
,0x132ea5a1,0xfdd279e0,0xa3d57d00,0xcff9cb40,0x9617f384,0x6411acfa,0xff908678,0x5c796b2c
,0x4471b62d,0xd38e3275,0xdb57912d,0x26bf953f,0xfc41b2a5,0xe64bcebd,0x190b7839,0x7e8e6a56
,0x9ca22311,0xef28aa60,0xe6b9208e,0xd257fb65,0x45781c2c,0x9a558ac3,0x2743e74d,0x839417a8
,0x06b54d5d,0x1a82bcb4,0x06e97a66,0x70abdd03,0xd163f30d,0x222ed322,0x777bfeda,0xab7a2e83
,0x8494e0cf,0x2dca2d4f,0x78f94278,0x33f04a09,0x402b6452,0x0cd8b709,0xdb72a39e,0x170e00a2
,0x26354faa,0x80e57453,0xcfe8d4e1,0x19e45254,0x04c291c3,0xeb503738,0x425af3bc,0x67836f2a
,0xfac22add,0xfafc2b8c,0x59b8c2a0,0x03e806f9,0xcb4938b9,0xccc942af,0xcee3ae2e,0xfbe748fa
,0xb223a075,0x85c49b5d,0xe4576ac9,0x0fbd46e2,0xb49f9cf5,0xf3e1e86a,0x7d7927fb,0x711afe12
,0xbf61c346,0x157c9956,0x86b6b046,0x2e402146,0xb2a57d8a,0x0d064bb1,0x30ce390c,0x3a3e1eb1
,0xbe7f6f8f,0xd8e30f87,0x5be2813c,0x73a3a901,0xa3aaf967,0x59ff092c,0x1705c798,0xf610dd66
,0xb17da91e,0x8e59534e,0x2211ea5b,0xa804ba03,0xd890efbb,0xb8b48110,0xff390068,0xc8c325b4
,0xf7289c07,0x787e104f,0x3d0df3d0,0x3526796d,0x10548055,0x1d59a42b,0xed1cc5a3,0xdd45372a
,0x31c50d57,0x65757cb7,0x3cfb85be,0xa329910d,0x6ad8ce39,0xa2de44de,0x0dd32432,0xd4a5b617
,0x8f3107fc,0x96485175,0x7f94d4f3,0x35097634,0xdb3ca782,0x2c0290b8,0x2045300b,0xe0f5d15a
,0x0e8cbffa,0xaa1cc38a,0x84008d6f,0xe9a9e794,0x5c602c25,0xfa3658fa,0x98d9d82b,0x3f1497e7
,0x84b6f031,0xe381eff9,0xfc7ae252,0xb239e05d,0xe3723d1f,0xcc3bda82,0xe21b1ad3,0x9104f7c8
,0x4bb2dfcd,0x4d14a8bc,0x6ba7f28c,0x8f89886c,0xad44c97e,0xb30fd975,0x633cdab1,0xf6c2d514
,0x067a49d2,0xdc461ad9,0xebaf9f3f,0x8dc6cac3,0x7a060f16,0xbab063ad,0xf42e25e6,0x60724ca6
,0xc7245c2e,0x4e48ea3c,0x9f89a609,0xa1c49890,0x4bb7f116,0xd722865c,0xa8ee3995,0x0ee070b1
,0xd9bffcc2,0xe55b64f9,0x25507a5a,0xc7a3e2b5,0x5f395f7e,0xe7957652,0x7381ba6a,0xde3d21f1
,0xdf1708dd,0xad0c9d0c,0x00cbc9e5,0x1160e833,0x6779582c,0x29d5d393,0x3f11d7d7,0x826a6b9b
,0xe73ff12f,0x8bad3d86,0xee41d3e5,0x7f0c8917,0x8089ef24,0x90c5cb28,0x2f7f8e6b,0x6966418a
,0x345453fb,0x7a2f8a68,0xf198593d,0xc079a532,0xc1971e81,0x1ab74e26,0x329ef347,0x7423d3d0
,0x942c510b,0x7f6c6382,0x14ae6acc,0x64b59da7,0x2356fa47,0xb6749d9c,0x499de1bb,0x92ffd191
,0xe8f2fb75,0x848dc913,0x3e8727d3,0x1dcffe61,0xb6e45245,0x49055738,0x827a6b55,0xb4788887
,0x7e680125,0xd19ce7ed,0x6b4b8e30,0xa8cadea2,0x216035d8,0x1c63bc3c,0xe1299056,0x1ad3dff4
,0x0aefd13c,0x0e7b921c,0xca0173c6,0x9995782d,0xcccfd494,0xd4b0ac88,0x53d552b1,0x630dae8b
,0xa8332dad,0x7139d9a2,0x5d76f2c4,0x7a4f8f1e,0x8d1aef97,0xd1cf285d,0xc8239153,0xce2608a9
,0x7b562475,0xe4b4bc83,0xf3db0c3a,0x70a65e48,0x6016b302,0xdebd5046,0x707e786a,0x6f10200c
};
static const ULong_t msk[] = { 0x11111111, 0x33333333, 0x77777777, 0xffffffff };
const UChar_t *uc = (const UChar_t *) txt;
ULong_t uu = 0;
union {
ULong_t u;
UShort_t s[2];
} u;
u.u = 0;
Int_t i, idx;
for (i = 0; i < ntxt; i++) {
idx = (uc[i] ^ i) & 255;
uu = (uu << 1) ^ (utab[idx] & msk[i & 3]);
if ((i & 3) == 3) u.u ^= uu;
}
if (i & 3) u.u ^= uu;
u.u *= 1879048201; // prime number
u.s[0] += u.s[1];
u.u *= 1979048191; // prime number
u.s[1] ^= u.s[0];
u.u *= 2079048197; // prime number
return u.u;
}
#endif
//______________________________________________________________________________
ULong_t TMath::Hash(const char *txt)
{
return Hash(txt, Int_t(strlen(txt)));
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::BesselI0(Double_t x)
{
// Compute the modified Bessel function I_0(x) for any real x.
//
//--- NvE 12-mar-2000 UU-SAP Utrecht
// Parameters of the polynomial approximation
const Double_t p1=1.0, p2=3.5156229, p3=3.0899424,
p4=1.2067492, p5=0.2659732, p6=3.60768e-2, p7=4.5813e-3;
const Double_t q1= 0.39894228, q2= 1.328592e-2, q3= 2.25319e-3,
q4=-1.57565e-3, q5= 9.16281e-3, q6=-2.057706e-2,
q7= 2.635537e-2, q8=-1.647633e-2, q9= 3.92377e-3;
const Double_t k1 = 3.75;
Double_t ax = TMath::Abs(x);
Double_t y=0, result=0;
if (ax < k1) {
Double_t xx = x/k1;
y = xx*xx;
result = p1+y*(p2+y*(p3+y*(p4+y*(p5+y*(p6+y*p7)))));
} else {
y = k1/ax;
result = (TMath::Exp(ax)/TMath::Sqrt(ax))*(q1+y*(q2+y*(q3+y*(q4+y*(q5+y*(q6+y*(q7+y*(q8+y*q9))))))));
}
return result;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::BesselK0(Double_t x)
{
// Compute the modified Bessel function K_0(x) for positive real x.
//
// M.Abramowitz and I.A.Stegun, Handbook of Mathematical Functions,
// Applied Mathematics Series vol. 55 (1964), Washington.
//
//--- NvE 12-mar-2000 UU-SAP Utrecht
// Parameters of the polynomial approximation
const Double_t p1=-0.57721566, p2=0.42278420, p3=0.23069756,
p4= 3.488590e-2, p5=2.62698e-3, p6=1.0750e-4, p7=7.4e-6;
const Double_t q1= 1.25331414, q2=-7.832358e-2, q3= 2.189568e-2,
q4=-1.062446e-2, q5= 5.87872e-3, q6=-2.51540e-3, q7=5.3208e-4;
if (x <= 0) {
Error("TMath::BesselK0", "*K0* Invalid argument x = %g\n",x);
return 0;
}
Double_t y=0, result=0;
if (x <= 2) {
y = x*x/4;
result = (-log(x/2.)*TMath::BesselI0(x))+(p1+y*(p2+y*(p3+y*(p4+y*(p5+y*(p6+y*p7))))));
} else {
y = 2/x;
result = (exp(-x)/sqrt(x))*(q1+y*(q2+y*(q3+y*(q4+y*(q5+y*(q6+y*q7))))));
}
return result;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::BesselI1(Double_t x)
{
// Compute the modified Bessel function I_1(x) for any real x.
//
// M.Abramowitz and I.A.Stegun, Handbook of Mathematical Functions,
// Applied Mathematics Series vol. 55 (1964), Washington.
//
//--- NvE 12-mar-2000 UU-SAP Utrecht
// Parameters of the polynomial approximation
const Double_t p1=0.5, p2=0.87890594, p3=0.51498869,
p4=0.15084934, p5=2.658733e-2, p6=3.01532e-3, p7=3.2411e-4;
const Double_t q1= 0.39894228, q2=-3.988024e-2, q3=-3.62018e-3,
q4= 1.63801e-3, q5=-1.031555e-2, q6= 2.282967e-2,
q7=-2.895312e-2, q8= 1.787654e-2, q9=-4.20059e-3;
const Double_t k1 = 3.75;
Double_t ax = TMath::Abs(x);
Double_t y=0, result=0;
if (ax < k1) {
Double_t xx = x/k1;
y = xx*xx;
result = x*(p1+y*(p2+y*(p3+y*(p4+y*(p5+y*(p6+y*p7))))));
} else {
y = k1/ax;
result = (exp(ax)/sqrt(ax))*(q1+y*(q2+y*(q3+y*(q4+y*(q5+y*(q6+y*(q7+y*(q8+y*q9))))))));
if (x < 0) result = -result;
}
return result;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::BesselK1(Double_t x)
{
// Compute the modified Bessel function K_1(x) for positive real x.
//
// M.Abramowitz and I.A.Stegun, Handbook of Mathematical Functions,
// Applied Mathematics Series vol. 55 (1964), Washington.
//
//--- NvE 12-mar-2000 UU-SAP Utrecht
// Parameters of the polynomial approximation
const Double_t p1= 1., p2= 0.15443144, p3=-0.67278579,
p4=-0.18156897, p5=-1.919402e-2, p6=-1.10404e-3, p7=-4.686e-5;
const Double_t q1= 1.25331414, q2= 0.23498619, q3=-3.655620e-2,
q4= 1.504268e-2, q5=-7.80353e-3, q6= 3.25614e-3, q7=-6.8245e-4;
if (x <= 0) {
Error("TMath::BesselK1", "*K1* Invalid argument x = %g\n",x);
return 0;
}
Double_t y=0,result=0;
if (x <= 2) {
y = x*x/4;
result = (log(x/2.)*TMath::BesselI1(x))+(1./x)*(p1+y*(p2+y*(p3+y*(p4+y*(p5+y*(p6+y*p7))))));
} else {
y = 2/x;
result = (exp(-x)/sqrt(x))*(q1+y*(q2+y*(q3+y*(q4+y*(q5+y*(q6+y*q7))))));
}
return result;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::BesselK(Int_t n,Double_t x)
{
// Compute the Integer Order Modified Bessel function K_n(x)
// for n=0,1,2,... and positive real x.
//
//--- NvE 12-mar-2000 UU-SAP Utrecht
if (x <= 0 || n < 0) {
Error("TMath::BesselK", "*K* Invalid argument(s) (n,x) = (%d, %g)\n",n,x);
return 0;
}
if (n==0) return TMath::BesselK0(x);
if (n==1) return TMath::BesselK1(x);
// Perform upward recurrence for all x
Double_t tox = 2/x;
Double_t bkm = TMath::BesselK0(x);
Double_t bk = TMath::BesselK1(x);
Double_t bkp = 0;
for (Int_t j=1; j<n; j++) {
bkp = bkm+Double_t(j)*tox*bk;
bkm = bk;
bk = bkp;
}
return bk;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::BesselI(Int_t n,Double_t x)
{
// Compute the Integer Order Modified Bessel function I_n(x)
// for n=0,1,2,... and any real x.
//
//--- NvE 12-mar-2000 UU-SAP Utrecht
Int_t iacc = 40; // Increase to enhance accuracy
const Double_t kBigPositive = 1.e10;
const Double_t kBigNegative = 1.e-10;
if (n < 0) {
Error("TMath::BesselI", "*I* Invalid argument (n,x) = (%d, %g)\n",n,x);
return 0;
}
if (n==0) return TMath::BesselI0(x);
if (n==1) return TMath::BesselI1(x);
if (x == 0) return 0;
if (TMath::Abs(x) > kBigPositive) return 0;
Double_t tox = 2/TMath::Abs(x);
Double_t bip = 0, bim = 0;
Double_t bi = 1;
Double_t result = 0;
Int_t m = 2*((n+Int_t(sqrt(Float_t(iacc*n)))));
for (Int_t j=m; j>=1; j--) {
bim = bip+Double_t(j)*tox*bi;
bip = bi;
bi = bim;
// Renormalise to prevent overflows
if (TMath::Abs(bi) > kBigPositive) {
result *= kBigNegative;
bi *= kBigNegative;
bip *= kBigNegative;
}
if (j==n) result=bip;
}
result *= TMath::BesselI0(x)/bi; // Normalise with BesselI0(x)
if ((x < 0) && (n%2 == 1)) result = -result;
return result;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::BesselJ0(Double_t x)
{
// Returns the Bessel function J0(x) for any real x.
Double_t ax,z;
Double_t xx,y,result,result1,result2;
const Double_t p1 = 57568490574.0, p2 = -13362590354.0, p3 = 651619640.7;
const Double_t p4 = -11214424.18, p5 = 77392.33017, p6 = -184.9052456;
const Double_t p7 = 57568490411.0, p8 = 1029532985.0, p9 = 9494680.718;
const Double_t p10 = 59272.64853, p11 = 267.8532712;
const Double_t q1 = 0.785398164;
const Double_t q2 = -0.1098628627e-2, q3 = 0.2734510407e-4;
const Double_t q4 = -0.2073370639e-5, q5 = 0.2093887211e-6;
const Double_t q6 = -0.1562499995e-1, q7 = 0.1430488765e-3;
const Double_t q8 = -0.6911147651e-5, q9 = 0.7621095161e-6;
const Double_t q10 = 0.934935152e-7, q11 = 0.636619772;
if ((ax=fabs(x)) < 8) {
y=x*x;
result1 = p1 + y*(p2 + y*(p3 + y*(p4 + y*(p5 + y*p6))));
result2 = p7 + y*(p8 + y*(p9 + y*(p10 + y*(p11 + y))));
result = result1/result2;
} else {
z = 8/ax;
y = z*z;
xx = ax-q1;
result1 = 1 + y*(q2 + y*(q3 + y*(q4 + y*q5)));
result2 = q6 + y*(q7 + y*(q8 + y*(q9 - y*q10)));
result = sqrt(q11/ax)*(cos(xx)*result1-z*sin(xx)*result2);
}
return result;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::BesselJ1(Double_t x)
{
// Returns the Bessel function J1(x) for any real x.
