// @(#)root/base:$Name: $:$Id: TBuffer.cxx,v 1.85 2005/09/02 07:51:51 brun Exp $
// Author: Fons Rademakers 04/05/96
/*************************************************************************
* Copyright (C) 1995-2000, Rene Brun and Fons Rademakers. *
* All rights reserved. *
* *
* For the licensing terms see $ROOTSYS/LICENSE. *
* For the list of contributors see $ROOTSYS/README/CREDITS. *
*************************************************************************/
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// //
// TBuffer //
// //
// Buffer base class used for serializing objects. //
// //
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
#include <string.h>
#include "TROOT.h"
#include "TFile.h"
#include "TBuffer.h"
#include "TExMap.h"
#include "TClass.h"
#include "TStorage.h"
#include "TMath.h"
#include "TError.h"
#include "TObjArray.h"
#include "TStreamer.h"
#include "TStreamerInfo.h"
#include "TStreamerElement.h"
#if defined(__linux) && defined(__i386__)
#define USE_BSWAPCPY
#endif
#ifdef USE_BSWAPCPY
#include "Bswapcpy.h"
#endif
const UInt_t kNullTag = 0;
const UInt_t kNewClassTag = 0xFFFFFFFF;
const UInt_t kClassMask = 0x80000000; // OR the class index with this
const UInt_t kByteCountMask = 0x40000000; // OR the byte count with this
const UInt_t kMaxMapCount = 0x3FFFFFFE; // last valid fMapCount and byte count
const Version_t kByteCountVMask = 0x4000; // OR the version byte count with this
const Version_t kMaxVersion = 0x3FFF; // highest possible version number
const Int_t kExtraSpace = 8; // extra space at end of buffer (used for free block count)
const Int_t kMapOffset = 2; // first 2 map entries are taken by null obj and self obj
Int_t TBuffer::fgMapSize = kMapSize;
ClassImp(TBuffer)
//______________________________________________________________________________
static inline ULong_t Void_Hash(const void *ptr)
{
// Return hash value for this object.
return TMath::Hash(&ptr, sizeof(void*));
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
TBuffer::TBuffer(EMode mode) :
fInfo(0), fInfos(10)
{
// Create an I/O buffer object. Mode should be either TBuffer::kRead or
// TBuffer::kWrite. By default the I/O buffer has a size of
// TBuffer::kInitialSize (1024) bytes.
fBufSize = kInitialSize;
fMode = mode;
fVersion = 0;
fMapCount = 0;
fMapSize = fgMapSize;
fMap = 0;
fClassMap = 0;
fParent = 0;
fDisplacement = 0;
SetBit(kIsOwner);
fBuffer = new char[fBufSize+kExtraSpace];
fBufCur = fBuffer;
fBufMax = fBuffer + fBufSize;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
TBuffer::TBuffer(EMode mode, Int_t bufsiz) :
fInfo(0), fInfos(10)
{
// Create an I/O buffer object. Mode should be either TBuffer::kRead or
// TBuffer::kWrite.
if (bufsiz < kMinimalSize) bufsiz = kMinimalSize;
fBufSize = bufsiz;
fMode = mode;
fVersion = 0;
fMapCount = 0;
fMapSize = fgMapSize;
fMap = 0;
fClassMap = 0;
fParent = 0;
fDisplacement = 0;
SetBit(kIsOwner);
fBuffer = new char[fBufSize+kExtraSpace];
fBufCur = fBuffer;
fBufMax = fBuffer + fBufSize;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
TBuffer::TBuffer(EMode mode, Int_t bufsiz, void *buf, Bool_t adopt) :
fInfo(0), fInfos(10)
{
// Create an I/O buffer object. Mode should be either TBuffer::kRead or
// TBuffer::kWrite. By default the I/O buffer has a size of
// TBuffer::kInitialSize (1024) bytes. An external buffer can be passed
// to TBuffer via the buf argument. By default this buffer will be adopted
// unless adopt is false.
if (!buf && bufsiz < kMinimalSize) bufsiz = kMinimalSize;
fBufSize = bufsiz;
fMode = mode;
fVersion = 0;
fMapCount = 0;
fMapSize = fgMapSize;
fMap = 0;
fClassMap = 0;
fParent = 0;
fDisplacement = 0;
SetBit(kIsOwner);
if (buf) {
fBuffer = (char *)buf;
if (!adopt) ResetBit(kIsOwner);
} else
fBuffer = new char[fBufSize+kExtraSpace];
fBufCur = fBuffer;
fBufMax = fBuffer + fBufSize;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
TBuffer::~TBuffer()
{
// Delete an I/O buffer object.
if (TestBit(kIsOwner)) {
//printf("Deleting fBuffer=%x\n",fBuffer);
delete [] fBuffer;
}
fBuffer = 0;
fParent = 0;
delete fMap;
delete fClassMap;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
static void frombufOld(char *&buf, Long_t *x)
{
// Files written with versions older than 3.00/06 had a non-portable
// implementation of Long_t/ULong_t. These
// used at all. However, because some users had already written many
// files with these types we provide this dirty patch for "backward
// compatibility"
#ifdef R__BYTESWAP
#ifdef R__B64
char *sw = (char *)x;
sw[0] = buf[7];
sw[1] = buf[6];
sw[2] = buf[5];
sw[3] = buf[4];
sw[4] = buf[3];
sw[5] = buf[2];
sw[6] = buf[1];
sw[7] = buf[0];
#else
char *sw = (char *)x;
sw[0] = buf[3];
sw[1] = buf[2];
sw[2] = buf[1];
sw[3] = buf[0];
#endif
#else
memcpy(x, buf, sizeof(Long_t));
#endif
buf += sizeof(Long_t);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
TBuffer &TBuffer::operator>>(Long_t &l)
{
TFile *file = (TFile*)fParent;
if (file && file->GetVersion() < 30006) {
frombufOld(fBufCur, &l);
} else {
frombuf(fBufCur, &l);
}
return *this;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::SetBuffer(void *buf, UInt_t newsiz, Bool_t adopt)
{
// Sets a new buffer in an existing TBuffer object. If newsiz=0 then the
// new buffer is expected to have the same size as the previous buffer.
// The current buffer position is reset to the start of the buffer.
// If the TBuffer owned the previous buffer, it will be deleted prior
// to accepting the new buffer. By default the new buffer will be
// adopted unless adopt is false.
if (fBuffer && TestBit(kIsOwner))
delete [] fBuffer;
if (adopt)
SetBit(kIsOwner);
else
ResetBit(kIsOwner);
fBuffer = (char *)buf;
fBufCur = fBuffer;
if (newsiz > 0) fBufSize = newsiz;
fBufMax = fBuffer + fBufSize;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::CheckCount(UInt_t offset)
{
// Check if offset is not too large (< kMaxMapCount) when writing.
if (IsWriting()) {
if (offset >= kMaxMapCount) {
Error("CheckCount", "buffer offset too large (larger than %d)", kMaxMapCount);
// exception
}
}
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
UInt_t TBuffer::CheckObject(UInt_t offset, const TClass *cl, Bool_t readClass)
{
// Check for object in the read map. If the object is 0 it still has to be
// read. Try to read it from the buffer starting at location offset. If the
// object is -1 then it really does not exist and we return 0. If the object
// exists just return the offset.
// in position 0 we always have the reference to the null object
if (!offset) return offset;
Long_t cli;
if (readClass) {
if ((cli = fMap->GetValue(offset)) == 0) {
// No class found at this location in map. It might have been skipped
// as part of a skipped object. Try to explicitely read the class.
// save fBufCur and set to place specified by offset (-kMapOffset-sizeof(bytecount))
char *bufsav = fBufCur;
fBufCur = (char *)(fBuffer + offset-kMapOffset-sizeof(UInt_t));
TClass *c = ReadClass(cl);
if (c == (TClass*) -1) {
// mark class as really not available
fMap->Remove(offset);
fMap->Add(offset, -1);
offset = 0;
if (cl)
Warning("CheckObject", "reference to unavailable class %s,"
" pointers of this type will be 0", cl->GetName());
else
Warning("CheckObject", "reference to an unavailable class,"
" pointers of that type will be 0");
}
fBufCur = bufsav;
} else if (cli == -1) {
// class really does not exist
return 0;
}
} else {
if ((cli = fMap->GetValue(offset)) == 0) {
// No object found at this location in map. It might have been skipped
// as part of a skipped object. Try to explicitely read the object.
// save fBufCur and set to place specified by offset (-kMapOffset)
char *bufsav = fBufCur;
fBufCur = (char *)(fBuffer + offset-kMapOffset);
TObject *obj = ReadObject(cl);
if (!obj) {
// mark object as really not available
fMap->Remove(offset);
fMap->Add(offset, -1);
Warning("CheckObject", "reference to object of unavailable class %s, offset=%d"
" pointer will be 0", cl ? cl->GetName() : "TObject",offset);
offset = 0;
}
fBufCur = bufsav;
} else if (cli == -1) {
// object really does not exist
return 0;
}
}
return offset;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Bool_t TBuffer::CheckObject(const TObject *obj)
{
// Check if the specified object is already in the buffer.
// Returns kTRUE if object already in the buffer, kFALSE otherwise
// (also if obj is 0 or TBuffer not in writing mode).
return CheckObject(obj, TObject::Class());
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Bool_t TBuffer::CheckObject(const void *obj, const TClass *ptrClass)
{
// Check if the specified object of the specified class is already in
// the buffer. Returns kTRUE if object already in the buffer,
// kFALSE otherwise (also if obj is 0 or TBuffer not in writing mode).
if (!obj || !fMap || !ptrClass || !IsWriting())
return kFALSE;
TClass *clActual = ptrClass->GetActualClass(obj);
ULong_t idx;
if (clActual) {
const char *temp = (const char*) obj;
Int_t offset = (ptrClass != clActual) ?
clActual->GetBaseClassOffset(ptrClass) : 0;
temp -= offset;
idx = (ULong_t)fMap->GetValue(Void_Hash(temp), (Long_t)temp);
} else {
idx = (ULong_t)fMap->GetValue(Void_Hash(obj), (Long_t)obj);
}
return idx ? kTRUE : kFALSE;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::Expand(Int_t newsize)
{
// Expand the I/O buffer to newsize bytes.
Int_t l = Length();
fBuffer = TStorage::ReAllocChar(fBuffer, newsize+kExtraSpace,
fBufSize+kExtraSpace);
fBufSize = newsize;
fBufCur = fBuffer + l;
fBufMax = fBuffer + fBufSize;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
TObject *TBuffer::GetParent() const
{
// Return pointer to parent of this buffer.
return fParent;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::SetParent(TObject *parent)
{
// Set parent owning this buffer.
fParent = parent;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::GetMappedObject(UInt_t tag, void* &ptr, TClass* &ClassPtr) const
{
// Retrieve the object stored in the buffer's object map at 'tag'
// Set ptr and ClassPtr respectively to the address of the object and
// a pointer to its TClass.
if (tag > (UInt_t)fMap->GetSize()) {
ptr = 0;
ClassPtr = 0;
} else {
ptr = (void*)fMap->GetValue(tag);
ClassPtr = (TClass*) fClassMap->GetValue(tag);
}
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::MapObject(const TObject *obj, UInt_t offset)
{
// Add object to the fMap container.
// If obj is not 0 add object to the map (in read mode also add 0 objects to
// the map). This method may only be called outside this class just before
// calling obj->Streamer() to prevent self reference of obj, in case obj
// contains (via via) a pointer to itself. In that case offset must be 1
// (default value for offset).
if (!fMap) InitMap();
if (IsWriting()) {
if (obj) {
CheckCount(offset);
ULong_t hash = ((TObject*)obj)->TObject::Hash();
fMap->Add(hash, (Long_t)obj, offset);
// No need to keep track of the class in write mode
// fClassMap->Add(hash, (Long_t)obj, (Long_t)((TObject*)obj)->IsA());
fMapCount++;
}
} else {
fMap->Add(offset, (Long_t)obj);
fClassMap->Add(offset,
(obj && obj != (TObject*)-1) ? (Long_t)((TObject*)obj)->IsA() : 0);
fMapCount++;
}
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::MapObject(const void *obj, const TClass* cl, UInt_t offset)
{
// Add object to the fMap container.
// If obj is not 0 add object to the map (in read mode also add 0 objects to
// the map). This method may only be called outside this class just before
// calling obj->Streamer() to prevent self reference of obj, in case obj
// contains (via via) a pointer to itself. In that case offset must be 1
// (default value for offset).
if (!fMap) InitMap();
if (IsWriting()) {
if (obj) {
CheckCount(offset);
ULong_t hash = Void_Hash(obj);
fMap->Add(hash, (Long_t)obj, offset);
// No need to keep track of the class in write mode
// fClassMap->Add(hash, (Long_t)obj, (Long_t)cl);
fMapCount++;
}
} else {
fMap->Add(offset, (Long_t)obj);
fClassMap->Add(offset, (Long_t)cl);
fMapCount++;
}
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::SetReadParam(Int_t mapsize)
{
// Set the initial size of the map used to store object and class
// references during reading. The default size is kMapSize=503.
// Increasing the default has the benefit that when reading many
// small objects the map does not need to be resized too often
// (the system is always dynamic, even with the default everything
// will work, only the initial resizing will cost some time).
// This method can only be called directly after the creation of
// the TBuffer, before any reading is done. Globally this option
// can be changed using SetGlobalReadParam().
Assert(IsReading());
Assert(fMap == 0);
fMapSize = mapsize;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::SetWriteParam(Int_t mapsize)
{
// Set the initial size of the hashtable used to store object and class
// references during writing. The default size is kMapSize=503.
// Increasing the default has the benefit that when writing many
// small objects the hashtable does not get too many collisions
// (the system is always dynamic, even with the default everything
// will work, only a large number of collisions will cost performance).
// For optimal performance hashsize should always be a prime.
// This method can only be called directly after the creation of
// the TBuffer, before any writing is done. Globally this option
// can be changed using SetGlobalWriteParam().
Assert(IsWriting());
Assert(fMap == 0);
fMapSize = mapsize;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::InitMap()
{
// Create the fMap container and initialize them
// with the null object.
if (IsWriting()) {
if (!fMap) {
fMap = new TExMap(fMapSize);
// No need to keep track of the class in write mode
// fClassMap = new TExMap(fMapSize);
fMapCount = 0;
}
} else {
if (!fMap) {
fMap = new TExMap(fMapSize);
fMap->Add(0, kNullTag); // put kNullTag in slot 0
fMapCount = 1;
}
if (!fClassMap) {
fClassMap = new TExMap(fMapSize);
fClassMap->Add(0, kNullTag); // put kNullTag in slot 0
}
}
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::IncrementLevel(TStreamerInfo* info)
{
fInfos.push_back(fInfo);
fInfo = info;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::DecrementLevel(TStreamerInfo* /*info*/)
{
fInfo = fInfos.back();
fInfos.pop_back();
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::ResetMap()
{
// Delete existing fMap and reset map counter.
delete fMap;
delete fClassMap;
fMap = 0;
fClassMap = 0;
fMapCount = 0;
fDisplacement = 0;
// reset user bits
ResetBit(kUser1);
ResetBit(kUser2);
ResetBit(kUser3);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::SetByteCount(UInt_t cntpos, Bool_t packInVersion)
{
// Set byte count at position cntpos in the buffer. Generate warning if
// count larger than kMaxMapCount. The count is excluded its own size.
UInt_t cnt = UInt_t(fBufCur - fBuffer) - cntpos - sizeof(UInt_t);
char *buf = (char *)(fBuffer + cntpos);
// if true, pack byte count in two consecutive shorts, so it can
// be read by ReadVersion()
if (packInVersion) {
union {
UInt_t cnt;
Version_t vers[2];
} v;
v.cnt = cnt;
#ifdef R__BYTESWAP
tobuf(buf, Version_t(v.vers[1] | kByteCountVMask));
tobuf(buf, v.vers[0]);
#else
tobuf(buf, Version_t(v.vers[0] | kByteCountVMask));
tobuf(buf, v.vers[1]);
#endif
} else
tobuf(buf, cnt | kByteCountMask);
if (cnt >= kMaxMapCount) {
Error("WriteByteCount", "bytecount too large (more than %d)", kMaxMapCount);
// exception
}
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TBuffer::CheckByteCount(UInt_t startpos, UInt_t bcnt, const TClass *clss, const char *classname)
{
// Check byte count with current buffer position. They should
// match. If not print warning and position buffer in correct
// place determined by the byte count. Startpos is position of
// first byte where the byte count is written in buffer.
// Returns 0 if everything is ok, otherwise the bytecount offset
// (< 0 when read too little, >0 when read too much).
if (!bcnt) return 0;
Int_t offset = 0;
Long_t endpos = Long_t(fBuffer) + startpos + bcnt + sizeof(UInt_t);
if (Long_t(fBufCur) != endpos) {
offset = Int_t(Long_t(fBufCur) - endpos);
const char *name = clss ? clss->GetName() : classname ? classname : 0;
if (name) {
if (offset < 0) {
Error("CheckByteCount", "object of class %s read too few bytes: %d instead of %d",
name,bcnt+offset,bcnt);
}
if (offset > 0) {
Error("CheckByteCount", "object of class %s read too many bytes: %d instead of %d",
name,bcnt+offset,bcnt);
if (fParent)
Warning("CheckByteCount","%s::Streamer() not in sync with data on file %s, fix Streamer()",
name, fParent->GetName());
else
Warning("CheckByteCount","%s::Streamer() not in sync with data, fix Streamer()",
name);
}
}
if ( ((char *)endpos) > fBufMax ) {
offset = fBufMax-fBufCur;
Error("CheckByteCount",
"Byte count probably corrupted around buffer position %d:\n\t%d for a possible maximum of %d",
startpos, bcnt, offset);
fBufCur = fBufMax;
} else {
fBufCur = (char *) endpos;
}
}
return offset;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TBuffer::CheckByteCount(UInt_t startpos, UInt_t bcnt, const TClass *clss)
{
// Check byte count with current buffer position. They should
// match. If not print warning and position buffer in correct
// place determined by the byte count. Startpos is position of
// first byte where the byte count is written in buffer.
// Returns 0 if everything is ok, otherwise the bytecount offset
// (< 0 when read too little, >0 when read too much).
if (!bcnt) return 0;
return CheckByteCount( startpos, bcnt, clss, 0);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TBuffer::CheckByteCount(UInt_t startpos, UInt_t bcnt, const char *classname)
{
// Check byte count with current buffer position. They should
// match. If not print warning and position buffer in correct
// place determined by the byte count. Startpos is position of
// first byte where the byte count is written in buffer.
// Returns 0 if everything is ok, otherwise the bytecount offset
// (< 0 when read too little, >0 when read too much).
if (!bcnt) return 0;
return CheckByteCount( startpos, bcnt, 0, classname);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TBuffer::ReadBuf(void *buf, Int_t max)
{
// Read max bytes from the I/O buffer into buf. The function returns
// the actual number of bytes read.
Assert(IsReading());
if (max == 0) return 0;
Int_t n = TMath::Min(max, (Int_t)(fBufMax - fBufCur));
memcpy(buf, fBufCur, n);
fBufCur += n;
return n;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::WriteBuf(const void *buf, Int_t max)
{
// Write max bytes from buf into the I/O buffer.
Assert(IsWriting());
if (max == 0) return;
if (fBufCur + max > fBufMax) Expand(TMath::Max(2*fBufSize, fBufSize+max));
memcpy(fBufCur, buf, max);
fBufCur += max;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Text_t *TBuffer::ReadString(Text_t *s, Int_t max)
{
// Read string from I/O buffer. String is read till 0 character is
// found or till max-1 characters are read (i.e. string s has max
// bytes allocated). If max = -1 no check on number of character is
// made, reading continues till 0 character is found.
Assert(IsReading());
char ch;
Int_t nr = 0;
if (max == -1) max = kMaxInt;
while (nr < max-1) {
*this >> ch;
// stop when 0 read
if (ch == 0) break;
s[nr++] = ch;
}
s[nr] = 0;
return s;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::WriteString(const Text_t *s)
{
// Write string to I/O buffer. Writes string upto and including the
// terminating 0.
WriteBuf(s, (strlen(s)+1)*sizeof(Text_t));
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::ReadDouble32 (Double_t *d, TStreamerElement *ele)
{
// read a Double32_t from the buffer
// see comments about Double32_t encoding at TBuffer::WriteDouble32
if (ele && ele->GetFactor() != 0) {
UInt_t aint; *this >> aint; d[0] = (Double_t)(aint/ele->GetFactor() + ele->GetXmin());
} else {
Float_t afloat; *this >> afloat; d[0] = (Double_t)afloat;
}
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::WriteDouble32 (Double_t *d, TStreamerElement *ele)
{
// write a Double32_t to the buffer
// The following cases are supported for streaming a Double32_t type
// depending on the range declaration in the comment field of the data member:
// A- Double32_t fNormal;
// B- Double32_t fTemperature; //[0,100]
// C- Double32_t fCharge; //[-1,1,2]
// D- Double32_t fVertex[3]; //[-30,30,10]
// E Int_t fNsp;
// Double32_t* fPointValue; //[fNsp][0,3]
//
// In case A fNormal is converted from a Double_t to a Float_t
// In case B fTemperature is converted to a 32 bit unsigned integer
// In case C fCharge is converted to a 2 bits unsigned integer
// In case D the array elements of fVertex are converted to an unsigned 10 bits integer
// In case E the fNsp elements of array fPointvalue are converted to an unsigned 32 bit integer
// Note that the range specifier must follow the dimension specifier.
// the case B has more precision (9 to 10 significative digits than case A (6 to 7 digits).
//
// The range specifier has the general format: [xmin,xmax] or [xmin,xmax,nbits]
// [0,1]
// [-10,100];
// [-pi,pi], [-pi/2,pi/4],[-2pi,2*pi]
// [-10,100,16]
// if nbits is not specified, or nbits <2 or nbits>32 it is set to 32
//
// see example of use of the Double32_t data type in tutorial double32.C
//
//
/*
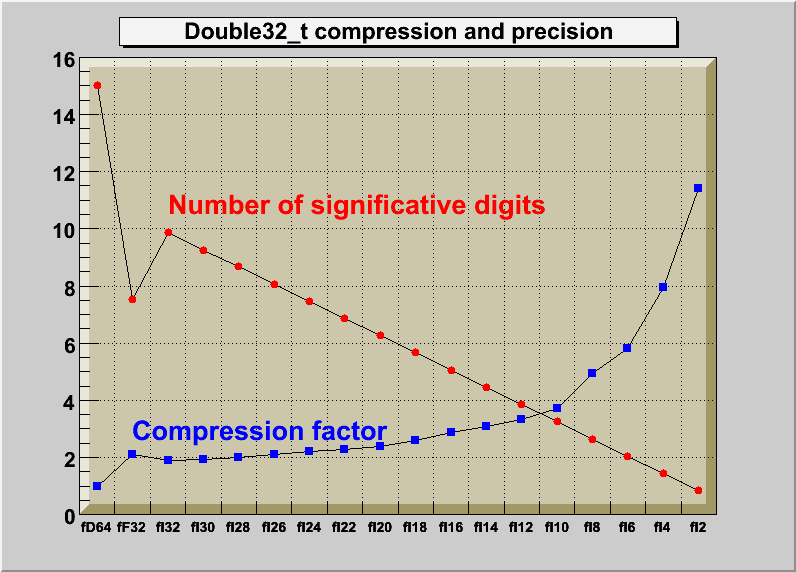 */
//
if (ele && ele->GetFactor() != 0) {
Double_t x = d[0];
Double_t xmin = ele->GetXmin();
Double_t xmax = ele->GetXmax();
if (x < xmin) x = xmin;
if (x > xmax) x = xmax;
UInt_t aint = UInt_t(0.5+ele->GetFactor()*(x-xmin)); *this << aint;
} else {
Float_t afloat = (Float_t)d[0]; *this << afloat;
}
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TBuffer::ReadArray(Bool_t *&b)
{
// Read array of bools from the I/O buffer. Returns the number of
// bools read. If argument is a 0 pointer then space will be
// allocated for the array.
Assert(IsReading());
Int_t n;
*this >> n;
if (n <= 0 || n > fBufSize) return 0;
if (!b) b = new Bool_t[n];
if (sizeof(Bool_t) > 1) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
frombuf(fBufCur, &b[i]);
} else {
Int_t l = sizeof(Bool_t)*n;
memcpy(b, fBufCur, l);
fBufCur += l;
}
return n;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TBuffer::ReadArray(Char_t *&c)
{
// Read array of characters from the I/O buffer. Returns the number of
// characters read. If argument is a 0 pointer then space will be
// allocated for the array.
Assert(IsReading());
Int_t n;
*this >> n;
Int_t l = sizeof(Char_t)*n;
if (l <= 0 || l > fBufSize) return 0;
if (!c) c = new Char_t[n];
memcpy(c, fBufCur, l);
fBufCur += l;
return n;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TBuffer::ReadArray(Short_t *&h)
{
// Read array of shorts from the I/O buffer. Returns the number of shorts
// read. If argument is a 0 pointer then space will be allocated for the
// array.
Assert(IsReading());
Int_t n;
*this >> n;
Int_t l = sizeof(Short_t)*n;
if (l <= 0 || l > fBufSize) return 0;
if (!h) h = new Short_t[n];
#ifdef R__BYTESWAP
# ifdef USE_BSWAPCPY
bswapcpy16(h, fBufCur, n);
fBufCur += l;
# else
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
frombuf(fBufCur, &h[i]);
# endif
#else
memcpy(h, fBufCur, l);
fBufCur += l;
#endif
return n;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TBuffer::ReadArray(Int_t *&ii)
{
// Read array of ints from the I/O buffer. Returns the number of ints
// read. If argument is a 0 pointer then space will be allocated for the
// array.