Double_t ax,z;
Double_t xx,y,result,result1,result2;
const Double_t p1 = 72362614232.0, p2 = -7895059235.0, p3 = 242396853.1;
const Double_t p4 = -2972611.439, p5 = 15704.48260, p6 = -30.16036606;
const Double_t p7 = 144725228442.0, p8 = 2300535178.0, p9 = 18583304.74;
const Double_t p10 = 99447.43394, p11 = 376.9991397;
const Double_t q1 = 2.356194491;
const Double_t q2 = 0.183105e-2, q3 = -0.3516396496e-4;
const Double_t q4 = 0.2457520174e-5, q5 = -0.240337019e-6;
const Double_t q6 = 0.04687499995, q7 = -0.2002690873e-3;
const Double_t q8 = 0.8449199096e-5, q9 = -0.88228987e-6;
const Double_t q10 = 0.105787412e-6, q11 = 0.636619772;
if ((ax=fabs(x)) < 8) {
y=x*x;
result1 = x*(p1 + y*(p2 + y*(p3 + y*(p4 + y*(p5 + y*p6)))));
result2 = p7 + y*(p8 + y*(p9 + y*(p10 + y*(p11 + y))));
result = result1/result2;
} else {
z = 8/ax;
y = z*z;
xx = ax-q1;
result1 = 1 + y*(q2 + y*(q3 + y*(q4 + y*q5)));
result2 = q6 + y*(q7 + y*(q8 + y*(q9 + y*q10)));
result = sqrt(q11/ax)*(cos(xx)*result1-z*sin(xx)*result2);
if (x < 0) result = -result;
}
return result;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::BesselY0(Double_t x)
{
// Returns the Bessel function Y0(x) for positive x.
Double_t z,xx,y,result,result1,result2;
const Double_t p1 = -2957821389., p2 = 7062834065.0, p3 = -512359803.6;
const Double_t p4 = 10879881.29, p5 = -86327.92757, p6 = 228.4622733;
const Double_t p7 = 40076544269., p8 = 745249964.8, p9 = 7189466.438;
const Double_t p10 = 47447.26470, p11 = 226.1030244, p12 = 0.636619772;
const Double_t q1 = 0.785398164;
const Double_t q2 = -0.1098628627e-2, q3 = 0.2734510407e-4;
const Double_t q4 = -0.2073370639e-5, q5 = 0.2093887211e-6;
const Double_t q6 = -0.1562499995e-1, q7 = 0.1430488765e-3;
const Double_t q8 = -0.6911147651e-5, q9 = 0.7621095161e-6;
const Double_t q10 = -0.934945152e-7, q11 = 0.636619772;
if (x < 8) {
y = x*x;
result1 = p1 + y*(p2 + y*(p3 + y*(p4 + y*(p5 + y*p6))));
result2 = p7 + y*(p8 + y*(p9 + y*(p10 + y*(p11 + y))));
result = (result1/result2) + p12*TMath::BesselJ0(x)*log(x);
} else {
z = 8/x;
y = z*z;
xx = x-q1;
result1 = 1 + y*(q2 + y*(q3 + y*(q4 + y*q5)));
result2 = q6 + y*(q7 + y*(q8 + y*(q9 + y*q10)));
result = sqrt(q11/x)*(sin(xx)*result1+z*cos(xx)*result2);
}
return result;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::BesselY1(Double_t x)
{
// Returns the Bessel function Y1(x) for positive x.
Double_t z,xx,y,result,result1,result2;
const Double_t p1 = -0.4900604943e13, p2 = 0.1275274390e13;
const Double_t p3 = -0.5153438139e11, p4 = 0.7349264551e9;
const Double_t p5 = -0.4237922726e7, p6 = 0.8511937935e4;
const Double_t p7 = 0.2499580570e14, p8 = 0.4244419664e12;
const Double_t p9 = 0.3733650367e10, p10 = 0.2245904002e8;
const Double_t p11 = 0.1020426050e6, p12 = 0.3549632885e3;
const Double_t p13 = 0.636619772;
const Double_t q1 = 2.356194491;
const Double_t q2 = 0.183105e-2, q3 = -0.3516396496e-4;
const Double_t q4 = 0.2457520174e-5, q5 = -0.240337019e-6;
const Double_t q6 = 0.04687499995, q7 = -0.2002690873e-3;
const Double_t q8 = 0.8449199096e-5, q9 = -0.88228987e-6;
const Double_t q10 = 0.105787412e-6, q11 = 0.636619772;
if (x < 8) {
y=x*x;
result1 = x*(p1 + y*(p2 + y*(p3 + y*(p4 + y*(p5 + y*p6)))));
result2 = p7 + y*(p8 + y*(p9 + y*(p10 + y*(p11 + y*(p12+y)))));
result = (result1/result2) + p13*(TMath::BesselJ1(x)*log(x)-1/x);
} else {
z = 8/x;
y = z*z;
xx = x-q1;
result1 = 1 + y*(q2 + y*(q3 + y*(q4 + y*q5)));
result2 = q6 + y*(q7 + y*(q8 + y*(q9 + y*q10)));
result = sqrt(q11/x)*(sin(xx)*result1+z*cos(xx)*result2);
}
return result;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::StruveH0(Double_t x)
{
// Struve Functions of Order 0
//
// Converted from CERNLIB M342 by Rene Brun.
const Int_t n1 = 15;
const Int_t n2 = 25;
const Double_t c1[16] = { 1.00215845609911981, -1.63969292681309147,
1.50236939618292819, -.72485115302121872,
.18955327371093136, -.03067052022988,
.00337561447375194, -2.6965014312602e-4,
1.637461692612e-5, -7.8244408508e-7,
3.021593188e-8, -9.6326645e-10,
2.579337e-11, -5.8854e-13,
1.158e-14, -2e-16 };
const Double_t c2[26] = { .99283727576423943, -.00696891281138625,
1.8205103787037e-4, -1.063258252844e-5,
9.8198294287e-7, -1.2250645445e-7,
1.894083312e-8, -3.44358226e-9,
7.1119102e-10, -1.6288744e-10,
4.065681e-11, -1.091505e-11,
3.12005e-12, -9.4202e-13,
2.9848e-13, -9.872e-14,
3.394e-14, -1.208e-14,
4.44e-15, -1.68e-15,
6.5e-16, -2.6e-16,
1.1e-16, -4e-17,
2e-17, -1e-17 };
const Double_t c0 = 2/TMath::Pi();
Int_t i;
Double_t alfa, h, r, y, b0, b1, b2;
Double_t v = TMath::Abs(x);
v = TMath::Abs(x);
if (v < 8) {
y = v/8;
h = 2*y*y -1;
alfa = h + h;
b0 = 0;
b1 = 0;
b2 = 0;
for (i = n1; i >= 0; --i) {
b0 = c1[i] + alfa*b1 - b2;
b2 = b1;
b1 = b0;
}
h = y*(b0 - h*b2);
} else {
r = 1/v;
h = 128*r*r -1;
alfa = h + h;
b0 = 0;
b1 = 0;
b2 = 0;
for (i = n2; i >= 0; --i) {
b0 = c2[i] + alfa*b1 - b2;
b2 = b1;
b1 = b0;
}
h = TMath::BesselY0(v) + r*c0*(b0 - h*b2);
}
if (x < 0) h = -h;
return h;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::StruveH1(Double_t x)
{
// Struve Functions of Order 1
//
// Converted from CERNLIB M342 by Rene Brun.
const Int_t n3 = 16;
const Int_t n4 = 22;
const Double_t c3[17] = { .5578891446481605, -.11188325726569816,
-.16337958125200939, .32256932072405902,
-.14581632367244242, .03292677399374035,
-.00460372142093573, 4.434706163314e-4,
-3.142099529341e-5, 1.7123719938e-6,
-7.416987005e-8, 2.61837671e-9,
-7.685839e-11, 1.9067e-12,
-4.052e-14, 7.5e-16,
-1e-17 };
const Double_t c4[23] = { 1.00757647293865641, .00750316051248257,
-7.043933264519e-5, 2.66205393382e-6,
-1.8841157753e-7, 1.949014958e-8,
-2.6126199e-9, 4.236269e-10,
-7.955156e-11, 1.679973e-11,
-3.9072e-12, 9.8543e-13,
-2.6636e-13, 7.645e-14,
-2.313e-14, 7.33e-15,
-2.42e-15, 8.3e-16,
-3e-16, 1.1e-16,
-4e-17, 2e-17,-1e-17 };
const Double_t c0 = 2/TMath::Pi();
const Double_t cc = 2/(3*TMath::Pi());
Int_t i, i1;
Double_t alfa, h, r, y, b0, b1, b2;
Double_t v = TMath::Abs(x);
if (v == 0) {
h = 0;
} else if (v <= 0.3) {
y = v*v;
r = 1;
h = 1;
i1 = (Int_t)(-8. / TMath::Log10(v));
for (i = 1; i <= i1; ++i) {
h = -h*y / ((2*i+ 1)*(2*i + 3));
r += h;
}
h = cc*y*r;
} else if (v < 8) {
h = v*v/32 -1;
alfa = h + h;
b0 = 0;
b1 = 0;
b2 = 0;
for (i = n3; i >= 0; --i) {
b0 = c3[i] + alfa*b1 - b2;
b2 = b1;
b1 = b0;
}
h = b0 - h*b2;
} else {
h = 128/(v*v) -1;
alfa = h + h;
b0 = 0;
b1 = 0;
b2 = 0;
for (i = n4; i >= 0; --i) {
b0 = c4[i] + alfa*b1 - b2;
b2 = b1;
b1 = b0;
}
h = TMath::BesselY1(v) + c0*(b0 - h*b2);
}
return h;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::StruveL0(Double_t x)
{
// Modified Struve Function of Order 0.
// By Kirill Filimonov.
const Double_t pi=TMath::Pi();
Double_t s=1.0;
Double_t r=1.0;
Double_t a0,sl0,a1,bi0;
Int_t km,i;
if (x<=20.) {
a0=2.0*x/pi;
for (int i=1; i<=60;i++) {
r*=(x/(2*i+1))*(x/(2*i+1));
s+=r;
if(TMath::Abs(r/s)<1.e-12) break;
}
sl0=a0*s;
} else {
km=int(5*(x+1.0));
if(x>=50.0)km=25;
for (i=1; i<=km; i++) {
r*=(2*i-1)*(2*i-1)/x/x;
s+=r;
if(TMath::Abs(r/s)<1.0e-12) break;
}
a1=TMath::Exp(x)/TMath::Sqrt(2*pi*x);
r=1.0;
bi0=1.0;
for (i=1; i<=16; i++) {
r=0.125*r*(2.0*i-1.0)*(2.0*i-1.0)/(i*x);
bi0+=r;
if(TMath::Abs(r/bi0)<1.0e-12) break;
}
bi0=a1*bi0;
sl0=-2.0/(pi*x)*s+bi0;
}
return sl0;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::StruveL1(Double_t x)
{
// Modified Struve Function of Order 1.
// By Kirill Filimonov.
const Double_t pi=TMath::Pi();
Double_t a1,sl1,bi1,s;
Double_t r=1.0;
Int_t km,i;
if (x<=20.) {
s=0.0;
for (i=1; i<=60;i++) {
r*=x*x/(4.0*i*i-1.0);
s+=r;
if(TMath::Abs(r)<TMath::Abs(s)*1.e-12) break;
}
sl1=2.0/pi*s;
} else {
s=1.0;
km=int(0.5*x);
if(x>50.0)km=25;
for (i=1; i<=km; i++) {
r*=(2*i+3)*(2*i+1)/x/x;
s+=r;
if(TMath::Abs(r/s)<1.0e-12) break;
}
sl1=2.0/pi*(-1.0+1.0/(x*x)+3.0*s/(x*x*x*x));
a1=TMath::Exp(x)/TMath::Sqrt(2*pi*x);
r=1.0;
bi1=1.0;
for (i=1; i<=16; i++) {
r=-0.125*r*(4.0-(2.0*i-1.0)*(2.0*i-1.0))/(i*x);
bi1+=r;
if(TMath::Abs(r/bi1)<1.0e-12) break;
}
sl1+=a1*bi1;
}
return sl1;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::Beta(Double_t p, Double_t q)
{
// Calculates Beta-function Gamma(p)*Gamma(q)/Gamma(p+q).
return TMath::Exp(TMath::LnGamma(p)+TMath::LnGamma(q)-TMath::LnGamma(p+q));
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::BetaCf(Double_t x, Double_t a, Double_t b)
{
// Continued fraction evaluation by modified Lentz's method
// used in calculation of incomplete Beta function.
Int_t itmax = 500;
Double_t eps = 3.e-14;
Double_t fpmin = 1.e-30;
Int_t m, m2;
Double_t aa, c, d, del, qab, qam, qap;
Double_t h;
qab = a+b;
qap = a+1.0;
qam = a-1.0;
c = 1.0;
d = 1.0 - qab*x/qap;
if (TMath::Abs(d)<fpmin) d=fpmin;
d=1.0/d;
h=d;
for (m=1; m<=itmax; m++) {
m2=m*2;
aa = m*(b-m)*x/((qam+ m2)*(a+m2));
d = 1.0 +aa*d;
if(TMath::Abs(d)<fpmin) d = fpmin;
c = 1 +aa/c;
if (TMath::Abs(c)<fpmin) c = fpmin;
d=1.0/d;
h*=d*c;
aa = -(a+m)*(qab +m)*x/((a+m2)*(qap+m2));
d=1.0+aa*d;
if(TMath::Abs(d)<fpmin) d = fpmin;
c = 1.0 +aa/c;
if (TMath::Abs(c)<fpmin) c = fpmin;
d=1.0/d;
del = d*c;
h*=del;
if (TMath::Abs(del-1)<=eps) break;
}
if (m>itmax) {
Info("TMath::BetaCf", "a or b too big, or itmax too small, a=%g, b=%g, x=%g, h=%g, itmax=%d",
a,b,x,h,itmax);
}
return h;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::BetaDist(Double_t x, Double_t p, Double_t q)
{
// Computes the probability density function of the Beta distribution
// (the distribution function is computed in BetaDistI).
// The first argument is the point, where the function will be
// computed, second and third are the function parameters.
// Since the Beta distribution is bounded on both sides, it's often
// used to represent processes with natural lower and upper limits.
if ((x<0) || (x>1) || (p<=0) || (q<=0)){
Error("TMath::BetaDist", "parameter value outside allowed range");
return 0;
}
Double_t beta = TMath::Beta(p, q);
Double_t r = TMath::Power(x, p-1)*TMath::Power(1-x, q-1)/beta;
return r;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::BetaDistI(Double_t x, Double_t p, Double_t q)
{
// Computes the distribution function of the Beta distribution.
// The first argument is the point, where the function will be
// computed, second and third are the function parameters.
// Since the Beta distribution is bounded on both sides, it's often
// used to represent processes with natural lower and upper limits.
if ((x<0) || (x>1) || (p<=0) || (q<=0)){
Error("TMath::BetaDistI", "parameter value outside allowed range");
return 0;
}
Double_t betai = TMath::BetaIncomplete(x, p, q);
return betai;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::BetaIncomplete(Double_t x, Double_t a, Double_t b)
{
// Calculates the incomplete Beta-function.
// -- implementation by Anna Kreshuk
Double_t bt;
if ((x<0.0)||(x>1.0)) {
Error("TMath::BetaIncomplete", "X must between 0 and 1");
return 0.0;
}
if ((x==0.0)||(x==1.0)) {
bt=0.0;
} else {
bt = TMath::Power(x, a)*TMath::Power(1-x, b)/Beta(a, b);
}
if (x<(a+1)/(a+b+2)) {
return bt*BetaCf(x, a, b)/a;
}
else {
return (1 - bt*BetaCf(1-x, b, a)/b);
}
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::Binomial(Int_t n,Int_t k)
{
// Calculate the binomial coefficient n over k.
if (k==0 || n==k) return 1;
if (n<=0 || k<0 || n<k) return 0;
Int_t k1=TMath::Min(k,n-k);
Int_t k2=n-k1;
Double_t fact=k2+1;
for (Int_t i=k1;i>1;i--)
fact*=static_cast<Double_t>(k2+i)/i;
return fact;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::BinomialI(Double_t p, Int_t n, Int_t k)
{
// Suppose an event occurs with probability _p_ per trial
// Then the probability P of its occuring _k_ or more times
// in _n_ trials is termed a cumulative binomial probability
// the formula is P = sum_from_j=k_to_n(TMath::Binomial(n, j)*
// *TMath::Power(p, j)*TMath::Power(1-p, n-j)
// For _n_ larger than 12 BetaIncomplete is a much better way
// to evaluate the sum than would be the straightforward sum calculation
// for _n_ smaller than 12 either method is acceptable
// ("Numerical Recipes")
// --implementation by Anna Kreshuk
return BetaIncomplete(p, Double_t(k), Double_t(n-k+1));
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::CauchyDist(Double_t x, Double_t t, Double_t s)
{
// Computes the density of Cauchy distribution at point x
// by default, standard Cauchy distribution is used (t=0, s=1)
// t is the location parameter
// s is the scale parameter
// The Cauchy distribution, also called Lorentzian distribution,
// is a continuous distribution describing resonance behavior
// The mean and standard deviation of the Cauchy distribution are undefined.
// The practical meaning of this is that collecting 1,000 data points gives
// no more accurate an estimate of the mean and standard deviation than
// does a single point.
// The formula was taken from "Engineering Statistics Handbook" on site
// http://www.itl.nist.gov/div898/handbook/eda/section3/eda3663.htm
// Implementation by Anna Kreshuk.
// Example:
// TF1* fc = new TF1("fc", "TMath::CauchyDist(x, [0], [1])", -5, 5);
// fc->SetParameters(0, 1);
// fc->Draw();
Double_t temp= (x-t)*(x-t)/(s*s);
Double_t result = 1/(s*TMath::Pi()*(1+temp));
return result;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::ChisquareQuantile(Double_t p, Double_t ndf)
{
// Evaluate the quantiles of the chi-squared probability distribution function.
// Algorithm AS 91 Appl. Statist. (1975) Vol.24, P.35
// implemented by Anna Kreshuk.
// Incorporates the suggested changes in AS R85 (vol.40(1), pp.233-5, 1991)
// Parameters:
// p - the probability value, at which the quantile is computed
// ndf - number of degrees of freedom
Double_t c[]={0, 0.01, 0.222222, 0.32, 0.4, 1.24, 2.2,
4.67, 6.66, 6.73, 13.32, 60.0, 70.0,
84.0, 105.0, 120.0, 127.0, 140.0, 175.0,
210.0, 252.0, 264.0, 294.0, 346.0, 420.0,
462.0, 606.0, 672.0, 707.0, 735.0, 889.0,
932.0, 966.0, 1141.0, 1182.0, 1278.0, 1740.0,
2520.0, 5040.0};
Double_t e = 5e-7;
Double_t aa = 0.6931471806;
Int_t maxit = 20;
Double_t ch, p1, p2, q, t, a, b, x;
Double_t s1, s2, s3, s4, s5, s6;
if (ndf <= 0) return 0;
Double_t g = TMath::LnGamma(0.5*ndf);
Double_t xx = 0.5 * ndf;
Double_t cp = xx - 1;
if (ndf >= TMath::Log(p)*(-c[5])){
//starting approximation for ndf less than or equal to 0.32
if (ndf > c[3]) {
x = TMath::NormQuantile(p);
//starting approximation using Wilson and Hilferty estimate
p1=c[2]/ndf;
ch = ndf*TMath::Power((x*TMath::Sqrt(p1) + 1 - p1), 3);
if (ch > c[6]*ndf + 6)
ch = -2 * (TMath::Log(1-p) - cp * TMath::Log(0.5 * ch) + g);
} else {
ch = c[4];
a = TMath::Log(1-p);
do{
q = ch;
p1 = 1 + ch * (c[7]+ch);
p2 = ch * (c[9] + ch * (c[8] + ch));
t = -0.5 + (c[7] + 2 * ch) / p1 - (c[9] + ch * (c[10] + 3 * ch)) / p2;
ch = ch - (1 - TMath::Exp(a + g + 0.5 * ch + cp * aa) *p2 / p1) / t;
}while (TMath::Abs(q/ch - 1) > c[1]);
}
} else {
ch = TMath::Power((p * xx * TMath::Exp(g + xx * aa)),(1./xx));
if (ch < e) return ch;
}
//call to algorithm AS 239 and calculation of seven term Taylor series
for (Int_t i=0; i<maxit; i++){
q = ch;
p1 = 0.5 * ch;
p2 = p - TMath::Gamma(xx, p1);
t = p2 * TMath::Exp(xx * aa + g + p1 - cp * TMath::Log(ch));
b = t / ch;
a = 0.5 * t - b * cp;
s1 = (c[19] + a * (c[17] + a * (c[14] + a * (c[13] + a * (c[12] +c[11] * a))))) / c[24];
s2 = (c[24] + a * (c[29] + a * (c[32] + a * (c[33] + c[35] * a)))) / c[37];
s3 = (c[19] + a * (c[25] + a * (c[28] + c[31] * a))) / c[37];
s4 = (c[20] + a * (c[27] + c[34] * a) + cp * (c[22] + a * (c[30] + c[36] * a))) / c[38];
s5 = (c[13] + c[21] * a + cp * (c[18] + c[26] * a)) / c[37];
s6 = (c[15] + cp * (c[23] + c[16] * cp)) / c[38];
ch = ch + t * (1 + 0.5 * t * s1 - b * cp * (s1 - b * (s2 - b * (s3 - b * (s4 - b * (s5 - b * s6))))));
if (TMath::Abs(q / ch - 1) > e) break;
}
return ch;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::FDist(Double_t F, Double_t N, Double_t M)
{
// Computes the density function of F-distribution
// (probability function, integral of density, is computed in FDistI).
//
// Parameters N and M stand for degrees of freedom of chi-squares
// mentioned above parameter F is the actual variable x of the
// density function p(x) and the point at which the density function
// is calculated.
//
// About F distribution:
// F-distribution arises in testing whether two random samples
// have the same variance. It is the ratio of two chi-square
// distributions, with N and M degrees of freedom respectively,
// where each chi-square is first divided by it's number of degrees
// of freedom.
// Implementation by Anna Kreshuk.
if ((F<0)||(N<1)||(M<1)){
return 0;
} else {
Double_t denom = TMath::Gamma(N/2)*TMath::Gamma(M/2)*TMath::Power(M+N*F, (N+M)/2);
Double_t div = TMath::Gamma((N+M)/2)*TMath::Power(N, N/2)*TMath::Power(M, M/2)*TMath::Power(F, 0.5*N-1);
return div/denom;
}
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::FDistI(Double_t F, Double_t N, Double_t M)
{
// Calculates the cumulative distribution function of F-distribution,
// this function occurs in the statistical test of whether two observed
// samples have the same variance. For this test a certain statistic F,
// the ratio of observed dispersion of the first sample to that of the
// second sample, is calculated. N and M stand for numbers of degrees
// of freedom in the samples 1-FDistI() is the significance level at
// which the hypothesis "1 has smaller variance than 2" can be rejected.
// A small numerical value of 1 - FDistI() implies a very significant
// rejection, in turn implying high confidence in the hypothesis
// "1 has variance greater than 2".
// Implementation by Anna Kreshuk.
Double_t fi = 1 - BetaIncomplete((M/(M+N*F)), M*0.5, N*0.5);
return fi;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::GammaDist(Double_t x, Double_t gamma, Double_t mu, Double_t beta)
{
// Computes the density function of Gamma distribution at point x.
// gamma - shape parameter
// mu - location parameter
// beta - scale parameter
// The formula was taken from "Engineering Statistics Handbook" on site
// http://www.itl.nist.gov/div898/handbook/eda/section3/eda366b.htm
// Implementation by Anna Kreshuk.
//
/*
 */
//
if ((x<mu) || (gamma<=0) || (beta <=0)) {
Error("TMath::GammaDist", "illegal parameter values");
return 0;
}
Double_t temp = (x-mu)/beta;
Double_t temp2 = beta * TMath::Gamma(gamma);
Double_t result = (TMath::Power(temp, gamma-1) * TMath::Exp(-temp))/temp2;
return result;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::LaplaceDist(Double_t x, Double_t alpha, Double_t beta)
{
// Computes the probability density funciton of Laplace distribution
// at point x, with location parameter alpha and shape parameter beta.
// By default, alpha=0, beta=1
// This distribution is known under different names, most common is
// double exponential distribution, but it also appears as
// the two-tailed exponential or the bilateral exponential distribution
Double_t temp;
temp = TMath::Exp(-TMath::Abs((x-alpha)/beta));
temp /= (2.*beta);
return temp;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::LaplaceDistI(Double_t x, Double_t alpha, Double_t beta)
{
// Computes the distribution funciton of Laplace distribution
// at point x, with location parameter alpha and shape parameter beta.
// By default, alpha=0, beta=1
// This distribution is known under different names, most common is
// double exponential distribution, but it also appears as
// the two-tailed exponential or the bilateral exponential distribution
Double_t temp;
if (x<=alpha){
temp = 0.5*TMath::Exp(-TMath::Abs((x-alpha)/beta));
} else {
temp = 1-0.5*TMath::Exp(-TMath::Abs((x-alpha)/beta));
}
return temp;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::LogNormal(Double_t x, Double_t sigma, Double_t theta, Double_t m)
{
// Computes the density of LogNormal distribution at point x.
// Variable X has lognormal distribution if Y=Ln(X) has normal distribution
// sigma is the shape parameter
// theta is the location parameter
// m is the scale parameter
// The formula was taken from "Engineering Statistics Handbook" on site
// http://www.itl.nist.gov/div898/handbook/eda/section3/eda3669.htm
// Implementation by Anna Kreshuk.
//
/*
*/
//
if ((x<mu) || (gamma<=0) || (beta <=0)) {
Error("TMath::GammaDist", "illegal parameter values");
return 0;
}
Double_t temp = (x-mu)/beta;
Double_t temp2 = beta * TMath::Gamma(gamma);
Double_t result = (TMath::Power(temp, gamma-1) * TMath::Exp(-temp))/temp2;
return result;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::LaplaceDist(Double_t x, Double_t alpha, Double_t beta)
{
// Computes the probability density funciton of Laplace distribution
// at point x, with location parameter alpha and shape parameter beta.
// By default, alpha=0, beta=1
// This distribution is known under different names, most common is
// double exponential distribution, but it also appears as
// the two-tailed exponential or the bilateral exponential distribution
Double_t temp;
temp = TMath::Exp(-TMath::Abs((x-alpha)/beta));
temp /= (2.*beta);
return temp;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::LaplaceDistI(Double_t x, Double_t alpha, Double_t beta)
{
// Computes the distribution funciton of Laplace distribution
// at point x, with location parameter alpha and shape parameter beta.
// By default, alpha=0, beta=1
// This distribution is known under different names, most common is
// double exponential distribution, but it also appears as
// the two-tailed exponential or the bilateral exponential distribution
Double_t temp;
if (x<=alpha){
temp = 0.5*TMath::Exp(-TMath::Abs((x-alpha)/beta));
} else {
temp = 1-0.5*TMath::Exp(-TMath::Abs((x-alpha)/beta));
}
return temp;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::LogNormal(Double_t x, Double_t sigma, Double_t theta, Double_t m)
{
// Computes the density of LogNormal distribution at point x.
// Variable X has lognormal distribution if Y=Ln(X) has normal distribution
// sigma is the shape parameter
// theta is the location parameter
// m is the scale parameter
// The formula was taken from "Engineering Statistics Handbook" on site
// http://www.itl.nist.gov/div898/handbook/eda/section3/eda3669.htm
// Implementation by Anna Kreshuk.