Assert(IsReading());
Int_t n;
*this >> n;
Int_t l = sizeof(Int_t)*n;
if (l <= 0 || l > fBufSize) return 0;
if (!ii) ii = new Int_t[n];
#ifdef R__BYTESWAP
# ifdef USE_BSWAPCPY
bswapcpy32(ii, fBufCur, n);
fBufCur += l;
# else
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
frombuf(fBufCur, &ii[i]);
# endif
#else
memcpy(ii, fBufCur, l);
fBufCur += l;
#endif
return n;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TBuffer::ReadArray(Long_t *&ll)
{
// Read array of longs from the I/O buffer. Returns the number of longs
// read. If argument is a 0 pointer then space will be allocated for the
// array.
Assert(IsReading());
Int_t n;
*this >> n;
Int_t l = sizeof(Long_t)*n;
if (l <= 0 || l > fBufSize) return 0;
if (!ll) ll = new Long_t[n];
TFile *file = (TFile*)fParent;
if (file && file->GetVersion() < 30006) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) frombufOld(fBufCur, &ll[i]);
} else {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) frombuf(fBufCur, &ll[i]);
}
return n;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TBuffer::ReadArray(Long64_t *&ll)
{
// Read array of long longs from the I/O buffer. Returns the number of
// long longs read. If argument is a 0 pointer then space will be
// allocated for the array.
Assert(IsReading());
Int_t n;
*this >> n;
Int_t l = sizeof(Long64_t)*n;
if (l <= 0 || l > fBufSize) return 0;
if (!ll) ll = new Long64_t[n];
#ifdef R__BYTESWAP
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
frombuf(fBufCur, &ll[i]);
#else
memcpy(ll, fBufCur, l);
fBufCur += l;
#endif
return n;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TBuffer::ReadArray(Float_t *&f)
{
// Read array of floats from the I/O buffer. Returns the number of floats
// read. If argument is a 0 pointer then space will be allocated for the
// array.
Assert(IsReading());
Int_t n;
*this >> n;
Int_t l = sizeof(Float_t)*n;
if (l <= 0 || l > fBufSize) return 0;
if (!f) f = new Float_t[n];
#ifdef R__BYTESWAP
# ifdef USE_BSWAPCPY
bswapcpy32(f, fBufCur, n);
fBufCur += l;
# else
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
frombuf(fBufCur, &f[i]);
# endif
#else
memcpy(f, fBufCur, l);
fBufCur += l;
#endif
return n;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TBuffer::ReadArray(Double_t *&d)
{
// Read array of doubles from the I/O buffer. Returns the number of doubles
// read. If argument is a 0 pointer then space will be allocated for the
// array.
Assert(IsReading());
Int_t n;
*this >> n;
Int_t l = sizeof(Double_t)*n;
if (l <= 0 || l > fBufSize) return 0;
if (!d) d = new Double_t[n];
#ifdef R__BYTESWAP
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
frombuf(fBufCur, &d[i]);
#else
memcpy(d, fBufCur, l);
fBufCur += l;
#endif
return n;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TBuffer::ReadArrayDouble32(Double_t *&d, TStreamerElement *ele)
{
// Read array of doubles (written as float) from the I/O buffer.
// Returns the number of doubles read.
// If argument is a 0 pointer then space will be allocated for the array.
// see comments about Double32_t encoding at TBuffer::WriteDouble32
Assert(IsReading());
Int_t n;
*this >> n;
if (n <= 0 || 4*n > fBufSize) return 0;
if (!d) d = new Double_t[n];
ReadFastArrayDouble32(d,n,ele);
return n;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TBuffer::ReadStaticArray(Bool_t *b)
{
// Read array of bools from the I/O buffer. Returns the number of bools
// read.
Assert(IsReading());
Int_t n;
*this >> n;
if (n <= 0 || n > fBufSize) return 0;
if (!b) return 0;
if (sizeof(Bool_t) > 1) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
frombuf(fBufCur, &b[i]);
} else {
Int_t l = sizeof(Bool_t)*n;
memcpy(b, fBufCur, l);
fBufCur += l;
}
return n;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TBuffer::ReadStaticArray(Char_t *c)
{
// Read array of characters from the I/O buffer. Returns the number of
// characters read.
Assert(IsReading());
Int_t n;
*this >> n;
Int_t l = sizeof(Char_t)*n;
if (l <= 0 || l > fBufSize) return 0;
if (!c) return 0;
memcpy(c, fBufCur, l);
fBufCur += l;
return n;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TBuffer::ReadStaticArray(Short_t *h)
{
// Read array of shorts from the I/O buffer. Returns the number of shorts
// read.
Assert(IsReading());
Int_t n;
*this >> n;
Int_t l = sizeof(Short_t)*n;
if (l <= 0 || l > fBufSize) return 0;
if (!h) return 0;
#ifdef R__BYTESWAP
# ifdef USE_BSWAPCPY
bswapcpy16(h, fBufCur, n);
fBufCur += l;
# else
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
frombuf(fBufCur, &h[i]);
# endif
#else
memcpy(h, fBufCur, l);
fBufCur += l;
#endif
return n;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TBuffer::ReadStaticArray(Int_t *ii)
{
// Read array of ints from the I/O buffer. Returns the number of ints
// read.
Assert(IsReading());
Int_t n;
*this >> n;
Int_t l = sizeof(Int_t)*n;
if (l <= 0 || l > fBufSize) return 0;
if (!ii) return 0;
#ifdef R__BYTESWAP
# ifdef USE_BSWAPCPY
bswapcpy32(ii, fBufCur, n);
fBufCur += sizeof(Int_t)*n;
# else
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
frombuf(fBufCur, &ii[i]);
# endif
#else
memcpy(ii, fBufCur, l);
fBufCur += l;
#endif
return n;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TBuffer::ReadStaticArray(Long_t *ll)
{
// Read array of longs from the I/O buffer. Returns the number of longs
// read.
Assert(IsReading());
Int_t n;
*this >> n;
Int_t l = sizeof(Long_t)*n;
if (l <= 0 || l > fBufSize) return 0;
if (!ll) return 0;
TFile *file = (TFile*)fParent;
if (file && file->GetVersion() < 30006) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) frombufOld(fBufCur, &ll[i]);
} else {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) frombuf(fBufCur, &ll[i]);
}
return n;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TBuffer::ReadStaticArray(Long64_t *ll)
{
// Read array of long longs from the I/O buffer. Returns the number of
// long longs read.
Assert(IsReading());
Int_t n;
*this >> n;
Int_t l = sizeof(Long64_t)*n;
if (l <= 0 || l > fBufSize) return 0;
if (!ll) return 0;
#ifdef R__BYTESWAP
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
frombuf(fBufCur, &ll[i]);
#else
memcpy(ll, fBufCur, l);
fBufCur += l;
#endif
return n;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TBuffer::ReadStaticArray(Float_t *f)
{
// Read array of floats from the I/O buffer. Returns the number of floats
// read.
Assert(IsReading());
Int_t n;
*this >> n;
Int_t l = sizeof(Float_t)*n;
if (n <= 0 || l > fBufSize) return 0;
if (!f) return 0;
#ifdef R__BYTESWAP
# ifdef USE_BSWAPCPY
bswapcpy32(f, fBufCur, n);
fBufCur += sizeof(Float_t)*n;
# else
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
frombuf(fBufCur, &f[i]);
# endif
#else
memcpy(f, fBufCur, l);
fBufCur += l;
#endif
return n;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TBuffer::ReadStaticArray(Double_t *d)
{
// Read array of doubles from the I/O buffer. Returns the number of doubles
// read.
Assert(IsReading());
Int_t n;
*this >> n;
Int_t l = sizeof(Double_t)*n;
if (n <= 0 || l > fBufSize) return 0;
if (!d) return 0;
#ifdef R__BYTESWAP
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
frombuf(fBufCur, &d[i]);
#else
memcpy(d, fBufCur, l);
fBufCur += l;
#endif
return n;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TBuffer::ReadStaticArrayDouble32(Double_t *d, TStreamerElement *ele)
{
// Read array of doubles (written as float) from the I/O buffer.
// Returns the number of doubles read.
// see comments about Double32_t encoding at TBuffer::WriteDouble32
Assert(IsReading());
Int_t n;
*this >> n;
if (n <= 0 || 4*n > fBufSize) return 0;
if (!d) return 0;
ReadFastArrayDouble32(d,n,ele);
return n;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::ReadFastArray(Bool_t *b, Int_t n)
{
// Read array of n bools from the I/O buffer.
if (n <= 0 || n > fBufSize) return;
if (sizeof(Bool_t) > 1) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
frombuf(fBufCur, &b[i]);
} else {
Int_t l = sizeof(Bool_t)*n;
memcpy(b, fBufCur, l);
fBufCur += l;
}
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::ReadFastArray(Char_t *c, Int_t n)
{
// Read array of n characters from the I/O buffer.
if (n <= 0 || n > fBufSize) return;
Int_t l = sizeof(Char_t)*n;
memcpy(c, fBufCur, l);
fBufCur += l;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::ReadFastArrayString(Char_t *c, Int_t n)
{
// Read array of n characters from the I/O buffer.
Int_t len;
UChar_t lenchar;
*this >> lenchar;
if (lenchar < 255) {
len = lenchar;
} else {
*this >> len;
}
if (len) {
if (len >= n) len = n-1;
if (n <= 0 || n > fBufSize) return;
Int_t l = sizeof(Char_t)*n;
memcpy(c, fBufCur, l);
fBufCur += l;
c[len] = 0;
} else {
c[0] = 0;
}
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::ReadFastArray(Short_t *h, Int_t n)
{
// Read array of n shorts from the I/O buffer.
Int_t l = sizeof(Short_t)*n;
if (n <= 0 || l > fBufSize) return;
#ifdef R__BYTESWAP
# ifdef USE_BSWAPCPY
bswapcpy16(h, fBufCur, n);
fBufCur += sizeof(Short_t)*n;
# else
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
frombuf(fBufCur, &h[i]);
# endif
#else
memcpy(h, fBufCur, l);
fBufCur += l;
#endif
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::ReadFastArray(Int_t *ii, Int_t n)
{
// Read array of n ints from the I/O buffer.
Int_t l = sizeof(Int_t)*n;
if (l <= 0 || l > fBufSize) return;
#ifdef R__BYTESWAP
# ifdef USE_BSWAPCPY
bswapcpy32(ii, fBufCur, n);
fBufCur += sizeof(Int_t)*n;
# else
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
frombuf(fBufCur, &ii[i]);
# endif
#else
memcpy(ii, fBufCur, l);
fBufCur += l;
#endif
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::ReadFastArray(Long_t *ll, Int_t n)
{
// Read array of n longs from the I/O buffer.
Int_t l = sizeof(Long_t)*n;
if (l <= 0 || l > fBufSize) return;
TFile *file = (TFile*)fParent;
if (file && file->GetVersion() < 30006) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) frombufOld(fBufCur, &ll[i]);
} else {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) frombuf(fBufCur, &ll[i]);
}
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::ReadFastArray(Long64_t *ll, Int_t n)
{
// Read array of n long longs from the I/O buffer.
Int_t l = sizeof(Long64_t)*n;
if (l <= 0 || l > fBufSize) return;
#ifdef R__BYTESWAP
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
frombuf(fBufCur, &ll[i]);
#else
memcpy(ll, fBufCur, l);
fBufCur += l;
#endif
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::ReadFastArray(Float_t *f, Int_t n)
{
// Read array of n floats from the I/O buffer.
Int_t l = sizeof(Float_t)*n;
if (l <= 0 || l > fBufSize) return;
#ifdef R__BYTESWAP
# ifdef USE_BSWAPCPY
bswapcpy32(f, fBufCur, n);
fBufCur += sizeof(Float_t)*n;
# else
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
frombuf(fBufCur, &f[i]);
# endif
#else
memcpy(f, fBufCur, l);
fBufCur += l;
#endif
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::ReadFastArray(Double_t *d, Int_t n)
{
// Read array of n doubles from the I/O buffer.
Int_t l = sizeof(Double_t)*n;
if (l <= 0 || l > fBufSize) return;
#ifdef R__BYTESWAP
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
frombuf(fBufCur, &d[i]);
#else
memcpy(d, fBufCur, l);
fBufCur += l;
#endif
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::ReadFastArrayDouble32(Double_t *d, Int_t n, TStreamerElement *ele)
{
// Read array of n doubles (written as float) from the I/O buffer.
// see comments about Double32_t encoding at TBuffer::WriteDouble32
if (n <= 0 || 4*n > fBufSize) return;
if (ele && ele->GetFactor() != 0) {
Double_t xmin = ele->GetXmin();
Double_t factor = ele->GetFactor();
for (int j=0;j < n; j++) {
UInt_t aint; *this >> aint; d[j] = (Double_t)(aint/factor + xmin);
}
} else {
Float_t afloat;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
frombuf(fBufCur, &afloat);
d[i]=afloat;
}
}
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::ReadFastArray(void *start, const TClass *cl, Int_t n,
TMemberStreamer *streamer)
{
// Read an array of 'n' objects from the I/O buffer.
// Stores the objects read starting at the address 'start'.
// The objects in the array are assume to be of class 'cl'.
if (streamer) {
(*streamer)(*this,start,0);
return;
}
int objectSize = cl->Size();
char *obj = (char*)start;
char *end = obj + n*objectSize;
for(; obj<end; obj+=objectSize) ((TClass*)cl)->Streamer(obj,*this);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::ReadFastArray(void **start, const TClass *cl, Int_t n,
Bool_t isPreAlloc, TMemberStreamer *streamer)
{
// Read an array of 'n' objects from the I/O buffer.
// The objects read are stored starting at the address '*start'
// The objects in the array are assumed to be of class 'cl' or a derived class.
// 'mode' indicates whether the data member is marked with '->'
// if isPreAlloc is true (data member has a ->) we can assume that the pointer (*start)
// is never 0.
if (streamer) {
if (isPreAlloc) {
for (Int_t j=0;j<n;j++) {
if (!start[j]) start[j] = ((TClass*)cl)->New();
}
}
(*streamer)(*this,(void*)start,0);
return;
}
if (!isPreAlloc) {
for (Int_t j=0; j<n; j++){
//delete the object or collection
if (start[j] && TStreamerInfo::CanDelete()) ((TClass*)cl)->Destructor(start[j],kFALSE); // call delete and desctructor
start[j] = ReadObjectAny(cl);
}
} else { //case //-> in comment
for (Int_t j=0; j<n; j++){
if (!start[j]) start[j] = ((TClass*)cl)->New();
((TClass*)cl)->Streamer(start[j],*this);
}
}
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::WriteArray(const Bool_t *b, Int_t n)
{
// Write array of n bools into the I/O buffer.
Assert(IsWriting());
*this << n;
if (n <= 0) return;
Assert(b);
Int_t l = sizeof(UChar_t)*n;
if (fBufCur + l > fBufMax) Expand(TMath::Max(2*fBufSize, fBufSize+l));
if (sizeof(Bool_t) > 1) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
tobuf(fBufCur, b[i]);
} else {
memcpy(fBufCur, b, l);
fBufCur += l;
}
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::WriteArray(const Char_t *c, Int_t n)
{
// Write array of n characters into the I/O buffer.
Assert(IsWriting());
*this << n;
if (n <= 0) return;
Assert(c);
Int_t l = sizeof(Char_t)*n;
if (fBufCur + l > fBufMax) Expand(TMath::Max(2*fBufSize, fBufSize+l));
memcpy(fBufCur, c, l);
fBufCur += l;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::WriteArray(const Short_t *h, Int_t n)
{
// Write array of n shorts into the I/O buffer.
Assert(IsWriting());
*this << n;
if (n <= 0) return;
Assert(h);
Int_t l = sizeof(Short_t)*n;
if (fBufCur + l > fBufMax) Expand(TMath::Max(2*fBufSize, fBufSize+l));
#ifdef R__BYTESWAP
# ifdef USE_BSWAPCPY
bswapcpy16(fBufCur, h, n);
fBufCur += l;
# else
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
tobuf(fBufCur, h[i]);
# endif
#else
memcpy(fBufCur, h, l);
fBufCur += l;
#endif
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::WriteArray(const Int_t *ii, Int_t n)
{
// Write array of n ints into the I/O buffer.
Assert(IsWriting());
*this << n;
if (n <= 0) return;
Assert(ii);
Int_t l = sizeof(Int_t)*n;
if (fBufCur + l > fBufMax) Expand(TMath::Max(2*fBufSize, fBufSize+l));
#ifdef R__BYTESWAP
# ifdef USE_BSWAPCPY
bswapcpy32(fBufCur, ii, n);
fBufCur += l;
# else
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
tobuf(fBufCur, ii[i]);
# endif
#else
memcpy(fBufCur, ii, l);
fBufCur += l;
#endif
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::WriteArray(const Long_t *ll, Int_t n)
{
// Write array of n longs into the I/O buffer.
Assert(IsWriting());
*this << n;
if (n <= 0) return;
Assert(ll);
Int_t l = 8*n;
if (fBufCur + l > fBufMax) Expand(TMath::Max(2*fBufSize, fBufSize+l));
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) tobuf(fBufCur, ll[i]);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::WriteArray(const ULong_t *ll, Int_t n)
{
// Write array of n unsigned longs into the I/O buffer.
// This is an explicit case for unsigned longs since signed longs
// have a special tobuf().
Assert(IsWriting());
*this << n;
if (n <= 0) return;
Assert(ll);
Int_t l = 8*n;
if (fBufCur + l > fBufMax) Expand(TMath::Max(2*fBufSize, fBufSize+l));
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) tobuf(fBufCur, ll[i]);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::WriteArray(const Long64_t *ll, Int_t n)
{
// Write array of n long longs into the I/O buffer.
Assert(IsWriting());
*this << n;
if (n <= 0) return;
Assert(ll);
Int_t l = sizeof(Long64_t)*n;
if (fBufCur + l > fBufMax) Expand(TMath::Max(2*fBufSize, fBufSize+l));
#ifdef R__BYTESWAP
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
tobuf(fBufCur, ll[i]);
#else
memcpy(fBufCur, ll, l);
fBufCur += l;
#endif
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::WriteArray(const Float_t *f, Int_t n)
{
// Write array of n floats into the I/O buffer.
Assert(IsWriting());
*this << n;
if (n <= 0) return;
Assert(f);
Int_t l = sizeof(Float_t)*n;
if (fBufCur + l > fBufMax) Expand(TMath::Max(2*fBufSize, fBufSize+l));
#ifdef R__BYTESWAP
# ifdef USE_BSWAPCPY
bswapcpy32(fBufCur, f, n);
fBufCur += l;
# else
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
tobuf(fBufCur, f[i]);
# endif
#else
memcpy(fBufCur, f, l);
fBufCur += l;
#endif
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::WriteArray(const Double_t *d, Int_t n)
{
// Write array of n doubles into the I/O buffer.
Assert(IsWriting());
*this << n;
if (n <= 0) return;
Assert(d);
Int_t l = sizeof(Double_t)*n;
if (fBufCur + l > fBufMax) Expand(TMath::Max(2*fBufSize, fBufSize+l));
#ifdef R__BYTESWAP
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
tobuf(fBufCur, d[i]);
#else
memcpy(fBufCur, d, l);
fBufCur += l;
#endif
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::WriteArrayDouble32(const Double_t *d, Int_t n, TStreamerElement *ele)
{
// Write array of n doubles (as float) into the I/O buffer.
// see comments about Double32_t encoding at TBuffer::WriteDouble32
Assert(IsWriting());
*this << n;
if (n <= 0) return;
Assert(d);
Int_t l = sizeof(Float_t)*n;
if (fBufCur + l > fBufMax) Expand(TMath::Max(2*fBufSize, fBufSize+l));
WriteFastArrayDouble32(d,n,ele);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::WriteFastArray(const Bool_t *b, Int_t n)
{
// Write array of n bools into the I/O buffer.
if (n <= 0) return;
Int_t l = sizeof(UChar_t)*n;
if (fBufCur + l > fBufMax) Expand(TMath::Max(2*fBufSize, fBufSize+l));
if (sizeof(Bool_t) > 1) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
tobuf(fBufCur, b[i]);
} else {
memcpy(fBufCur, b, l);
fBufCur += l;
}
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::WriteFastArray(const Char_t *c, Int_t n)
{
// Write array of n characters into the I/O buffer.
if (n <= 0) return;
Int_t l = sizeof(Char_t)*n;
if (fBufCur + l > fBufMax) Expand(TMath::Max(2*fBufSize, fBufSize+l));
memcpy(fBufCur, c, l);
fBufCur += l;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::WriteFastArrayString(const Char_t *c, Int_t n)
{
// Write array of n characters into the I/O buffer.
if (n < 255) {
*this << (UChar_t)n;
} else {
*this << (UChar_t)255;
*this << n;
}
if (n <= 0) return;
Int_t l = sizeof(Char_t)*n;
if (fBufCur + l > fBufMax) Expand(TMath::Max(2*fBufSize, fBufSize+l));
memcpy(fBufCur, c, l);
fBufCur += l;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::WriteFastArray(const Short_t *h, Int_t n)
{
// Write array of n shorts into the I/O buffer.
if (n <= 0) return;
Int_t l = sizeof(Short_t)*n;
if (fBufCur + l > fBufMax) Expand(TMath::Max(2*fBufSize, fBufSize+l));
#ifdef R__BYTESWAP
# ifdef USE_BSWAPCPY
bswapcpy16(fBufCur, h, n);
fBufCur += l;
# else
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
tobuf(fBufCur, h[i]);
# endif
#else
memcpy(fBufCur, h, l);
fBufCur += l;
#endif
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::WriteFastArray(const Int_t *ii, Int_t n)
{
// Write array of n ints into the I/O buffer.
if (n <= 0) return;
Int_t l = sizeof(Int_t)*n;
if (fBufCur + l > fBufMax) Expand(TMath::Max(2*fBufSize, fBufSize+l));
#ifdef R__BYTESWAP
# ifdef USE_BSWAPCPY
bswapcpy32(fBufCur, ii, n);
fBufCur += l;
# else
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
tobuf(fBufCur, ii[i]);
# endif
#else
memcpy(fBufCur, ii, l);
fBufCur += l;
#endif
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::WriteFastArray(const Long_t *ll, Int_t n)
{
// Write array of n longs into the I/O buffer.
if (n <= 0) return;
Int_t l = 8*n;
if (fBufCur + l > fBufMax) Expand(TMath::Max(2*fBufSize, fBufSize+l));
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) tobuf(fBufCur, ll[i]);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::WriteFastArray(const ULong_t *ll, Int_t n)
{
// Write array of n unsigned longs into the I/O buffer.
// This is an explicit case for unsigned longs since signed longs
// have a special tobuf().
if (n <= 0) return;
Int_t l = 8*n;
if (fBufCur + l > fBufMax) Expand(TMath::Max(2*fBufSize, fBufSize+l));
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) tobuf(fBufCur, ll[i]);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::WriteFastArray(const Long64_t *ll, Int_t n)
{
// Write array of n long longs into the I/O buffer.
if (n <= 0) return;
Int_t l = sizeof(Long64_t)*n;
if (fBufCur + l > fBufMax) Expand(TMath::Max(2*fBufSize, fBufSize+l));
#ifdef R__BYTESWAP
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
tobuf(fBufCur, ll[i]);
#else
memcpy(fBufCur, ll, l);
fBufCur += l;
#endif
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::WriteFastArray(const Float_t *f, Int_t n)
{
// Write array of n floats into the I/O buffer.
if (n <= 0) return;
Int_t l = sizeof(Float_t)*n;
if (fBufCur + l > fBufMax) Expand(TMath::Max(2*fBufSize, fBufSize+l));
#ifdef R__BYTESWAP
# ifdef USE_BSWAPCPY
bswapcpy32(fBufCur, f, n);
fBufCur += l;
# else
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
tobuf(fBufCur, f[i]);
# endif
#else
memcpy(fBufCur, f, l);
fBufCur += l;
#endif
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::WriteFastArray(const Double_t *d, Int_t n)
{
// Write array of n doubles into the I/O buffer.
if (n <= 0) return;
Int_t l = sizeof(Double_t)*n;
if (fBufCur + l > fBufMax) Expand(TMath::Max(2*fBufSize, fBufSize+l));
#ifdef R__BYTESWAP
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
tobuf(fBufCur, d[i]);
#else
memcpy(fBufCur, d, l);
fBufCur += l;
#endif
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::WriteFastArrayDouble32(const Double_t *d, Int_t n, TStreamerElement *ele)
{
// Write array of n doubles (as float) into the I/O buffer.
// see comments about Double32_t encoding at TBuffer::WriteDouble32
if (n <= 0) return;
Int_t l = sizeof(Float_t)*n;
if (fBufCur + l > fBufMax) Expand(TMath::Max(2*fBufSize, fBufSize+l));
if (ele && ele->GetFactor()) {
Double_t factor = ele->GetFactor();
Double_t xmin = ele->GetXmin();
Double_t xmax = ele->GetXmax();
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
Double_t x = d[j];
if (x < xmin) x = xmin;
if (x > xmax) x = xmax;
UInt_t aint = UInt_t(0.5+factor*(x-xmin)); *this << aint;
}
} else {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
tobuf(fBufCur, Float_t(d[i]));
}
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::WriteFastArray(void *start, const TClass *cl, Int_t n,
TMemberStreamer *streamer)
{
// Write an array of object starting at the address 'start' and of length 'n'
// the objects in the array are assumed to be of class 'cl'
if (streamer) {
(*streamer)(*this, start, 0);
return;
}
char *obj = (char*)start;
if (!n) n=1;
int size = cl->Size();
for(Int_t j=0; j<n; j++,obj+=size) {
((TClass*)cl)->Streamer(obj,*this);
}
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TBuffer::WriteFastArray(void **start, const TClass *cl, Int_t n,
Bool_t isPreAlloc, TMemberStreamer *streamer)
{
// Write an array of object starting at the address '*start' and of length 'n'
// the objects in the array are of class 'cl'
// 'isPreAlloc' indicates whether the data member is marked with '->'
// Return:
// 0: success
// 2: truncated success (i.e actual class is missing. Only ptrClass saved.)