//
/*
 */
//
if ((x<theta) || (sigma<=0) || (m<=0)) {
Error("TMath::Lognormal", "illegal parameter values");
return 0;
}
Double_t templog2 = TMath::Log((x-theta)/m)*TMath::Log((x-theta)/m);
Double_t temp1 = TMath::Exp(-templog2/(2*sigma*sigma));
Double_t temp2 = (x-theta)*sigma*TMath::Sqrt(2*TMath::Pi());
return temp1/temp2;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::NormQuantile(Double_t p)
{
// Computes quantiles for standard normal distribution N(0, 1)
// at probability p
// ALGORITHM AS241 APPL. STATIST. (1988) VOL. 37, NO. 3, 477-484.
if ((p<=0)||(p>=1)) {
Error("TMath::NormQuantile", "probability outside (0, 1)");
return 0;
}
Double_t a0 = 3.3871328727963666080e0;
Double_t a1 = 1.3314166789178437745e+2;
Double_t a2 = 1.9715909503065514427e+3;
Double_t a3 = 1.3731693765509461125e+4;
Double_t a4 = 4.5921953931549871457e+4;
Double_t a5 = 6.7265770927008700853e+4;
Double_t a6 = 3.3430575583588128105e+4;
Double_t a7 = 2.5090809287301226727e+3;
Double_t b1 = 4.2313330701600911252e+1;
Double_t b2 = 6.8718700749205790830e+2;
Double_t b3 = 5.3941960214247511077e+3;
Double_t b4 = 2.1213794301586595867e+4;
Double_t b5 = 3.9307895800092710610e+4;
Double_t b6 = 2.8729085735721942674e+4;
Double_t b7 = 5.2264952788528545610e+3;
Double_t c0 = 1.42343711074968357734e0;
Double_t c1 = 4.63033784615654529590e0;
Double_t c2 = 5.76949722146069140550e0;
Double_t c3 = 3.64784832476320460504e0;
Double_t c4 = 1.27045825245236838258e0;
Double_t c5 = 2.41780725177450611770e-1;
Double_t c6 = 2.27238449892691845833e-2;
Double_t c7 = 7.74545014278341407640e-4;
Double_t d1 = 2.05319162663775882187e0;
Double_t d2 = 1.67638483018380384940e0;
Double_t d3 = 6.89767334985100004550e-1;
Double_t d4 = 1.48103976427480074590e-1;
Double_t d5 = 1.51986665636164571966e-2;
Double_t d6 = 5.47593808499534494600e-4;
Double_t d7 = 1.05075007164441684324e-9;
Double_t e0 = 6.65790464350110377720e0;
Double_t e1 = 5.46378491116411436990e0;
Double_t e2 = 1.78482653991729133580e0;
Double_t e3 = 2.96560571828504891230e-1;
Double_t e4 = 2.65321895265761230930e-2;
Double_t e5 = 1.24266094738807843860e-3;
Double_t e6 = 2.71155556874348757815e-5;
Double_t e7 = 2.01033439929228813265e-7;
Double_t f1 = 5.99832206555887937690e-1;
Double_t f2 = 1.36929880922735805310e-1;
Double_t f3 = 1.48753612908506148525e-2;
Double_t f4 = 7.86869131145613259100e-4;
Double_t f5 = 1.84631831751005468180e-5;
Double_t f6 = 1.42151175831644588870e-7;
Double_t f7 = 2.04426310338993978564e-15;
Double_t split1 = 0.425;
Double_t split2=5.;
Double_t konst1=0.180625;
Double_t konst2=1.6;
Double_t q, r, quantile;
q=p-0.5;
if (TMath::Abs(q)<split1) {
r=konst1-q*q;
quantile = q* (((((((a7 * r + a6) * r + a5) * r + a4) * r + a3)
* r + a2) * r + a1) * r + a0) /
(((((((b7 * r + b6) * r + b5) * r + b4) * r + b3)
* r + b2) * r + b1) * r + 1.);
} else {
if(q<0) r=p;
else r=1-p;
//error case
if (r<=0)
quantile=0;
else {
r=TMath::Sqrt(-TMath::Log(r));
if (r<=split2) {
r=r-konst2;
quantile=(((((((c7 * r + c6) * r + c5) * r + c4) * r + c3)
* r + c2) * r + c1) * r + c0) /
(((((((d7 * r + d6) * r + d5) * r + d4) * r + d3)
* r + d2) * r + d1) * r + 1);
} else{
r=r-split2;
quantile=(((((((e7 * r + e6) * r + e5) * r + e4) * r + e3)
* r + e2) * r + e1) * r + e0) /
(((((((f7 * r + f6) * r + f5) * r + f4) * r + f3)
* r + f2) * r + f1) * r + 1);
}
if (q<0) quantile=-quantile;
}
}
return quantile;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Bool_t TMath::Permute(Int_t n, Int_t *a)
{
// Simple recursive algorithm to find the permutations of
// n natural numbers, not necessarily all distinct
// adapted from CERNLIB routine PERMU.
// The input array has to be initialised with a non descending
// sequence. The method returns kFALSE when
// all combinations are exhausted.
Int_t i,itmp;
Int_t i1=-1;
// find rightmost upward transition
for(i=n-2; i>-1; i--) {
if(a[i]<a[i+1]) {
i1=i;
break;
}
}
// no more upward transitions, end of the story
if(i1==-1) return kFALSE;
else {
// find lower right element higher than the lower
// element of the upward transition
for(i=n-1;i>i1;i--) {
if(a[i] > a[i1]) {
// swap the two
itmp=a[i1];
a[i1]=a[i];
a[i]=itmp;
break;
}
}
// order the rest, in fact just invert, as there
// are only downward transitions from here on
for(i=0;i<(n-i1-1)/2;i++) {
itmp=a[i1+i+1];
a[i1+i+1]=a[n-i-1];
a[n-i-1]=itmp;
}
}
return kTRUE;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::Student(Double_t T, Double_t ndf)
{
// Computes density function for Student's t- distribution
// (the probability function (integral of density) is computed in StudentI).
//
// First parameter stands for x - the actual variable of the
// density function p(x) and the point at which the density is calculated.
// Second parameter stands for number of degrees of freedom.
//
// About Student distribution:
// Student's t-distribution is used for many significance tests, for example,
// for the Student's t-tests for the statistical significance of difference
// between two sample means and for confidence intervals for the difference
// between two population means.
//
// Example: suppose we have a random sample of size n drawn from normal
// distribution with mean Mu and st.deviation Sigma. Then the variable
//
// t = (sample_mean - Mu)/(sample_deviation / sqrt(n))
//
// has Student's t-distribution with n-1 degrees of freedom.
//
// NOTE that this function's second argument is number of degrees of freedom,
// not the sample size.
//
// As the number of degrees of freedom grows, t-distribution approaches
// Normal(0,1) distribution.
// Implementation by Anna Kreshuk.
if (ndf < 1) {
return 0;
}
Double_t r = ndf;
Double_t rh = 0.5*r;
Double_t rh1 = rh + 0.5;
Double_t denom = TMath::Sqrt(r*TMath::Pi())*TMath::Gamma(rh)*TMath::Power(1+T*T/r, rh1);
return TMath::Gamma(rh1)/denom;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::StudentI(Double_t T, Double_t ndf)
{
// Calculates the cumulative distribution function of Student's
// t-distribution second parameter stands for number of degrees of freedom,
// not for the number of samples
// if x has Student's t-distribution, the function returns the probability of
// x being less than T.
// Implementation by Anna Kreshuk.
Double_t r = ndf;
Double_t si = (T>0) ?
(1 - 0.5*BetaIncomplete((r/(r + T*T)), r*0.5, 0.5)) :
0.5*BetaIncomplete((r/(r + T*T)), r*0.5, 0.5);
return si;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::StudentQuantile(Double_t p, Double_t ndf, Bool_t lower_tail)
{
// Computes quantiles of the Student's t-distribution
// 1st argument is the probability, at which the quantile is computed
// 2nd argument - the number of degrees of freedom of the
// Student distribution
// When the 3rd argument lower_tail is kTRUE (default)-
// the algorithm returns such x0, that
// P(x < x0)=p
// upper tail (lower_tail is kFALSE)- the algorithm returns such x0, that
// P(x > x0)=p
// the algorithm was taken from
// G.W.Hill, "Algorithm 396, Student's t-quantiles"
// "Communications of the ACM", 13(10), October 1970
Double_t quantile;
Double_t temp;
Bool_t neg;
Double_t q;
if (ndf<1 || p>=1 || p<=0) {
Error("TMath::StudentQuantile", "illegal parameter values");
return 0;
}
if ((lower_tail && p>0.5)||(!lower_tail && p<0.5)){
neg=kFALSE;
q=2*(lower_tail ? (1-p) : p);
} else {
neg=kTRUE;
q=2*(lower_tail? p : (1-p));
}
if ((ndf-2)<1e-8) {
quantile = TMath::Sqrt(2./(q*(2-q))-2);
} else {
if ((ndf-1)<1e-8) {
temp=TMath::PiOver2()*q;
quantile = TMath::Cos(temp)/TMath::Sin(temp);
} else {
Double_t a=1./(ndf-0.5);
Double_t b=48./(a*a);
Double_t c=((20700*a/b -98)*a-16)*a+96.36;
Double_t d=((94.5/(b+c)-3.)/b+1)*TMath::Sqrt(a*TMath::PiOver2())*ndf;
Double_t x=q*d;
Double_t y=TMath::Power(x, (2./ndf));
if (y>0.05+a){
//asymptotic inverse expansion about normal
x=NormQuantile(q*0.5);
y=x*x;
if (ndf<5) c+=0.3*(ndf-4.5)*(x+0.6);
c+=(((0.05*d*x-5.)*x-7.)*x-2.)*x +b;
y=(((((0.4*y+6.3)*y+36.)*y+94.5)/c - y-3.)/b+1)*x;
y=a*y*y;
if(y>0.002) y = TMath::Exp(y)-1;
else y += 0.5*y*y;
} else {
y=((1./(((ndf+6.)/(ndf*y)-0.089*d-0.822)*(ndf+2.)*3)+0.5/(ndf+4.))*y-1.)*
(ndf+1.)/(ndf+2.)+1/y;
}
quantile = TMath::Sqrt(ndf*y);
}
}
if(neg) quantile=-quantile;
return quantile;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::Vavilov(Double_t x, Double_t kappa, Double_t beta2)
{
//Returns the value of the Vavilov density function
//Parameters: 1st - the point were the density function is evaluated
// 2nd - value of kappa (distribution parameter)
// 3rd - value of beta2 (distribution parameter)
//The algorithm was taken from the CernLib function vavden(G115)
//Reference: A.Rotondi and P.Montagna, Fast Calculation of Vavilov distribution
//Nucl.Instr. and Meth. B47(1990), 215-224
//Accuracy: quote from the reference above:
//"The resuls of our code have been compared with the values of the Vavilov
//density function computed numerically in an accurate way: our approximation
//shows a difference of less than 3% around the peak of the density function, slowly
//increasing going towards the extreme tails to the right and to the left"
//
/*
*/
//
if ((x<theta) || (sigma<=0) || (m<=0)) {
Error("TMath::Lognormal", "illegal parameter values");
return 0;
}
Double_t templog2 = TMath::Log((x-theta)/m)*TMath::Log((x-theta)/m);
Double_t temp1 = TMath::Exp(-templog2/(2*sigma*sigma));
Double_t temp2 = (x-theta)*sigma*TMath::Sqrt(2*TMath::Pi());
return temp1/temp2;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::NormQuantile(Double_t p)
{
// Computes quantiles for standard normal distribution N(0, 1)
// at probability p
// ALGORITHM AS241 APPL. STATIST. (1988) VOL. 37, NO. 3, 477-484.
if ((p<=0)||(p>=1)) {
Error("TMath::NormQuantile", "probability outside (0, 1)");
return 0;
}
Double_t a0 = 3.3871328727963666080e0;
Double_t a1 = 1.3314166789178437745e+2;
Double_t a2 = 1.9715909503065514427e+3;
Double_t a3 = 1.3731693765509461125e+4;
Double_t a4 = 4.5921953931549871457e+4;
Double_t a5 = 6.7265770927008700853e+4;
Double_t a6 = 3.3430575583588128105e+4;
Double_t a7 = 2.5090809287301226727e+3;
Double_t b1 = 4.2313330701600911252e+1;
Double_t b2 = 6.8718700749205790830e+2;
Double_t b3 = 5.3941960214247511077e+3;
Double_t b4 = 2.1213794301586595867e+4;
Double_t b5 = 3.9307895800092710610e+4;
Double_t b6 = 2.8729085735721942674e+4;
Double_t b7 = 5.2264952788528545610e+3;
Double_t c0 = 1.42343711074968357734e0;
Double_t c1 = 4.63033784615654529590e0;
Double_t c2 = 5.76949722146069140550e0;
Double_t c3 = 3.64784832476320460504e0;
Double_t c4 = 1.27045825245236838258e0;
Double_t c5 = 2.41780725177450611770e-1;
Double_t c6 = 2.27238449892691845833e-2;
Double_t c7 = 7.74545014278341407640e-4;
Double_t d1 = 2.05319162663775882187e0;
Double_t d2 = 1.67638483018380384940e0;
Double_t d3 = 6.89767334985100004550e-1;
Double_t d4 = 1.48103976427480074590e-1;
Double_t d5 = 1.51986665636164571966e-2;
Double_t d6 = 5.47593808499534494600e-4;
Double_t d7 = 1.05075007164441684324e-9;
Double_t e0 = 6.65790464350110377720e0;
Double_t e1 = 5.46378491116411436990e0;
Double_t e2 = 1.78482653991729133580e0;
Double_t e3 = 2.96560571828504891230e-1;
Double_t e4 = 2.65321895265761230930e-2;
Double_t e5 = 1.24266094738807843860e-3;
Double_t e6 = 2.71155556874348757815e-5;
Double_t e7 = 2.01033439929228813265e-7;
Double_t f1 = 5.99832206555887937690e-1;
Double_t f2 = 1.36929880922735805310e-1;
Double_t f3 = 1.48753612908506148525e-2;
Double_t f4 = 7.86869131145613259100e-4;
Double_t f5 = 1.84631831751005468180e-5;
Double_t f6 = 1.42151175831644588870e-7;
Double_t f7 = 2.04426310338993978564e-15;
Double_t split1 = 0.425;
Double_t split2=5.;
Double_t konst1=0.180625;
Double_t konst2=1.6;
Double_t q, r, quantile;
q=p-0.5;
if (TMath::Abs(q)<split1) {
r=konst1-q*q;
quantile = q* (((((((a7 * r + a6) * r + a5) * r + a4) * r + a3)
* r + a2) * r + a1) * r + a0) /
(((((((b7 * r + b6) * r + b5) * r + b4) * r + b3)
* r + b2) * r + b1) * r + 1.);
} else {
if(q<0) r=p;
else r=1-p;
//error case
if (r<=0)
quantile=0;
else {
r=TMath::Sqrt(-TMath::Log(r));
if (r<=split2) {
r=r-konst2;
quantile=(((((((c7 * r + c6) * r + c5) * r + c4) * r + c3)
* r + c2) * r + c1) * r + c0) /
(((((((d7 * r + d6) * r + d5) * r + d4) * r + d3)
* r + d2) * r + d1) * r + 1);
} else{
r=r-split2;
quantile=(((((((e7 * r + e6) * r + e5) * r + e4) * r + e3)
* r + e2) * r + e1) * r + e0) /
(((((((f7 * r + f6) * r + f5) * r + f4) * r + f3)
* r + f2) * r + f1) * r + 1);
}
if (q<0) quantile=-quantile;
}
}
return quantile;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Bool_t TMath::Permute(Int_t n, Int_t *a)
{
// Simple recursive algorithm to find the permutations of
// n natural numbers, not necessarily all distinct
// adapted from CERNLIB routine PERMU.
// The input array has to be initialised with a non descending
// sequence. The method returns kFALSE when
// all combinations are exhausted.
Int_t i,itmp;
Int_t i1=-1;
// find rightmost upward transition
for(i=n-2; i>-1; i--) {
if(a[i]<a[i+1]) {
i1=i;
break;
}
}
// no more upward transitions, end of the story
if(i1==-1) return kFALSE;
else {
// find lower right element higher than the lower
// element of the upward transition
for(i=n-1;i>i1;i--) {
if(a[i] > a[i1]) {
// swap the two
itmp=a[i1];
a[i1]=a[i];
a[i]=itmp;
break;
}
}
// order the rest, in fact just invert, as there
// are only downward transitions from here on
for(i=0;i<(n-i1-1)/2;i++) {
itmp=a[i1+i+1];
a[i1+i+1]=a[n-i-1];
a[n-i-1]=itmp;
}
}
return kTRUE;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::Student(Double_t T, Double_t ndf)
{
// Computes density function for Student's t- distribution
// (the probability function (integral of density) is computed in StudentI).
//
// First parameter stands for x - the actual variable of the
// density function p(x) and the point at which the density is calculated.
// Second parameter stands for number of degrees of freedom.
//
// About Student distribution:
// Student's t-distribution is used for many significance tests, for example,
// for the Student's t-tests for the statistical significance of difference
// between two sample means and for confidence intervals for the difference
// between two population means.
//
// Example: suppose we have a random sample of size n drawn from normal
// distribution with mean Mu and st.deviation Sigma. Then the variable
//
// t = (sample_mean - Mu)/(sample_deviation / sqrt(n))
//
// has Student's t-distribution with n-1 degrees of freedom.
//
// NOTE that this function's second argument is number of degrees of freedom,
// not the sample size.
//
// As the number of degrees of freedom grows, t-distribution approaches
// Normal(0,1) distribution.
// Implementation by Anna Kreshuk.
if (ndf < 1) {
return 0;
}
Double_t r = ndf;
Double_t rh = 0.5*r;
Double_t rh1 = rh + 0.5;
Double_t denom = TMath::Sqrt(r*TMath::Pi())*TMath::Gamma(rh)*TMath::Power(1+T*T/r, rh1);
return TMath::Gamma(rh1)/denom;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::StudentI(Double_t T, Double_t ndf)
{
// Calculates the cumulative distribution function of Student's
// t-distribution second parameter stands for number of degrees of freedom,
// not for the number of samples
// if x has Student's t-distribution, the function returns the probability of
// x being less than T.
// Implementation by Anna Kreshuk.
Double_t r = ndf;
Double_t si = (T>0) ?
(1 - 0.5*BetaIncomplete((r/(r + T*T)), r*0.5, 0.5)) :
0.5*BetaIncomplete((r/(r + T*T)), r*0.5, 0.5);
return si;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::StudentQuantile(Double_t p, Double_t ndf, Bool_t lower_tail)
{
// Computes quantiles of the Student's t-distribution
// 1st argument is the probability, at which the quantile is computed
// 2nd argument - the number of degrees of freedom of the
// Student distribution
// When the 3rd argument lower_tail is kTRUE (default)-
// the algorithm returns such x0, that
// P(x < x0)=p
// upper tail (lower_tail is kFALSE)- the algorithm returns such x0, that
// P(x > x0)=p
// the algorithm was taken from
// G.W.Hill, "Algorithm 396, Student's t-quantiles"
// "Communications of the ACM", 13(10), October 1970
Double_t quantile;
Double_t temp;
Bool_t neg;
Double_t q;
if (ndf<1 || p>=1 || p<=0) {
Error("TMath::StudentQuantile", "illegal parameter values");
return 0;
}
if ((lower_tail && p>0.5)||(!lower_tail && p<0.5)){
neg=kFALSE;
q=2*(lower_tail ? (1-p) : p);
} else {
neg=kTRUE;
q=2*(lower_tail? p : (1-p));
}
if ((ndf-2)<1e-8) {
quantile = TMath::Sqrt(2./(q*(2-q))-2);
} else {
if ((ndf-1)<1e-8) {
temp=TMath::PiOver2()*q;
quantile = TMath::Cos(temp)/TMath::Sin(temp);
} else {
Double_t a=1./(ndf-0.5);
Double_t b=48./(a*a);
Double_t c=((20700*a/b -98)*a-16)*a+96.36;
Double_t d=((94.5/(b+c)-3.)/b+1)*TMath::Sqrt(a*TMath::PiOver2())*ndf;
Double_t x=q*d;
Double_t y=TMath::Power(x, (2./ndf));
if (y>0.05+a){
//asymptotic inverse expansion about normal
x=NormQuantile(q*0.5);
y=x*x;
if (ndf<5) c+=0.3*(ndf-4.5)*(x+0.6);
c+=(((0.05*d*x-5.)*x-7.)*x-2.)*x +b;
y=(((((0.4*y+6.3)*y+36.)*y+94.5)/c - y-3.)/b+1)*x;
y=a*y*y;
if(y>0.002) y = TMath::Exp(y)-1;
else y += 0.5*y*y;
} else {
y=((1./(((ndf+6.)/(ndf*y)-0.089*d-0.822)*(ndf+2.)*3)+0.5/(ndf+4.))*y-1.)*
(ndf+1.)/(ndf+2.)+1/y;
}
quantile = TMath::Sqrt(ndf*y);
}
}
if(neg) quantile=-quantile;
return quantile;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::Vavilov(Double_t x, Double_t kappa, Double_t beta2)
{
//Returns the value of the Vavilov density function
//Parameters: 1st - the point were the density function is evaluated
// 2nd - value of kappa (distribution parameter)
// 3rd - value of beta2 (distribution parameter)
//The algorithm was taken from the CernLib function vavden(G115)
//Reference: A.Rotondi and P.Montagna, Fast Calculation of Vavilov distribution
//Nucl.Instr. and Meth. B47(1990), 215-224
//Accuracy: quote from the reference above:
//"The resuls of our code have been compared with the values of the Vavilov
//density function computed numerically in an accurate way: our approximation
//shows a difference of less than 3% around the peak of the density function, slowly
//increasing going towards the extreme tails to the right and to the left"
//
/*
 */
//
Double_t *ac = new Double_t[14];
Double_t *hc = new Double_t[9];
Int_t itype;
Int_t npt;
TMath::VavilovSet(kappa, beta2, 0, 0, ac, hc, itype, npt);
Double_t v = TMath::VavilovDenEval(x, ac, hc, itype);
delete [] ac;
delete [] hc;
return v;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::VavilovI(Double_t x, Double_t kappa, Double_t beta2)
{
//Returns the value of the Vavilov distribution function
//Parameters: 1st - the point were the density function is evaluated
// 2nd - value of kappa (distribution parameter)
// 3rd - value of beta2 (distribution parameter)
//The algorithm was taken from the CernLib function vavden(G115)
//Reference: A.Rotondi and P.Montagna, Fast Calculation of Vavilov distribution
//Nucl.Instr. and Meth. B47(1990), 215-224
//Accuracy: quote from the reference above:
//"The resuls of our code have been compared with the values of the Vavilov
//density function computed numerically in an accurate way: our approximation
//shows a difference of less than 3% around the peak of the density function, slowly
//increasing going towards the extreme tails to the right and to the left"
Double_t *ac = new Double_t[14];
Double_t *hc = new Double_t[9];
Double_t *wcm = new Double_t[200];
Int_t itype;
Int_t npt;
Int_t k;
Double_t xx, v;
TMath::VavilovSet(kappa, beta2, 1, wcm, ac, hc, itype, npt);
if (x < ac[0]) v = 0;
else if (x >=ac[8]) v = 1;
else {
xx = x - ac[0];
k = Int_t(xx*ac[10]);
v = TMath::Min(wcm[k] + (xx - k*ac[9])*(wcm[k+1]-wcm[k])*ac[10], 1.);
}
delete [] ac;
delete [] hc;
delete [] wcm;
return v;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::LandauI(Double_t x)
{
//Returns the value of the Landau distribution function at point x.
//The algorithm was taken from the Cernlib function dislan(G110)
//Reference: K.S.Kolbig and B.Schorr, "A program package for the Landau
//distribution", Computer Phys.Comm., 31(1984), 97-111
Double_t p1[] = {0.2514091491e+0,-0.6250580444e-1, 0.1458381230e-1, -0.2108817737e-2, 0.7411247290e-3};
Double_t q1[] = {1.0 ,-0.5571175625e-2, 0.6225310236e-1, -0.3137378427e-2, 0.1931496439e-2};
Double_t p2[] = {0.2868328584e+0, 0.3564363231e+0, 0.1523518695e+0, 0.2251304883e-1};
Double_t q2[] = {1.0 , 0.6191136137e+0, 0.1720721448e+0, 0.2278594771e-1};
Double_t p3[] = {0.2868329066e+0, 0.3003828436e+0, 0.9950951941e-1, 0.8733827185e-2};
Double_t q3[] = {1.0 , 0.4237190502e+0, 0.1095631512e+0, 0.8693851567e-2};
Double_t p4[] = {0.1000351630e+1, 0.4503592498e+1, 0.1085883880e+2, 0.7536052269e+1};
Double_t q4[] = {1.0 , 0.5539969678e+1, 0.1933581111e+2, 0.2721321508e+2};
Double_t p5[] = {0.1000006517e+1, 0.4909414111e+2, 0.8505544753e+2, 0.1532153455e+3};
Double_t q5[] = {1.0 , 0.5009928881e+2, 0.1399819104e+3, 0.4200002909e+3};
Double_t p6[] = {0.1000000983e+1, 0.1329868456e+3, 0.9162149244e+3, -0.9605054274e+3};
Double_t q6[] = {1.0 , 0.1339887843e+3, 0.1055990413e+4, 0.5532224619e+3};
Double_t a1[] = {0, -0.4583333333e+0, 0.6675347222e+0,-0.1641741416e+1};
Double_t a2[] = {0, 1.0 ,-0.4227843351e+0,-0.2043403138e+1};
Double_t u, v;
Double_t lan;
v = x;
if (v < -5.5) {
u = TMath::Exp(v+1);
lan = 0.3989422803*TMath::Exp(-1./u)*TMath::Sqrt(u)*(1+(a1[1]+(a1[2]+a1[3]*u)*u)*u);
}
else if (v < -1 ) {
u = TMath::Exp(-v-1);
lan = (TMath::Exp(-u)/TMath::Sqrt(u))*(p1[0]+(p1[1]+(p1[2]+(p1[3]+p1[4]*v)*v)*v)*v)/
(q1[0]+(q1[1]+(q1[2]+(q1[3]+q1[4]*v)*v)*v)*v);
}
else if (v < 1)
lan = (p2[0]+(p2[1]+(p2[2]+p2[3]*v)*v)*v)/(q2[0]+(q2[1]+(q2[2]+q2[3]*v)*v)*v);
else if (v < 4)
lan = (p3[0]+(p3[1]+(p3[2]+p3[3]*v)*v)*v)/(q3[0]+(q3[1]+(q3[2]+q3[3]*v)*v)*v);
else if (v < 12) {
u = 1./v;
lan = (p4[0]+(p4[1]+(p4[2]+p4[3]*u)*u)*u)/(q4[0]+(q4[1]+(q4[2]+q4[3]*u)*u)*u);
}
else if (v < 50) {
u = 1./v;
lan = (p5[0]+(p5[1]+(p5[2]+p5[3]*u)*u)*u)/(q5[0]+(q5[1]+(q5[2]+q5[3]*u)*u)*u);
}
else if (v < 300) {
u = 1./v;