// if isPreAlloc is true (data member has a ->) we can assume that the pointer
// is never 0.
if (streamer) {
(*streamer)(*this,(void*)start,0);
return 0;
}
int strInfo = 0;
Int_t res = 0;
if (!isPreAlloc) {
for (Int_t j=0;j<n;j++) {
//must write StreamerInfo if pointer is null
if (!strInfo && !start[j] ) ((TClass*)cl)->GetStreamerInfo()->ForceWriteInfo((TFile *)GetParent());
strInfo = 2003;
res |= WriteObjectAny(start[j],cl);
}
} else { //case //-> in comment
for (Int_t j=0;j<n;j++) {
if (!start[j]) start[j] = ((TClass*)cl)->New();
((TClass*)cl)->Streamer(start[j],*this);
}
}
return res;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
TObject *TBuffer::ReadObject(const TClass * /*clReq*/)
{
// Read object from I/O buffer. clReq is NOT used.
// The value returned is the address of the actual start in memory of
// the object. Note that if the actual class of the object does not
// inherit first from TObject, the type of the pointer is NOT 'TObject*'.
// [More accurately, the class needs to start with the TObject part, for
// the pointer to be a real TOject*].
// We recommend using ReadObjectAny instead of ReadObject
return (TObject*) ReadObjectAny(0);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::SkipObjectAny()
{
// Skip any kind of object from buffer
UInt_t start, count;
ReadVersion(&start, &count);
SetBufferOffset(start+count+sizeof(UInt_t));
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void *TBuffer::ReadObjectAny(const TClass *clCast)
{
// Read object from I/O buffer.
// A typical use for this function is:
// MyClass *ptr = (MyClass*)b.ReadObjectAny(MyClass::Class());
// I.e. clCast should point to a TClass object describing the class pointed
// to by your pointer.
// In case of multiple inheritance, the return value might not be the
// real beginning of the object in memory. You will need to use a
// dynamic_cast later if you need to retrieve it.
Assert(IsReading());
// make sure fMap is initialized
InitMap();
// before reading object save start position
UInt_t startpos = UInt_t(fBufCur-fBuffer);
// attempt to load next object as TClass clCast
UInt_t tag; // either tag or byte count
TClass *clRef = ReadClass(clCast, &tag);
Int_t baseOffset = 0;
if (clRef && (clRef!=(TClass*)(-1)) && clCast) {
//baseOffset will be -1 if clRef does not inherit from clCast.
baseOffset = clRef->GetBaseClassOffset(clCast);
if (baseOffset == -1) {
Error("ReadObject", "got object of wrong class! requested %s but got %s",
clCast->GetName(), clRef->GetName());
CheckByteCount(startpos, tag, (TClass*)0); // avoid mis-leading byte count error message
return 0; // We better return at this point
}
if (clCast->GetClassInfo() && !clRef->GetClassInfo()) {
//we cannot mix a compiled class with an emulated class in the inheritance
Error("ReadObject", "trying to read an emulated class (%s) to store in a compiled pointer (%s)",
clRef->GetName(),clCast->GetName());
CheckByteCount(startpos, tag, (TClass*)0); // avoid mis-leading byte count error message
return 0;
}
}
// check if object has not already been read
// (this can only happen when called via CheckObject())
char *obj;
if (fVersion > 0) {
obj = (char *) fMap->GetValue(startpos+kMapOffset);
if (obj == (void*) -1) obj = 0;
if (obj) {
CheckByteCount(startpos, tag, (TClass*)0);
return (obj+baseOffset);
}
}
// unknown class, skip to next object and return 0 obj
if (clRef == (TClass*) -1) {
if (fBufCur >= fBufMax) return 0;
if (fVersion > 0)
MapObject((TObject*) -1, startpos+kMapOffset);
else
MapObject((void*)0, 0, fMapCount);
CheckByteCount(startpos, tag, (TClass*)0);
return 0;
}
if (!clRef) {
// got a reference to an already read object
if (fVersion > 0) {
tag += fDisplacement;
tag = CheckObject(tag, clCast);
} else {
if (tag > (UInt_t)fMap->GetSize()) {
Error("ReadObject", "object tag too large, I/O buffer corrupted");
return 0;
// exception
}
}
obj = (char *) fMap->GetValue(tag);
clRef = (TClass*) fClassMap->GetValue(tag);
if (clRef && (clRef!=(TClass*)(-1)) && clCast) {
//baseOffset will be -1 if clRef does not inherit from clCast.
baseOffset = clRef->GetBaseClassOffset(clCast);
if (baseOffset == -1) {
Error("ReadObject", "Got object of wrong class (Got %s while expecting %s)",
clRef->GetName(),clCast->GetName());
// exception
baseOffset = 0;
}
}
// There used to be a warning printed here when:
// obj && isTObject && !((TObject*)obj)->IsA()->InheritsFrom(clReq)
// however isTObject was based on clReq (now clCast).
// If the test was to fail, then it is as likely that the object is not a TObject
// and then we have a potential core dump.
// At this point (missing clRef), we do NOT have enough information to really
// answer the question: is the object read of the type I requested.
} else {
// allocate a new object based on the class found
obj = (char *)clRef->New();
if (!obj) {
Error("ReadObject", "could not create object of class %s",
clRef->GetName());
// exception
return 0;
}
// add to fMap before reading rest of object
if (fVersion > 0)
MapObject(obj, clRef, startpos+kMapOffset);
else
MapObject(obj, clRef, fMapCount);
// let the object read itself
clRef->Streamer(obj, *this);
CheckByteCount(startpos, tag, clRef);
}
return obj+baseOffset;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::WriteObject(const TObject *obj)
{
// Write object to I/O buffer.
WriteObjectAny(obj, TObject::Class());
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::WriteObject(const void *actualObjectStart, const TClass *actualClass)
{
// Write object to I/O buffer.
// This function assumes that the value of 'actualObjectStart' is the actual start of
// the object of class 'actualClass'
Assert(IsWriting());
// make sure fMap is initialized
InitMap();
ULong_t idx;
if (!actualObjectStart) {
// save kNullTag to represent NULL pointer
*this << kNullTag;
} else if ((idx = (ULong_t)fMap->GetValue(Void_Hash(actualObjectStart), (Long_t)actualObjectStart)) != 0) {
// truncation is OK the value we did put in the map is an 30-bit offset
// and not a pointer
UInt_t objIdx = UInt_t(idx);
// save index of already stored object
*this << objIdx;
} else {
// A warning to let the user know it will need to change the class code
// to be able to read this back.
if (actualClass->HasDefaultConstructor() == 0) {
Warning("WriteObjectAny", "since %s had no public constructor\n"
"\twhich can be called without argument, objects of this class\n"
"\tcan not be read with the current library. You would need to\n"
"\tadd a default constructor before attempting to read it.",
actualClass->GetName());
}
// reserve space for leading byte count
UInt_t cntpos = UInt_t(fBufCur-fBuffer);
fBufCur += sizeof(UInt_t);
// write class of object first
WriteClass(actualClass);
// add to map before writing rest of object (to handle self reference)
// (+kMapOffset so it's != kNullTag)
MapObject(actualObjectStart, actualClass, cntpos+kMapOffset);
((TClass*)actualClass)->Streamer((void*)actualObjectStart,*this);
// write byte count
SetByteCount(cntpos);
}
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TBuffer::WriteObjectAny(const void *obj, const TClass *ptrClass)
{
// Write object to I/O buffer.
// This function assumes that the value in 'obj' is the value stored in
// a pointer to a "ptrClass". The actual type of the object pointed to
// can be any class derived from "ptrClass".
// Return:
// 0: failure
// 1: success
// 2: truncated success (i.e actual class is missing. Only ptrClass saved.)
if (!obj) {
WriteObject(0, 0);
return 1;
}
if (!ptrClass) {
Error("WriteObjectAny", "ptrClass argument may not be 0");
return 0;
}
TClass *clActual = ptrClass->GetActualClass(obj);
if (clActual) {
const char *temp = (const char*) obj;
// clActual->GetStreamerInfo();
Int_t offset = (ptrClass != clActual) ?
clActual->GetBaseClassOffset(ptrClass) : 0;
temp -= offset;
WriteObject(temp, clActual);
return 1;
} else {
WriteObject(obj, ptrClass);
return 2;
}
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
TClass *TBuffer::ReadClass(const TClass *clReq, UInt_t *objTag)
{
// Read class definition from I/O buffer. clReq can be used to cross check
// if the actually read object is of the requested class. objTag is
// set in case the object is a reference to an already read object.
Assert(IsReading());
// read byte count and/or tag (older files don't have byte count)
TClass *cl;
if (fBufCur < fBuffer || fBufCur > fBufMax) {
fBufCur = fBufMax;
cl = (TClass*)-1;
return cl;
}
UInt_t bcnt, tag, startpos = 0;
*this >> bcnt;
if (!(bcnt & kByteCountMask) || bcnt == kNewClassTag) {
tag = bcnt;
bcnt = 0;
} else {
fVersion = 1;
startpos = UInt_t(fBufCur-fBuffer);
*this >> tag;
}
// in case tag is object tag return tag
if (!(tag & kClassMask)) {
if (objTag) *objTag = tag;
return 0;
}
if (tag == kNewClassTag) {
// got a new class description followed by a new object
// (class can be 0 if class dictionary is not found, in that
// case object of this class must be skipped)
cl = TClass::Load(*this);
// add class to fMap for later reference
if (fVersion > 0) {
// check if class was already read
TClass *cl1 = (TClass *)fMap->GetValue(startpos+kMapOffset);
if (cl1 != cl)
MapObject(cl ? cl : (TObject*) -1, startpos+kMapOffset);
} else
MapObject(cl, fMapCount);
} else {
// got a tag to an already seen class
UInt_t clTag = (tag & ~kClassMask);
if (fVersion > 0) {
clTag += fDisplacement;
clTag = CheckObject(clTag, clReq, kTRUE);
} else {
if (clTag == 0 || clTag > (UInt_t)fMap->GetSize()) {
Error("ReadClass", "illegal class tag=%d (0<tag<=%d), I/O buffer corrupted",
clTag, fMap->GetSize());
// exception
}
}
// class can be 0 if dictionary was not found
cl = (TClass *)fMap->GetValue(clTag);
}
if (cl && clReq && !cl->InheritsFrom(clReq)) {
Error("ReadClass", "got wrong class: %s", cl->GetName());
// exception
}
// return bytecount in objTag
if (objTag) *objTag = (bcnt & ~kByteCountMask);
// case of unknown class
if (!cl) cl = (TClass*)-1;
return cl;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::WriteClass(const TClass *cl)
{
// Write class description to I/O buffer.
Assert(IsWriting());
ULong_t idx;
if ((idx = (ULong_t)fMap->GetValue(((TObject *)cl)->TObject::Hash(), (Long_t)cl)) != 0) {
// truncation is OK the value we did put in the map is an 30-bit offset
// and not a pointer
UInt_t clIdx = UInt_t(idx);
// save index of already stored class
*this << (clIdx | kClassMask);
} else {
// offset in buffer where class info is written
UInt_t offset = UInt_t(fBufCur-fBuffer);
// save new class tag
*this << kNewClassTag;
// write class name
cl->Store(*this);
// store new class reference in fMap (+kMapOffset so it's != kNullTag)
MapObject(cl, offset+kMapOffset);
}
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
static Version_t R__FindStreamerInfoVersion(const TClass *cl, UInt_t checksum)
{
//find the version number in the StreamerInfos corresponding to checksum
Version_t version = 0;
Int_t ninfos = cl->GetStreamerInfos()->GetEntriesFast();
for (Int_t i=1;i<ninfos;i++) {
// TClass::fStreamerInfos has a lower bound not equal to 0,
// so we should use At and not use UncheckedAt
TStreamerInfo *info = (TStreamerInfo*)cl->GetStreamerInfos()->At(i);
if (!info) continue;
if (info->GetCheckSum() == checksum) {
version = i;
//printf("ReadVersion, setting version=%d\n",version);
break;
}
}
return version;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Version_t TBuffer::ReadVersion(UInt_t *startpos, UInt_t *bcnt, const TClass *cl)
{
// Read class version from I/O buffer.
Version_t version;
if (startpos && bcnt) {
// before reading object save start position
*startpos = UInt_t(fBufCur-fBuffer);
// read byte count (older files don't have byte count)
// byte count is packed in two individual shorts, this to be
// backward compatible with old files that have at this location
// only a single short (i.e. the version)
union {
UInt_t cnt;
Version_t vers[2];
} v;
#ifdef R__BYTESWAP
*this >> v.vers[1];
*this >> v.vers[0];
#else
*this >> v.vers[0];
*this >> v.vers[1];
#endif
// no bytecount, backup and read version
if (!(v.cnt & kByteCountMask)) {
fBufCur -= sizeof(UInt_t);
v.cnt = 0;
}
*bcnt = (v.cnt & ~kByteCountMask);
*this >> version;
} else {
// not interested in byte count
*this >> version;
// if this is a byte count, then skip next short and read version
if (version & kByteCountVMask) {
*this >> version;
*this >> version;
}
}
if (cl && cl->GetClassVersion() != 0) {
if (version <= 0) {
UInt_t checksum = 0;
*this >> checksum;
version = R__FindStreamerInfoVersion(cl,checksum);
} else if (version == 1 && fParent && ((TFile*)fParent)->GetVersion()<40000 ) {
// We could have a file created using a Foreign class before
// the introduction of the CheckSum. We need to check
if ((!cl->IsLoaded() || cl->IsForeign()) &&
cl->GetStreamerInfos()->GetLast()>1 ) {
const TList *list = ((TFile*)fParent)->GetStreamerInfoCache();
const TStreamerInfo *local = (TStreamerInfo*)list->FindObject(cl->GetName());
if ( local ) {
UInt_t checksum = local->GetCheckSum();
version = R__FindStreamerInfoVersion(cl,checksum);
}
else {
Error("ReadVersion", "Class %s not known to file %s.",
cl->GetName(), ((TFile*)fParent)->GetName());
version = 0;
}
}
}
}
return version;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
UInt_t TBuffer::WriteVersion(const TClass *cl, Bool_t useBcnt)
{
// Write class version to I/O buffer.
UInt_t cntpos = 0;
if (useBcnt) {
// reserve space for leading byte count
cntpos = UInt_t(fBufCur-fBuffer);
fBufCur += sizeof(UInt_t);
}
Version_t version = cl->GetClassVersion();
if (version > kMaxVersion) {
Error("WriteVersion", "version number cannot be larger than %hd)",
kMaxVersion);
version = kMaxVersion;
}
if (cl->IsForeign() && version<=1) {
*this << Version_t(0);
*this << cl->GetCheckSum();
} else {
*this <<version;
}
// return position where to store possible byte count
return cntpos;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
UInt_t TBuffer::WriteVersionMemberWise(const TClass *cl, Bool_t useBcnt)
{
// Write class version to I/O buffer after setting the kStreamedMemberWise
// bit in the version number.
UInt_t cntpos = 0;
if (useBcnt) {
// reserve space for leading byte count
cntpos = UInt_t(fBufCur-fBuffer);
fBufCur += sizeof(UInt_t);
}
Version_t version = cl->GetClassVersion();
if (version > kMaxVersion) {
Error("WriteVersionMemberWise", "version number cannot be larger than %hd)",
kMaxVersion);
version = kMaxVersion;
}
if (cl->IsForeign() && version<=1) {
Error("WriteVersionMemberWise", "Member-wise streaming of foreign collection not yet implemented!");
*this << Version_t(0);
*this << cl->GetCheckSum();
} else {
version |= kStreamedMemberWise;
*this <<version;
}
// return position where to store possible byte count
return cntpos;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::SetReadMode()
{
// Set buffer in read mode.
fMode = kRead;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::SetWriteMode()
{
// Set buffer in write mode.
fMode = kWrite;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::StreamObject(void *obj, const type_info &typeinfo)
{
// Stream an object given its C++ typeinfo information.
TClass *cl = gROOT->GetClass(typeinfo);
cl->Streamer(obj, *this);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::StreamObject(void *obj, const char *className)
{
// Stream an object given the name of its actual class.
TClass *cl = gROOT->GetClass(className);
cl->Streamer(obj, *this);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::StreamObject(void *obj, const TClass *cl)
{
// Stream an object given a pointer to its actual class.
((TClass*)cl)->Streamer(obj, *this);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
TClass *TBuffer::GetClass(const type_info &typeinfo)
{
// Forward to TROOT::GetClass
return gROOT->GetClass(typeinfo);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
TClass *TBuffer::GetClass(const char *className)
{
// Forward to TROOT::GetClass
return gROOT->GetClass(className);
}
//---- Static functions --------------------------------------------------------
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::SetGlobalReadParam(Int_t mapsize)
{
// Set the initial size of the map used to store object and class
// references during reading. The default size is kMapSize=503.
// Increasing the default has the benefit that when reading many
// small objects the array does not need to be resized too often
// (the system is always dynamic, even with the default everything
// will work, only the initial resizing will cost some time).
// Per TBuffer object this option can be changed using SetReadParam().
fgMapSize = mapsize;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::SetGlobalWriteParam(Int_t mapsize)
{
// Set the initial size of the hashtable used to store object and class
// references during writing. The default size is kMapSize=503.
// Increasing the default has the benefit that when writing many
// small objects the hashtable does not get too many collisions
// (the system is always dynamic, even with the default everything
// will work, only a large number of collisions will cost performance).
// For optimal performance hashsize should always be a prime.
// Per TBuffer object this option can be changed using SetWriteParam().
fgMapSize = mapsize;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TBuffer::GetGlobalReadParam()
{
// Get default read map size.
return fgMapSize;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TBuffer::GetGlobalWriteParam()
{
// Get default write map size.
return fgMapSize;
}
*/
//
if (ele && ele->GetFactor() != 0) {
Double_t x = d[0];
Double_t xmin = ele->GetXmin();
Double_t xmax = ele->GetXmax();
if (x < xmin) x = xmin;
if (x > xmax) x = xmax;
UInt_t aint = UInt_t(0.5+ele->GetFactor()*(x-xmin)); *this << aint;
} else {
Float_t afloat = (Float_t)d[0]; *this << afloat;
}
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TBuffer::ReadArray(Bool_t *&b)
{
// Read array of bools from the I/O buffer. Returns the number of
// bools read. If argument is a 0 pointer then space will be
// allocated for the array.
Assert(IsReading());
Int_t n;
*this >> n;
if (n <= 0 || n > fBufSize) return 0;
if (!b) b = new Bool_t[n];
if (sizeof(Bool_t) > 1) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
frombuf(fBufCur, &b[i]);
} else {
Int_t l = sizeof(Bool_t)*n;
memcpy(b, fBufCur, l);
fBufCur += l;
}
return n;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TBuffer::ReadArray(Char_t *&c)
{
// Read array of characters from the I/O buffer. Returns the number of
// characters read. If argument is a 0 pointer then space will be
// allocated for the array.
Assert(IsReading());
Int_t n;
*this >> n;
Int_t l = sizeof(Char_t)*n;
if (l <= 0 || l > fBufSize) return 0;
if (!c) c = new Char_t[n];
memcpy(c, fBufCur, l);
fBufCur += l;
return n;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TBuffer::ReadArray(Short_t *&h)
{
// Read array of shorts from the I/O buffer. Returns the number of shorts
// read. If argument is a 0 pointer then space will be allocated for the
// array.
Assert(IsReading());
Int_t n;
*this >> n;
Int_t l = sizeof(Short_t)*n;
if (l <= 0 || l > fBufSize) return 0;
if (!h) h = new Short_t[n];
#ifdef R__BYTESWAP
# ifdef USE_BSWAPCPY
bswapcpy16(h, fBufCur, n);
fBufCur += l;
# else
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
frombuf(fBufCur, &h[i]);
# endif
#else
memcpy(h, fBufCur, l);
fBufCur += l;
#endif
return n;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TBuffer::ReadArray(Int_t *&ii)
{
// Read array of ints from the I/O buffer. Returns the number of ints
// read. If argument is a 0 pointer then space will be allocated for the
// array.
Assert(IsReading());
Int_t n;
*this >> n;
Int_t l = sizeof(Int_t)*n;
if (l <= 0 || l > fBufSize) return 0;
if (!ii) ii = new Int_t[n];
#ifdef R__BYTESWAP
# ifdef USE_BSWAPCPY
bswapcpy32(ii, fBufCur, n);
fBufCur += l;
# else
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
frombuf(fBufCur, &ii[i]);
# endif
#else
memcpy(ii, fBufCur, l);
fBufCur += l;
#endif
return n;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TBuffer::ReadArray(Long_t *&ll)
{
// Read array of longs from the I/O buffer. Returns the number of longs
// read. If argument is a 0 pointer then space will be allocated for the
// array.
Assert(IsReading());
Int_t n;
*this >> n;
Int_t l = sizeof(Long_t)*n;
if (l <= 0 || l > fBufSize) return 0;
if (!ll) ll = new Long_t[n];
TFile *file = (TFile*)fParent;
if (file && file->GetVersion() < 30006) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) frombufOld(fBufCur, &ll[i]);
} else {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) frombuf(fBufCur, &ll[i]);
}
return n;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TBuffer::ReadArray(Long64_t *&ll)
{
// Read array of long longs from the I/O buffer. Returns the number of
// long longs read. If argument is a 0 pointer then space will be
// allocated for the array.
Assert(IsReading());
Int_t n;
*this >> n;
Int_t l = sizeof(Long64_t)*n;
if (l <= 0 || l > fBufSize) return 0;
if (!ll) ll = new Long64_t[n];
#ifdef R__BYTESWAP
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
frombuf(fBufCur, &ll[i]);
#else
memcpy(ll, fBufCur, l);
fBufCur += l;
#endif
return n;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TBuffer::ReadArray(Float_t *&f)
{
// Read array of floats from the I/O buffer. Returns the number of floats
// read. If argument is a 0 pointer then space will be allocated for the
// array.
Assert(IsReading());
Int_t n;
*this >> n;
Int_t l = sizeof(Float_t)*n;
if (l <= 0 || l > fBufSize) return 0;
if (!f) f = new Float_t[n];
#ifdef R__BYTESWAP
# ifdef USE_BSWAPCPY
bswapcpy32(f, fBufCur, n);
fBufCur += l;
# else
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
frombuf(fBufCur, &f[i]);
# endif
#else
memcpy(f, fBufCur, l);
fBufCur += l;
#endif
return n;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TBuffer::ReadArray(Double_t *&d)
{
// Read array of doubles from the I/O buffer. Returns the number of doubles
// read. If argument is a 0 pointer then space will be allocated for the
// array.
Assert(IsReading());
Int_t n;
*this >> n;
Int_t l = sizeof(Double_t)*n;
if (l <= 0 || l > fBufSize) return 0;
if (!d) d = new Double_t[n];
#ifdef R__BYTESWAP
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
frombuf(fBufCur, &d[i]);
#else
memcpy(d, fBufCur, l);
fBufCur += l;
#endif
return n;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TBuffer::ReadArrayDouble32(Double_t *&d, TStreamerElement *ele)
{
// Read array of doubles (written as float) from the I/O buffer.
// Returns the number of doubles read.
// If argument is a 0 pointer then space will be allocated for the array.
// see comments about Double32_t encoding at TBuffer::WriteDouble32
Assert(IsReading());
Int_t n;
*this >> n;
if (n <= 0 || 4*n > fBufSize) return 0;
if (!d) d = new Double_t[n];
ReadFastArrayDouble32(d,n,ele);
return n;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TBuffer::ReadStaticArray(Bool_t *b)
{
// Read array of bools from the I/O buffer. Returns the number of bools
// read.
Assert(IsReading());
Int_t n;
*this >> n;
if (n <= 0 || n > fBufSize) return 0;
if (!b) return 0;
if (sizeof(Bool_t) > 1) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
frombuf(fBufCur, &b[i]);
} else {
Int_t l = sizeof(Bool_t)*n;
memcpy(b, fBufCur, l);
fBufCur += l;
}
return n;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TBuffer::ReadStaticArray(Char_t *c)
{
// Read array of characters from the I/O buffer. Returns the number of
// characters read.
Assert(IsReading());
Int_t n;
*this >> n;
Int_t l = sizeof(Char_t)*n;
if (l <= 0 || l > fBufSize) return 0;
if (!c) return 0;
memcpy(c, fBufCur, l);
fBufCur += l;
return n;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TBuffer::ReadStaticArray(Short_t *h)
{
// Read array of shorts from the I/O buffer. Returns the number of shorts
// read.
Assert(IsReading());
Int_t n;
*this >> n;
Int_t l = sizeof(Short_t)*n;
if (l <= 0 || l > fBufSize) return 0;
if (!h) return 0;
#ifdef R__BYTESWAP
# ifdef USE_BSWAPCPY
bswapcpy16(h, fBufCur, n);
fBufCur += l;
# else
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
frombuf(fBufCur, &h[i]);
# endif
#else
memcpy(h, fBufCur, l);
fBufCur += l;
#endif
return n;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TBuffer::ReadStaticArray(Int_t *ii)
{
// Read array of ints from the I/O buffer. Returns the number of ints
// read.
Assert(IsReading());
Int_t n;
*this >> n;
Int_t l = sizeof(Int_t)*n;
if (l <= 0 || l > fBufSize) return 0;
if (!ii) return 0;
#ifdef R__BYTESWAP
# ifdef USE_BSWAPCPY
bswapcpy32(ii, fBufCur, n);
fBufCur += sizeof(Int_t)*n;
# else
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
frombuf(fBufCur, &ii[i]);
# endif
#else
memcpy(ii, fBufCur, l);
fBufCur += l;
#endif
return n;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TBuffer::ReadStaticArray(Long_t *ll)
{
// Read array of longs from the I/O buffer. Returns the number of longs
// read.
Assert(IsReading());
Int_t n;
*this >> n;
Int_t l = sizeof(Long_t)*n;
if (l <= 0 || l > fBufSize) return 0;
if (!ll) return 0;
TFile *file = (TFile*)fParent;
if (file && file->GetVersion() < 30006) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) frombufOld(fBufCur, &ll[i]);
} else {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) frombuf(fBufCur, &ll[i]);
}
return n;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TBuffer::ReadStaticArray(Long64_t *ll)
{
// Read array of long longs from the I/O buffer. Returns the number of
// long longs read.