lan = (p6[0]+(p6[1]+(p6[2]+p6[3]*u)*u)*u)/(q6[0]+(q6[1]+(q6[2]+q6[3]*u)*u)*u);
}
else {
u = 1./(v-v*TMath::Log(v)/(v+1));
lan = 1-(a2[1]+(a2[2]+a2[3]*u)*u)*u;
}
return lan;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TMath::VavilovSet(Double_t rkappa, Double_t beta2, Bool_t mode, Double_t *WCM, Double_t *AC, Double_t *HC, Int_t &itype, Int_t &npt)
{
//Internal function, called by Vavilov and VavilovI
Double_t BKMNX1 = 0.02, BKMNY1 = 0.05, BKMNX2 = 0.12, BKMNY2 = 0.05,
BKMNX3 = 0.22, BKMNY3 = 0.05, BKMXX1 = 0.1 , BKMXY1 = 1,
BKMXX2 = 0.2 , BKMXY2 = 1 , BKMXX3 = 0.3 , BKMXY3 = 1;
Double_t FBKX1 = 2/(BKMXX1-BKMNX1), FBKX2 = 2/(BKMXX2-BKMNX2),
FBKX3 = 2/(BKMXX3-BKMNX3), FBKY1 = 2/(BKMXY1-BKMNY1),
FBKY2 = 2/(BKMXY2-BKMNY2), FBKY3 = 2/(BKMXY3-BKMNY3);
Double_t FNINV[] = {0, 1, 0.5, 0.33333333, 0.25, 0.2};
Double_t EDGEC[]= {0, 0, 0.16666667e+0, 0.41666667e-1, 0.83333333e-2,
0.13888889e-1, 0.69444444e-2, 0.77160493e-3};
Double_t U1[] = {0, 0.25850868e+0, 0.32477982e-1, -0.59020496e-2,
0. , 0.24880692e-1, 0.47404356e-2,
-0.74445130e-3, 0.73225731e-2, 0. ,
0.11668284e-2, 0. , -0.15727318e-2,-0.11210142e-2};
Double_t U2[] = {0, 0.43142611e+0, 0.40797543e-1, -0.91490215e-2,
0. , 0.42127077e-1, 0.73167928e-2,
-0.14026047e-2, 0.16195241e-1, 0.24714789e-2,
0.20751278e-2, 0. , -0.25141668e-2,-0.14064022e-2};
Double_t U3[] = {0, 0.25225955e+0, 0.64820468e-1, -0.23615759e-1,
0. , 0.23834176e-1, 0.21624675e-2,
-0.26865597e-2, -0.54891384e-2, 0.39800522e-2,
0.48447456e-2, -0.89439554e-2, -0.62756944e-2,-0.24655436e-2};
Double_t U4[] = {0, 0.12593231e+1, -0.20374501e+0, 0.95055662e-1,
-0.20771531e-1, -0.46865180e-1, -0.77222986e-2,
0.32241039e-2, 0.89882920e-2, -0.67167236e-2,
-0.13049241e-1, 0.18786468e-1, 0.14484097e-1};
Double_t U5[] = {0, -0.24864376e-1, -0.10368495e-2, 0.14330117e-2,
0.20052730e-3, 0.18751903e-2, 0.12668869e-2,
0.48736023e-3, 0.34850854e-2, 0. ,
-0.36597173e-3, 0.19372124e-2, 0.70761825e-3, 0.46898375e-3};
Double_t U6[] = {0, 0.35855696e-1, -0.27542114e-1, 0.12631023e-1,
-0.30188807e-2, -0.84479939e-3, 0. ,
0.45675843e-3, -0.69836141e-2, 0.39876546e-2,
-0.36055679e-2, 0. , 0.15298434e-2, 0.19247256e-2};
Double_t U7[] = {0, 0.10234691e+2, -0.35619655e+1, 0.69387764e+0,
-0.14047599e+0, -0.19952390e+1, -0.45679694e+0,
0. , 0.50505298e+0};
Double_t U8[] = {0, 0.21487518e+2, -0.11825253e+2, 0.43133087e+1,
-0.14500543e+1, -0.34343169e+1, -0.11063164e+1,
-0.21000819e+0, 0.17891643e+1, -0.89601916e+0,
0.39120793e+0, 0.73410606e+0, 0. ,-0.32454506e+0};
Double_t V1[] = {0, 0.27827257e+0, -0.14227603e-2, 0.24848327e-2,
0. , 0.45091424e-1, 0.80559636e-2,
-0.38974523e-2, 0. , -0.30634124e-2,
0.75633702e-3, 0.54730726e-2, 0.19792507e-2};
Double_t V2[] = {0, 0.41421789e+0, -0.30061649e-1, 0.52249697e-2,
0. , 0.12693873e+0, 0.22999801e-1,
-0.86792801e-2, 0.31875584e-1, -0.61757928e-2,
0. , 0.19716857e-1, 0.32596742e-2};
Double_t V3[] = {0, 0.20191056e+0, -0.46831422e-1, 0.96777473e-2,
-0.17995317e-2, 0.53921588e-1, 0.35068740e-2,
-0.12621494e-1, -0.54996531e-2, -0.90029985e-2,
0.34958743e-2, 0.18513506e-1, 0.68332334e-2,-0.12940502e-2};
Double_t V4[] = {0, 0.13206081e+1, 0.10036618e+0, -0.22015201e-1,
0.61667091e-2, -0.14986093e+0, -0.12720568e-1,
0.24972042e-1, -0.97751962e-2, 0.26087455e-1,
-0.11399062e-1, -0.48282515e-1, -0.98552378e-2};
Double_t V5[] = {0, 0.16435243e-1, 0.36051400e-1, 0.23036520e-2,
-0.61666343e-3, -0.10775802e-1, 0.51476061e-2,
0.56856517e-2, -0.13438433e-1, 0. ,
0. , -0.25421507e-2, 0.20169108e-2,-0.15144931e-2};
Double_t V6[] = {0, 0.33432405e-1, 0.60583916e-2, -0.23381379e-2,
0.83846081e-3, -0.13346861e-1, -0.17402116e-2,
0.21052496e-2, 0.15528195e-2, 0.21900670e-2,
-0.13202847e-2, -0.45124157e-2, -0.15629454e-2, 0.22499176e-3};
Double_t V7[] = {0, 0.54529572e+1, -0.90906096e+0, 0.86122438e-1,
0. , -0.12218009e+1, -0.32324120e+0,
-0.27373591e-1, 0.12173464e+0, 0. ,
0. , 0.40917471e-1};
Double_t V8[] = {0, 0.93841352e+1, -0.16276904e+1, 0.16571423e+0,
0. , -0.18160479e+1, -0.50919193e+0,
-0.51384654e-1, 0.21413992e+0, 0. ,
0. , 0.66596366e-1};
Double_t W1[] = {0, 0.29712951e+0, 0.97572934e-2, 0. ,
-0.15291686e-2, 0.35707399e-1, 0.96221631e-2,
-0.18402821e-2, -0.49821585e-2, 0.18831112e-2,
0.43541673e-2, 0.20301312e-2, -0.18723311e-2,-0.73403108e-3};
Double_t W2[] = {0, 0.40882635e+0, 0.14474912e-1, 0.25023704e-2,
-0.37707379e-2, 0.18719727e+0, 0.56954987e-1,
0. , 0.23020158e-1, 0.50574313e-2,
0.94550140e-2, 0.19300232e-1};
Double_t W3[] = {0, 0.16861629e+0, 0. , 0.36317285e-2,
-0.43657818e-2, 0.30144338e-1, 0.13891826e-1,
-0.58030495e-2, -0.38717547e-2, 0.85359607e-2,
0.14507659e-1, 0.82387775e-2, -0.10116105e-1,-0.55135670e-2};
Double_t W4[] = {0, 0.13493891e+1, -0.26863185e-2, -0.35216040e-2,
0.24434909e-1, -0.83447911e-1, -0.48061360e-1,
0.76473951e-2, 0.24494430e-1, -0.16209200e-1,
-0.37768479e-1, -0.47890063e-1, 0.17778596e-1, 0.13179324e-1};
Double_t W5[] = {0, 0.10264945e+0, 0.32738857e-1, 0. ,
0.43608779e-2, -0.43097757e-1, -0.22647176e-2,
0.94531290e-2, -0.12442571e-1, -0.32283517e-2,
-0.75640352e-2, -0.88293329e-2, 0.52537299e-2, 0.13340546e-2};
Double_t W6[] = {0, 0.29568177e-1, -0.16300060e-2, -0.21119745e-3,
0.23599053e-2, -0.48515387e-2, -0.40797531e-2,
0.40403265e-3, 0.18200105e-2, -0.14346306e-2,
-0.39165276e-2, -0.37432073e-2, 0.19950380e-2, 0.12222675e-2};
Double_t W8[] = {0, 0.66184645e+1, -0.73866379e+0, 0.44693973e-1,
0. , -0.14540925e+1, -0.39529833e+0,
-0.44293243e-1, 0.88741049e-1};
itype = 0;
if (rkappa <0.01 || rkappa >12) {
Error("Vavilov distribution", "illegal value of kappa");
return;
}
Double_t DRK[6];
Double_t DSIGM[6];
Double_t ALFA[8];
Int_t j;
Double_t x, y, xx, yy, x2, x3, y2, y3, xy, p2, p3, q2, q3, pq;
if (rkappa >= 0.29) {
itype = 1;
npt = 100;
Double_t wk = 1./TMath::Sqrt(rkappa);
AC[0] = (-0.032227*beta2-0.074275)*rkappa + (0.24533*beta2+0.070152)*wk + (-0.55610*beta2-3.1579);
AC[8] = (-0.013483*beta2-0.048801)*rkappa + (-1.6921*beta2+8.3656)*wk + (-0.73275*beta2-3.5226);
DRK[1] = wk*wk;
DSIGM[1] = TMath::Sqrt(rkappa/(1-0.5*beta2));
for (j=1; j<=4; j++) {
DRK[j+1] = DRK[1]*DRK[j];
DSIGM[j+1] = DSIGM[1]*DSIGM[j];
ALFA[j+1] = (FNINV[j]-beta2*FNINV[j+1])*DRK[j];
}
HC[0]=TMath::Log(rkappa)+beta2+0.42278434;
HC[1]=DSIGM[1];
HC[2]=ALFA[3]*DSIGM[3];
HC[3]=(3*ALFA[2]*ALFA[2] + ALFA[4])*DSIGM[4]-3;
HC[4]=(10*ALFA[2]*ALFA[3]+ALFA[5])*DSIGM[5]-10*HC[2];
HC[5]=HC[2]*HC[2];
HC[6]=HC[2]*HC[3];
HC[7]=HC[2]*HC[5];
for (j=2; j<=7; j++)
HC[j]*=EDGEC[j];
HC[8]=0.39894228*HC[1];
}
else if (rkappa >=0.22) {
itype = 2;
npt = 150;
x = 1+(rkappa-BKMXX3)*FBKX3;
y = 1+(TMath::Sqrt(beta2)-BKMXY3)*FBKY3;
xx = 2*x;
yy = 2*y;
x2 = xx*x-1;
x3 = xx*x2-x;
y2 = yy*y-1;
y3 = yy*y2-y;
xy = x*y;
p2 = x2*y;
p3 = x3*y;
q2 = y2*x;
q3 = y3*x;
pq = x2*y2;
AC[1] = W1[1] + W1[2]*x + W1[4]*x3 + W1[5]*y + W1[6]*y2 + W1[7]*y3 +
W1[8]*xy + W1[9]*p2 + W1[10]*p3 + W1[11]*q2 + W1[12]*q3 + W1[13]*pq;
AC[2] = W2[1] + W2[2]*x + W2[3]*x2 + W2[4]*x3 + W2[5]*y + W2[6]*y2 +
W2[8]*xy + W2[9]*p2 + W2[10]*p3 + W2[11]*q2;
AC[3] = W3[1] + W3[3]*x2 + W3[4]*x3 + W3[5]*y + W3[6]*y2 + W3[7]*y3 +
W3[8]*xy + W3[9]*p2 + W3[10]*p3 + W3[11]*q2 + W3[12]*q3 + W3[13]*pq;
AC[4] = W4[1] + W4[2]*x + W4[3]*x2 + W4[4]*x3 + W4[5]*y + W4[6]*y2 + W4[7]*y3 +
W4[8]*xy + W4[9]*p2 + W4[10]*p3 + W4[11]*q2 + W4[12]*q3 + W4[13]*pq;
AC[5] = W5[1] + W5[2]*x + W5[4]*x3 + W5[5]*y + W5[6]*y2 + W5[7]*y3 +
W5[8]*xy + W5[9]*p2 + W5[10]*p3 + W5[11]*q2 + W5[12]*q3 + W5[13]*pq;
AC[6] = W6[1] + W6[2]*x + W6[3]*x2 + W6[4]*x3 + W6[5]*y + W6[6]*y2 + W6[7]*y3 +
W6[8]*xy + W6[9]*p2 + W6[10]*p3 + W6[11]*q2 + W6[12]*q3 + W6[13]*pq;
AC[8] = W8[1] + W8[2]*x + W8[3]*x2 + W8[5]*y + W8[6]*y2 + W8[7]*y3 + W8[8]*xy;
AC[0] = -3.05;
} else if (rkappa >= 0.12) {
itype = 3;
npt = 200;
x = 1 + (rkappa-BKMXX2)*FBKX2;
y = 1 + (TMath::Sqrt(beta2)-BKMXY2)*FBKY2;
xx = 2*x;
yy = 2*y;
x2 = xx*x-1;
x3 = xx*x2-x;
y2 = yy*y-1;
y3 = yy*y2-y;
xy = x*y;
p2 = x2*y;
p3 = x3*y;
q2 = y2*x;
q3 = y3*x;
pq = x2*y2;
AC[1] = V1[1] + V1[2]*x + V1[3]*x2 + V1[5]*y + V1[6]*y2 + V1[7]*y3 +
V1[9]*p2 + V1[10]*p3 + V1[11]*q2 + V1[12]*q3;
AC[2] = V2[1] + V2[2]*x + V2[3]*x2 + V2[5]*y + V2[6]*y2 + V2[7]*y3 +
V2[8]*xy + V2[9]*p2 + V2[11]*q2 + V2[12]*q3;
AC[3] = V3[1] + V3[2]*x + V3[3]*x2 + V3[4]*x3 + V3[5]*y + V3[6]*y2 + V3[7]*y3 +
V3[8]*xy + V3[9]*p2 + V3[10]*p3 + V3[11]*q2 + V3[12]*q3 + V3[13]*pq;
AC[4] = V4[1] + V4[2]*x + V4[3]*x2 + V4[4]*x3 + V4[5]*y + V4[6]*y2 + V4[7]*y3 +
V4[8]*xy + V4[9]*p2 + V4[10]*p3 + V4[11]*q2 + V4[12]*q3;
AC[5] = V5[1] + V5[2]*x + V5[3]*x2 + V5[4]*x3 + V5[5]*y + V5[6]*y2 + V5[7]*y3 +
V5[8]*xy + V5[11]*q2 + V5[12]*q3 + V5[13]*pq;
AC[6] = V6[1] + V6[2]*x + V6[3]*x2 + V6[4]*x3 + V6[5]*y + V6[6]*y2 + V6[7]*y3 +
V6[8]*xy + V6[9]*p2 + V6[10]*p3 + V6[11]*q2 + V6[12]*q3 + V6[13]*pq;
AC[7] = V7[1] + V7[2]*x + V7[3]*x2 + V7[5]*y + V7[6]*y2 + V7[7]*y3 +
V7[8]*xy + V7[11]*q2;
AC[8] = V8[1] + V8[2]*x + V8[3]*x2 + V8[5]*y + V8[6]*y2 + V8[7]*y3 +
V8[8]*xy + V8[11]*q2;
AC[0] = -3.04;
} else {
itype = 4;
if (rkappa >=0.02) itype = 3;
npt = 200;
x = 1+(rkappa-BKMXX1)*FBKX1;
y = 1+(TMath::Sqrt(beta2)-BKMXY1)*FBKY1;
xx = 2*x;
yy = 2*y;
x2 = xx*x-1;
x3 = xx*x2-x;
y2 = yy*y-1;
y3 = yy*y2-y;
xy = x*y;
p2 = x2*y;
p3 = x3*y;
q2 = y2*x;
q3 = y3*x;
pq = x2*y2;
if (itype==3){
AC[1] = U1[1] + U1[2]*x + U1[3]*x2 + U1[5]*y + U1[6]*y2 + U1[7]*y3 +
U1[8]*xy + U1[10]*p3 + U1[12]*q3 + U1[13]*pq;
AC[2] = U2[1] + U2[2]*x + U2[3]*x2 + U2[5]*y + U2[6]*y2 + U2[7]*y3 +
U2[8]*xy + U2[9]*p2 + U2[10]*p3 + U2[12]*q3 + U2[13]*pq;
AC[3] = U3[1] + U3[2]*x + U3[3]*x2 + U3[5]*y + U3[6]*y2 + U3[7]*y3 +
U3[8]*xy + U3[9]*p2 + U3[10]*p3 + U3[11]*q2 + U3[12]*q3 + U3[13]*pq;
AC[4] = U4[1] + U4[2]*x + U4[3]*x2 + U4[4]*x3 + U4[5]*y + U4[6]*y2 + U4[7]*y3 +
U4[8]*xy + U4[9]*p2 + U4[10]*p3 + U4[11]*q2 + U4[12]*q3;
AC[5] = U5[1] + U5[2]*x + U5[3]*x2 + U5[4]*x3 + U5[5]*y + U5[6]*y2 + U5[7]*y3 +
U5[8]*xy + U5[10]*p3 + U5[11]*q2 + U5[12]*q3 + U5[13]*pq;
AC[6] = U6[1] + U6[2]*x + U6[3]*x2 + U6[4]*x3 + U6[5]*y + U6[7]*y3 +
U6[8]*xy + U6[9]*p2 + U6[10]*p3 + U6[12]*q3 + U6[13]*pq;
AC[7] = U7[1] + U7[2]*x + U7[3]*x2 + U7[4]*x3 + U7[5]*y + U7[6]*y2 + U7[8]*xy;
}
AC[8] = U8[1] + U8[2]*x + U8[3]*x2 + U8[4]*x3 + U8[5]*y + U8[6]*y2 + U8[7]*y3 +
U8[8]*xy + U8[9]*p2 + U8[10]*p3 + U8[11]*q2 + U8[13]*pq;
AC[0] = -3.03;
}
AC[9] = (AC[8] - AC[0])/npt;
AC[10] = 1./AC[9];
if (itype == 3) {
x = (AC[7]-AC[8])/(AC[7]*AC[8]);
y = 1./TMath::Log(AC[8]/AC[7]);
p2 = AC[7]*AC[7];
AC[11] = p2*(AC[1]*TMath::Exp(-AC[2]*(AC[7]+AC[5]*p2)-
AC[3]*TMath::Exp(-AC[4]*(AC[7]+AC[6]*p2)))-0.045*y/AC[7])/(1+x*y*AC[7]);
AC[12] = (0.045+x*AC[11])*y;
}
if (itype == 4) AC[13] = 0.995/LandauI(AC[8]);
if (mode==0) return;
//
x = AC[0];
WCM[0] = 0;
Double_t fl, fu;
Int_t k;
fl = TMath::VavilovDenEval(x, AC, HC, itype);
for (k=1; k<=npt; k++) {
x += AC[9];
fu = TMath::VavilovDenEval(x, AC, HC, itype);
WCM[k] = WCM[k-1] + fl + fu;
fl = fu;
}
x = 0.5*AC[9];
for (k=1; k<=npt; k++)
WCM[k]*=x;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::VavilovDenEval(Double_t rlam, Double_t *AC, Double_t *HC, Int_t itype)
{
//Internal function, called by Vavilov and VavilovSet
Double_t v = 0;
if (rlam < AC[0] || rlam > AC[8])
return 0;
Int_t k;
Double_t x, fn, s;
Double_t h[10];
if (itype ==1 ) {
fn = 1;
x = (rlam + HC[0])*HC[1];
h[1] = x;
h[2] = x*x -1;
for (k=2; k<=8; k++) {
fn++;
h[k+1] = x*h[k]-fn*h[k-1];
}
s = 1 + HC[7]*h[9];
for (k=2; k<=6; k++)
s+=HC[k]*h[k+1];
v = HC[8]*TMath::Exp(-0.5*x*x)*TMath::Max(s, 0.);
}
else if (itype == 2) {
x = rlam*rlam;
v = AC[1]*TMath::Exp(-AC[2]*(rlam+AC[5]*x) - AC[3]*TMath::Exp(-AC[4]*(rlam+AC[6]*x)));
}
else if (itype == 3) {
if (rlam < AC[7]) {
x = rlam*rlam;
v = AC[1]*TMath::Exp(-AC[2]*(rlam+AC[5]*x)-AC[3]*TMath::Exp(-AC[4]*(rlam+AC[6]*x)));
} else {
x = 1./rlam;
v = (AC[11]*x + AC[12])*x;
}
}
else if (itype == 4) {
v = AC[13]*TMath::Landau(rlam);
}
return v;
}
*/
//
Double_t *ac = new Double_t[14];
Double_t *hc = new Double_t[9];
Int_t itype;
Int_t npt;
TMath::VavilovSet(kappa, beta2, 0, 0, ac, hc, itype, npt);
Double_t v = TMath::VavilovDenEval(x, ac, hc, itype);
delete [] ac;
delete [] hc;
return v;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::VavilovI(Double_t x, Double_t kappa, Double_t beta2)
{
//Returns the value of the Vavilov distribution function
//Parameters: 1st - the point were the density function is evaluated
// 2nd - value of kappa (distribution parameter)
// 3rd - value of beta2 (distribution parameter)
//The algorithm was taken from the CernLib function vavden(G115)
//Reference: A.Rotondi and P.Montagna, Fast Calculation of Vavilov distribution
//Nucl.Instr. and Meth. B47(1990), 215-224
//Accuracy: quote from the reference above:
//"The resuls of our code have been compared with the values of the Vavilov
//density function computed numerically in an accurate way: our approximation
//shows a difference of less than 3% around the peak of the density function, slowly
//increasing going towards the extreme tails to the right and to the left"
Double_t *ac = new Double_t[14];
Double_t *hc = new Double_t[9];
Double_t *wcm = new Double_t[200];
Int_t itype;
Int_t npt;
Int_t k;
Double_t xx, v;
TMath::VavilovSet(kappa, beta2, 1, wcm, ac, hc, itype, npt);
if (x < ac[0]) v = 0;
else if (x >=ac[8]) v = 1;
else {
xx = x - ac[0];
k = Int_t(xx*ac[10]);
v = TMath::Min(wcm[k] + (xx - k*ac[9])*(wcm[k+1]-wcm[k])*ac[10], 1.);
}
delete [] ac;
delete [] hc;
delete [] wcm;
return v;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::LandauI(Double_t x)
{
//Returns the value of the Landau distribution function at point x.
//The algorithm was taken from the Cernlib function dislan(G110)
//Reference: K.S.Kolbig and B.Schorr, "A program package for the Landau
//distribution", Computer Phys.Comm., 31(1984), 97-111
Double_t p1[] = {0.2514091491e+0,-0.6250580444e-1, 0.1458381230e-1, -0.2108817737e-2, 0.7411247290e-3};
Double_t q1[] = {1.0 ,-0.5571175625e-2, 0.6225310236e-1, -0.3137378427e-2, 0.1931496439e-2};
Double_t p2[] = {0.2868328584e+0, 0.3564363231e+0, 0.1523518695e+0, 0.2251304883e-1};
Double_t q2[] = {1.0 , 0.6191136137e+0, 0.1720721448e+0, 0.2278594771e-1};
Double_t p3[] = {0.2868329066e+0, 0.3003828436e+0, 0.9950951941e-1, 0.8733827185e-2};
Double_t q3[] = {1.0 , 0.4237190502e+0, 0.1095631512e+0, 0.8693851567e-2};
Double_t p4[] = {0.1000351630e+1, 0.4503592498e+1, 0.1085883880e+2, 0.7536052269e+1};
Double_t q4[] = {1.0 , 0.5539969678e+1, 0.1933581111e+2, 0.2721321508e+2};
Double_t p5[] = {0.1000006517e+1, 0.4909414111e+2, 0.8505544753e+2, 0.1532153455e+3};
Double_t q5[] = {1.0 , 0.5009928881e+2, 0.1399819104e+3, 0.4200002909e+3};
Double_t p6[] = {0.1000000983e+1, 0.1329868456e+3, 0.9162149244e+3, -0.9605054274e+3};
Double_t q6[] = {1.0 , 0.1339887843e+3, 0.1055990413e+4, 0.5532224619e+3};
Double_t a1[] = {0, -0.4583333333e+0, 0.6675347222e+0,-0.1641741416e+1};
Double_t a2[] = {0, 1.0 ,-0.4227843351e+0,-0.2043403138e+1};
Double_t u, v;
Double_t lan;
v = x;
if (v < -5.5) {
u = TMath::Exp(v+1);
lan = 0.3989422803*TMath::Exp(-1./u)*TMath::Sqrt(u)*(1+(a1[1]+(a1[2]+a1[3]*u)*u)*u);
}
else if (v < -1 ) {
u = TMath::Exp(-v-1);
lan = (TMath::Exp(-u)/TMath::Sqrt(u))*(p1[0]+(p1[1]+(p1[2]+(p1[3]+p1[4]*v)*v)*v)*v)/
(q1[0]+(q1[1]+(q1[2]+(q1[3]+q1[4]*v)*v)*v)*v);
}
else if (v < 1)
lan = (p2[0]+(p2[1]+(p2[2]+p2[3]*v)*v)*v)/(q2[0]+(q2[1]+(q2[2]+q2[3]*v)*v)*v);
else if (v < 4)
lan = (p3[0]+(p3[1]+(p3[2]+p3[3]*v)*v)*v)/(q3[0]+(q3[1]+(q3[2]+q3[3]*v)*v)*v);
else if (v < 12) {
u = 1./v;
lan = (p4[0]+(p4[1]+(p4[2]+p4[3]*u)*u)*u)/(q4[0]+(q4[1]+(q4[2]+q4[3]*u)*u)*u);
}
else if (v < 50) {
u = 1./v;
lan = (p5[0]+(p5[1]+(p5[2]+p5[3]*u)*u)*u)/(q5[0]+(q5[1]+(q5[2]+q5[3]*u)*u)*u);
}
else if (v < 300) {
u = 1./v;
lan = (p6[0]+(p6[1]+(p6[2]+p6[3]*u)*u)*u)/(q6[0]+(q6[1]+(q6[2]+q6[3]*u)*u)*u);
}
else {
u = 1./(v-v*TMath::Log(v)/(v+1));
lan = 1-(a2[1]+(a2[2]+a2[3]*u)*u)*u;
}
return lan;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TMath::VavilovSet(Double_t rkappa, Double_t beta2, Bool_t mode, Double_t *WCM, Double_t *AC, Double_t *HC, Int_t &itype, Int_t &npt)
{
//Internal function, called by Vavilov and VavilovI
Double_t BKMNX1 = 0.02, BKMNY1 = 0.05, BKMNX2 = 0.12, BKMNY2 = 0.05,
BKMNX3 = 0.22, BKMNY3 = 0.05, BKMXX1 = 0.1 , BKMXY1 = 1,
BKMXX2 = 0.2 , BKMXY2 = 1 , BKMXX3 = 0.3 , BKMXY3 = 1;
Double_t FBKX1 = 2/(BKMXX1-BKMNX1), FBKX2 = 2/(BKMXX2-BKMNX2),
FBKX3 = 2/(BKMXX3-BKMNX3), FBKY1 = 2/(BKMXY1-BKMNY1),
FBKY2 = 2/(BKMXY2-BKMNY2), FBKY3 = 2/(BKMXY3-BKMNY3);
Double_t FNINV[] = {0, 1, 0.5, 0.33333333, 0.25, 0.2};
Double_t EDGEC[]= {0, 0, 0.16666667e+0, 0.41666667e-1, 0.83333333e-2,
0.13888889e-1, 0.69444444e-2, 0.77160493e-3};
Double_t U1[] = {0, 0.25850868e+0, 0.32477982e-1, -0.59020496e-2,
0. , 0.24880692e-1, 0.47404356e-2,
-0.74445130e-3, 0.73225731e-2, 0. ,
0.11668284e-2, 0. , -0.15727318e-2,-0.11210142e-2};
Double_t U2[] = {0, 0.43142611e+0, 0.40797543e-1, -0.91490215e-2,
0. , 0.42127077e-1, 0.73167928e-2,
-0.14026047e-2, 0.16195241e-1, 0.24714789e-2,
0.20751278e-2, 0. , -0.25141668e-2,-0.14064022e-2};
Double_t U3[] = {0, 0.25225955e+0, 0.64820468e-1, -0.23615759e-1,
0. , 0.23834176e-1, 0.21624675e-2,
-0.26865597e-2, -0.54891384e-2, 0.39800522e-2,
0.48447456e-2, -0.89439554e-2, -0.62756944e-2,-0.24655436e-2};
Double_t U4[] = {0, 0.12593231e+1, -0.20374501e+0, 0.95055662e-1,
-0.20771531e-1, -0.46865180e-1, -0.77222986e-2,
0.32241039e-2, 0.89882920e-2, -0.67167236e-2,
-0.13049241e-1, 0.18786468e-1, 0.14484097e-1};
Double_t U5[] = {0, -0.24864376e-1, -0.10368495e-2, 0.14330117e-2,
0.20052730e-3, 0.18751903e-2, 0.12668869e-2,
0.48736023e-3, 0.34850854e-2, 0. ,
-0.36597173e-3, 0.19372124e-2, 0.70761825e-3, 0.46898375e-3};
Double_t U6[] = {0, 0.35855696e-1, -0.27542114e-1, 0.12631023e-1,
-0.30188807e-2, -0.84479939e-3, 0. ,
0.45675843e-3, -0.69836141e-2, 0.39876546e-2,
-0.36055679e-2, 0. , 0.15298434e-2, 0.19247256e-2};
Double_t U7[] = {0, 0.10234691e+2, -0.35619655e+1, 0.69387764e+0,
-0.14047599e+0, -0.19952390e+1, -0.45679694e+0,
0. , 0.50505298e+0};
Double_t U8[] = {0, 0.21487518e+2, -0.11825253e+2, 0.43133087e+1,
-0.14500543e+1, -0.34343169e+1, -0.11063164e+1,
-0.21000819e+0, 0.17891643e+1, -0.89601916e+0,
0.39120793e+0, 0.73410606e+0, 0. ,-0.32454506e+0};
Double_t V1[] = {0, 0.27827257e+0, -0.14227603e-2, 0.24848327e-2,
0. , 0.45091424e-1, 0.80559636e-2,
-0.38974523e-2, 0. , -0.30634124e-2,