Assert(IsReading());
Int_t n;
*this >> n;
Int_t l = sizeof(Long64_t)*n;
if (l <= 0 || l > fBufSize) return 0;
if (!ll) return 0;
#ifdef R__BYTESWAP
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
frombuf(fBufCur, &ll[i]);
#else
memcpy(ll, fBufCur, l);
fBufCur += l;
#endif
return n;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TBuffer::ReadStaticArray(Float_t *f)
{
// Read array of floats from the I/O buffer. Returns the number of floats
// read.
Assert(IsReading());
Int_t n;
*this >> n;
Int_t l = sizeof(Float_t)*n;
if (n <= 0 || l > fBufSize) return 0;
if (!f) return 0;
#ifdef R__BYTESWAP
# ifdef USE_BSWAPCPY
bswapcpy32(f, fBufCur, n);
fBufCur += sizeof(Float_t)*n;
# else
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
frombuf(fBufCur, &f[i]);
# endif
#else
memcpy(f, fBufCur, l);
fBufCur += l;
#endif
return n;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TBuffer::ReadStaticArray(Double_t *d)
{
// Read array of doubles from the I/O buffer. Returns the number of doubles
// read.
Assert(IsReading());
Int_t n;
*this >> n;
Int_t l = sizeof(Double_t)*n;
if (n <= 0 || l > fBufSize) return 0;
if (!d) return 0;
#ifdef R__BYTESWAP
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
frombuf(fBufCur, &d[i]);
#else
memcpy(d, fBufCur, l);
fBufCur += l;
#endif
return n;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TBuffer::ReadStaticArrayDouble32(Double_t *d, TStreamerElement *ele)
{
// Read array of doubles (written as float) from the I/O buffer.
// Returns the number of doubles read.
// see comments about Double32_t encoding at TBuffer::WriteDouble32
Assert(IsReading());
Int_t n;
*this >> n;
if (n <= 0 || 4*n > fBufSize) return 0;
if (!d) return 0;
ReadFastArrayDouble32(d,n,ele);
return n;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::ReadFastArray(Bool_t *b, Int_t n)
{
// Read array of n bools from the I/O buffer.
if (n <= 0 || n > fBufSize) return;
if (sizeof(Bool_t) > 1) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
frombuf(fBufCur, &b[i]);
} else {
Int_t l = sizeof(Bool_t)*n;
memcpy(b, fBufCur, l);
fBufCur += l;
}
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::ReadFastArray(Char_t *c, Int_t n)
{
// Read array of n characters from the I/O buffer.
if (n <= 0 || n > fBufSize) return;
Int_t l = sizeof(Char_t)*n;
memcpy(c, fBufCur, l);
fBufCur += l;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::ReadFastArrayString(Char_t *c, Int_t n)
{
// Read array of n characters from the I/O buffer.
Int_t len;
UChar_t lenchar;
*this >> lenchar;
if (lenchar < 255) {
len = lenchar;
} else {
*this >> len;
}
if (len) {
if (len >= n) len = n-1;
if (n <= 0 || n > fBufSize) return;
Int_t l = sizeof(Char_t)*n;
memcpy(c, fBufCur, l);
fBufCur += l;
c[len] = 0;
} else {
c[0] = 0;
}
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::ReadFastArray(Short_t *h, Int_t n)
{
// Read array of n shorts from the I/O buffer.
Int_t l = sizeof(Short_t)*n;
if (n <= 0 || l > fBufSize) return;
#ifdef R__BYTESWAP
# ifdef USE_BSWAPCPY
bswapcpy16(h, fBufCur, n);
fBufCur += sizeof(Short_t)*n;
# else
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
frombuf(fBufCur, &h[i]);
# endif
#else
memcpy(h, fBufCur, l);
fBufCur += l;
#endif
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::ReadFastArray(Int_t *ii, Int_t n)
{
// Read array of n ints from the I/O buffer.
Int_t l = sizeof(Int_t)*n;
if (l <= 0 || l > fBufSize) return;
#ifdef R__BYTESWAP
# ifdef USE_BSWAPCPY
bswapcpy32(ii, fBufCur, n);
fBufCur += sizeof(Int_t)*n;
# else
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
frombuf(fBufCur, &ii[i]);
# endif
#else
memcpy(ii, fBufCur, l);
fBufCur += l;
#endif
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::ReadFastArray(Long_t *ll, Int_t n)
{
// Read array of n longs from the I/O buffer.
Int_t l = sizeof(Long_t)*n;
if (l <= 0 || l > fBufSize) return;
TFile *file = (TFile*)fParent;
if (file && file->GetVersion() < 30006) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) frombufOld(fBufCur, &ll[i]);
} else {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) frombuf(fBufCur, &ll[i]);
}
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::ReadFastArray(Long64_t *ll, Int_t n)
{
// Read array of n long longs from the I/O buffer.
Int_t l = sizeof(Long64_t)*n;
if (l <= 0 || l > fBufSize) return;
#ifdef R__BYTESWAP
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
frombuf(fBufCur, &ll[i]);
#else
memcpy(ll, fBufCur, l);
fBufCur += l;
#endif
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::ReadFastArray(Float_t *f, Int_t n)
{
// Read array of n floats from the I/O buffer.
Int_t l = sizeof(Float_t)*n;
if (l <= 0 || l > fBufSize) return;
#ifdef R__BYTESWAP
# ifdef USE_BSWAPCPY
bswapcpy32(f, fBufCur, n);
fBufCur += sizeof(Float_t)*n;
# else
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
frombuf(fBufCur, &f[i]);
# endif
#else
memcpy(f, fBufCur, l);
fBufCur += l;
#endif
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::ReadFastArray(Double_t *d, Int_t n)
{
// Read array of n doubles from the I/O buffer.
Int_t l = sizeof(Double_t)*n;
if (l <= 0 || l > fBufSize) return;
#ifdef R__BYTESWAP
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
frombuf(fBufCur, &d[i]);
#else
memcpy(d, fBufCur, l);
fBufCur += l;
#endif
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::ReadFastArrayDouble32(Double_t *d, Int_t n, TStreamerElement *ele)
{
// Read array of n doubles (written as float) from the I/O buffer.
// see comments about Double32_t encoding at TBuffer::WriteDouble32
if (n <= 0 || 4*n > fBufSize) return;
if (ele && ele->GetFactor() != 0) {
Double_t xmin = ele->GetXmin();
Double_t factor = ele->GetFactor();
for (int j=0;j < n; j++) {
UInt_t aint; *this >> aint; d[j] = (Double_t)(aint/factor + xmin);
}
} else {
Float_t afloat;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
frombuf(fBufCur, &afloat);
d[i]=afloat;
}
}
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::ReadFastArray(void *start, const TClass *cl, Int_t n,
TMemberStreamer *streamer)
{
// Read an array of 'n' objects from the I/O buffer.
// Stores the objects read starting at the address 'start'.
// The objects in the array are assume to be of class 'cl'.
if (streamer) {
(*streamer)(*this,start,0);
return;
}
int objectSize = cl->Size();
char *obj = (char*)start;
char *end = obj + n*objectSize;
for(; obj<end; obj+=objectSize) ((TClass*)cl)->Streamer(obj,*this);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::ReadFastArray(void **start, const TClass *cl, Int_t n,
Bool_t isPreAlloc, TMemberStreamer *streamer)
{
// Read an array of 'n' objects from the I/O buffer.
// The objects read are stored starting at the address '*start'
// The objects in the array are assumed to be of class 'cl' or a derived class.
// 'mode' indicates whether the data member is marked with '->'
// if isPreAlloc is true (data member has a ->) we can assume that the pointer (*start)
// is never 0.
if (streamer) {
if (isPreAlloc) {
for (Int_t j=0;j<n;j++) {
if (!start[j]) start[j] = ((TClass*)cl)->New();
}
}
(*streamer)(*this,(void*)start,0);
return;
}
if (!isPreAlloc) {
for (Int_t j=0; j<n; j++){
//delete the object or collection
if (start[j] && TStreamerInfo::CanDelete()) ((TClass*)cl)->Destructor(start[j],kFALSE); // call delete and desctructor
start[j] = ReadObjectAny(cl);
}
} else { //case //-> in comment
for (Int_t j=0; j<n; j++){
if (!start[j]) start[j] = ((TClass*)cl)->New();
((TClass*)cl)->Streamer(start[j],*this);
}
}
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::WriteArray(const Bool_t *b, Int_t n)
{
// Write array of n bools into the I/O buffer.
Assert(IsWriting());
*this << n;
if (n <= 0) return;
Assert(b);
Int_t l = sizeof(UChar_t)*n;
if (fBufCur + l > fBufMax) Expand(TMath::Max(2*fBufSize, fBufSize+l));
if (sizeof(Bool_t) > 1) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
tobuf(fBufCur, b[i]);
} else {
memcpy(fBufCur, b, l);
fBufCur += l;
}
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::WriteArray(const Char_t *c, Int_t n)
{
// Write array of n characters into the I/O buffer.
Assert(IsWriting());
*this << n;
if (n <= 0) return;
Assert(c);
Int_t l = sizeof(Char_t)*n;
if (fBufCur + l > fBufMax) Expand(TMath::Max(2*fBufSize, fBufSize+l));
memcpy(fBufCur, c, l);
fBufCur += l;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::WriteArray(const Short_t *h, Int_t n)
{
// Write array of n shorts into the I/O buffer.
Assert(IsWriting());
*this << n;
if (n <= 0) return;
Assert(h);
Int_t l = sizeof(Short_t)*n;
if (fBufCur + l > fBufMax) Expand(TMath::Max(2*fBufSize, fBufSize+l));
#ifdef R__BYTESWAP
# ifdef USE_BSWAPCPY
bswapcpy16(fBufCur, h, n);
fBufCur += l;
# else
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
tobuf(fBufCur, h[i]);
# endif
#else
memcpy(fBufCur, h, l);
fBufCur += l;
#endif
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::WriteArray(const Int_t *ii, Int_t n)
{
// Write array of n ints into the I/O buffer.
Assert(IsWriting());
*this << n;
if (n <= 0) return;
Assert(ii);
Int_t l = sizeof(Int_t)*n;
if (fBufCur + l > fBufMax) Expand(TMath::Max(2*fBufSize, fBufSize+l));
#ifdef R__BYTESWAP
# ifdef USE_BSWAPCPY
bswapcpy32(fBufCur, ii, n);
fBufCur += l;
# else
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
tobuf(fBufCur, ii[i]);
# endif
#else
memcpy(fBufCur, ii, l);
fBufCur += l;
#endif
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::WriteArray(const Long_t *ll, Int_t n)
{
// Write array of n longs into the I/O buffer.
Assert(IsWriting());
*this << n;
if (n <= 0) return;
Assert(ll);
Int_t l = 8*n;
if (fBufCur + l > fBufMax) Expand(TMath::Max(2*fBufSize, fBufSize+l));
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) tobuf(fBufCur, ll[i]);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::WriteArray(const ULong_t *ll, Int_t n)
{
// Write array of n unsigned longs into the I/O buffer.
// This is an explicit case for unsigned longs since signed longs
// have a special tobuf().
Assert(IsWriting());
*this << n;
if (n <= 0) return;
Assert(ll);
Int_t l = 8*n;
if (fBufCur + l > fBufMax) Expand(TMath::Max(2*fBufSize, fBufSize+l));
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) tobuf(fBufCur, ll[i]);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::WriteArray(const Long64_t *ll, Int_t n)
{
// Write array of n long longs into the I/O buffer.
Assert(IsWriting());
*this << n;
if (n <= 0) return;
Assert(ll);
Int_t l = sizeof(Long64_t)*n;
if (fBufCur + l > fBufMax) Expand(TMath::Max(2*fBufSize, fBufSize+l));
#ifdef R__BYTESWAP
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
tobuf(fBufCur, ll[i]);
#else
memcpy(fBufCur, ll, l);
fBufCur += l;
#endif
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::WriteArray(const Float_t *f, Int_t n)
{
// Write array of n floats into the I/O buffer.
Assert(IsWriting());
*this << n;
if (n <= 0) return;
Assert(f);
Int_t l = sizeof(Float_t)*n;
if (fBufCur + l > fBufMax) Expand(TMath::Max(2*fBufSize, fBufSize+l));
#ifdef R__BYTESWAP
# ifdef USE_BSWAPCPY
bswapcpy32(fBufCur, f, n);
fBufCur += l;
# else
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
tobuf(fBufCur, f[i]);
# endif
#else
memcpy(fBufCur, f, l);
fBufCur += l;
#endif
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::WriteArray(const Double_t *d, Int_t n)
{
// Write array of n doubles into the I/O buffer.
Assert(IsWriting());
*this << n;
if (n <= 0) return;
Assert(d);
Int_t l = sizeof(Double_t)*n;
if (fBufCur + l > fBufMax) Expand(TMath::Max(2*fBufSize, fBufSize+l));
#ifdef R__BYTESWAP
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
tobuf(fBufCur, d[i]);
#else
memcpy(fBufCur, d, l);
fBufCur += l;
#endif
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::WriteArrayDouble32(const Double_t *d, Int_t n, TStreamerElement *ele)
{
// Write array of n doubles (as float) into the I/O buffer.
// see comments about Double32_t encoding at TBuffer::WriteDouble32
Assert(IsWriting());
*this << n;
if (n <= 0) return;
Assert(d);
Int_t l = sizeof(Float_t)*n;
if (fBufCur + l > fBufMax) Expand(TMath::Max(2*fBufSize, fBufSize+l));
WriteFastArrayDouble32(d,n,ele);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::WriteFastArray(const Bool_t *b, Int_t n)
{
// Write array of n bools into the I/O buffer.
if (n <= 0) return;
Int_t l = sizeof(UChar_t)*n;
if (fBufCur + l > fBufMax) Expand(TMath::Max(2*fBufSize, fBufSize+l));
if (sizeof(Bool_t) > 1) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
tobuf(fBufCur, b[i]);
} else {
memcpy(fBufCur, b, l);
fBufCur += l;
}
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::WriteFastArray(const Char_t *c, Int_t n)
{
// Write array of n characters into the I/O buffer.
if (n <= 0) return;
Int_t l = sizeof(Char_t)*n;
if (fBufCur + l > fBufMax) Expand(TMath::Max(2*fBufSize, fBufSize+l));
memcpy(fBufCur, c, l);
fBufCur += l;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::WriteFastArrayString(const Char_t *c, Int_t n)
{
// Write array of n characters into the I/O buffer.
if (n < 255) {
*this << (UChar_t)n;
} else {
*this << (UChar_t)255;
*this << n;
}
if (n <= 0) return;
Int_t l = sizeof(Char_t)*n;
if (fBufCur + l > fBufMax) Expand(TMath::Max(2*fBufSize, fBufSize+l));
memcpy(fBufCur, c, l);
fBufCur += l;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::WriteFastArray(const Short_t *h, Int_t n)
{
// Write array of n shorts into the I/O buffer.
if (n <= 0) return;
Int_t l = sizeof(Short_t)*n;
if (fBufCur + l > fBufMax) Expand(TMath::Max(2*fBufSize, fBufSize+l));
#ifdef R__BYTESWAP
# ifdef USE_BSWAPCPY
bswapcpy16(fBufCur, h, n);
fBufCur += l;
# else
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
tobuf(fBufCur, h[i]);
# endif
#else
memcpy(fBufCur, h, l);
fBufCur += l;
#endif
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::WriteFastArray(const Int_t *ii, Int_t n)
{
// Write array of n ints into the I/O buffer.
if (n <= 0) return;
Int_t l = sizeof(Int_t)*n;
if (fBufCur + l > fBufMax) Expand(TMath::Max(2*fBufSize, fBufSize+l));
#ifdef R__BYTESWAP
# ifdef USE_BSWAPCPY
bswapcpy32(fBufCur, ii, n);
fBufCur += l;
# else
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
tobuf(fBufCur, ii[i]);
# endif
#else
memcpy(fBufCur, ii, l);
fBufCur += l;
#endif
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::WriteFastArray(const Long_t *ll, Int_t n)
{
// Write array of n longs into the I/O buffer.
if (n <= 0) return;
Int_t l = 8*n;
if (fBufCur + l > fBufMax) Expand(TMath::Max(2*fBufSize, fBufSize+l));
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) tobuf(fBufCur, ll[i]);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::WriteFastArray(const ULong_t *ll, Int_t n)
{
// Write array of n unsigned longs into the I/O buffer.
// This is an explicit case for unsigned longs since signed longs
// have a special tobuf().
if (n <= 0) return;
Int_t l = 8*n;
if (fBufCur + l > fBufMax) Expand(TMath::Max(2*fBufSize, fBufSize+l));
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) tobuf(fBufCur, ll[i]);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::WriteFastArray(const Long64_t *ll, Int_t n)
{
// Write array of n long longs into the I/O buffer.
if (n <= 0) return;
Int_t l = sizeof(Long64_t)*n;
if (fBufCur + l > fBufMax) Expand(TMath::Max(2*fBufSize, fBufSize+l));
#ifdef R__BYTESWAP
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
tobuf(fBufCur, ll[i]);
#else
memcpy(fBufCur, ll, l);
fBufCur += l;
#endif
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::WriteFastArray(const Float_t *f, Int_t n)
{
// Write array of n floats into the I/O buffer.
if (n <= 0) return;
Int_t l = sizeof(Float_t)*n;
if (fBufCur + l > fBufMax) Expand(TMath::Max(2*fBufSize, fBufSize+l));
#ifdef R__BYTESWAP
# ifdef USE_BSWAPCPY
bswapcpy32(fBufCur, f, n);
fBufCur += l;
# else
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
tobuf(fBufCur, f[i]);
# endif
#else
memcpy(fBufCur, f, l);
fBufCur += l;
#endif
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::WriteFastArray(const Double_t *d, Int_t n)
{
// Write array of n doubles into the I/O buffer.
if (n <= 0) return;
Int_t l = sizeof(Double_t)*n;
if (fBufCur + l > fBufMax) Expand(TMath::Max(2*fBufSize, fBufSize+l));
#ifdef R__BYTESWAP
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
tobuf(fBufCur, d[i]);
#else
memcpy(fBufCur, d, l);
fBufCur += l;
#endif
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::WriteFastArrayDouble32(const Double_t *d, Int_t n, TStreamerElement *ele)
{
// Write array of n doubles (as float) into the I/O buffer.
// see comments about Double32_t encoding at TBuffer::WriteDouble32
if (n <= 0) return;
Int_t l = sizeof(Float_t)*n;
if (fBufCur + l > fBufMax) Expand(TMath::Max(2*fBufSize, fBufSize+l));
if (ele && ele->GetFactor()) {
Double_t factor = ele->GetFactor();
Double_t xmin = ele->GetXmin();
Double_t xmax = ele->GetXmax();
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
Double_t x = d[j];
if (x < xmin) x = xmin;
if (x > xmax) x = xmax;
UInt_t aint = UInt_t(0.5+factor*(x-xmin)); *this << aint;
}
} else {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
tobuf(fBufCur, Float_t(d[i]));
}
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::WriteFastArray(void *start, const TClass *cl, Int_t n,
TMemberStreamer *streamer)
{
// Write an array of object starting at the address 'start' and of length 'n'
// the objects in the array are assumed to be of class 'cl'
if (streamer) {
(*streamer)(*this, start, 0);
return;
}
char *obj = (char*)start;
if (!n) n=1;
int size = cl->Size();
for(Int_t j=0; j<n; j++,obj+=size) {
((TClass*)cl)->Streamer(obj,*this);
}
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TBuffer::WriteFastArray(void **start, const TClass *cl, Int_t n,
Bool_t isPreAlloc, TMemberStreamer *streamer)
{
// Write an array of object starting at the address '*start' and of length 'n'
// the objects in the array are of class 'cl'
// 'isPreAlloc' indicates whether the data member is marked with '->'
// Return:
// 0: success
// 2: truncated success (i.e actual class is missing. Only ptrClass saved.)
// if isPreAlloc is true (data member has a ->) we can assume that the pointer
// is never 0.
if (streamer) {
(*streamer)(*this,(void*)start,0);
return 0;
}
int strInfo = 0;
Int_t res = 0;
if (!isPreAlloc) {
for (Int_t j=0;j<n;j++) {
//must write StreamerInfo if pointer is null
if (!strInfo && !start[j] ) ((TClass*)cl)->GetStreamerInfo()->ForceWriteInfo((TFile *)GetParent());
strInfo = 2003;
res |= WriteObjectAny(start[j],cl);
}
} else { //case //-> in comment
for (Int_t j=0;j<n;j++) {
if (!start[j]) start[j] = ((TClass*)cl)->New();
((TClass*)cl)->Streamer(start[j],*this);
}
}
return res;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
TObject *TBuffer::ReadObject(const TClass * /*clReq*/)
{
// Read object from I/O buffer. clReq is NOT used.
// The value returned is the address of the actual start in memory of
// the object. Note that if the actual class of the object does not
// inherit first from TObject, the type of the pointer is NOT 'TObject*'.
// [More accurately, the class needs to start with the TObject part, for
// the pointer to be a real TOject*].
// We recommend using ReadObjectAny instead of ReadObject
return (TObject*) ReadObjectAny(0);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::SkipObjectAny()
{
// Skip any kind of object from buffer
UInt_t start, count;
ReadVersion(&start, &count);
SetBufferOffset(start+count+sizeof(UInt_t));
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void *TBuffer::ReadObjectAny(const TClass *clCast)
{
// Read object from I/O buffer.
// A typical use for this function is:
// MyClass *ptr = (MyClass*)b.ReadObjectAny(MyClass::Class());
// I.e. clCast should point to a TClass object describing the class pointed
// to by your pointer.
// In case of multiple inheritance, the return value might not be the
// real beginning of the object in memory. You will need to use a
// dynamic_cast later if you need to retrieve it.
Assert(IsReading());
// make sure fMap is initialized
InitMap();
// before reading object save start position
UInt_t startpos = UInt_t(fBufCur-fBuffer);
// attempt to load next object as TClass clCast
UInt_t tag; // either tag or byte count
TClass *clRef = ReadClass(clCast, &tag);
Int_t baseOffset = 0;
if (clRef && (clRef!=(TClass*)(-1)) && clCast) {
//baseOffset will be -1 if clRef does not inherit from clCast.
baseOffset = clRef->GetBaseClassOffset(clCast);
if (baseOffset == -1) {
Error("ReadObject", "got object of wrong class! requested %s but got %s",
clCast->GetName(), clRef->GetName());
CheckByteCount(startpos, tag, (TClass*)0); // avoid mis-leading byte count error message
return 0; // We better return at this point
}
if (clCast->GetClassInfo() && !clRef->GetClassInfo()) {
//we cannot mix a compiled class with an emulated class in the inheritance
Error("ReadObject", "trying to read an emulated class (%s) to store in a compiled pointer (%s)",
clRef->GetName(),clCast->GetName());
CheckByteCount(startpos, tag, (TClass*)0); // avoid mis-leading byte count error message
return 0;
}
}
// check if object has not already been read
// (this can only happen when called via CheckObject())
char *obj;
if (fVersion > 0) {
obj = (char *) fMap->GetValue(startpos+kMapOffset);
if (obj == (void*) -1) obj = 0;
if (obj) {
CheckByteCount(startpos, tag, (TClass*)0);
return (obj+baseOffset);
}
}
// unknown class, skip to next object and return 0 obj
if (clRef == (TClass*) -1) {
if (fBufCur >= fBufMax) return 0;
if (fVersion > 0)
MapObject((TObject*) -1, startpos+kMapOffset);
else
MapObject((void*)0, 0, fMapCount);
CheckByteCount(startpos, tag, (TClass*)0);
return 0;
}
if (!clRef) {
// got a reference to an already read object
if (fVersion > 0) {
tag += fDisplacement;
tag = CheckObject(tag, clCast);
} else {
if (tag > (UInt_t)fMap->GetSize()) {
Error("ReadObject", "object tag too large, I/O buffer corrupted");
return 0;
// exception
}
}
obj = (char *) fMap->GetValue(tag);
clRef = (TClass*) fClassMap->GetValue(tag);
if (clRef && (clRef!=(TClass*)(-1)) && clCast) {
//baseOffset will be -1 if clRef does not inherit from clCast.
baseOffset = clRef->GetBaseClassOffset(clCast);
if (baseOffset == -1) {
Error("ReadObject", "Got object of wrong class (Got %s while expecting %s)",
clRef->GetName(),clCast->GetName());
// exception
baseOffset = 0;
}
}
// There used to be a warning printed here when:
// obj && isTObject && !((TObject*)obj)->IsA()->InheritsFrom(clReq)
// however isTObject was based on clReq (now clCast).
// If the test was to fail, then it is as likely that the object is not a TObject
// and then we have a potential core dump.
// At this point (missing clRef), we do NOT have enough information to really
// answer the question: is the object read of the type I requested.
} else {
// allocate a new object based on the class found
obj = (char *)clRef->New();
if (!obj) {
Error("ReadObject", "could not create object of class %s",
clRef->GetName());
// exception
return 0;
}
// add to fMap before reading rest of object
if (fVersion > 0)
MapObject(obj, clRef, startpos+kMapOffset);
else
MapObject(obj, clRef, fMapCount);
// let the object read itself
clRef->Streamer(obj, *this);
CheckByteCount(startpos, tag, clRef);
}
return obj+baseOffset;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::WriteObject(const TObject *obj)
{
// Write object to I/O buffer.
WriteObjectAny(obj, TObject::Class());
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::WriteObject(const void *actualObjectStart, const TClass *actualClass)
{
// Write object to I/O buffer.
// This function assumes that the value of 'actualObjectStart' is the actual start of
// the object of class 'actualClass'
Assert(IsWriting());
// make sure fMap is initialized
InitMap();
ULong_t idx;
if (!actualObjectStart) {
// save kNullTag to represent NULL pointer
*this << kNullTag;
} else if ((idx = (ULong_t)fMap->GetValue(Void_Hash(actualObjectStart), (Long_t)actualObjectStart)) != 0) {
// truncation is OK the value we did put in the map is an 30-bit offset
// and not a pointer
UInt_t objIdx = UInt_t(idx);
// save index of already stored object
*this << objIdx;
} else {
// A warning to let the user know it will need to change the class code
// to be able to read this back.
if (actualClass->HasDefaultConstructor() == 0) {
Warning("WriteObjectAny", "since %s had no public constructor\n"
"\twhich can be called without argument, objects of this class\n"
"\tcan not be read with the current library. You would need to\n"
"\tadd a default constructor before attempting to read it.",
actualClass->GetName());
}
// reserve space for leading byte count
UInt_t cntpos = UInt_t(fBufCur-fBuffer);
fBufCur += sizeof(UInt_t);
// write class of object first
WriteClass(actualClass);
// add to map before writing rest of object (to handle self reference)
// (+kMapOffset so it's != kNullTag)
MapObject(actualObjectStart, actualClass, cntpos+kMapOffset);
((TClass*)actualClass)->Streamer((void*)actualObjectStart,*this);
// write byte count
SetByteCount(cntpos);
}
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TBuffer::WriteObjectAny(const void *obj, const TClass *ptrClass)
{
// Write object to I/O buffer.
// This function assumes that the value in 'obj' is the value stored in
// a pointer to a "ptrClass". The actual type of the object pointed to
// can be any class derived from "ptrClass".
// Return:
// 0: failure
// 1: success
// 2: truncated success (i.e actual class is missing. Only ptrClass saved.)
if (!obj) {
WriteObject(0, 0);
return 1;
}
if (!ptrClass) {
Error("WriteObjectAny", "ptrClass argument may not be 0");
return 0;
}
TClass *clActual = ptrClass->GetActualClass(obj);
if (clActual) {
const char *temp = (const char*) obj;
// clActual->GetStreamerInfo();
Int_t offset = (ptrClass != clActual) ?
clActual->GetBaseClassOffset(ptrClass) : 0;
temp -= offset;
WriteObject(temp, clActual);
return 1;
} else {
WriteObject(obj, ptrClass);
return 2;
}
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
TClass *TBuffer::ReadClass(const TClass *clReq, UInt_t *objTag)
{
// Read class definition from I/O buffer. clReq can be used to cross check
// if the actually read object is of the requested class. objTag is
// set in case the object is a reference to an already read object.
Assert(IsReading());
// read byte count and/or tag (older files don't have byte count)
TClass *cl;
if (fBufCur < fBuffer || fBufCur > fBufMax) {
fBufCur = fBufMax;
cl = (TClass*)-1;
return cl;
}
UInt_t bcnt, tag, startpos = 0;
*this >> bcnt;
if (!(bcnt & kByteCountMask) || bcnt == kNewClassTag) {
tag = bcnt;
bcnt = 0;
} else {
fVersion = 1;
startpos = UInt_t(fBufCur-fBuffer);
*this >> tag;
}
// in case tag is object tag return tag
if (!(tag & kClassMask)) {
if (objTag) *objTag = tag;
return 0;
}
if (tag == kNewClassTag) {
// got a new class description followed by a new object
// (class can be 0 if class dictionary is not found, in that
// case object of this class must be skipped)
cl = TClass::Load(*this);
// add class to fMap for later reference
if (fVersion > 0) {
// check if class was already read
TClass *cl1 = (TClass *)fMap->GetValue(startpos+kMapOffset);
if (cl1 != cl)
MapObject(cl ? cl : (TObject*) -1, startpos+kMapOffset);
} else
MapObject(cl, fMapCount);
} else {
// got a tag to an already seen class
UInt_t clTag = (tag & ~kClassMask);
if (fVersion > 0) {
clTag += fDisplacement;
clTag = CheckObject(clTag, clReq, kTRUE);
} else {
if (clTag == 0 || clTag > (UInt_t)fMap->GetSize()) {
Error("ReadClass", "illegal class tag=%d (0<tag<=%d), I/O buffer corrupted",
clTag, fMap->GetSize());
// exception
}
}
// class can be 0 if dictionary was not found
cl = (TClass *)fMap->GetValue(clTag);
}
if (cl && clReq && !cl->InheritsFrom(clReq)) {
Error("ReadClass", "got wrong class: %s", cl->GetName());
// exception
}
// return bytecount in objTag
if (objTag) *objTag = (bcnt & ~kByteCountMask);
// case of unknown class
if (!cl) cl = (TClass*)-1;
return cl;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::WriteClass(const TClass *cl)
{
// Write class description to I/O buffer.
Assert(IsWriting());
ULong_t idx;
if ((idx = (ULong_t)fMap->GetValue(((TObject *)cl)->TObject::Hash(), (Long_t)cl)) != 0) {
// truncation is OK the value we did put in the map is an 30-bit offset
// and not a pointer
UInt_t clIdx = UInt_t(idx);
// save index of already stored class
*this << (clIdx | kClassMask);
} else {
// offset in buffer where class info is written
UInt_t offset = UInt_t(fBufCur-fBuffer);
// save new class tag
*this << kNewClassTag;
// write class name
cl->Store(*this);
// store new class reference in fMap (+kMapOffset so it's != kNullTag)
MapObject(cl, offset+kMapOffset);
}
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
static Version_t R__FindStreamerInfoVersion(const TClass *cl, UInt_t checksum)
{
//find the version number in the StreamerInfos corresponding to checksum
Version_t version = 0;
Int_t ninfos = cl->GetStreamerInfos()->GetEntriesFast();
for (Int_t i=1;i<ninfos;i++) {
// TClass::fStreamerInfos has a lower bound not equal to 0,
// so we should use At and not use UncheckedAt
TStreamerInfo *info = (TStreamerInfo*)cl->GetStreamerInfos()->At(i);
if (!info) continue;
if (info->GetCheckSum() == checksum) {
version = i;
//printf("ReadVersion, setting version=%d\n",version);
break;
}
}
return version;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Version_t TBuffer::ReadVersion(UInt_t *startpos, UInt_t *bcnt, const TClass *cl)
{
// Read class version from I/O buffer.
Version_t version;
if (startpos && bcnt) {
// before reading object save start position
*startpos = UInt_t(fBufCur-fBuffer);
// read byte count (older files don't have byte count)
// byte count is packed in two individual shorts, this to be
// backward compatible with old files that have at this location
// only a single short (i.e. the version)
union {
UInt_t cnt;
Version_t vers[2];
} v;
#ifdef R__BYTESWAP
*this >> v.vers[1];
*this >> v.vers[0];
#else
*this >> v.vers[0];
*this >> v.vers[1];
#endif
// no bytecount, backup and read version
if (!(v.cnt & kByteCountMask)) {
fBufCur -= sizeof(UInt_t);
v.cnt = 0;
}
*bcnt = (v.cnt & ~kByteCountMask);
*this >> version;
} else {
// not interested in byte count
*this >> version;
// if this is a byte count, then skip next short and read version
if (version & kByteCountVMask) {
*this >> version;
*this >> version;
}
}
if (cl && cl->GetClassVersion() != 0) {
if (version <= 0) {
UInt_t checksum = 0;
*this >> checksum;
version = R__FindStreamerInfoVersion(cl,checksum);
} else if (version == 1 && fParent && ((TFile*)fParent)->GetVersion()<40000 ) {
// We could have a file created using a Foreign class before
// the introduction of the CheckSum. We need to check
if ((!cl->IsLoaded() || cl->IsForeign()) &&
cl->GetStreamerInfos()->GetLast()>1 ) {
const TList *list = ((TFile*)fParent)->GetStreamerInfoCache();
const TStreamerInfo *local = (TStreamerInfo*)list->FindObject(cl->GetName());
if ( local ) {
UInt_t checksum = local->GetCheckSum();
version = R__FindStreamerInfoVersion(cl,checksum);
}
else {
Error("ReadVersion", "Class %s not known to file %s.",
cl->GetName(), ((TFile*)fParent)->GetName());
version = 0;
}
}
}
}
return version;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
UInt_t TBuffer::WriteVersion(const TClass *cl, Bool_t useBcnt)
{
// Write class version to I/O buffer.
UInt_t cntpos = 0;
if (useBcnt) {
// reserve space for leading byte count
cntpos = UInt_t(fBufCur-fBuffer);
fBufCur += sizeof(UInt_t);
}
Version_t version = cl->GetClassVersion();
if (version > kMaxVersion) {
Error("WriteVersion", "version number cannot be larger than %hd)",
kMaxVersion);
version = kMaxVersion;
}
if (cl->IsForeign() && version<=1) {
*this << Version_t(0);
*this << cl->GetCheckSum();
} else {
*this <<version;
}
// return position where to store possible byte count
return cntpos;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
UInt_t TBuffer::WriteVersionMemberWise(const TClass *cl, Bool_t useBcnt)
{
// Write class version to I/O buffer after setting the kStreamedMemberWise
// bit in the version number.
UInt_t cntpos = 0;
if (useBcnt) {
// reserve space for leading byte count
cntpos = UInt_t(fBufCur-fBuffer);
fBufCur += sizeof(UInt_t);
}
Version_t version = cl->GetClassVersion();
if (version > kMaxVersion) {
Error("WriteVersionMemberWise", "version number cannot be larger than %hd)",
kMaxVersion);
version = kMaxVersion;
}
if (cl->IsForeign() && version<=1) {
Error("WriteVersionMemberWise", "Member-wise streaming of foreign collection not yet implemented!");
*this << Version_t(0);
*this << cl->GetCheckSum();
} else {
version |= kStreamedMemberWise;
*this <<version;
}
// return position where to store possible byte count
return cntpos;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::SetReadMode()
{
// Set buffer in read mode.
fMode = kRead;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::SetWriteMode()
{
// Set buffer in write mode.
fMode = kWrite;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::StreamObject(void *obj, const type_info &typeinfo)
{
// Stream an object given its C++ typeinfo information.
TClass *cl = gROOT->GetClass(typeinfo);
cl->Streamer(obj, *this);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::StreamObject(void *obj, const char *className)
{
// Stream an object given the name of its actual class.
TClass *cl = gROOT->GetClass(className);
cl->Streamer(obj, *this);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::StreamObject(void *obj, const TClass *cl)
{
// Stream an object given a pointer to its actual class.
((TClass*)cl)->Streamer(obj, *this);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
TClass *TBuffer::GetClass(const type_info &typeinfo)
{
// Forward to TROOT::GetClass
return gROOT->GetClass(typeinfo);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
TClass *TBuffer::GetClass(const char *className)
{
// Forward to TROOT::GetClass
return gROOT->GetClass(className);
}
//---- Static functions --------------------------------------------------------
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::SetGlobalReadParam(Int_t mapsize)
{
// Set the initial size of the map used to store object and class
// references during reading. The default size is kMapSize=503.
// Increasing the default has the benefit that when reading many
// small objects the array does not need to be resized too often
// (the system is always dynamic, even with the default everything
// will work, only the initial resizing will cost some time).
// Per TBuffer object this option can be changed using SetReadParam().
fgMapSize = mapsize;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::SetGlobalWriteParam(Int_t mapsize)
{
// Set the initial size of the hashtable used to store object and class
// references during writing. The default size is kMapSize=503.
// Increasing the default has the benefit that when writing many
// small objects the hashtable does not get too many collisions
// (the system is always dynamic, even with the default everything
// will work, only a large number of collisions will cost performance).
// For optimal performance hashsize should always be a prime.
// Per TBuffer object this option can be changed using SetWriteParam().
fgMapSize = mapsize;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TBuffer::GetGlobalReadParam()
{
// Get default read map size.
return fgMapSize;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TBuffer::GetGlobalWriteParam()
{
// Get default write map size.
return fgMapSize;
}
ROOT page - Class index - Class Hierarchy - Top of the page
This page has been automatically generated. If you have any comments or suggestions about the page layout send a mail to ROOT support, or contact the developers with any questions or problems regarding ROOT.
 */
//
if (ele && ele->GetFactor() != 0) {
Double_t x = d[0];
Double_t xmin = ele->GetXmin();
Double_t xmax = ele->GetXmax();
if (x < xmin) x = xmin;
if (x > xmax) x = xmax;
UInt_t aint = UInt_t(0.5+ele->GetFactor()*(x-xmin)); *this << aint;
} else {
Float_t afloat = (Float_t)d[0]; *this << afloat;
}
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TBuffer::ReadArray(Bool_t *&b)
{
// Read array of bools from the I/O buffer. Returns the number of
// bools read. If argument is a 0 pointer then space will be
// allocated for the array.
Assert(IsReading());
Int_t n;
*this >> n;
if (n <= 0 || n > fBufSize) return 0;
if (!b) b = new Bool_t[n];
if (sizeof(Bool_t) > 1) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
frombuf(fBufCur, &b[i]);
} else {
Int_t l = sizeof(Bool_t)*n;
memcpy(b, fBufCur, l);
fBufCur += l;
}
return n;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TBuffer::ReadArray(Char_t *&c)
{
// Read array of characters from the I/O buffer. Returns the number of
// characters read. If argument is a 0 pointer then space will be
// allocated for the array.
Assert(IsReading());
Int_t n;
*this >> n;
Int_t l = sizeof(Char_t)*n;
if (l <= 0 || l > fBufSize) return 0;
if (!c) c = new Char_t[n];
memcpy(c, fBufCur, l);
fBufCur += l;
return n;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TBuffer::ReadArray(Short_t *&h)
{
// Read array of shorts from the I/O buffer. Returns the number of shorts
// read. If argument is a 0 pointer then space will be allocated for the
// array.
Assert(IsReading());
Int_t n;
*this >> n;
Int_t l = sizeof(Short_t)*n;
if (l <= 0 || l > fBufSize) return 0;
if (!h) h = new Short_t[n];
#ifdef R__BYTESWAP
# ifdef USE_BSWAPCPY
bswapcpy16(h, fBufCur, n);
fBufCur += l;
# else
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
frombuf(fBufCur, &h[i]);
# endif
#else
memcpy(h, fBufCur, l);
fBufCur += l;
#endif
return n;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TBuffer::ReadArray(Int_t *&ii)
{
// Read array of ints from the I/O buffer. Returns the number of ints
// read. If argument is a 0 pointer then space will be allocated for the
// array.
Assert(IsReading());
Int_t n;
*this >> n;
Int_t l = sizeof(Int_t)*n;
if (l <= 0 || l > fBufSize) return 0;
if (!ii) ii = new Int_t[n];
#ifdef R__BYTESWAP
# ifdef USE_BSWAPCPY
bswapcpy32(ii, fBufCur, n);
fBufCur += l;
# else
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
frombuf(fBufCur, &ii[i]);
# endif
#else
memcpy(ii, fBufCur, l);
fBufCur += l;
#endif
return n;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TBuffer::ReadArray(Long_t *&ll)
{
// Read array of longs from the I/O buffer. Returns the number of longs
// read. If argument is a 0 pointer then space will be allocated for the
// array.
Assert(IsReading());
Int_t n;
*this >> n;
Int_t l = sizeof(Long_t)*n;
if (l <= 0 || l > fBufSize) return 0;
if (!ll) ll = new Long_t[n];
TFile *file = (TFile*)fParent;
if (file && file->GetVersion() < 30006) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) frombufOld(fBufCur, &ll[i]);
} else {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) frombuf(fBufCur, &ll[i]);
}
return n;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TBuffer::ReadArray(Long64_t *&ll)
{
// Read array of long longs from the I/O buffer. Returns the number of
// long longs read. If argument is a 0 pointer then space will be
// allocated for the array.
Assert(IsReading());
Int_t n;
*this >> n;
Int_t l = sizeof(Long64_t)*n;
if (l <= 0 || l > fBufSize) return 0;
if (!ll) ll = new Long64_t[n];
#ifdef R__BYTESWAP
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
frombuf(fBufCur, &ll[i]);
#else
memcpy(ll, fBufCur, l);
fBufCur += l;
#endif
return n;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TBuffer::ReadArray(Float_t *&f)
{
// Read array of floats from the I/O buffer. Returns the number of floats
// read. If argument is a 0 pointer then space will be allocated for the
// array.
Assert(IsReading());
Int_t n;
*this >> n;
Int_t l = sizeof(Float_t)*n;
if (l <= 0 || l > fBufSize) return 0;
if (!f) f = new Float_t[n];
#ifdef R__BYTESWAP
# ifdef USE_BSWAPCPY
bswapcpy32(f, fBufCur, n);
fBufCur += l;
# else
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
frombuf(fBufCur, &f[i]);
# endif
#else
memcpy(f, fBufCur, l);
fBufCur += l;
#endif
return n;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TBuffer::ReadArray(Double_t *&d)
{
// Read array of doubles from the I/O buffer. Returns the number of doubles
// read. If argument is a 0 pointer then space will be allocated for the
// array.
Assert(IsReading());
Int_t n;
*this >> n;
Int_t l = sizeof(Double_t)*n;
if (l <= 0 || l > fBufSize) return 0;
if (!d) d = new Double_t[n];
#ifdef R__BYTESWAP
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
frombuf(fBufCur, &d[i]);
#else
memcpy(d, fBufCur, l);
fBufCur += l;
#endif
return n;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TBuffer::ReadArrayDouble32(Double_t *&d, TStreamerElement *ele)
{
// Read array of doubles (written as float) from the I/O buffer.
// Returns the number of doubles read.
// If argument is a 0 pointer then space will be allocated for the array.
// see comments about Double32_t encoding at TBuffer::WriteDouble32
Assert(IsReading());
Int_t n;
*this >> n;
if (n <= 0 || 4*n > fBufSize) return 0;
if (!d) d = new Double_t[n];
ReadFastArrayDouble32(d,n,ele);
return n;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TBuffer::ReadStaticArray(Bool_t *b)
{
// Read array of bools from the I/O buffer. Returns the number of bools
// read.
Assert(IsReading());
Int_t n;
*this >> n;
if (n <= 0 || n > fBufSize) return 0;
if (!b) return 0;
if (sizeof(Bool_t) > 1) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
frombuf(fBufCur, &b[i]);
} else {
Int_t l = sizeof(Bool_t)*n;
memcpy(b, fBufCur, l);
fBufCur += l;
}
return n;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TBuffer::ReadStaticArray(Char_t *c)
{
// Read array of characters from the I/O buffer. Returns the number of
// characters read.
Assert(IsReading());
Int_t n;
*this >> n;
Int_t l = sizeof(Char_t)*n;
if (l <= 0 || l > fBufSize) return 0;
if (!c) return 0;
memcpy(c, fBufCur, l);
fBufCur += l;
return n;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TBuffer::ReadStaticArray(Short_t *h)
{
// Read array of shorts from the I/O buffer. Returns the number of shorts
// read.
Assert(IsReading());
Int_t n;
*this >> n;
Int_t l = sizeof(Short_t)*n;
if (l <= 0 || l > fBufSize) return 0;
if (!h) return 0;
#ifdef R__BYTESWAP
# ifdef USE_BSWAPCPY
bswapcpy16(h, fBufCur, n);
fBufCur += l;
# else
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
frombuf(fBufCur, &h[i]);
# endif
#else
memcpy(h, fBufCur, l);
fBufCur += l;
#endif
return n;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TBuffer::ReadStaticArray(Int_t *ii)
{
// Read array of ints from the I/O buffer. Returns the number of ints
// read.
Assert(IsReading());
Int_t n;
*this >> n;
Int_t l = sizeof(Int_t)*n;
if (l <= 0 || l > fBufSize) return 0;
if (!ii) return 0;
#ifdef R__BYTESWAP
# ifdef USE_BSWAPCPY
bswapcpy32(ii, fBufCur, n);
fBufCur += sizeof(Int_t)*n;
# else
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
frombuf(fBufCur, &ii[i]);
# endif
#else
memcpy(ii, fBufCur, l);
fBufCur += l;
#endif
return n;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TBuffer::ReadStaticArray(Long_t *ll)
{
// Read array of longs from the I/O buffer. Returns the number of longs
// read.
Assert(IsReading());
Int_t n;
*this >> n;
Int_t l = sizeof(Long_t)*n;
if (l <= 0 || l > fBufSize) return 0;
if (!ll) return 0;
TFile *file = (TFile*)fParent;
if (file && file->GetVersion() < 30006) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) frombufOld(fBufCur, &ll[i]);
} else {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) frombuf(fBufCur, &ll[i]);
}
return n;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TBuffer::ReadStaticArray(Long64_t *ll)
{
// Read array of long longs from the I/O buffer. Returns the number of
// long longs read.
Assert(IsReading());
Int_t n;
*this >> n;
Int_t l = sizeof(Long64_t)*n;
if (l <= 0 || l > fBufSize) return 0;
if (!ll) return 0;
#ifdef R__BYTESWAP
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
frombuf(fBufCur, &ll[i]);
#else
memcpy(ll, fBufCur, l);
fBufCur += l;
#endif
return n;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TBuffer::ReadStaticArray(Float_t *f)
{
// Read array of floats from the I/O buffer. Returns the number of floats
// read.
Assert(IsReading());
Int_t n;
*this >> n;
Int_t l = sizeof(Float_t)*n;
if (n <= 0 || l > fBufSize) return 0;
if (!f) return 0;
#ifdef R__BYTESWAP
# ifdef USE_BSWAPCPY
bswapcpy32(f, fBufCur, n);
fBufCur += sizeof(Float_t)*n;
# else
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
frombuf(fBufCur, &f[i]);
# endif
#else
memcpy(f, fBufCur, l);
fBufCur += l;
#endif
return n;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TBuffer::ReadStaticArray(Double_t *d)
{
// Read array of doubles from the I/O buffer. Returns the number of doubles
// read.
Assert(IsReading());
Int_t n;
*this >> n;
Int_t l = sizeof(Double_t)*n;
if (n <= 0 || l > fBufSize) return 0;
if (!d) return 0;
#ifdef R__BYTESWAP
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
frombuf(fBufCur, &d[i]);
#else
memcpy(d, fBufCur, l);
fBufCur += l;
#endif
return n;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TBuffer::ReadStaticArrayDouble32(Double_t *d, TStreamerElement *ele)
{
// Read array of doubles (written as float) from the I/O buffer.
// Returns the number of doubles read.
// see comments about Double32_t encoding at TBuffer::WriteDouble32
Assert(IsReading());
Int_t n;
*this >> n;
if (n <= 0 || 4*n > fBufSize) return 0;
if (!d) return 0;
ReadFastArrayDouble32(d,n,ele);
return n;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::ReadFastArray(Bool_t *b, Int_t n)
{
// Read array of n bools from the I/O buffer.
if (n <= 0 || n > fBufSize) return;
if (sizeof(Bool_t) > 1) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
frombuf(fBufCur, &b[i]);
} else {
Int_t l = sizeof(Bool_t)*n;
memcpy(b, fBufCur, l);
fBufCur += l;
}
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::ReadFastArray(Char_t *c, Int_t n)
{
// Read array of n characters from the I/O buffer.
if (n <= 0 || n > fBufSize) return;
Int_t l = sizeof(Char_t)*n;
memcpy(c, fBufCur, l);
fBufCur += l;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::ReadFastArrayString(Char_t *c, Int_t n)
{
// Read array of n characters from the I/O buffer.
Int_t len;
UChar_t lenchar;
*this >> lenchar;
if (lenchar < 255) {
len = lenchar;
} else {
*this >> len;
}
if (len) {
if (len >= n) len = n-1;
if (n <= 0 || n > fBufSize) return;
Int_t l = sizeof(Char_t)*n;
memcpy(c, fBufCur, l);
fBufCur += l;
c[len] = 0;
} else {
c[0] = 0;
}
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::ReadFastArray(Short_t *h, Int_t n)
{
// Read array of n shorts from the I/O buffer.
Int_t l = sizeof(Short_t)*n;
if (n <= 0 || l > fBufSize) return;
#ifdef R__BYTESWAP
# ifdef USE_BSWAPCPY
bswapcpy16(h, fBufCur, n);
fBufCur += sizeof(Short_t)*n;
# else
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
frombuf(fBufCur, &h[i]);
# endif
#else
memcpy(h, fBufCur, l);
fBufCur += l;
#endif
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::ReadFastArray(Int_t *ii, Int_t n)
{
// Read array of n ints from the I/O buffer.
Int_t l = sizeof(Int_t)*n;
if (l <= 0 || l > fBufSize) return;
#ifdef R__BYTESWAP
# ifdef USE_BSWAPCPY
bswapcpy32(ii, fBufCur, n);
fBufCur += sizeof(Int_t)*n;
# else
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
frombuf(fBufCur, &ii[i]);
# endif
#else
memcpy(ii, fBufCur, l);
fBufCur += l;
#endif
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::ReadFastArray(Long_t *ll, Int_t n)
{
// Read array of n longs from the I/O buffer.
Int_t l = sizeof(Long_t)*n;
if (l <= 0 || l > fBufSize) return;
TFile *file = (TFile*)fParent;
if (file && file->GetVersion() < 30006) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) frombufOld(fBufCur, &ll[i]);
} else {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) frombuf(fBufCur, &ll[i]);
}
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::ReadFastArray(Long64_t *ll, Int_t n)
{
// Read array of n long longs from the I/O buffer.
Int_t l = sizeof(Long64_t)*n;
if (l <= 0 || l > fBufSize) return;
#ifdef R__BYTESWAP
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
frombuf(fBufCur, &ll[i]);
#else
memcpy(ll, fBufCur, l);
fBufCur += l;
#endif
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::ReadFastArray(Float_t *f, Int_t n)
{
// Read array of n floats from the I/O buffer.
Int_t l = sizeof(Float_t)*n;
if (l <= 0 || l > fBufSize) return;
#ifdef R__BYTESWAP
# ifdef USE_BSWAPCPY
bswapcpy32(f, fBufCur, n);
fBufCur += sizeof(Float_t)*n;
# else
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
frombuf(fBufCur, &f[i]);
# endif
#else
memcpy(f, fBufCur, l);
fBufCur += l;
#endif
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::ReadFastArray(Double_t *d, Int_t n)
{
// Read array of n doubles from the I/O buffer.