0.75633702e-3, 0.54730726e-2, 0.19792507e-2};
Double_t V2[] = {0, 0.41421789e+0, -0.30061649e-1, 0.52249697e-2,
0. , 0.12693873e+0, 0.22999801e-1,
-0.86792801e-2, 0.31875584e-1, -0.61757928e-2,
0. , 0.19716857e-1, 0.32596742e-2};
Double_t V3[] = {0, 0.20191056e+0, -0.46831422e-1, 0.96777473e-2,
-0.17995317e-2, 0.53921588e-1, 0.35068740e-2,
-0.12621494e-1, -0.54996531e-2, -0.90029985e-2,
0.34958743e-2, 0.18513506e-1, 0.68332334e-2,-0.12940502e-2};
Double_t V4[] = {0, 0.13206081e+1, 0.10036618e+0, -0.22015201e-1,
0.61667091e-2, -0.14986093e+0, -0.12720568e-1,
0.24972042e-1, -0.97751962e-2, 0.26087455e-1,
-0.11399062e-1, -0.48282515e-1, -0.98552378e-2};
Double_t V5[] = {0, 0.16435243e-1, 0.36051400e-1, 0.23036520e-2,
-0.61666343e-3, -0.10775802e-1, 0.51476061e-2,
0.56856517e-2, -0.13438433e-1, 0. ,
0. , -0.25421507e-2, 0.20169108e-2,-0.15144931e-2};
Double_t V6[] = {0, 0.33432405e-1, 0.60583916e-2, -0.23381379e-2,
0.83846081e-3, -0.13346861e-1, -0.17402116e-2,
0.21052496e-2, 0.15528195e-2, 0.21900670e-2,
-0.13202847e-2, -0.45124157e-2, -0.15629454e-2, 0.22499176e-3};
Double_t V7[] = {0, 0.54529572e+1, -0.90906096e+0, 0.86122438e-1,
0. , -0.12218009e+1, -0.32324120e+0,
-0.27373591e-1, 0.12173464e+0, 0. ,
0. , 0.40917471e-1};
Double_t V8[] = {0, 0.93841352e+1, -0.16276904e+1, 0.16571423e+0,
0. , -0.18160479e+1, -0.50919193e+0,
-0.51384654e-1, 0.21413992e+0, 0. ,
0. , 0.66596366e-1};
Double_t W1[] = {0, 0.29712951e+0, 0.97572934e-2, 0. ,
-0.15291686e-2, 0.35707399e-1, 0.96221631e-2,
-0.18402821e-2, -0.49821585e-2, 0.18831112e-2,
0.43541673e-2, 0.20301312e-2, -0.18723311e-2,-0.73403108e-3};
Double_t W2[] = {0, 0.40882635e+0, 0.14474912e-1, 0.25023704e-2,
-0.37707379e-2, 0.18719727e+0, 0.56954987e-1,
0. , 0.23020158e-1, 0.50574313e-2,
0.94550140e-2, 0.19300232e-1};
Double_t W3[] = {0, 0.16861629e+0, 0. , 0.36317285e-2,
-0.43657818e-2, 0.30144338e-1, 0.13891826e-1,
-0.58030495e-2, -0.38717547e-2, 0.85359607e-2,
0.14507659e-1, 0.82387775e-2, -0.10116105e-1,-0.55135670e-2};
Double_t W4[] = {0, 0.13493891e+1, -0.26863185e-2, -0.35216040e-2,
0.24434909e-1, -0.83447911e-1, -0.48061360e-1,
0.76473951e-2, 0.24494430e-1, -0.16209200e-1,
-0.37768479e-1, -0.47890063e-1, 0.17778596e-1, 0.13179324e-1};
Double_t W5[] = {0, 0.10264945e+0, 0.32738857e-1, 0. ,
0.43608779e-2, -0.43097757e-1, -0.22647176e-2,
0.94531290e-2, -0.12442571e-1, -0.32283517e-2,
-0.75640352e-2, -0.88293329e-2, 0.52537299e-2, 0.13340546e-2};
Double_t W6[] = {0, 0.29568177e-1, -0.16300060e-2, -0.21119745e-3,
0.23599053e-2, -0.48515387e-2, -0.40797531e-2,
0.40403265e-3, 0.18200105e-2, -0.14346306e-2,
-0.39165276e-2, -0.37432073e-2, 0.19950380e-2, 0.12222675e-2};
Double_t W8[] = {0, 0.66184645e+1, -0.73866379e+0, 0.44693973e-1,
0. , -0.14540925e+1, -0.39529833e+0,
-0.44293243e-1, 0.88741049e-1};
itype = 0;
if (rkappa <0.01 || rkappa >12) {
Error("Vavilov distribution", "illegal value of kappa");
return;
}
Double_t DRK[6];
Double_t DSIGM[6];
Double_t ALFA[8];
Int_t j;
Double_t x, y, xx, yy, x2, x3, y2, y3, xy, p2, p3, q2, q3, pq;
if (rkappa >= 0.29) {
itype = 1;
npt = 100;
Double_t wk = 1./TMath::Sqrt(rkappa);
AC[0] = (-0.032227*beta2-0.074275)*rkappa + (0.24533*beta2+0.070152)*wk + (-0.55610*beta2-3.1579);
AC[8] = (-0.013483*beta2-0.048801)*rkappa + (-1.6921*beta2+8.3656)*wk + (-0.73275*beta2-3.5226);
DRK[1] = wk*wk;
DSIGM[1] = TMath::Sqrt(rkappa/(1-0.5*beta2));
for (j=1; j<=4; j++) {
DRK[j+1] = DRK[1]*DRK[j];
DSIGM[j+1] = DSIGM[1]*DSIGM[j];
ALFA[j+1] = (FNINV[j]-beta2*FNINV[j+1])*DRK[j];
}
HC[0]=TMath::Log(rkappa)+beta2+0.42278434;
HC[1]=DSIGM[1];
HC[2]=ALFA[3]*DSIGM[3];
HC[3]=(3*ALFA[2]*ALFA[2] + ALFA[4])*DSIGM[4]-3;
HC[4]=(10*ALFA[2]*ALFA[3]+ALFA[5])*DSIGM[5]-10*HC[2];
HC[5]=HC[2]*HC[2];
HC[6]=HC[2]*HC[3];
HC[7]=HC[2]*HC[5];
for (j=2; j<=7; j++)
HC[j]*=EDGEC[j];
HC[8]=0.39894228*HC[1];
}
else if (rkappa >=0.22) {
itype = 2;
npt = 150;
x = 1+(rkappa-BKMXX3)*FBKX3;
y = 1+(TMath::Sqrt(beta2)-BKMXY3)*FBKY3;
xx = 2*x;
yy = 2*y;
x2 = xx*x-1;
x3 = xx*x2-x;
y2 = yy*y-1;
y3 = yy*y2-y;
xy = x*y;
p2 = x2*y;
p3 = x3*y;
q2 = y2*x;
q3 = y3*x;
pq = x2*y2;
AC[1] = W1[1] + W1[2]*x + W1[4]*x3 + W1[5]*y + W1[6]*y2 + W1[7]*y3 +
W1[8]*xy + W1[9]*p2 + W1[10]*p3 + W1[11]*q2 + W1[12]*q3 + W1[13]*pq;
AC[2] = W2[1] + W2[2]*x + W2[3]*x2 + W2[4]*x3 + W2[5]*y + W2[6]*y2 +
W2[8]*xy + W2[9]*p2 + W2[10]*p3 + W2[11]*q2;
AC[3] = W3[1] + W3[3]*x2 + W3[4]*x3 + W3[5]*y + W3[6]*y2 + W3[7]*y3 +
W3[8]*xy + W3[9]*p2 + W3[10]*p3 + W3[11]*q2 + W3[12]*q3 + W3[13]*pq;
AC[4] = W4[1] + W4[2]*x + W4[3]*x2 + W4[4]*x3 + W4[5]*y + W4[6]*y2 + W4[7]*y3 +
W4[8]*xy + W4[9]*p2 + W4[10]*p3 + W4[11]*q2 + W4[12]*q3 + W4[13]*pq;
AC[5] = W5[1] + W5[2]*x + W5[4]*x3 + W5[5]*y + W5[6]*y2 + W5[7]*y3 +
W5[8]*xy + W5[9]*p2 + W5[10]*p3 + W5[11]*q2 + W5[12]*q3 + W5[13]*pq;
AC[6] = W6[1] + W6[2]*x + W6[3]*x2 + W6[4]*x3 + W6[5]*y + W6[6]*y2 + W6[7]*y3 +
W6[8]*xy + W6[9]*p2 + W6[10]*p3 + W6[11]*q2 + W6[12]*q3 + W6[13]*pq;
AC[8] = W8[1] + W8[2]*x + W8[3]*x2 + W8[5]*y + W8[6]*y2 + W8[7]*y3 + W8[8]*xy;
AC[0] = -3.05;
} else if (rkappa >= 0.12) {
itype = 3;
npt = 200;
x = 1 + (rkappa-BKMXX2)*FBKX2;
y = 1 + (TMath::Sqrt(beta2)-BKMXY2)*FBKY2;
xx = 2*x;
yy = 2*y;
x2 = xx*x-1;
x3 = xx*x2-x;
y2 = yy*y-1;
y3 = yy*y2-y;
xy = x*y;
p2 = x2*y;
p3 = x3*y;
q2 = y2*x;
q3 = y3*x;
pq = x2*y2;
AC[1] = V1[1] + V1[2]*x + V1[3]*x2 + V1[5]*y + V1[6]*y2 + V1[7]*y3 +
V1[9]*p2 + V1[10]*p3 + V1[11]*q2 + V1[12]*q3;
AC[2] = V2[1] + V2[2]*x + V2[3]*x2 + V2[5]*y + V2[6]*y2 + V2[7]*y3 +
V2[8]*xy + V2[9]*p2 + V2[11]*q2 + V2[12]*q3;
AC[3] = V3[1] + V3[2]*x + V3[3]*x2 + V3[4]*x3 + V3[5]*y + V3[6]*y2 + V3[7]*y3 +
V3[8]*xy + V3[9]*p2 + V3[10]*p3 + V3[11]*q2 + V3[12]*q3 + V3[13]*pq;
AC[4] = V4[1] + V4[2]*x + V4[3]*x2 + V4[4]*x3 + V4[5]*y + V4[6]*y2 + V4[7]*y3 +
V4[8]*xy + V4[9]*p2 + V4[10]*p3 + V4[11]*q2 + V4[12]*q3;
AC[5] = V5[1] + V5[2]*x + V5[3]*x2 + V5[4]*x3 + V5[5]*y + V5[6]*y2 + V5[7]*y3 +
V5[8]*xy + V5[11]*q2 + V5[12]*q3 + V5[13]*pq;
AC[6] = V6[1] + V6[2]*x + V6[3]*x2 + V6[4]*x3 + V6[5]*y + V6[6]*y2 + V6[7]*y3 +
V6[8]*xy + V6[9]*p2 + V6[10]*p3 + V6[11]*q2 + V6[12]*q3 + V6[13]*pq;
AC[7] = V7[1] + V7[2]*x + V7[3]*x2 + V7[5]*y + V7[6]*y2 + V7[7]*y3 +
V7[8]*xy + V7[11]*q2;
AC[8] = V8[1] + V8[2]*x + V8[3]*x2 + V8[5]*y + V8[6]*y2 + V8[7]*y3 +
V8[8]*xy + V8[11]*q2;
AC[0] = -3.04;
} else {
itype = 4;
if (rkappa >=0.02) itype = 3;
npt = 200;
x = 1+(rkappa-BKMXX1)*FBKX1;
y = 1+(TMath::Sqrt(beta2)-BKMXY1)*FBKY1;
xx = 2*x;
yy = 2*y;
x2 = xx*x-1;
x3 = xx*x2-x;
y2 = yy*y-1;
y3 = yy*y2-y;
xy = x*y;
p2 = x2*y;
p3 = x3*y;
q2 = y2*x;
q3 = y3*x;
pq = x2*y2;
if (itype==3){
AC[1] = U1[1] + U1[2]*x + U1[3]*x2 + U1[5]*y + U1[6]*y2 + U1[7]*y3 +
U1[8]*xy + U1[10]*p3 + U1[12]*q3 + U1[13]*pq;
AC[2] = U2[1] + U2[2]*x + U2[3]*x2 + U2[5]*y + U2[6]*y2 + U2[7]*y3 +
U2[8]*xy + U2[9]*p2 + U2[10]*p3 + U2[12]*q3 + U2[13]*pq;
AC[3] = U3[1] + U3[2]*x + U3[3]*x2 + U3[5]*y + U3[6]*y2 + U3[7]*y3 +
U3[8]*xy + U3[9]*p2 + U3[10]*p3 + U3[11]*q2 + U3[12]*q3 + U3[13]*pq;
AC[4] = U4[1] + U4[2]*x + U4[3]*x2 + U4[4]*x3 + U4[5]*y + U4[6]*y2 + U4[7]*y3 +
U4[8]*xy + U4[9]*p2 + U4[10]*p3 + U4[11]*q2 + U4[12]*q3;
AC[5] = U5[1] + U5[2]*x + U5[3]*x2 + U5[4]*x3 + U5[5]*y + U5[6]*y2 + U5[7]*y3 +
U5[8]*xy + U5[10]*p3 + U5[11]*q2 + U5[12]*q3 + U5[13]*pq;
AC[6] = U6[1] + U6[2]*x + U6[3]*x2 + U6[4]*x3 + U6[5]*y + U6[7]*y3 +
U6[8]*xy + U6[9]*p2 + U6[10]*p3 + U6[12]*q3 + U6[13]*pq;
AC[7] = U7[1] + U7[2]*x + U7[3]*x2 + U7[4]*x3 + U7[5]*y + U7[6]*y2 + U7[8]*xy;
}
AC[8] = U8[1] + U8[2]*x + U8[3]*x2 + U8[4]*x3 + U8[5]*y + U8[6]*y2 + U8[7]*y3 +
U8[8]*xy + U8[9]*p2 + U8[10]*p3 + U8[11]*q2 + U8[13]*pq;
AC[0] = -3.03;
}
AC[9] = (AC[8] - AC[0])/npt;
AC[10] = 1./AC[9];
if (itype == 3) {
x = (AC[7]-AC[8])/(AC[7]*AC[8]);
y = 1./TMath::Log(AC[8]/AC[7]);
p2 = AC[7]*AC[7];
AC[11] = p2*(AC[1]*TMath::Exp(-AC[2]*(AC[7]+AC[5]*p2)-
AC[3]*TMath::Exp(-AC[4]*(AC[7]+AC[6]*p2)))-0.045*y/AC[7])/(1+x*y*AC[7]);
AC[12] = (0.045+x*AC[11])*y;
}
if (itype == 4) AC[13] = 0.995/LandauI(AC[8]);
if (mode==0) return;
//
x = AC[0];
WCM[0] = 0;
Double_t fl, fu;
Int_t k;
fl = TMath::VavilovDenEval(x, AC, HC, itype);
for (k=1; k<=npt; k++) {
x += AC[9];
fu = TMath::VavilovDenEval(x, AC, HC, itype);
WCM[k] = WCM[k-1] + fl + fu;
fl = fu;
}
x = 0.5*AC[9];
for (k=1; k<=npt; k++)
WCM[k]*=x;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMath::VavilovDenEval(Double_t rlam, Double_t *AC, Double_t *HC, Int_t itype)
{
//Internal function, called by Vavilov and VavilovSet
Double_t v = 0;
if (rlam < AC[0] || rlam > AC[8])
return 0;
Int_t k;
Double_t x, fn, s;
Double_t h[10];
if (itype ==1 ) {
fn = 1;
x = (rlam + HC[0])*HC[1];
h[1] = x;
h[2] = x*x -1;
for (k=2; k<=8; k++) {
fn++;
h[k+1] = x*h[k]-fn*h[k-1];
}
s = 1 + HC[7]*h[9];
for (k=2; k<=6; k++)
s+=HC[k]*h[k+1];
v = HC[8]*TMath::Exp(-0.5*x*x)*TMath::Max(s, 0.);
}
else if (itype == 2) {
x = rlam*rlam;
v = AC[1]*TMath::Exp(-AC[2]*(rlam+AC[5]*x) - AC[3]*TMath::Exp(-AC[4]*(rlam+AC[6]*x)));
}
else if (itype == 3) {
if (rlam < AC[7]) {
x = rlam*rlam;
v = AC[1]*TMath::Exp(-AC[2]*(rlam+AC[5]*x)-AC[3]*TMath::Exp(-AC[4]*(rlam+AC[6]*x)));
} else {
x = 1./rlam;
v = (AC[11]*x + AC[12])*x;
}
}
else if (itype == 4) {
v = AC[13]*TMath::Landau(rlam);
}
return v;
}