Int_t l = sizeof(Double_t)*n;
if (l <= 0 || l > fBufSize) return;
#ifdef R__BYTESWAP
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
frombuf(fBufCur, &d[i]);
#else
memcpy(d, fBufCur, l);
fBufCur += l;
#endif
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::ReadFastArrayDouble32(Double_t *d, Int_t n, TStreamerElement *ele)
{
// Read array of n doubles (written as float) from the I/O buffer.
// see comments about Double32_t encoding at TBuffer::WriteDouble32
if (n <= 0 || 4*n > fBufSize) return;
if (ele && ele->GetFactor() != 0) {
Double_t xmin = ele->GetXmin();
Double_t factor = ele->GetFactor();
for (int j=0;j < n; j++) {
UInt_t aint; *this >> aint; d[j] = (Double_t)(aint/factor + xmin);
}
} else {
Float_t afloat;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
frombuf(fBufCur, &afloat);
d[i]=afloat;
}
}
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::ReadFastArray(void *start, const TClass *cl, Int_t n,
TMemberStreamer *streamer)
{
// Read an array of 'n' objects from the I/O buffer.
// Stores the objects read starting at the address 'start'.
// The objects in the array are assume to be of class 'cl'.
if (streamer) {
(*streamer)(*this,start,0);
return;
}
int objectSize = cl->Size();
char *obj = (char*)start;
char *end = obj + n*objectSize;
for(; obj<end; obj+=objectSize) ((TClass*)cl)->Streamer(obj,*this);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::ReadFastArray(void **start, const TClass *cl, Int_t n,
Bool_t isPreAlloc, TMemberStreamer *streamer)
{
// Read an array of 'n' objects from the I/O buffer.
// The objects read are stored starting at the address '*start'
// The objects in the array are assumed to be of class 'cl' or a derived class.
// 'mode' indicates whether the data member is marked with '->'
// if isPreAlloc is true (data member has a ->) we can assume that the pointer (*start)
// is never 0.
if (streamer) {
if (isPreAlloc) {
for (Int_t j=0;j<n;j++) {
if (!start[j]) start[j] = ((TClass*)cl)->New();
}
}
(*streamer)(*this,(void*)start,0);
return;
}
if (!isPreAlloc) {
for (Int_t j=0; j<n; j++){
//delete the object or collection
if (start[j] && TStreamerInfo::CanDelete()) ((TClass*)cl)->Destructor(start[j],kFALSE); // call delete and desctructor
start[j] = ReadObjectAny(cl);
}
} else { //case //-> in comment
for (Int_t j=0; j<n; j++){
if (!start[j]) start[j] = ((TClass*)cl)->New();
((TClass*)cl)->Streamer(start[j],*this);
}
}
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::WriteArray(const Bool_t *b, Int_t n)
{
// Write array of n bools into the I/O buffer.
Assert(IsWriting());
*this << n;
if (n <= 0) return;
Assert(b);
Int_t l = sizeof(UChar_t)*n;
if (fBufCur + l > fBufMax) Expand(TMath::Max(2*fBufSize, fBufSize+l));
if (sizeof(Bool_t) > 1) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
tobuf(fBufCur, b[i]);
} else {
memcpy(fBufCur, b, l);
fBufCur += l;
}
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::WriteArray(const Char_t *c, Int_t n)
{
// Write array of n characters into the I/O buffer.
Assert(IsWriting());
*this << n;
if (n <= 0) return;
Assert(c);
Int_t l = sizeof(Char_t)*n;
if (fBufCur + l > fBufMax) Expand(TMath::Max(2*fBufSize, fBufSize+l));
memcpy(fBufCur, c, l);
fBufCur += l;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::WriteArray(const Short_t *h, Int_t n)
{
// Write array of n shorts into the I/O buffer.
Assert(IsWriting());
*this << n;
if (n <= 0) return;
Assert(h);
Int_t l = sizeof(Short_t)*n;
if (fBufCur + l > fBufMax) Expand(TMath::Max(2*fBufSize, fBufSize+l));
#ifdef R__BYTESWAP
# ifdef USE_BSWAPCPY
bswapcpy16(fBufCur, h, n);
fBufCur += l;
# else
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
tobuf(fBufCur, h[i]);
# endif
#else
memcpy(fBufCur, h, l);
fBufCur += l;
#endif
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::WriteArray(const Int_t *ii, Int_t n)
{
// Write array of n ints into the I/O buffer.
Assert(IsWriting());
*this << n;
if (n <= 0) return;
Assert(ii);
Int_t l = sizeof(Int_t)*n;
if (fBufCur + l > fBufMax) Expand(TMath::Max(2*fBufSize, fBufSize+l));
#ifdef R__BYTESWAP
# ifdef USE_BSWAPCPY
bswapcpy32(fBufCur, ii, n);
fBufCur += l;
# else
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
tobuf(fBufCur, ii[i]);
# endif
#else
memcpy(fBufCur, ii, l);
fBufCur += l;
#endif
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::WriteArray(const Long_t *ll, Int_t n)
{
// Write array of n longs into the I/O buffer.
Assert(IsWriting());
*this << n;
if (n <= 0) return;
Assert(ll);
Int_t l = 8*n;
if (fBufCur + l > fBufMax) Expand(TMath::Max(2*fBufSize, fBufSize+l));
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) tobuf(fBufCur, ll[i]);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::WriteArray(const ULong_t *ll, Int_t n)
{
// Write array of n unsigned longs into the I/O buffer.
// This is an explicit case for unsigned longs since signed longs
// have a special tobuf().
Assert(IsWriting());
*this << n;
if (n <= 0) return;
Assert(ll);
Int_t l = 8*n;
if (fBufCur + l > fBufMax) Expand(TMath::Max(2*fBufSize, fBufSize+l));
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) tobuf(fBufCur, ll[i]);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::WriteArray(const Long64_t *ll, Int_t n)
{
// Write array of n long longs into the I/O buffer.
Assert(IsWriting());
*this << n;
if (n <= 0) return;
Assert(ll);
Int_t l = sizeof(Long64_t)*n;
if (fBufCur + l > fBufMax) Expand(TMath::Max(2*fBufSize, fBufSize+l));
#ifdef R__BYTESWAP
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
tobuf(fBufCur, ll[i]);
#else
memcpy(fBufCur, ll, l);
fBufCur += l;
#endif
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::WriteArray(const Float_t *f, Int_t n)
{
// Write array of n floats into the I/O buffer.
Assert(IsWriting());
*this << n;
if (n <= 0) return;
Assert(f);
Int_t l = sizeof(Float_t)*n;
if (fBufCur + l > fBufMax) Expand(TMath::Max(2*fBufSize, fBufSize+l));
#ifdef R__BYTESWAP
# ifdef USE_BSWAPCPY
bswapcpy32(fBufCur, f, n);
fBufCur += l;
# else
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
tobuf(fBufCur, f[i]);
# endif
#else
memcpy(fBufCur, f, l);
fBufCur += l;
#endif
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::WriteArray(const Double_t *d, Int_t n)
{
// Write array of n doubles into the I/O buffer.
Assert(IsWriting());
*this << n;
if (n <= 0) return;
Assert(d);
Int_t l = sizeof(Double_t)*n;
if (fBufCur + l > fBufMax) Expand(TMath::Max(2*fBufSize, fBufSize+l));
#ifdef R__BYTESWAP
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
tobuf(fBufCur, d[i]);
#else
memcpy(fBufCur, d, l);
fBufCur += l;
#endif
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::WriteArrayDouble32(const Double_t *d, Int_t n, TStreamerElement *ele)
{
// Write array of n doubles (as float) into the I/O buffer.
// see comments about Double32_t encoding at TBuffer::WriteDouble32
Assert(IsWriting());
*this << n;
if (n <= 0) return;
Assert(d);
Int_t l = sizeof(Float_t)*n;
if (fBufCur + l > fBufMax) Expand(TMath::Max(2*fBufSize, fBufSize+l));
WriteFastArrayDouble32(d,n,ele);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::WriteFastArray(const Bool_t *b, Int_t n)
{
// Write array of n bools into the I/O buffer.
if (n <= 0) return;
Int_t l = sizeof(UChar_t)*n;
if (fBufCur + l > fBufMax) Expand(TMath::Max(2*fBufSize, fBufSize+l));
if (sizeof(Bool_t) > 1) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
tobuf(fBufCur, b[i]);
} else {
memcpy(fBufCur, b, l);
fBufCur += l;
}
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::WriteFastArray(const Char_t *c, Int_t n)
{
// Write array of n characters into the I/O buffer.
if (n <= 0) return;
Int_t l = sizeof(Char_t)*n;
if (fBufCur + l > fBufMax) Expand(TMath::Max(2*fBufSize, fBufSize+l));
memcpy(fBufCur, c, l);
fBufCur += l;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::WriteFastArrayString(const Char_t *c, Int_t n)
{
// Write array of n characters into the I/O buffer.
if (n < 255) {
*this << (UChar_t)n;
} else {
*this << (UChar_t)255;
*this << n;
}
if (n <= 0) return;
Int_t l = sizeof(Char_t)*n;
if (fBufCur + l > fBufMax) Expand(TMath::Max(2*fBufSize, fBufSize+l));
memcpy(fBufCur, c, l);
fBufCur += l;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::WriteFastArray(const Short_t *h, Int_t n)
{
// Write array of n shorts into the I/O buffer.
if (n <= 0) return;
Int_t l = sizeof(Short_t)*n;
if (fBufCur + l > fBufMax) Expand(TMath::Max(2*fBufSize, fBufSize+l));
#ifdef R__BYTESWAP
# ifdef USE_BSWAPCPY
bswapcpy16(fBufCur, h, n);
fBufCur += l;
# else
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
tobuf(fBufCur, h[i]);
# endif
#else
memcpy(fBufCur, h, l);
fBufCur += l;
#endif
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::WriteFastArray(const Int_t *ii, Int_t n)
{
// Write array of n ints into the I/O buffer.
if (n <= 0) return;
Int_t l = sizeof(Int_t)*n;
if (fBufCur + l > fBufMax) Expand(TMath::Max(2*fBufSize, fBufSize+l));
#ifdef R__BYTESWAP
# ifdef USE_BSWAPCPY
bswapcpy32(fBufCur, ii, n);
fBufCur += l;
# else
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
tobuf(fBufCur, ii[i]);
# endif
#else
memcpy(fBufCur, ii, l);
fBufCur += l;
#endif
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::WriteFastArray(const Long_t *ll, Int_t n)
{
// Write array of n longs into the I/O buffer.
if (n <= 0) return;
Int_t l = 8*n;
if (fBufCur + l > fBufMax) Expand(TMath::Max(2*fBufSize, fBufSize+l));
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) tobuf(fBufCur, ll[i]);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::WriteFastArray(const ULong_t *ll, Int_t n)
{
// Write array of n unsigned longs into the I/O buffer.
// This is an explicit case for unsigned longs since signed longs
// have a special tobuf().
if (n <= 0) return;
Int_t l = 8*n;
if (fBufCur + l > fBufMax) Expand(TMath::Max(2*fBufSize, fBufSize+l));
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) tobuf(fBufCur, ll[i]);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::WriteFastArray(const Long64_t *ll, Int_t n)
{
// Write array of n long longs into the I/O buffer.
if (n <= 0) return;
Int_t l = sizeof(Long64_t)*n;
if (fBufCur + l > fBufMax) Expand(TMath::Max(2*fBufSize, fBufSize+l));
#ifdef R__BYTESWAP
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
tobuf(fBufCur, ll[i]);
#else
memcpy(fBufCur, ll, l);
fBufCur += l;
#endif
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::WriteFastArray(const Float_t *f, Int_t n)
{
// Write array of n floats into the I/O buffer.
if (n <= 0) return;
Int_t l = sizeof(Float_t)*n;
if (fBufCur + l > fBufMax) Expand(TMath::Max(2*fBufSize, fBufSize+l));
#ifdef R__BYTESWAP
# ifdef USE_BSWAPCPY
bswapcpy32(fBufCur, f, n);
fBufCur += l;
# else
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
tobuf(fBufCur, f[i]);
# endif
#else
memcpy(fBufCur, f, l);
fBufCur += l;
#endif
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::WriteFastArray(const Double_t *d, Int_t n)
{
// Write array of n doubles into the I/O buffer.
if (n <= 0) return;
Int_t l = sizeof(Double_t)*n;
if (fBufCur + l > fBufMax) Expand(TMath::Max(2*fBufSize, fBufSize+l));
#ifdef R__BYTESWAP
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
tobuf(fBufCur, d[i]);
#else
memcpy(fBufCur, d, l);
fBufCur += l;
#endif
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::WriteFastArrayDouble32(const Double_t *d, Int_t n, TStreamerElement *ele)
{
// Write array of n doubles (as float) into the I/O buffer.
// see comments about Double32_t encoding at TBuffer::WriteDouble32
if (n <= 0) return;
Int_t l = sizeof(Float_t)*n;
if (fBufCur + l > fBufMax) Expand(TMath::Max(2*fBufSize, fBufSize+l));
if (ele && ele->GetFactor()) {
Double_t factor = ele->GetFactor();
Double_t xmin = ele->GetXmin();
Double_t xmax = ele->GetXmax();
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
Double_t x = d[j];
if (x < xmin) x = xmin;
if (x > xmax) x = xmax;
UInt_t aint = UInt_t(0.5+factor*(x-xmin)); *this << aint;
}
} else {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
tobuf(fBufCur, Float_t(d[i]));
}
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::WriteFastArray(void *start, const TClass *cl, Int_t n,
TMemberStreamer *streamer)
{
// Write an array of object starting at the address 'start' and of length 'n'
// the objects in the array are assumed to be of class 'cl'
if (streamer) {
(*streamer)(*this, start, 0);
return;
}
char *obj = (char*)start;
if (!n) n=1;
int size = cl->Size();
for(Int_t j=0; j<n; j++,obj+=size) {
((TClass*)cl)->Streamer(obj,*this);
}
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TBuffer::WriteFastArray(void **start, const TClass *cl, Int_t n,
Bool_t isPreAlloc, TMemberStreamer *streamer)
{
// Write an array of object starting at the address '*start' and of length 'n'
// the objects in the array are of class 'cl'
// 'isPreAlloc' indicates whether the data member is marked with '->'
// Return:
// 0: success
// 2: truncated success (i.e actual class is missing. Only ptrClass saved.)
// if isPreAlloc is true (data member has a ->) we can assume that the pointer
// is never 0.
if (streamer) {
(*streamer)(*this,(void*)start,0);
return 0;
}
int strInfo = 0;
Int_t res = 0;
if (!isPreAlloc) {
for (Int_t j=0;j<n;j++) {
//must write StreamerInfo if pointer is null
if (!strInfo && !start[j] ) ((TClass*)cl)->GetStreamerInfo()->ForceWriteInfo((TFile *)GetParent());
strInfo = 2003;
res |= WriteObjectAny(start[j],cl);
}
} else { //case //-> in comment
for (Int_t j=0;j<n;j++) {
if (!start[j]) start[j] = ((TClass*)cl)->New();
((TClass*)cl)->Streamer(start[j],*this);
}
}
return res;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
TObject *TBuffer::ReadObject(const TClass * /*clReq*/)
{
// Read object from I/O buffer. clReq is NOT used.
// The value returned is the address of the actual start in memory of
// the object. Note that if the actual class of the object does not
// inherit first from TObject, the type of the pointer is NOT 'TObject*'.
// [More accurately, the class needs to start with the TObject part, for
// the pointer to be a real TOject*].
// We recommend using ReadObjectAny instead of ReadObject
return (TObject*) ReadObjectAny(0);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::SkipObjectAny()
{
// Skip any kind of object from buffer
UInt_t start, count;
ReadVersion(&start, &count);
SetBufferOffset(start+count+sizeof(UInt_t));
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void *TBuffer::ReadObjectAny(const TClass *clCast)
{
// Read object from I/O buffer.
// A typical use for this function is:
// MyClass *ptr = (MyClass*)b.ReadObjectAny(MyClass::Class());
// I.e. clCast should point to a TClass object describing the class pointed
// to by your pointer.
// In case of multiple inheritance, the return value might not be the
// real beginning of the object in memory. You will need to use a
// dynamic_cast later if you need to retrieve it.
Assert(IsReading());
// make sure fMap is initialized
InitMap();
// before reading object save start position
UInt_t startpos = UInt_t(fBufCur-fBuffer);
// attempt to load next object as TClass clCast
UInt_t tag; // either tag or byte count
TClass *clRef = ReadClass(clCast, &tag);
Int_t baseOffset = 0;
if (clRef && (clRef!=(TClass*)(-1)) && clCast) {
//baseOffset will be -1 if clRef does not inherit from clCast.
baseOffset = clRef->GetBaseClassOffset(clCast);
if (baseOffset == -1) {
Error("ReadObject", "got object of wrong class! requested %s but got %s",
clCast->GetName(), clRef->GetName());
CheckByteCount(startpos, tag, (TClass*)0); // avoid mis-leading byte count error message
return 0; // We better return at this point
}
if (clCast->GetClassInfo() && !clRef->GetClassInfo()) {
//we cannot mix a compiled class with an emulated class in the inheritance
Error("ReadObject", "trying to read an emulated class (%s) to store in a compiled pointer (%s)",
clRef->GetName(),clCast->GetName());
CheckByteCount(startpos, tag, (TClass*)0); // avoid mis-leading byte count error message
return 0;
}
}
// check if object has not already been read
// (this can only happen when called via CheckObject())
char *obj;
if (fVersion > 0) {
obj = (char *) fMap->GetValue(startpos+kMapOffset);
if (obj == (void*) -1) obj = 0;
if (obj) {
CheckByteCount(startpos, tag, (TClass*)0);
return (obj+baseOffset);
}
}
// unknown class, skip to next object and return 0 obj
if (clRef == (TClass*) -1) {
if (fBufCur >= fBufMax) return 0;
if (fVersion > 0)
MapObject((TObject*) -1, startpos+kMapOffset);
else
MapObject((void*)0, 0, fMapCount);
CheckByteCount(startpos, tag, (TClass*)0);
return 0;
}
if (!clRef) {
// got a reference to an already read object
if (fVersion > 0) {
tag += fDisplacement;
tag = CheckObject(tag, clCast);
} else {
if (tag > (UInt_t)fMap->GetSize()) {
Error("ReadObject", "object tag too large, I/O buffer corrupted");
return 0;
// exception
}
}
obj = (char *) fMap->GetValue(tag);
clRef = (TClass*) fClassMap->GetValue(tag);
if (clRef && (clRef!=(TClass*)(-1)) && clCast) {
//baseOffset will be -1 if clRef does not inherit from clCast.
baseOffset = clRef->GetBaseClassOffset(clCast);
if (baseOffset == -1) {
Error("ReadObject", "Got object of wrong class (Got %s while expecting %s)",
clRef->GetName(),clCast->GetName());
// exception
baseOffset = 0;
}
}
// There used to be a warning printed here when:
// obj && isTObject && !((TObject*)obj)->IsA()->InheritsFrom(clReq)
// however isTObject was based on clReq (now clCast).
// If the test was to fail, then it is as likely that the object is not a TObject
// and then we have a potential core dump.
// At this point (missing clRef), we do NOT have enough information to really
// answer the question: is the object read of the type I requested.
} else {
// allocate a new object based on the class found
obj = (char *)clRef->New();
if (!obj) {
Error("ReadObject", "could not create object of class %s",
clRef->GetName());
// exception
return 0;
}
// add to fMap before reading rest of object
if (fVersion > 0)
MapObject(obj, clRef, startpos+kMapOffset);
else
MapObject(obj, clRef, fMapCount);
// let the object read itself
clRef->Streamer(obj, *this);
CheckByteCount(startpos, tag, clRef);
}
return obj+baseOffset;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::WriteObject(const TObject *obj)
{
// Write object to I/O buffer.
WriteObjectAny(obj, TObject::Class());
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::WriteObject(const void *actualObjectStart, const TClass *actualClass)
{
// Write object to I/O buffer.
// This function assumes that the value of 'actualObjectStart' is the actual start of
// the object of class 'actualClass'
Assert(IsWriting());
// make sure fMap is initialized
InitMap();
ULong_t idx;
if (!actualObjectStart) {
// save kNullTag to represent NULL pointer
*this << kNullTag;
} else if ((idx = (ULong_t)fMap->GetValue(Void_Hash(actualObjectStart), (Long_t)actualObjectStart)) != 0) {
// truncation is OK the value we did put in the map is an 30-bit offset
// and not a pointer
UInt_t objIdx = UInt_t(idx);
// save index of already stored object
*this << objIdx;
} else {
// A warning to let the user know it will need to change the class code
// to be able to read this back.
if (actualClass->HasDefaultConstructor() == 0) {
Warning("WriteObjectAny", "since %s had no public constructor\n"
"\twhich can be called without argument, objects of this class\n"
"\tcan not be read with the current library. You would need to\n"
"\tadd a default constructor before attempting to read it.",
actualClass->GetName());
}
// reserve space for leading byte count
UInt_t cntpos = UInt_t(fBufCur-fBuffer);
fBufCur += sizeof(UInt_t);
// write class of object first
WriteClass(actualClass);
// add to map before writing rest of object (to handle self reference)
// (+kMapOffset so it's != kNullTag)
MapObject(actualObjectStart, actualClass, cntpos+kMapOffset);
((TClass*)actualClass)->Streamer((void*)actualObjectStart,*this);
// write byte count
SetByteCount(cntpos);
}
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TBuffer::WriteObjectAny(const void *obj, const TClass *ptrClass)
{
// Write object to I/O buffer.
// This function assumes that the value in 'obj' is the value stored in
// a pointer to a "ptrClass". The actual type of the object pointed to
// can be any class derived from "ptrClass".
// Return:
// 0: failure
// 1: success
// 2: truncated success (i.e actual class is missing. Only ptrClass saved.)
if (!obj) {
WriteObject(0, 0);
return 1;
}
if (!ptrClass) {
Error("WriteObjectAny", "ptrClass argument may not be 0");
return 0;
}
TClass *clActual = ptrClass->GetActualClass(obj);
if (clActual) {
const char *temp = (const char*) obj;
// clActual->GetStreamerInfo();
Int_t offset = (ptrClass != clActual) ?
clActual->GetBaseClassOffset(ptrClass) : 0;
temp -= offset;
WriteObject(temp, clActual);
return 1;
} else {
WriteObject(obj, ptrClass);
return 2;
}
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
TClass *TBuffer::ReadClass(const TClass *clReq, UInt_t *objTag)
{
// Read class definition from I/O buffer. clReq can be used to cross check
// if the actually read object is of the requested class. objTag is
// set in case the object is a reference to an already read object.
Assert(IsReading());
// read byte count and/or tag (older files don't have byte count)
TClass *cl;
if (fBufCur < fBuffer || fBufCur > fBufMax) {
fBufCur = fBufMax;
cl = (TClass*)-1;
return cl;
}
UInt_t bcnt, tag, startpos = 0;
*this >> bcnt;
if (!(bcnt & kByteCountMask) || bcnt == kNewClassTag) {
tag = bcnt;
bcnt = 0;
} else {
fVersion = 1;
startpos = UInt_t(fBufCur-fBuffer);
*this >> tag;
}
// in case tag is object tag return tag
if (!(tag & kClassMask)) {
if (objTag) *objTag = tag;
return 0;
}
if (tag == kNewClassTag) {
// got a new class description followed by a new object
// (class can be 0 if class dictionary is not found, in that
// case object of this class must be skipped)
cl = TClass::Load(*this);
// add class to fMap for later reference
if (fVersion > 0) {
// check if class was already read
TClass *cl1 = (TClass *)fMap->GetValue(startpos+kMapOffset);
if (cl1 != cl)
MapObject(cl ? cl : (TObject*) -1, startpos+kMapOffset);
} else
MapObject(cl, fMapCount);
} else {
// got a tag to an already seen class
UInt_t clTag = (tag & ~kClassMask);
if (fVersion > 0) {
clTag += fDisplacement;
clTag = CheckObject(clTag, clReq, kTRUE);
} else {
if (clTag == 0 || clTag > (UInt_t)fMap->GetSize()) {
Error("ReadClass", "illegal class tag=%d (0<tag<=%d), I/O buffer corrupted",
clTag, fMap->GetSize());
// exception
}
}
// class can be 0 if dictionary was not found
cl = (TClass *)fMap->GetValue(clTag);
}
if (cl && clReq && !cl->InheritsFrom(clReq)) {
Error("ReadClass", "got wrong class: %s", cl->GetName());
// exception
}
// return bytecount in objTag
if (objTag) *objTag = (bcnt & ~kByteCountMask);
// case of unknown class
if (!cl) cl = (TClass*)-1;
return cl;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::WriteClass(const TClass *cl)
{
// Write class description to I/O buffer.
Assert(IsWriting());
ULong_t idx;
if ((idx = (ULong_t)fMap->GetValue(((TObject *)cl)->TObject::Hash(), (Long_t)cl)) != 0) {
// truncation is OK the value we did put in the map is an 30-bit offset
// and not a pointer
UInt_t clIdx = UInt_t(idx);
// save index of already stored class
*this << (clIdx | kClassMask);
} else {
// offset in buffer where class info is written
UInt_t offset = UInt_t(fBufCur-fBuffer);
// save new class tag
*this << kNewClassTag;
// write class name
cl->Store(*this);
// store new class reference in fMap (+kMapOffset so it's != kNullTag)
MapObject(cl, offset+kMapOffset);
}
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
static Version_t R__FindStreamerInfoVersion(const TClass *cl, UInt_t checksum)
{
//find the version number in the StreamerInfos corresponding to checksum
Version_t version = 0;
Int_t ninfos = cl->GetStreamerInfos()->GetEntriesFast();
for (Int_t i=1;i<ninfos;i++) {
// TClass::fStreamerInfos has a lower bound not equal to 0,
// so we should use At and not use UncheckedAt
TStreamerInfo *info = (TStreamerInfo*)cl->GetStreamerInfos()->At(i);
if (!info) continue;
if (info->GetCheckSum() == checksum) {
version = i;
//printf("ReadVersion, setting version=%d\n",version);
break;
}
}
return version;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Version_t TBuffer::ReadVersion(UInt_t *startpos, UInt_t *bcnt, const TClass *cl)
{
// Read class version from I/O buffer.
Version_t version;
if (startpos && bcnt) {
// before reading object save start position
*startpos = UInt_t(fBufCur-fBuffer);
// read byte count (older files don't have byte count)
// byte count is packed in two individual shorts, this to be
// backward compatible with old files that have at this location
// only a single short (i.e. the version)
union {
UInt_t cnt;
Version_t vers[2];
} v;
#ifdef R__BYTESWAP
*this >> v.vers[1];
*this >> v.vers[0];
#else
*this >> v.vers[0];
*this >> v.vers[1];
#endif
// no bytecount, backup and read version
if (!(v.cnt & kByteCountMask)) {
fBufCur -= sizeof(UInt_t);
v.cnt = 0;
}
*bcnt = (v.cnt & ~kByteCountMask);
*this >> version;
} else {
// not interested in byte count
*this >> version;
// if this is a byte count, then skip next short and read version
if (version & kByteCountVMask) {
*this >> version;
*this >> version;
}
}
if (cl && cl->GetClassVersion() != 0) {
if (version <= 0) {
UInt_t checksum = 0;
*this >> checksum;
version = R__FindStreamerInfoVersion(cl,checksum);
} else if (version == 1 && fParent && ((TFile*)fParent)->GetVersion()<40000 ) {
// We could have a file created using a Foreign class before
// the introduction of the CheckSum. We need to check
if ((!cl->IsLoaded() || cl->IsForeign()) &&
cl->GetStreamerInfos()->GetLast()>1 ) {
const TList *list = ((TFile*)fParent)->GetStreamerInfoCache();
const TStreamerInfo *local = (TStreamerInfo*)list->FindObject(cl->GetName());
if ( local ) {
UInt_t checksum = local->GetCheckSum();
version = R__FindStreamerInfoVersion(cl,checksum);
}
else {
Error("ReadVersion", "Class %s not known to file %s.",
cl->GetName(), ((TFile*)fParent)->GetName());
version = 0;
}
}
}
}
return version;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
UInt_t TBuffer::WriteVersion(const TClass *cl, Bool_t useBcnt)
{
// Write class version to I/O buffer.
UInt_t cntpos = 0;
if (useBcnt) {
// reserve space for leading byte count
cntpos = UInt_t(fBufCur-fBuffer);
fBufCur += sizeof(UInt_t);
}
Version_t version = cl->GetClassVersion();
if (version > kMaxVersion) {
Error("WriteVersion", "version number cannot be larger than %hd)",
kMaxVersion);
version = kMaxVersion;
}
if (cl->IsForeign() && version<=1) {
*this << Version_t(0);
*this << cl->GetCheckSum();
} else {
*this <<version;
}
// return position where to store possible byte count
return cntpos;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
UInt_t TBuffer::WriteVersionMemberWise(const TClass *cl, Bool_t useBcnt)
{
// Write class version to I/O buffer after setting the kStreamedMemberWise
// bit in the version number.
UInt_t cntpos = 0;
if (useBcnt) {
// reserve space for leading byte count
cntpos = UInt_t(fBufCur-fBuffer);
fBufCur += sizeof(UInt_t);
}
Version_t version = cl->GetClassVersion();
if (version > kMaxVersion) {
Error("WriteVersionMemberWise", "version number cannot be larger than %hd)",
kMaxVersion);
version = kMaxVersion;
}
if (cl->IsForeign() && version<=1) {
Error("WriteVersionMemberWise", "Member-wise streaming of foreign collection not yet implemented!");
*this << Version_t(0);
*this << cl->GetCheckSum();
} else {
version |= kStreamedMemberWise;
*this <<version;
}
// return position where to store possible byte count
return cntpos;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::SetReadMode()
{
// Set buffer in read mode.
fMode = kRead;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::SetWriteMode()
{
// Set buffer in write mode.
fMode = kWrite;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::StreamObject(void *obj, const type_info &typeinfo)
{
// Stream an object given its C++ typeinfo information.
TClass *cl = gROOT->GetClass(typeinfo);
cl->Streamer(obj, *this);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::StreamObject(void *obj, const char *className)
{
// Stream an object given the name of its actual class.
TClass *cl = gROOT->GetClass(className);
cl->Streamer(obj, *this);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::StreamObject(void *obj, const TClass *cl)
{
// Stream an object given a pointer to its actual class.
((TClass*)cl)->Streamer(obj, *this);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
TClass *TBuffer::GetClass(const type_info &typeinfo)
{
// Forward to TROOT::GetClass
return gROOT->GetClass(typeinfo);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
TClass *TBuffer::GetClass(const char *className)
{
// Forward to TROOT::GetClass
return gROOT->GetClass(className);
}
//---- Static functions --------------------------------------------------------
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::SetGlobalReadParam(Int_t mapsize)
{
// Set the initial size of the map used to store object and class
// references during reading. The default size is kMapSize=503.
// Increasing the default has the benefit that when reading many
// small objects the array does not need to be resized too often
// (the system is always dynamic, even with the default everything
// will work, only the initial resizing will cost some time).
// Per TBuffer object this option can be changed using SetReadParam().
fgMapSize = mapsize;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::SetGlobalWriteParam(Int_t mapsize)
{
// Set the initial size of the hashtable used to store object and class
// references during writing. The default size is kMapSize=503.
// Increasing the default has the benefit that when writing many
// small objects the hashtable does not get too many collisions
// (the system is always dynamic, even with the default everything
// will work, only a large number of collisions will cost performance).
// For optimal performance hashsize should always be a prime.
// Per TBuffer object this option can be changed using SetWriteParam().
fgMapSize = mapsize;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TBuffer::GetGlobalReadParam()
{
// Get default read map size.
return fgMapSize;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TBuffer::GetGlobalWriteParam()
{
// Get default write map size.
return fgMapSize;
}
*/
//
if (ele && ele->GetFactor() != 0) {
Double_t x = d[0];
Double_t xmin = ele->GetXmin();
Double_t xmax = ele->GetXmax();
if (x < xmin) x = xmin;
if (x > xmax) x = xmax;
UInt_t aint = UInt_t(0.5+ele->GetFactor()*(x-xmin)); *this << aint;
} else {
Float_t afloat = (Float_t)d[0]; *this << afloat;
}
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TBuffer::ReadArray(Bool_t *&b)
{
// Read array of bools from the I/O buffer. Returns the number of
// bools read. If argument is a 0 pointer then space will be
// allocated for the array.
Assert(IsReading());
Int_t n;
*this >> n;
if (n <= 0 || n > fBufSize) return 0;
if (!b) b = new Bool_t[n];
if (sizeof(Bool_t) > 1) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
frombuf(fBufCur, &b[i]);
} else {
Int_t l = sizeof(Bool_t)*n;
memcpy(b, fBufCur, l);
fBufCur += l;
}
return n;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TBuffer::ReadArray(Char_t *&c)
{
// Read array of characters from the I/O buffer. Returns the number of
// characters read. If argument is a 0 pointer then space will be
// allocated for the array.
Assert(IsReading());
Int_t n;
*this >> n;
Int_t l = sizeof(Char_t)*n;
if (l <= 0 || l > fBufSize) return 0;
if (!c) c = new Char_t[n];
memcpy(c, fBufCur, l);
fBufCur += l;
return n;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TBuffer::ReadArray(Short_t *&h)
{
// Read array of shorts from the I/O buffer. Returns the number of shorts
// read. If argument is a 0 pointer then space will be allocated for the
// array.
Assert(IsReading());
Int_t n;
*this >> n;
Int_t l = sizeof(Short_t)*n;
if (l <= 0 || l > fBufSize) return 0;
if (!h) h = new Short_t[n];
#ifdef R__BYTESWAP
# ifdef USE_BSWAPCPY
bswapcpy16(h, fBufCur, n);
fBufCur += l;
# else
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
frombuf(fBufCur, &h[i]);
# endif
#else
memcpy(h, fBufCur, l);
fBufCur += l;
#endif
return n;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TBuffer::ReadArray(Int_t *&ii)
{
// Read array of ints from the I/O buffer. Returns the number of ints
// read. If argument is a 0 pointer then space will be allocated for the
// array.
Assert(IsReading());
Int_t n;
*this >> n;
Int_t l = sizeof(Int_t)*n;
if (l <= 0 || l > fBufSize) return 0;
if (!ii) ii = new Int_t[n];
#ifdef R__BYTESWAP
# ifdef USE_BSWAPCPY
bswapcpy32(ii, fBufCur, n);
fBufCur += l;
# else
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
frombuf(fBufCur, &ii[i]);
# endif
#else
memcpy(ii, fBufCur, l);
fBufCur += l;
#endif
return n;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TBuffer::ReadArray(Long_t *&ll)
{
// Read array of longs from the I/O buffer. Returns the number of longs
// read. If argument is a 0 pointer then space will be allocated for the
// array.
Assert(IsReading());
Int_t n;
*this >> n;
Int_t l = sizeof(Long_t)*n;
if (l <= 0 || l > fBufSize) return 0;
if (!ll) ll = new Long_t[n];
TFile *file = (TFile*)fParent;
if (file && file->GetVersion() < 30006) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) frombufOld(fBufCur, &ll[i]);
} else {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) frombuf(fBufCur, &ll[i]);
}
return n;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TBuffer::ReadArray(Long64_t *&ll)
{
// Read array of long longs from the I/O buffer. Returns the number of
// long longs read. If argument is a 0 pointer then space will be
// allocated for the array.
Assert(IsReading());
Int_t n;
*this >> n;
Int_t l = sizeof(Long64_t)*n;
if (l <= 0 || l > fBufSize) return 0;
if (!ll) ll = new Long64_t[n];
#ifdef R__BYTESWAP
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
frombuf(fBufCur, &ll[i]);
#else
memcpy(ll, fBufCur, l);
fBufCur += l;
#endif
return n;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TBuffer::ReadArray(Float_t *&f)
{
// Read array of floats from the I/O buffer. Returns the number of floats
// read. If argument is a 0 pointer then space will be allocated for the
// array.
Assert(IsReading());
Int_t n;
*this >> n;
Int_t l = sizeof(Float_t)*n;
if (l <= 0 || l > fBufSize) return 0;
if (!f) f = new Float_t[n];
#ifdef R__BYTESWAP
# ifdef USE_BSWAPCPY
bswapcpy32(f, fBufCur, n);
fBufCur += l;
# else
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
frombuf(fBufCur, &f[i]);
# endif
#else
memcpy(f, fBufCur, l);
fBufCur += l;
#endif
return n;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TBuffer::ReadArray(Double_t *&d)
{
// Read array of doubles from the I/O buffer. Returns the number of doubles
// read. If argument is a 0 pointer then space will be allocated for the
// array.
Assert(IsReading());
Int_t n;
*this >> n;
Int_t l = sizeof(Double_t)*n;
if (l <= 0 || l > fBufSize) return 0;
if (!d) d = new Double_t[n];
#ifdef R__BYTESWAP
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
frombuf(fBufCur, &d[i]);
#else
memcpy(d, fBufCur, l);
fBufCur += l;
#endif
return n;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TBuffer::ReadArrayDouble32(Double_t *&d, TStreamerElement *ele)
{
// Read array of doubles (written as float) from the I/O buffer.
// Returns the number of doubles read.
// If argument is a 0 pointer then space will be allocated for the array.
// see comments about Double32_t encoding at TBuffer::WriteDouble32
Assert(IsReading());
Int_t n;
*this >> n;
if (n <= 0 || 4*n > fBufSize) return 0;
if (!d) d = new Double_t[n];
ReadFastArrayDouble32(d,n,ele);
return n;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TBuffer::ReadStaticArray(Bool_t *b)
{
// Read array of bools from the I/O buffer. Returns the number of bools
// read.
Assert(IsReading());
Int_t n;
*this >> n;
if (n <= 0 || n > fBufSize) return 0;
if (!b) return 0;
if (sizeof(Bool_t) > 1) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
frombuf(fBufCur, &b[i]);
} else {
Int_t l = sizeof(Bool_t)*n;
memcpy(b, fBufCur, l);
fBufCur += l;
}
return n;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TBuffer::ReadStaticArray(Char_t *c)
{
// Read array of characters from the I/O buffer. Returns the number of
// characters read.
Assert(IsReading());
Int_t n;
*this >> n;
Int_t l = sizeof(Char_t)*n;
if (l <= 0 || l > fBufSize) return 0;
if (!c) return 0;
memcpy(c, fBufCur, l);
fBufCur += l;
return n;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TBuffer::ReadStaticArray(Short_t *h)
{
// Read array of shorts from the I/O buffer. Returns the number of shorts
// read.
Assert(IsReading());
Int_t n;
*this >> n;
Int_t l = sizeof(Short_t)*n;
if (l <= 0 || l > fBufSize) return 0;
if (!h) return 0;
#ifdef R__BYTESWAP
# ifdef USE_BSWAPCPY
bswapcpy16(h, fBufCur, n);
fBufCur += l;
# else
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
frombuf(fBufCur, &h[i]);
# endif
#else
memcpy(h, fBufCur, l);
fBufCur += l;
#endif
return n;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TBuffer::ReadStaticArray(Int_t *ii)
{
// Read array of ints from the I/O buffer. Returns the number of ints
// read.
Assert(IsReading());
Int_t n;
*this >> n;
Int_t l = sizeof(Int_t)*n;
if (l <= 0 || l > fBufSize) return 0;
if (!ii) return 0;
#ifdef R__BYTESWAP
# ifdef USE_BSWAPCPY
bswapcpy32(ii, fBufCur, n);
fBufCur += sizeof(Int_t)*n;
# else
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
frombuf(fBufCur, &ii[i]);
# endif
#else
memcpy(ii, fBufCur, l);
fBufCur += l;
#endif
return n;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TBuffer::ReadStaticArray(Long_t *ll)
{
// Read array of longs from the I/O buffer. Returns the number of longs
// read.
Assert(IsReading());
Int_t n;
*this >> n;
Int_t l = sizeof(Long_t)*n;
if (l <= 0 || l > fBufSize) return 0;
if (!ll) return 0;
TFile *file = (TFile*)fParent;
if (file && file->GetVersion() < 30006) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) frombufOld(fBufCur, &ll[i]);
} else {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) frombuf(fBufCur, &ll[i]);
}
return n;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TBuffer::ReadStaticArray(Long64_t *ll)
{
// Read array of long longs from the I/O buffer. Returns the number of
// long longs read.
Assert(IsReading());
Int_t n;
*this >> n;
Int_t l = sizeof(Long64_t)*n;
if (l <= 0 || l > fBufSize) return 0;
if (!ll) return 0;
#ifdef R__BYTESWAP
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
frombuf(fBufCur, &ll[i]);
#else
memcpy(ll, fBufCur, l);
fBufCur += l;
#endif
return n;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TBuffer::ReadStaticArray(Float_t *f)
{
// Read array of floats from the I/O buffer. Returns the number of floats
// read.
Assert(IsReading());
Int_t n;
*this >> n;
Int_t l = sizeof(Float_t)*n;
if (n <= 0 || l > fBufSize) return 0;
if (!f) return 0;
#ifdef R__BYTESWAP
# ifdef USE_BSWAPCPY
bswapcpy32(f, fBufCur, n);
fBufCur += sizeof(Float_t)*n;
# else
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
frombuf(fBufCur, &f[i]);
# endif
#else
memcpy(f, fBufCur, l);
fBufCur += l;
#endif
return n;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TBuffer::ReadStaticArray(Double_t *d)
{
// Read array of doubles from the I/O buffer. Returns the number of doubles
// read.
Assert(IsReading());
Int_t n;
*this >> n;
Int_t l = sizeof(Double_t)*n;
if (n <= 0 || l > fBufSize) return 0;
if (!d) return 0;
#ifdef R__BYTESWAP
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
frombuf(fBufCur, &d[i]);
#else
memcpy(d, fBufCur, l);
fBufCur += l;
#endif
return n;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TBuffer::ReadStaticArrayDouble32(Double_t *d, TStreamerElement *ele)
{
// Read array of doubles (written as float) from the I/O buffer.
// Returns the number of doubles read.
// see comments about Double32_t encoding at TBuffer::WriteDouble32
Assert(IsReading());
Int_t n;
*this >> n;
if (n <= 0 || 4*n > fBufSize) return 0;
if (!d) return 0;
ReadFastArrayDouble32(d,n,ele);
return n;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::ReadFastArray(Bool_t *b, Int_t n)
{
// Read array of n bools from the I/O buffer.
if (n <= 0 || n > fBufSize) return;
if (sizeof(Bool_t) > 1) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
frombuf(fBufCur, &b[i]);
} else {
Int_t l = sizeof(Bool_t)*n;
memcpy(b, fBufCur, l);
fBufCur += l;
}
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::ReadFastArray(Char_t *c, Int_t n)
{
// Read array of n characters from the I/O buffer.
if (n <= 0 || n > fBufSize) return;
Int_t l = sizeof(Char_t)*n;
memcpy(c, fBufCur, l);
fBufCur += l;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::ReadFastArrayString(Char_t *c, Int_t n)
{
// Read array of n characters from the I/O buffer.
Int_t len;
UChar_t lenchar;
*this >> lenchar;
if (lenchar < 255) {
len = lenchar;
} else {
*this >> len;
}
if (len) {
if (len >= n) len = n-1;
if (n <= 0 || n > fBufSize) return;
Int_t l = sizeof(Char_t)*n;
memcpy(c, fBufCur, l);
fBufCur += l;
c[len] = 0;
} else {
c[0] = 0;
}
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::ReadFastArray(Short_t *h, Int_t n)
{
// Read array of n shorts from the I/O buffer.
Int_t l = sizeof(Short_t)*n;
if (n <= 0 || l > fBufSize) return;
#ifdef R__BYTESWAP
# ifdef USE_BSWAPCPY
bswapcpy16(h, fBufCur, n);
fBufCur += sizeof(Short_t)*n;
# else
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
frombuf(fBufCur, &h[i]);
# endif
#else
memcpy(h, fBufCur, l);
fBufCur += l;
#endif
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::ReadFastArray(Int_t *ii, Int_t n)
{
// Read array of n ints from the I/O buffer.
Int_t l = sizeof(Int_t)*n;
if (l <= 0 || l > fBufSize) return;
#ifdef R__BYTESWAP
# ifdef USE_BSWAPCPY
bswapcpy32(ii, fBufCur, n);
fBufCur += sizeof(Int_t)*n;
# else
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
frombuf(fBufCur, &ii[i]);
# endif
#else
memcpy(ii, fBufCur, l);
fBufCur += l;
#endif
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::ReadFastArray(Long_t *ll, Int_t n)
{
// Read array of n longs from the I/O buffer.
Int_t l = sizeof(Long_t)*n;
if (l <= 0 || l > fBufSize) return;
TFile *file = (TFile*)fParent;
if (file && file->GetVersion() < 30006) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) frombufOld(fBufCur, &ll[i]);
} else {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) frombuf(fBufCur, &ll[i]);
}
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::ReadFastArray(Long64_t *ll, Int_t n)
{
// Read array of n long longs from the I/O buffer.
Int_t l = sizeof(Long64_t)*n;
if (l <= 0 || l > fBufSize) return;
#ifdef R__BYTESWAP
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
frombuf(fBufCur, &ll[i]);
#else
memcpy(ll, fBufCur, l);
fBufCur += l;
#endif
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::ReadFastArray(Float_t *f, Int_t n)
{
// Read array of n floats from the I/O buffer.
Int_t l = sizeof(Float_t)*n;
if (l <= 0 || l > fBufSize) return;
#ifdef R__BYTESWAP
# ifdef USE_BSWAPCPY
bswapcpy32(f, fBufCur, n);
fBufCur += sizeof(Float_t)*n;
# else
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
frombuf(fBufCur, &f[i]);
# endif
#else
memcpy(f, fBufCur, l);
fBufCur += l;
#endif
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::ReadFastArray(Double_t *d, Int_t n)
{
// Read array of n doubles from the I/O buffer.
Int_t l = sizeof(Double_t)*n;
if (l <= 0 || l > fBufSize) return;
#ifdef R__BYTESWAP
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
frombuf(fBufCur, &d[i]);
#else
memcpy(d, fBufCur, l);
fBufCur += l;
#endif
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::ReadFastArrayDouble32(Double_t *d, Int_t n, TStreamerElement *ele)
{
// Read array of n doubles (written as float) from the I/O buffer.
// see comments about Double32_t encoding at TBuffer::WriteDouble32
if (n <= 0 || 4*n > fBufSize) return;
if (ele && ele->GetFactor() != 0) {
Double_t xmin = ele->GetXmin();
Double_t factor = ele->GetFactor();
for (int j=0;j < n; j++) {
UInt_t aint; *this >> aint; d[j] = (Double_t)(aint/factor + xmin);
}
} else {
Float_t afloat;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
frombuf(fBufCur, &afloat);
d[i]=afloat;
}
}
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::ReadFastArray(void *start, const TClass *cl, Int_t n,
TMemberStreamer *streamer)
{
// Read an array of 'n' objects from the I/O buffer.
// Stores the objects read starting at the address 'start'.
// The objects in the array are assume to be of class 'cl'.
if (streamer) {
(*streamer)(*this,start,0);
return;
}
int objectSize = cl->Size();
char *obj = (char*)start;
char *end = obj + n*objectSize;
for(; obj<end; obj+=objectSize) ((TClass*)cl)->Streamer(obj,*this);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::ReadFastArray(void **start, const TClass *cl, Int_t n,
Bool_t isPreAlloc, TMemberStreamer *streamer)
{
// Read an array of 'n' objects from the I/O buffer.
// The objects read are stored starting at the address '*start'
// The objects in the array are assumed to be of class 'cl' or a derived class.
// 'mode' indicates whether the data member is marked with '->'
// if isPreAlloc is true (data member has a ->) we can assume that the pointer (*start)
// is never 0.
if (streamer) {
if (isPreAlloc) {
for (Int_t j=0;j<n;j++) {
if (!start[j]) start[j] = ((TClass*)cl)->New();
}
}
(*streamer)(*this,(void*)start,0);
return;
}
if (!isPreAlloc) {
for (Int_t j=0; j<n; j++){
//delete the object or collection
if (start[j] && TStreamerInfo::CanDelete()) ((TClass*)cl)->Destructor(start[j],kFALSE); // call delete and desctructor
start[j] = ReadObjectAny(cl);
}
} else { //case //-> in comment
for (Int_t j=0; j<n; j++){
if (!start[j]) start[j] = ((TClass*)cl)->New();
((TClass*)cl)->Streamer(start[j],*this);
}
}
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::WriteArray(const Bool_t *b, Int_t n)
{
// Write array of n bools into the I/O buffer.
Assert(IsWriting());
*this << n;
if (n <= 0) return;
Assert(b);
Int_t l = sizeof(UChar_t)*n;
if (fBufCur + l > fBufMax) Expand(TMath::Max(2*fBufSize, fBufSize+l));
if (sizeof(Bool_t) > 1) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
tobuf(fBufCur, b[i]);
} else {
memcpy(fBufCur, b, l);
fBufCur += l;
}
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::WriteArray(const Char_t *c, Int_t n)
{
// Write array of n characters into the I/O buffer.
Assert(IsWriting());
*this << n;
if (n <= 0) return;
Assert(c);
Int_t l = sizeof(Char_t)*n;
if (fBufCur + l > fBufMax) Expand(TMath::Max(2*fBufSize, fBufSize+l));
memcpy(fBufCur, c, l);
fBufCur += l;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::WriteArray(const Short_t *h, Int_t n)
{
// Write array of n shorts into the I/O buffer.
Assert(IsWriting());
*this << n;
if (n <= 0) return;
Assert(h);
Int_t l = sizeof(Short_t)*n;
if (fBufCur + l > fBufMax) Expand(TMath::Max(2*fBufSize, fBufSize+l));
#ifdef R__BYTESWAP
# ifdef USE_BSWAPCPY
bswapcpy16(fBufCur, h, n);
fBufCur += l;
# else
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
tobuf(fBufCur, h[i]);
# endif
#else
memcpy(fBufCur, h, l);
fBufCur += l;
#endif
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::WriteArray(const Int_t *ii, Int_t n)
{
// Write array of n ints into the I/O buffer.
Assert(IsWriting());
*this << n;
if (n <= 0) return;
Assert(ii);
Int_t l = sizeof(Int_t)*n;
if (fBufCur + l > fBufMax) Expand(TMath::Max(2*fBufSize, fBufSize+l));
#ifdef R__BYTESWAP
# ifdef USE_BSWAPCPY
bswapcpy32(fBufCur, ii, n);
fBufCur += l;
# else
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
tobuf(fBufCur, ii[i]);
# endif
#else
memcpy(fBufCur, ii, l);
fBufCur += l;
#endif
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::WriteArray(const Long_t *ll, Int_t n)
{
// Write array of n longs into the I/O buffer.
Assert(IsWriting());
*this << n;
if (n <= 0) return;
Assert(ll);
Int_t l = 8*n;
if (fBufCur + l > fBufMax) Expand(TMath::Max(2*fBufSize, fBufSize+l));
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) tobuf(fBufCur, ll[i]);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::WriteArray(const ULong_t *ll, Int_t n)
{
// Write array of n unsigned longs into the I/O buffer.
// This is an explicit case for unsigned longs since signed longs
// have a special tobuf().
Assert(IsWriting());
*this << n;
if (n <= 0) return;
Assert(ll);
Int_t l = 8*n;
if (fBufCur + l > fBufMax) Expand(TMath::Max(2*fBufSize, fBufSize+l));
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) tobuf(fBufCur, ll[i]);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::WriteArray(const Long64_t *ll, Int_t n)
{
// Write array of n long longs into the I/O buffer.
Assert(IsWriting());
*this << n;
if (n <= 0) return;
Assert(ll);
Int_t l = sizeof(Long64_t)*n;
if (fBufCur + l > fBufMax) Expand(TMath::Max(2*fBufSize, fBufSize+l));
#ifdef R__BYTESWAP
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
tobuf(fBufCur, ll[i]);
#else
memcpy(fBufCur, ll, l);
fBufCur += l;
#endif
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::WriteArray(const Float_t *f, Int_t n)
{
// Write array of n floats into the I/O buffer.
Assert(IsWriting());
*this << n;
if (n <= 0) return;
Assert(f);
Int_t l = sizeof(Float_t)*n;
if (fBufCur + l > fBufMax) Expand(TMath::Max(2*fBufSize, fBufSize+l));
#ifdef R__BYTESWAP
# ifdef USE_BSWAPCPY
bswapcpy32(fBufCur, f, n);
fBufCur += l;
# else
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
tobuf(fBufCur, f[i]);
# endif
#else
memcpy(fBufCur, f, l);
fBufCur += l;
#endif
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::WriteArray(const Double_t *d, Int_t n)
{
// Write array of n doubles into the I/O buffer.
Assert(IsWriting());
*this << n;
if (n <= 0) return;
Assert(d);
Int_t l = sizeof(Double_t)*n;
if (fBufCur + l > fBufMax) Expand(TMath::Max(2*fBufSize, fBufSize+l));
#ifdef R__BYTESWAP
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
tobuf(fBufCur, d[i]);
#else
memcpy(fBufCur, d, l);
fBufCur += l;
#endif
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::WriteArrayDouble32(const Double_t *d, Int_t n, TStreamerElement *ele)
{
// Write array of n doubles (as float) into the I/O buffer.
// see comments about Double32_t encoding at TBuffer::WriteDouble32
Assert(IsWriting());
*this << n;
if (n <= 0) return;
Assert(d);
Int_t l = sizeof(Float_t)*n;
if (fBufCur + l > fBufMax) Expand(TMath::Max(2*fBufSize, fBufSize+l));
WriteFastArrayDouble32(d,n,ele);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::WriteFastArray(const Bool_t *b, Int_t n)
{
// Write array of n bools into the I/O buffer.
if (n <= 0) return;
Int_t l = sizeof(UChar_t)*n;
if (fBufCur + l > fBufMax) Expand(TMath::Max(2*fBufSize, fBufSize+l));
if (sizeof(Bool_t) > 1) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
tobuf(fBufCur, b[i]);
} else {
memcpy(fBufCur, b, l);
fBufCur += l;
}
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::WriteFastArray(const Char_t *c, Int_t n)
{
// Write array of n characters into the I/O buffer.
if (n <= 0) return;
Int_t l = sizeof(Char_t)*n;
if (fBufCur + l > fBufMax) Expand(TMath::Max(2*fBufSize, fBufSize+l));
memcpy(fBufCur, c, l);
fBufCur += l;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::WriteFastArrayString(const Char_t *c, Int_t n)
{
// Write array of n characters into the I/O buffer.
if (n < 255) {
*this << (UChar_t)n;
} else {
*this << (UChar_t)255;
*this << n;
}
if (n <= 0) return;
Int_t l = sizeof(Char_t)*n;
if (fBufCur + l > fBufMax) Expand(TMath::Max(2*fBufSize, fBufSize+l));
memcpy(fBufCur, c, l);
fBufCur += l;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::WriteFastArray(const Short_t *h, Int_t n)
{
// Write array of n shorts into the I/O buffer.
if (n <= 0) return;
Int_t l = sizeof(Short_t)*n;
if (fBufCur + l > fBufMax) Expand(TMath::Max(2*fBufSize, fBufSize+l));
#ifdef R__BYTESWAP
# ifdef USE_BSWAPCPY
bswapcpy16(fBufCur, h, n);
fBufCur += l;
# else
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
tobuf(fBufCur, h[i]);
# endif
#else
memcpy(fBufCur, h, l);
fBufCur += l;
#endif
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::WriteFastArray(const Int_t *ii, Int_t n)
{
// Write array of n ints into the I/O buffer.
if (n <= 0) return;
Int_t l = sizeof(Int_t)*n;
if (fBufCur + l > fBufMax) Expand(TMath::Max(2*fBufSize, fBufSize+l));
#ifdef R__BYTESWAP
# ifdef USE_BSWAPCPY
bswapcpy32(fBufCur, ii, n);
fBufCur += l;
# else
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
tobuf(fBufCur, ii[i]);
# endif
#else
memcpy(fBufCur, ii, l);
fBufCur += l;
#endif
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::WriteFastArray(const Long_t *ll, Int_t n)
{
// Write array of n longs into the I/O buffer.
if (n <= 0) return;
Int_t l = 8*n;
if (fBufCur + l > fBufMax) Expand(TMath::Max(2*fBufSize, fBufSize+l));
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) tobuf(fBufCur, ll[i]);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::WriteFastArray(const ULong_t *ll, Int_t n)
{
// Write array of n unsigned longs into the I/O buffer.
// This is an explicit case for unsigned longs since signed longs
// have a special tobuf().
if (n <= 0) return;
Int_t l = 8*n;
if (fBufCur + l > fBufMax) Expand(TMath::Max(2*fBufSize, fBufSize+l));
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) tobuf(fBufCur, ll[i]);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::WriteFastArray(const Long64_t *ll, Int_t n)
{
// Write array of n long longs into the I/O buffer.
if (n <= 0) return;
Int_t l = sizeof(Long64_t)*n;
if (fBufCur + l > fBufMax) Expand(TMath::Max(2*fBufSize, fBufSize+l));
#ifdef R__BYTESWAP
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
tobuf(fBufCur, ll[i]);
#else
memcpy(fBufCur, ll, l);
fBufCur += l;
#endif
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::WriteFastArray(const Float_t *f, Int_t n)
{
// Write array of n floats into the I/O buffer.
if (n <= 0) return;
Int_t l = sizeof(Float_t)*n;
if (fBufCur + l > fBufMax) Expand(TMath::Max(2*fBufSize, fBufSize+l));
#ifdef R__BYTESWAP
# ifdef USE_BSWAPCPY
bswapcpy32(fBufCur, f, n);
fBufCur += l;
# else
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
tobuf(fBufCur, f[i]);
# endif
#else
memcpy(fBufCur, f, l);
fBufCur += l;
#endif
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::WriteFastArray(const Double_t *d, Int_t n)
{
// Write array of n doubles into the I/O buffer.
if (n <= 0) return;
Int_t l = sizeof(Double_t)*n;
if (fBufCur + l > fBufMax) Expand(TMath::Max(2*fBufSize, fBufSize+l));
#ifdef R__BYTESWAP
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
tobuf(fBufCur, d[i]);
#else
memcpy(fBufCur, d, l);
fBufCur += l;
#endif
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::WriteFastArrayDouble32(const Double_t *d, Int_t n, TStreamerElement *ele)
{
// Write array of n doubles (as float) into the I/O buffer.
// see comments about Double32_t encoding at TBuffer::WriteDouble32
if (n <= 0) return;
Int_t l = sizeof(Float_t)*n;
if (fBufCur + l > fBufMax) Expand(TMath::Max(2*fBufSize, fBufSize+l));
if (ele && ele->GetFactor()) {
Double_t factor = ele->GetFactor();
Double_t xmin = ele->GetXmin();
Double_t xmax = ele->GetXmax();
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
Double_t x = d[j];
if (x < xmin) x = xmin;
if (x > xmax) x = xmax;
UInt_t aint = UInt_t(0.5+factor*(x-xmin)); *this << aint;
}
} else {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
tobuf(fBufCur, Float_t(d[i]));
}
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::WriteFastArray(void *start, const TClass *cl, Int_t n,
TMemberStreamer *streamer)
{
// Write an array of object starting at the address 'start' and of length 'n'
// the objects in the array are assumed to be of class 'cl'
if (streamer) {
(*streamer)(*this, start, 0);
return;
}
char *obj = (char*)start;
if (!n) n=1;
int size = cl->Size();
for(Int_t j=0; j<n; j++,obj+=size) {
((TClass*)cl)->Streamer(obj,*this);
}
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TBuffer::WriteFastArray(void **start, const TClass *cl, Int_t n,
Bool_t isPreAlloc, TMemberStreamer *streamer)
{
// Write an array of object starting at the address '*start' and of length 'n'
// the objects in the array are of class 'cl'
// 'isPreAlloc' indicates whether the data member is marked with '->'
// Return:
// 0: success
// 2: truncated success (i.e actual class is missing. Only ptrClass saved.)
// if isPreAlloc is true (data member has a ->) we can assume that the pointer
// is never 0.
if (streamer) {
(*streamer)(*this,(void*)start,0);
return 0;
}
int strInfo = 0;
Int_t res = 0;
if (!isPreAlloc) {
for (Int_t j=0;j<n;j++) {
//must write StreamerInfo if pointer is null
if (!strInfo && !start[j] ) ((TClass*)cl)->GetStreamerInfo()->ForceWriteInfo((TFile *)GetParent());
strInfo = 2003;
res |= WriteObjectAny(start[j],cl);
}
} else { //case //-> in comment
for (Int_t j=0;j<n;j++) {
if (!start[j]) start[j] = ((TClass*)cl)->New();
((TClass*)cl)->Streamer(start[j],*this);
}
}
return res;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
TObject *TBuffer::ReadObject(const TClass * /*clReq*/)
{
// Read object from I/O buffer. clReq is NOT used.
// The value returned is the address of the actual start in memory of
// the object. Note that if the actual class of the object does not
// inherit first from TObject, the type of the pointer is NOT 'TObject*'.
// [More accurately, the class needs to start with the TObject part, for
// the pointer to be a real TOject*].
// We recommend using ReadObjectAny instead of ReadObject
return (TObject*) ReadObjectAny(0);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::SkipObjectAny()
{
// Skip any kind of object from buffer
UInt_t start, count;
ReadVersion(&start, &count);
SetBufferOffset(start+count+sizeof(UInt_t));
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void *TBuffer::ReadObjectAny(const TClass *clCast)
{
// Read object from I/O buffer.
// A typical use for this function is:
// MyClass *ptr = (MyClass*)b.ReadObjectAny(MyClass::Class());
// I.e. clCast should point to a TClass object describing the class pointed
// to by your pointer.
// In case of multiple inheritance, the return value might not be the
// real beginning of the object in memory. You will need to use a
// dynamic_cast later if you need to retrieve it.
Assert(IsReading());
// make sure fMap is initialized
InitMap();
// before reading object save start position
UInt_t startpos = UInt_t(fBufCur-fBuffer);
// attempt to load next object as TClass clCast
UInt_t tag; // either tag or byte count
TClass *clRef = ReadClass(clCast, &tag);
Int_t baseOffset = 0;
if (clRef && (clRef!=(TClass*)(-1)) && clCast) {
//baseOffset will be -1 if clRef does not inherit from clCast.
baseOffset = clRef->GetBaseClassOffset(clCast);
if (baseOffset == -1) {
Error("ReadObject", "got object of wrong class! requested %s but got %s",
clCast->GetName(), clRef->GetName());
CheckByteCount(startpos, tag, (TClass*)0); // avoid mis-leading byte count error message
return 0; // We better return at this point
}
if (clCast->GetClassInfo() && !clRef->GetClassInfo()) {
//we cannot mix a compiled class with an emulated class in the inheritance
Error("ReadObject", "trying to read an emulated class (%s) to store in a compiled pointer (%s)",
clRef->GetName(),clCast->GetName());
CheckByteCount(startpos, tag, (TClass*)0); // avoid mis-leading byte count error message
return 0;
}
}
// check if object has not already been read
// (this can only happen when called via CheckObject())
char *obj;
if (fVersion > 0) {
obj = (char *) fMap->GetValue(startpos+kMapOffset);
if (obj == (void*) -1) obj = 0;
if (obj) {
CheckByteCount(startpos, tag, (TClass*)0);
return (obj+baseOffset);
}
}
// unknown class, skip to next object and return 0 obj
if (clRef == (TClass*) -1) {
if (fBufCur >= fBufMax) return 0;
if (fVersion > 0)
MapObject((TObject*) -1, startpos+kMapOffset);
else
MapObject((void*)0, 0, fMapCount);
CheckByteCount(startpos, tag, (TClass*)0);
return 0;
}
if (!clRef) {
// got a reference to an already read object
if (fVersion > 0) {
tag += fDisplacement;
tag = CheckObject(tag, clCast);
} else {
if (tag > (UInt_t)fMap->GetSize()) {
Error("ReadObject", "object tag too large, I/O buffer corrupted");
return 0;
// exception
}
}
obj = (char *) fMap->GetValue(tag);
clRef = (TClass*) fClassMap->GetValue(tag);
if (clRef && (clRef!=(TClass*)(-1)) && clCast) {
//baseOffset will be -1 if clRef does not inherit from clCast.
baseOffset = clRef->GetBaseClassOffset(clCast);
if (baseOffset == -1) {
Error("ReadObject", "Got object of wrong class (Got %s while expecting %s)",
clRef->GetName(),clCast->GetName());
// exception
baseOffset = 0;
}
}
// There used to be a warning printed here when:
// obj && isTObject && !((TObject*)obj)->IsA()->InheritsFrom(clReq)
// however isTObject was based on clReq (now clCast).
// If the test was to fail, then it is as likely that the object is not a TObject
// and then we have a potential core dump.
// At this point (missing clRef), we do NOT have enough information to really
// answer the question: is the object read of the type I requested.
} else {
// allocate a new object based on the class found
obj = (char *)clRef->New();
if (!obj) {
Error("ReadObject", "could not create object of class %s",
clRef->GetName());
// exception
return 0;
}
// add to fMap before reading rest of object
if (fVersion > 0)
MapObject(obj, clRef, startpos+kMapOffset);
else
MapObject(obj, clRef, fMapCount);
// let the object read itself
clRef->Streamer(obj, *this);
CheckByteCount(startpos, tag, clRef);
}
return obj+baseOffset;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::WriteObject(const TObject *obj)
{
// Write object to I/O buffer.
WriteObjectAny(obj, TObject::Class());
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::WriteObject(const void *actualObjectStart, const TClass *actualClass)
{
// Write object to I/O buffer.
// This function assumes that the value of 'actualObjectStart' is the actual start of
// the object of class 'actualClass'
Assert(IsWriting());
// make sure fMap is initialized
InitMap();
ULong_t idx;
if (!actualObjectStart) {
// save kNullTag to represent NULL pointer
*this << kNullTag;
} else if ((idx = (ULong_t)fMap->GetValue(Void_Hash(actualObjectStart), (Long_t)actualObjectStart)) != 0) {
// truncation is OK the value we did put in the map is an 30-bit offset
// and not a pointer
UInt_t objIdx = UInt_t(idx);
// save index of already stored object
*this << objIdx;
} else {
// A warning to let the user know it will need to change the class code
// to be able to read this back.
if (actualClass->HasDefaultConstructor() == 0) {
Warning("WriteObjectAny", "since %s had no public constructor\n"
"\twhich can be called without argument, objects of this class\n"
"\tcan not be read with the current library. You would need to\n"
"\tadd a default constructor before attempting to read it.",
actualClass->GetName());
}
// reserve space for leading byte count
UInt_t cntpos = UInt_t(fBufCur-fBuffer);
fBufCur += sizeof(UInt_t);
// write class of object first
WriteClass(actualClass);
// add to map before writing rest of object (to handle self reference)
// (+kMapOffset so it's != kNullTag)
MapObject(actualObjectStart, actualClass, cntpos+kMapOffset);
((TClass*)actualClass)->Streamer((void*)actualObjectStart,*this);
// write byte count
SetByteCount(cntpos);
}
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TBuffer::WriteObjectAny(const void *obj, const TClass *ptrClass)
{
// Write object to I/O buffer.
// This function assumes that the value in 'obj' is the value stored in
// a pointer to a "ptrClass". The actual type of the object pointed to
// can be any class derived from "ptrClass".
// Return:
// 0: failure
// 1: success
// 2: truncated success (i.e actual class is missing. Only ptrClass saved.)
if (!obj) {
WriteObject(0, 0);
return 1;
}
if (!ptrClass) {
Error("WriteObjectAny", "ptrClass argument may not be 0");
return 0;
}
TClass *clActual = ptrClass->GetActualClass(obj);
if (clActual) {
const char *temp = (const char*) obj;
// clActual->GetStreamerInfo();
Int_t offset = (ptrClass != clActual) ?
clActual->GetBaseClassOffset(ptrClass) : 0;
temp -= offset;
WriteObject(temp, clActual);
return 1;
} else {
WriteObject(obj, ptrClass);
return 2;
}
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
TClass *TBuffer::ReadClass(const TClass *clReq, UInt_t *objTag)
{
// Read class definition from I/O buffer. clReq can be used to cross check
// if the actually read object is of the requested class. objTag is
// set in case the object is a reference to an already read object.
Assert(IsReading());
// read byte count and/or tag (older files don't have byte count)
TClass *cl;
if (fBufCur < fBuffer || fBufCur > fBufMax) {
fBufCur = fBufMax;
cl = (TClass*)-1;
return cl;
}
UInt_t bcnt, tag, startpos = 0;
*this >> bcnt;
if (!(bcnt & kByteCountMask) || bcnt == kNewClassTag) {
tag = bcnt;
bcnt = 0;
} else {
fVersion = 1;
startpos = UInt_t(fBufCur-fBuffer);
*this >> tag;
}
// in case tag is object tag return tag
if (!(tag & kClassMask)) {
if (objTag) *objTag = tag;
return 0;
}
if (tag == kNewClassTag) {
// got a new class description followed by a new object
// (class can be 0 if class dictionary is not found, in that
// case object of this class must be skipped)
cl = TClass::Load(*this);
// add class to fMap for later reference
if (fVersion > 0) {
// check if class was already read
TClass *cl1 = (TClass *)fMap->GetValue(startpos+kMapOffset);
if (cl1 != cl)
MapObject(cl ? cl : (TObject*) -1, startpos+kMapOffset);
} else
MapObject(cl, fMapCount);
} else {
// got a tag to an already seen class
UInt_t clTag = (tag & ~kClassMask);
if (fVersion > 0) {
clTag += fDisplacement;
clTag = CheckObject(clTag, clReq, kTRUE);
} else {
if (clTag == 0 || clTag > (UInt_t)fMap->GetSize()) {
Error("ReadClass", "illegal class tag=%d (0<tag<=%d), I/O buffer corrupted",
clTag, fMap->GetSize());
// exception
}
}
// class can be 0 if dictionary was not found
cl = (TClass *)fMap->GetValue(clTag);
}
if (cl && clReq && !cl->InheritsFrom(clReq)) {
Error("ReadClass", "got wrong class: %s", cl->GetName());
// exception
}
// return bytecount in objTag
if (objTag) *objTag = (bcnt & ~kByteCountMask);
// case of unknown class
if (!cl) cl = (TClass*)-1;
return cl;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::WriteClass(const TClass *cl)
{
// Write class description to I/O buffer.
Assert(IsWriting());
ULong_t idx;
if ((idx = (ULong_t)fMap->GetValue(((TObject *)cl)->TObject::Hash(), (Long_t)cl)) != 0) {
// truncation is OK the value we did put in the map is an 30-bit offset
// and not a pointer
UInt_t clIdx = UInt_t(idx);
// save index of already stored class
*this << (clIdx | kClassMask);
} else {
// offset in buffer where class info is written
UInt_t offset = UInt_t(fBufCur-fBuffer);
// save new class tag
*this << kNewClassTag;
// write class name
cl->Store(*this);
// store new class reference in fMap (+kMapOffset so it's != kNullTag)
MapObject(cl, offset+kMapOffset);
}
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
static Version_t R__FindStreamerInfoVersion(const TClass *cl, UInt_t checksum)
{
//find the version number in the StreamerInfos corresponding to checksum
Version_t version = 0;
Int_t ninfos = cl->GetStreamerInfos()->GetEntriesFast();
for (Int_t i=1;i<ninfos;i++) {
// TClass::fStreamerInfos has a lower bound not equal to 0,
// so we should use At and not use UncheckedAt
TStreamerInfo *info = (TStreamerInfo*)cl->GetStreamerInfos()->At(i);
if (!info) continue;
if (info->GetCheckSum() == checksum) {
version = i;
//printf("ReadVersion, setting version=%d\n",version);
break;
}
}
return version;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Version_t TBuffer::ReadVersion(UInt_t *startpos, UInt_t *bcnt, const TClass *cl)
{
// Read class version from I/O buffer.
Version_t version;
if (startpos && bcnt) {
// before reading object save start position
*startpos = UInt_t(fBufCur-fBuffer);
// read byte count (older files don't have byte count)
// byte count is packed in two individual shorts, this to be
// backward compatible with old files that have at this location
// only a single short (i.e. the version)
union {
UInt_t cnt;
Version_t vers[2];
} v;
#ifdef R__BYTESWAP
*this >> v.vers[1];
*this >> v.vers[0];
#else
*this >> v.vers[0];
*this >> v.vers[1];
#endif
// no bytecount, backup and read version
if (!(v.cnt & kByteCountMask)) {
fBufCur -= sizeof(UInt_t);
v.cnt = 0;
}
*bcnt = (v.cnt & ~kByteCountMask);
*this >> version;
} else {
// not interested in byte count
*this >> version;
// if this is a byte count, then skip next short and read version
if (version & kByteCountVMask) {
*this >> version;
*this >> version;
}
}
if (cl && cl->GetClassVersion() != 0) {
if (version <= 0) {
UInt_t checksum = 0;
*this >> checksum;
version = R__FindStreamerInfoVersion(cl,checksum);
} else if (version == 1 && fParent && ((TFile*)fParent)->GetVersion()<40000 ) {
// We could have a file created using a Foreign class before
// the introduction of the CheckSum. We need to check
if ((!cl->IsLoaded() || cl->IsForeign()) &&
cl->GetStreamerInfos()->GetLast()>1 ) {
const TList *list = ((TFile*)fParent)->GetStreamerInfoCache();
const TStreamerInfo *local = (TStreamerInfo*)list->FindObject(cl->GetName());
if ( local ) {
UInt_t checksum = local->GetCheckSum();
version = R__FindStreamerInfoVersion(cl,checksum);
}
else {
Error("ReadVersion", "Class %s not known to file %s.",
cl->GetName(), ((TFile*)fParent)->GetName());
version = 0;
}
}
}
}
return version;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
UInt_t TBuffer::WriteVersion(const TClass *cl, Bool_t useBcnt)
{
// Write class version to I/O buffer.
UInt_t cntpos = 0;
if (useBcnt) {
// reserve space for leading byte count
cntpos = UInt_t(fBufCur-fBuffer);
fBufCur += sizeof(UInt_t);
}
Version_t version = cl->GetClassVersion();
if (version > kMaxVersion) {
Error("WriteVersion", "version number cannot be larger than %hd)",
kMaxVersion);
version = kMaxVersion;
}
if (cl->IsForeign() && version<=1) {
*this << Version_t(0);
*this << cl->GetCheckSum();
} else {
*this <<version;
}
// return position where to store possible byte count
return cntpos;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
UInt_t TBuffer::WriteVersionMemberWise(const TClass *cl, Bool_t useBcnt)
{
// Write class version to I/O buffer after setting the kStreamedMemberWise
// bit in the version number.
UInt_t cntpos = 0;
if (useBcnt) {
// reserve space for leading byte count
cntpos = UInt_t(fBufCur-fBuffer);
fBufCur += sizeof(UInt_t);
}
Version_t version = cl->GetClassVersion();
if (version > kMaxVersion) {
Error("WriteVersionMemberWise", "version number cannot be larger than %hd)",
kMaxVersion);
version = kMaxVersion;
}
if (cl->IsForeign() && version<=1) {
Error("WriteVersionMemberWise", "Member-wise streaming of foreign collection not yet implemented!");
*this << Version_t(0);
*this << cl->GetCheckSum();
} else {
version |= kStreamedMemberWise;
*this <<version;
}
// return position where to store possible byte count
return cntpos;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::SetReadMode()
{
// Set buffer in read mode.
fMode = kRead;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::SetWriteMode()
{
// Set buffer in write mode.
fMode = kWrite;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::StreamObject(void *obj, const type_info &typeinfo)
{
// Stream an object given its C++ typeinfo information.
TClass *cl = gROOT->GetClass(typeinfo);
cl->Streamer(obj, *this);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::StreamObject(void *obj, const char *className)
{
// Stream an object given the name of its actual class.
TClass *cl = gROOT->GetClass(className);
cl->Streamer(obj, *this);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::StreamObject(void *obj, const TClass *cl)
{
// Stream an object given a pointer to its actual class.
((TClass*)cl)->Streamer(obj, *this);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
TClass *TBuffer::GetClass(const type_info &typeinfo)
{
// Forward to TROOT::GetClass
return gROOT->GetClass(typeinfo);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
TClass *TBuffer::GetClass(const char *className)
{
// Forward to TROOT::GetClass
return gROOT->GetClass(className);
}
//---- Static functions --------------------------------------------------------
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::SetGlobalReadParam(Int_t mapsize)
{
// Set the initial size of the map used to store object and class
// references during reading. The default size is kMapSize=503.
// Increasing the default has the benefit that when reading many
// small objects the array does not need to be resized too often
// (the system is always dynamic, even with the default everything
// will work, only the initial resizing will cost some time).
// Per TBuffer object this option can be changed using SetReadParam().
fgMapSize = mapsize;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TBuffer::SetGlobalWriteParam(Int_t mapsize)
{
// Set the initial size of the hashtable used to store object and class
// references during writing. The default size is kMapSize=503.
// Increasing the default has the benefit that when writing many
// small objects the hashtable does not get too many collisions
// (the system is always dynamic, even with the default everything
// will work, only a large number of collisions will cost performance).
// For optimal performance hashsize should always be a prime.
// Per TBuffer object this option can be changed using SetWriteParam().
fgMapSize = mapsize;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TBuffer::GetGlobalReadParam()
{
// Get default read map size.
return fgMapSize;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TBuffer::GetGlobalWriteParam()
{
// Get default write map size.
return fgMapSize;
}